Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acfrogb9w Nt7aitghqvxsfbis4dxyrqwl1fexu6nsy7vza3ddbb Bplzjubs4tvh Ajclqu9w P P0w6nduoedtjiwdk7omtyigbjohwpmkytcp1faxil3 Zmty3hsv 6sjnxlu1zepz5iin2nm
Uploaded by
Monica GOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Acfrogb9w Nt7aitghqvxsfbis4dxyrqwl1fexu6nsy7vza3ddbb Bplzjubs4tvh Ajclqu9w P P0w6nduoedtjiwdk7omtyigbjohwpmkytcp1faxil3 Zmty3hsv 6sjnxlu1zepz5iin2nm
Uploaded by
Monica GCopyright:
Available Formats
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.
net
POWER PLANT ENGINEERING
UNIT-1THERMALPOWER PLANTS
1.Statethermodynamiclaw:
1. Zerothlawreferstothermodynamicequilibriumandtemperature
ww2.Firstlawreferstoheat,workandenergy
w.E
3.Secondlawreferstoentropy
2.Statezerothlawof thermodynamics:
“Twosystemsinthermal asy equilibriumwithathirdsystemareinthermal
En
equilibrium witheachother”
gin
3. StateFirstlawof thermodynamicsandenergyconversion.
Thefirstlawofthermodynamicsisoften called asLawofconversionofenergy.This
lawsuggeststhat
ee
energycanbetransferredfromonesystemto
anotherinmanyforms. Also,itcannotbedestroyedorcreated.
rin
4.Statesecondandthirdlawof thermodynamics:
Thesecondlawofthermodynamicsanotherstatevariablecalled entropy. Inanyg.n
closedsystem,theentropyofthesystemwill
eitherathermodynamicprocess,thesystem
cannevercompletelyreturnpreciselythesamestateitwasinbefore.
et
Thethirdlawofthermodynamicsstatesthat if all thethermalmotionof
molecules(kineticenergy)couldberemoved,astatecalled
absolutezerowilloccur. Absolutezeroresultsinatemperatureof0kelvinor-
273.15celcius.
5.Whatis thermodynamiccycle?
AThermodynamiccycle
isaseriesofthermodynamicprocessestransferringheat
andwork,whilevaryingpressure,temperature,andotherstatevariables,eventu
ally returningasystemtoitsinitial state.
65
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
6.Listthevariousthermodynamicprocesses:
1.Adiabaticprocess-aprocesswithnoheat transferintooroutofthesystem
2.Isochoricprocess-aprocesswithnochangeinvolume,insuchcasethesystem
doesnowork
3.Isobaricprocess-aprocesswithnochangeinpressure
4.Isothermalprocess-aprocesswithnochangeintemperature
7.Whatismeantbypowerplant?
Powercanbedefinedastherateof flowofenergyandstatethat apowerplantisa
wwunitbuilt forproductionanddeliveryof a flowof mechanicalworkandelectrical
energy. Amachineor assemblingofequipmentthat
flowofmechanical andelectrical energyisapowerplant.
producesanddeliversa
w.E
8.Listthefactorsof powerplantperformance.
asy
Theperformanceofapowerplantcanbeexpressedthroughsomecommo
n performancefactors as
1.Heat rate
2.Capacityfactor En
3.Economicefficiency
4.Load factor gin
5.Operationalefficiency
ee
9.Whatareavailableenergysourcesforvariouspowerplants?
1.Conventionalenergysourcesor Non-renewableenergysources rin
2.NonconventionalenergysourcesorRenewableenergysources
g.n
10.Whatarethe majorpowerlimitationsof conventionalenergysources?
1.Resourcesforpowergenerationi.e, coal,gasetc., arelimited
2.Thehydropowerisseasonalandvariesdependingupontherainfallinth
e catchmentareas
et
3.Submersionoflandareadueto raiseinwaterlevel
4.Centralizedpowergenerationanddistributionofthesametolongdistanceswi
ll resultinhighlosses.
5.Theenergyconversionprocessfromthermalpowerprojectsresultsinemission
of greenhousegases
11.Listoutthevariousconventionalandnon conventionalpowerplant:
Typesofconventionalpowerplant:
1.Hydropowerplant
2.Steampowerplant
66
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
3.Nuclearpowerplant
4.Gasturbinepowerplant
Typesofnon-conventionalpowerplant:
1.Tidalpowerplant
2.Windpowerplant
3.Geothermalpowerplant
4.Solarpowerplant
5.Wavepowerplant
6.MHDGeneration
12.Whatishydraulic/Pneumatictypeashhandlingsystem?
Thehydraulicsystemcarriedtheashwiththeflowofwaterhighvelocitythrougha
channelandfinallydumpsintoasump.Thehydraulicsystemisdividedintoalow
wwvelocityandhighvelocitysystem.The
clean,large
advantagesofthissystemarethat its
ashhandlingcapacity,
considerabledistancecanbetraversed,absenceofworkingparts in contactwithash
w.E
Inpneumatictypeashhandlingisthemostpopularmethodusedinmediumlevel
powerplants.It
usesdensephaseconveyingsystemforconveyingashistotallyenclosed
asy
withoutanyleakage.Thesystemcan conveymaterialsuptodistanceofaround200-250
mts.
En
13.Listthechallengesofashhandling:
2.Designofthesystemhasto gin
1.Indiancoal containshighashcontentgenerallywhichtendstobeinconsistent.
adequatelycover
ee
anticipatedvariationsandbecapable ofhandlingtheworstscenario
3.Systemhastobeenvironmentallyfriendly
4.Systemhastobeenergyefficient
rin
14.Whatis crusheranditscrushingmethod?
g.n
Acrusherisamachinedesignedtoreducelargesolidchunksofrawmaterialsiinto
t thestartingmaterial.
CrushingMethods:
1.Impact
et
smallerchunks.Crushersarecommonlyclassifiedbythedegreetowhichtheytragmen
2.Shear
3.Attrition4.Compression
15.Whatareall thetypesof Mechanicaldrafts?
There arethreetypesof mechanicaldrafts:Theyare:
1.Induceddraft
2.Forceddraft
3.Balanceddraft
16.WhatisDeaeration?
67
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
Mechanicalandchemicalldeaearationis
anintegralpartofmodernboilerwater
protectionandcontrol.Deaerationcoupledwithotheraspectsofexternal
treatment,providesthebest andhighestqualityfeedwaterforboileruse.
17.Whatis thepurposeof deaeration?
Thepurposeofdeaerationare:
1.Toremoveoxygen,carbondioxideandothernoncondensablegasesfr
om feedwater.
2.Toheat theincomingmakeupwaterandreturn condensateto
anpptimum temperature
3.Minimizingsolubilityofundesirablegases
4.Providingthehighesttemperaturewaterforinjectiontotheboiler.
ww18.Whatarethetypesof deaerators?
1.Tary-TypeDeaeratingheaters
w.E
2.Spray-TypeDeaeratingheaters
19.WhatismeantbycoolingTowers?
It
asy
isatowerorbuildinglikedeviceinwhichatmosphericaircirculatesindirector
indirectcontactwithwarmerwaterandwateristherebycooled.Coolingtowersmay
En
eitherusetheevaporationofwatertoremoveprocessheatandcooltheworkingfluid.
20.Listthetypesof coolingtowers:
1.Evaporativeor wet coolingtower gin
2.Nonevaporativeordrycoolingtower
ee
(a)Air cooledcondensers(b)Aircooled exchangers
21.Listthetypesof coolingfunctionstocondensethesteam: rin
1.Once-throughwet cooling
2.Recirculatingwetcooling3.Drycooling g.n
22.Listthefactorstobeconsideredwhilechoosingasiteforsteampowerstation:
1.Supplyoffuel
2.Availabilityofwater
et
3.Transportationfacilities
4.Costandtypeofland
5.Nearnesstoloadcentres
6.Distancefrompopulatedarea
23.Listthethermalpowerplantin Tamilnadu.
Alathiur(2*18MW),Tamilnadu,Madrascements
Ennore(2*60MW,3*110MW)TamilnaduElectricityBoard
Neyveli(6*50MW,2*100MW)TamilnaduNeyvelilignitecor
p Ltd.
68
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
24.Definesuperheater:
ASuperheaterisadeviceusedto convertsaturatedsteamintoadrysteam used
forpowergenerationorprosessessteamwhichhasbeensuperheatedisknownas
superheatedsteam.
25.Listthetypesof superheaters:
1.Radientsuperheater- absorbheat byradiation
2.Conventionsuperheater-absorbheat viaa fluid
3.Separatelyfixedsuperheaters-it istotallyseparatedfromtheboiler
UNIT-IIHYDRO ELECTRIC POWER PLANT
ww1.Writetheformulatocalculatethehydraulicpowerproducedbya
hydroturbine: Thehydraulicpowerisgivenbytheformula:
P=GpQH
w.E
WhereP isthehydraulicenergyinwatts
Gis
accelerationduetogravity(9.81M/s2)
P iswaterdensity
Qistheflowordischarge asy
En
Histheheightof fall of waterorheadinmeter.
gin
2.Listanyfouradvantagesof hydropower:
1.Watersourceisperenniallyavailable
2.Runningcostisverylow
3.Non-polluting
ee
4.Powergenerationcanbeswitchedonandoffinaveryshortperiod.
rin
3.Listanyfourdisadvantagesof hydropower:
1.Highcapital investmentandlowrateof return g.n
2.Gestationperiodisverylarge
3.Powergenerationdependsonavailabilityofwater
4.Transmissioncost andlossesarehigh
et
4.Listthefactorstobeconsideredfortheselectionof siteforhydropowerplant:
1.Availabilityofwaterandwaterhead
2.Accessibilityofsite
3.Waterstoragecapacity
4.Distancefromtheloadcenter
5.Typeofland
5.Listtheclassificationof dams:
69
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
1.Basedontheirfunc
tions:
(a)storagedams
(b)Diversiondams
(c)Detentiondams
2.Basedontheirshape:
(a)Trapezoidaldams
(b)Archdams
3.Basedonthematerialsofconstruc
tion:
(a)Earthdams(b)Rockpiecesdams
(c)Stonemasonarydams (d)concretedams
(e)RCCdams(f)TimberandRubberdams
ww4.Basedonhydraulicd
esign:
(a)Overflowtypedam
w.E
(b)Non-overflowtypedam
5.BasedonstructuralD
esign: (a)Gravitydam
(b)Archdam
(c) Buttressesdam asy
6.Whatisasurgetank? En
gin
Asurgetankisasmallreservoirinwhichthewaterlevel risesor fallsto reduce
thepressureswingsduringopeningandclosingof inlet
7.WhatisaDrafttube? ee
valve.Thesurgetankisnot requiredforrunoffplantsandmediumheadplants.
rin
Thedrafttube allowsthe turbinetobeset abovethetailraceto facilitateinspection
g.n
andmaintenance. It alsoregainsthemajorportionofthekineticenergyattherunner
outletbydiffuseraction.Thedrafttube canbeastraight conicaltubeoranallowtube.
8.Listtheequipmentspresentin apowerhouse:
1.Hydraulicturbines
2.Electric generators
et
3.Governors
4.Gatevalves andrehetvalves
5.Watercirculatingpumps
6.Airduct
7.Switchboardandinstruments
8.Storagebatteries andcranes
9.Listthetypesof hydropowerplantsbasedonavailabilityofhead;
1.Highheadpowerplant(head>100m)
2.Mediumheadpowerplant(30m-100m)
70
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
3.Lowheadpowerplants(head<30m)
10.Listtheadvantagesof pumpedstoragepowerplants:
1.Increasesthepeakloadcapacityat lowcost
2.Highoperatingefficiency
3.Betterloadfactor
4.Independenceofsteam flowconditions
11.Listtheadvantagesof impulseturbine:
1.Greatertoleranceofsandandotherparticlesinthewater
2.Betteraccesstoworkingparts
3.Nopressuresealsaroundtheshaft
ww4.Easierto fabricate and maintain
5.Betterpart-flowefficiency
w.E
12.Listanyfourpumpedstoragehydropowerplantsin India:
1.Bihar,Maharastra,150MW
2.Kadamparai,Coimbatore,Tamilnadu,400MW
asy
3.NagarjunaSagarPH,AndhraPradesh,810MW
4.Puruliapumpedstorageproject,Avodhvahills,WestBengal,900MW
En
5.SrisailamLeft BankPH,AndhraPradesh,900MW
6.TehriDam,Uttranchal,1000MW
gin
13.Whataretheessentialelementsof hydropowerplant?
ee
1.Catchmentarea
2.Reservation
3.Dam
4.Surgetanks rin
5.Drafttubes
6.Powerhouse
g.n
7.Switchedfortransmissionofpower
14.Whatismeantbycatchmentareaandexplainitsfunction:
Thewholeareabehindthedamis calledthecatchmentarea.Therainwaterinthe
et
areawillbedrainedinto thedamthroughadamorriver.
15.ExplainReservoir:
Areservoirmaybenatural,likealakeonamountainorartificiallybuiltby
erectingadamacrossa river.
16.Definesurgetank:
ASurgetankisasmallreservoirinwhichthewaterlevel risesswingsduring
openingandclosingofinlet valve.
17.Whatispowerhouse?
71
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
Apowerhouseisastablestructurewhichhousestheequipmentinthepowerplant
18.Whatismeantbypumpedstoragepowerplant?
Thepumpedstorageplantsareusedforloadbalancing.Duringpeakloadwateris
usedtoworkonturbinestoproduceelectricity.Waterafterworkinginturbinesisstored
inthetailracereservoir.
19.WhatisminiHydroplants?
Theminipowerplantsoperatewith5m-20mheadandproduceabout1MWto5
MWofpower.
ww20.Whatismicrohydroplants?
Themicropowerplantsrequireaheadlessthan5mandproduce0.1MWto1
MW.
w.E
21.Defineturbines:
Aturbineconvertsenergyintheformoffallingwaterintorotatingshaftpower.
asy
Theselectionofbestturbineforanyparticularsitedependsonthesitecharacteristics.
En
22.Whatarethedisadvantagesof impulseturbine?
Theyareunsuitableforlow-headsitesbecauseof theirlowspecificspeeds.
23.Whatispeltonturbine?
gin
ee
Apeltonturbineconsistsofaset ofspeciallyspreadbucketsmountedona
peripheryof a circulardisc. It isturnedbyjetsof waterwhich
aredischargedfromoneor morenozzles.
rin
24.Whatismeantbyreactionturbines?
Francisturbineandpropellerturbinesarethereactionturbines.Thereacti
g.n
on turbinesrotatefasterthan impulseturbine.
25.Whatismeantbypropellerturbine?
Thebasicpropellerturbineconsistsofapropeller.Insideitconsistof
et
a continuationofthepenstocktube.
26.Whatismeantby Kaplanturbine?
Thepitchofthepropellerbladestogetherwithwicketgateadjustment,enables
reasonableefficiencytobemaintainedunderpartflowconditions.Suchturbinesar
e called asKaplanturbines.
27.Definetwinrunners:
Tworunnerscanbeplacedonthesameshafteithersidebysideoronopposite
sidesofthegenerator.Thisconfigurationisunusualandwouldonlybeusedifthe
numberofjetsper runnerhadmaximized.
72
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
28.Statetheadvantagesof impulseturbineoverreactionturbine:
Impulseturbineareusuallycheaperthenreactionturbinebecausethereisnonee
d foraspecialistpressurecasing.
29.Explainimpulseturbinein termsof heads?
Highhead-peltonTurgo
Mediumhead-Multijetpeltonturgo
Lowhead- crossflow
30.Explainreactionturbinein termsof head:
Highhead-
wwFrancis
Mediumhead-
Propeller
w.E
Lowhead-
Kaplan
asy
UNIT-IIINUCLEAR POWER PLANTS
1.Whatismeantbyradioactivity?
En
gin
It referstothegermannameofRadio-Activitat.Radioactivityisthespontaneous
disintegrationof
ee
atomicnuclei.Thenucleusemitsparticlesorelectromagneticrays
duringthisprocess.
2.Whatis theunitof Radioactivity?
rin
1.Roentgen2.RAD(RadiationAbsorbedDose)
g.n
3.RBE(RelativeBiologicalEffectiveness)4.REM(RoentgenEquivalentinMan)
5.Gray(GY)-100rads6.Sievert(SV)
et
3.WhatarethetypesofRadioactivedecay?
1.Alphadecay2.Betadecay
3.Gammadecay4.Poistronemission(Betapositivedecay)
5.Electroncapture
73
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
4.Define-Decaytiming.
Thenumberofdecayevents–dNexpectedtooccurinasmallintervaloftimedt is
proportionaltothenumberofatomspresent.If N isthenumberofatoms,thenthe
probabilityofdecay(-dN/N)isproportionaltodt.
5.WhatisUraniumenrichment?
Inmosttypesof reactor, ahigherconcentrationofuraniumisusedtomake fuel rod.
Thisproducedbyaprocesstermedenrichment.Theenricheduraniumcontainingmor
e thannatural0.7%U-235.
6.Whatarethetwowaysof uraniumenrichment?
1.Gascentrifugeprocess
ww2.Gasdiffusion
7.Whatis thepurposeof reprocessingof nuclearwaste?
w.E Theusedfuelcontains96%uranium,1%plutoniumand3%radioactivewastes.
Reprocessingisusedtoseparatethewastefromtheuraniumandplutoniumwhichcanbe
recycledinti newfuel.Thereprocessingeffectivelyreducesthevolumeof wasteand
asy
limitstheneedtominenewsuppliesofuranium,sothat extendingthetimeofresources.
8.DefineNuclear Fission.
En
Anatom’snucleuscanbesplit apart.Whenthisisdoneatremendousamountof
energyis
gin
released.Theenergyisbothheat andlight
energy.Thisenergy,whenletout slowlycanbeharnessedtogenerateelectricity.
9.DefineNuclear Fusion.
ee rin
Fusionmeansjoiningsmallernucleitomakealargernucleus.Thesunusesnuclear
fusionofhydrogenatomsintoheliumatoms.Thisgivesoffheatandother radiation.
10.WhatisNeutronlifetime?
g.n
Thepromptneutronlifetime,istheaveragetimebetweentheemissionofneutronsan
d eithertheir
et
absorbtioninthesystemortheir
escapefromthesystem.Thetermlifetimeisusedbecausetheemissionofaneutroniso
ftenconsidereditsbirth,andthe subsequentabsorptionis considereditsdeath.
11.WhatisUranium-235chainReactor?
Ina chainreaction,particlesreleasedbythesplittingoftheatom gooffandstrike
otheruraniumatomssplittingthose.Thoseparticlesgivenoffsplitstill otheratomsina
chainreaction.If anleastoneneutronfromU-235fissionstrikesanothernucleusand
causesit to fission,Thenthechainreactionwill continue.
12.Whatisfourfactorformula?
Thefourfactor formulaisusedinnuclear engineeringtodeterminethe
multiplicationofanuclearchainreactionin
aninfinitemedium.Theformulais:
74
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
-ReproductionFactor-Thethermalutilizationfactor
-Theresonanceescapeprobability-Thefast fissionfactor
13.Listthefourtypesofradiationassociatedwithnuclearfission.
1.Alpharadiation
2.Beta radiation
3.Gammaradiation
4.Neutronradiation
14.DefineAlpharadiation.
Thisisbasicallytheatomicnucleusoftheelement(He)consistingoftwoprotons
andtwoneutrons.It isnotverypenetrativeandthedangertomanarisesifan alpha
emittingelement,suchasplutonium,thenthealpharadiationbeverydamaging.
ww15.DefineBetaradiation.
Beta radiationconsistsof
w.E
electronsortheirpositivelychargedcounterparts.This
canpenetratetheskin,butnotveryfar.
16.DefineGammaradiation.
asy
GammaradiationispenetrativeinamannersimilartoX-raysandhassimilar
En
physicalproperties.Itcanbestoppedonlybythickshieldsofleadorconcrete.
17.DefineNeutronradiation.
gin
Neutronradiationconsistsoftheneutronsemitted
ee
duringthefissionprocess.
Neutronsarealsoverypenetrative,butlesssothengamma-radiation.
18.Definewaterasmoderator.
rin
Neutronsfromfissionhaveveryhighspeedsand
g.n
mustslowedgreatlybywater
moderationtomaintainthechainraction.TheUranium-235is enrichedto2.5-3.5%to
chainreactionifthepropermoderationandfueldensityisprovided.
19.Listthetypesof Nuclearreactors.
et
allowordinarywatertobethemoderator.Enoughspontaneouseventsoccurtoinitiatea
Thereactorsareclassifiedbasedonthefollowing:
1.Typeoffuelused
2.Neutronflux spectrum
3.Thecoolant
20.Listthevariouswidespreadpowerplantreactortypes.
1.Pressurizedwaterreactor(PWR)
2.Bolingwater reactor(BWR)
3.PressurizedHeavywaterreactor(PHWR)
4.Liquidmetalfast BreederReactors(LMFBR)
5.HightemperatureGas cooledreactors(HTGCR)
75
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
21.Whatispressurizedwaterreactors(PWR)?
ThePWRbelongstothelidhtwatertype.Themoderatorandthecoolant areboth
lightwater(H2O).Thecoolingwatercirculatesintwoloops,whicharefullyseparated
fromoneanother.PWRkeepwaterunderpressure,sothewaterheatsbutdoesnotboil
evenat thehighoperatingtemperature.
22.Whatisboilingwaterreactor(BWR)?
Inaboilingwaterreactor, Lightwaterplaystheroleofmoderatorandcoolantas
well.Partofthewaterboilsawayinthereactorpressurevessel,thusamixtureofwater
andsteamleavesthereactorcore.
ww23.Whatis MoltenSaltReactor(MSR)?
Amoltensalt reactorisatypeofnuclearreactorwheretheprimarycoolantisa
moltensalt.Moltensalt referstoasalt that isintheliquidphasethat isnormallyasolidat
w.E
standardtemperatureionicliquid,althoughtechnicallymoltensaltsarea classofionic
liquids.
asy
24.NuclearPowerplantsafety.
Radiationdosescanbecontrolledthroughthefollowingprocedures:
En
1.Thehandlingofequipmentviaremoteinthecoreofthereactor
2.Physicalshielding
gin
3.Limitonthetimeaworkerspendsinareaswithsignificantradiationlevels
4.Monitoringofindividualdosesandoftheworkingenvironment
ee
5.Safetymechanismof aNuclearpowerreactor
25.ListtheNuclearpowerplantsin India.
1.Kaiga(3*22MWPHWR),Karnataka
rin
2.Kakrapar(2*22MWPHWR),Gujarat
3.Kudankulam(2*100MWPWR),Tamilnadu
g.n
4.Madras(2*17MWPHWR),Tamilnadu
26.Definemeangenerationtime.
It istheaveragetimefromaneutronemissiontoa captureresultsin fission.The
et
mean
generationtimeisdifferentfrompromptneutronlifetimebecausethemean
generationtimeonlyincludesneutronabsorptionthat leadsto fissionreaction.
UNIT IV GAS DIESEL POWER PLANT
1.Listtheadvantagesofgasturbinepowerplant.
1.Lowcapital cost
2.Highreliability
3.Flexibilityinoperation
76
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
4.Capabilitytoquickstart
5.Highefficiencye.t.c.
2.Listthe majorcomponentsof gasturbine.
1.Compressor
2.Combustionchamberand
3.Turbine
3.Listthetypesof gasturbinepowerplants.
1.Opencyclegasturbinepower plant
2.Closedcyclegasturbinepowerplant
4.Listthedisadvantagesof gasturbinepowerplant.
1.NoloadandPartialloadefficiencyislow
ww2.Highsensitiveto componentefficiency
3.Theefficiencydependsonambientpressureandambienttemperature
4.Highair rateisrequiredtolimitthemaximuminlet
w.E
airtemperature.Henceexhaust lossesarehigh
5.Airandgasfilterisrequiredtopreventdustintothecombustionchambers.
asy
5.Defineregeneratorefficiency.
Theregeneratorefficiencyisdefinedas:
En
=Actualtemperaturerise ofair/ Maximumtemperaturerisepossible
gin
6.Listthefactorswhichaffecttheperformanceof gasturbinepowerplants.
1.Partloadefficiency
ee
2.Fuelconsumption
3.Airmassflowrate
4.Thermalefficiency
5.Regeneration
rin
7.Whataretheworkingfluidsin gasturbine?
g.n
1.Air
2.Helium
3.Argon
4.Carbondioxide
et
8.Listthevarioustypesof dieselplants.
Basedonnumberofstr
okes:
(a)Twostrokediesel
engine
(b)Foursrtokediesele
ngine
Basedonorientation:
77
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
(a)Horizontaldiesel
engine (b)
Verticaldiesel engine
Basedonnumberof
cylinders:
(a)singlecylinder
(b)Multicylinder
Andothertypelikenaturallyaspirated,superheatedetc.,
9.Listthecomponentsof dieselpowerplant.
1.Dieselengine
2.Airintakesystem
ww3.Exhaustsystem
4.Fuelsystem
5.Coolingsystem
w.E
6.Lubricatingsystem
7.Startingofengine
asy
10.Listthevariousfunctionsoffuelinjectionsystem.
1.Itfiltersthefuel
En
2.Monitorthecorrectquantityoffueltobeinjected
3.Timingoftheinjectionprocess
4.Regulatesthefuelsupply
5.Fineatomizationoffueloil
gin
ee
6.Distributestheautomizedfuelproperlyinsidethecombustionchamber
11.Listtheclassificationof oilinjectionsystem.
(a)Commonrail injectionsystem
rin
(b)Individualpumpinjectionsystem
(c)Distributorsystem
g.n
12.Listthereasonwhythecoolingsystemisnecessaryforadiesel engine.
1.Toavoiddetemiationoflubricatingoil
2.Toavoiddamagesandoverheatingofpiston
et
3.Toavoidunevenexpansionwhichresultsin craking
4.Toavoidpre-ignitionanddetonationorknocking
5.Toavoidreductioninvolumetricefficiencyandpoweroutputoftheengine
13.Whatarethe methodsof coolingsystemused?
1.Aircooling
2.Watercooling
14.Listthemethodsadoptedforcirculatingthewaterin a coolingsystem.
1.Thermosiphoncooling
2.Forcedcoolingbypump
78
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
3.Thermostatcooling
4.Pressurisedwatercooling
5.Evaporativecooling
15.Whataretheimportantfunctionsof alubricatingsystem?
1.Lubricating
2.Cooling
3.Cleaning
4.Sealing
5.Noiseabsorption
16.Listthevarioustypesof lubricatingsystemusedin diesel engine.
1.Mistlubricatingsystem
2.Wetsumplubricationsystem
ww3.Drysumplubricationsystem
17.Whatarethestartingmethodsof diesel engine?
w.E
1.Byanauxiliaryengine
2.Byanelectricmotor
3.Bycompressedair
asy
18.Listanyfouradvantagesof dieselpowerplant.
1.It iseasytodesignand install
En
2.It iseasilyavailableinstandardcapacities
3.Theycanrespondtoloadchanges
4.Theyhavelessstandbylosses
gin
1.Highoperatingcost
2.Highmaintenanceand lubricationcost
ee
19.Listanyfourdisadvantagesof dieselpowerplant.
rin
3.Capacityisrestricted
4.Noisepollution
g.n
20.Listanyfourapplicationsof dieselpowerplant.
1.Usedaspeakloadplants
2.Suitableformobileplants
et
3.Usedasstandbyunits
4. Usedas emergencyplant
UNIT-V NON CONVENTIONAL POWERGENERATION
1.Whatarethecomponentsof solarenergy?
1.Collector
2.Storageunit
2.Whatis concentrationratio?
79
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
Concentrationratioisdefinedastheratiobetweentheapertureareaandthereceiver
absorberareaofthecollector.
3.Listthevarioustypesof solarenergycollectors.
1.Stationarycollectors(or)Non-concentrating
(a) Flateplatecollectors
(b)Compoundparaboliccollectors
(c)Evaculatedtube collectors
2.Suntrackingconcentratingcollector
(a)singleaxistracking
(b)Two-axistracking
ww4.Listanyfourapplicationsof solarcollectors.
1.Solarwaterheating
2.Solarspaceheatingsystems
w.E
3.Solarrefrigeration
4.Industrialprocessheatsystems
asy
5.Listthefourimportantsolarsystems.
1.Lowtemperaturecyclesusingflat plat collectororsolarpond
En
2.Powertowerorcentralreceiversystem
3.Distributedcollectorsystem
gin
4.Concentratingcollectorsformediumandhightemperaturecycle
ee
6.ListtheadvantagesofsolarEnergy.
1.Solarenergyisfree frompollution
2.Theycollect
toasinglereceiver,thus
solar
rin
energyopticallyandtransferit
minimizingthermal-
energytransportrequirements
3.Theytypicallyachieve
g.n
concentrationratiosof300to1500andsoarehighly
collectingenergyandconvertingit to electricity.
4.Theplant requireslittlemaintenanceorhelpaftersetup
5.It iseconomical
efficientbothin
et
7.Listanyfourdisadvantagesof solarenergy.
1.Avilableindaytimeonly
2.Needstoragefacilities
3.Itneedsabackuppowerplant
4.Keepingbackupplantshotincludesan energycostwhichincludescoal burning
8.Listtheclassificationof OTECbasedonlocation.
1.Landbasedplant
2.Shelfbasedplant
3.Floatingplant
80
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
9.Listtheclassificationof OTECbasedoncycle.
1.Opencycle
2.Closedcycle
3.Hybridcycle
10.Listanyfourbenefitsof OTEC.
1.Airconditioning
2.Chilledsoil agriculture
3.Aquaculture
4.Desalination
11.Listanyfourdisadvantagesof OTEC.
1.Degradationofheatexchangerperformanceasdissolvedgases.
ww2.Degradationofheatexchangerperformancebymicrobialfouling
3.Impropersealing
4.Parasiticpowerconsumptionbyexhaustcompressor
w.E
12.Listthevariouscomponentsofwindenergysystem.
1.Rotor
2.Gearbox
3.Enclosure asy
4.Tailvane
En
gin
13.Whatarethetwobasicdesignof turbines?
1.Verticalaxis(or)Eggbeaterstyle
ee
2.Horizontalaxis(propellerstyle)machines
14.Writedownthevarioustypesofwindpowerplants.
1.Remote
rin
2.Hybrid
3.Gridconnected
g.n
15.Listanyfouradvantagesof windturbine.
1.Inexhaustiblefuelsource
2.Nopollution
et
3.Excellentsupplementtootherrenewablesource
4.Itsfree
16.Listthedisadvantagesof windpowergeneration.
1.Lowenergyproduction
2.Expensivemaintenance
17.Whatarethevariouswaysof creatingtidalenergy?
1.TidalBarrager
2.Tidalfences
3.Tidalturbines
81
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
18.Listthevarioustypesof turbinesusedin tidalpowerstation.
1.Buldturbine
2.Rimturbine
3.Tubularturbines
19.Whatarethecomponentsof tidalpowerstation?
1.Barrage
2.Turbines
3.Sluices
4.Embankments
20.Listanyfouradvantagesof tidalpowergeneration.
1.Renewableandsustainableenergy
ww2.NoliquidorSolidpollution
3.Littlevisualimpact
4.Reducesdependenceuponfossilfuels
w.E
21.Listthelimitationsof tidalenergy.
1.Orientationproblem
2.Requiresstoragedevices
asy
3.Availableatalowerratingandtime
4.Highcapital cost
En
gin
22.Whatarethe mainpartsof geothermalpowerplant?
1.Productionwell
ee
2.Vaporizer
3.Circulatingpump
4.Expansionturbine
5.Generator
rin
6.Condenser
7.Transformer
g.n
23.Whataretheclassificationsof geothermalenergyconversionsystem?
1.Singlecyclegeothermalpowerplant
2.Binarycyclepowerplant
et
24.Whataretheapplicationsof geothermalenergy?
1.Generationofelectricpower
2.Spaceheatingforbuilding
3.Industrialprocessheat
25.Whataretheadvantagesof geothermalenergy?
1.Cheaper
2.Versatileinitsuse
3.Deliversgreater amountofenergy
82
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
26.Whatarethedisadvantagesof geothermalenergy?
1.Drillingoperationisnoisy
2.Itneedslargeareasof exploitationof geothermalenergy
3.Lowoverallpowerproductionefficiency.
27.Whataretheclassificationof MHDsystem?
1.Opencyclesystems
2.Closedcyclesystems
(a)Seededinertgassystems
(b)Liquidmetalsystems
28.Whataretheadvantagesof MHDsystems?
1.Largeamountofpowerisgenerated
ww2.Nomovingparts,somorereliable.
3.Closedcyclesystemproducespower,freeofpollution
4.Abilitytoreachits fullpowerassoonasstarted.
w.E
29.Listtheclassificationof oilinjectionsystem.
(a)Commonrail injectionsystem
asy
(b)Individualpumpinjectionsystem
(c)Distributorsystem
En
30.Listthedisadvantagesof MHDsystems.
gin
1.Needsverylargemagnets(highexpenses)
2.Veryhighfrictionandheat transferlosses
ee
3.Itsuffersfromthereverseflowof
electronsthroughtheconductingfluidsaround theendsofthemagneticfield.
rin
PART B 16 MARKS
UNIT – 1: THERMAL POWER PLANTS g.n
circuits. et
1. Draw a general lay out of a thermal power plant and explain the working of different
2. What factors are considered for selecting a site for a big thermal power plant?
3. How much coal, cooling water and combustion air are required for a thermal power
station of 500 MW capacity per hour.
4. How much ash and SO2 are produced per day from a plant of Koradi size if Indian low
grade coal is used.
5. What is the importance of thermal power plant in the national power grid?
6. What is meant by overfeed and underfeed principles of coal firing? Which is preferred
for high volatile coal and why.
7. What are the advantages of burning the fuels in pulverized form?
8. Why ash and dust handling problem is more difficult than coal handling problems.
83
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
9. What are different ash handling systems? Discuss the relative merits and demerits.
10. How the ash produced carries the importance in the selection of thermal power plant
site
11 Draw a general lay out of a thermal power plant and explain the working of different
circuits.
12 What factors are considered for selecting a site for a big thermal power plant?
13 How much coal, cooling water and combustion air are required for a thermal power
station of 500 MW capacity per hour.
14 How much ash and SO2 are produced per day from a plant of Koradi size if Indian low
grade coal is used.
15 What is the importance of thermal power plant in the national power grid?
16 What is meant by overfeed and underfeed principles of coal firing? Which is preferred
ww for high volatile coal and why.
17 What are the advantages of burning the fuels in pulverized form?
w.E
18 Why ash and dust handling problem is more difficult than coal handling problems.
19 What are different ash handling systems? Discuss the relative merits and demerits.
asy
20. How the ash produced carries the importance in the selection of thermal power plant
site.
En
UNIT – 2: HYDROELECTRIC POWER PLANTS
1. What are the different factors to be considered while selecting the site for hydroelectric
power plant?
gin
2. How the hydroelectric power plants are classified.
ee
3. How the most economical capacity of hydroelectric power plant is decided.
4. What do you understand by run-off river power plant and how its performance is
increased by introducing a pondage in the plant?
rin
5. Explain in detail about pump storage plant.
g.n
6. Draw a neat diagram of storage type hydroelectric power plant and describe the function
of each component used in the plant.
et
7. Mention the advantages and disadvantages of hydroelectric power plants compared with
thermal power plants.
8. Why the combined operation of hydro and thermal plants is more economical than
individual operation of the plant.
9. What do you understand by pump storage plant and what are the advantages and
limitations of this plant.
10. What are the specific advantages of storage reservoir type power plant? How they differ
from other types of hydro power plant?
UNIT – 3: NUCLEAR POWER PLANTS
1. Why uranium oxide is preferred over uranium as fuel.
2. Why cladding is necessary. What are the requirements of a good cladding material?
3. What properties are required for a good coolant? Which gases are used as coolant?
84
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
4. What are the desirable properties of a good moderator? Compare H2O, D2O and C as
moderators.
5. What are the desirable properties of control rod materials? Compare the merits and
demerits of different control rod materials.
6. Why shielding of a reactor is necessary. What do you understand by thermal shielding?
7. Compare the properties of stainless steel and zirconium for use as reactor fuel element
cladding.
8. How induced radioactivity affects the cost of shielding.
9. Considering the problem of induced radioactivity which coolant among water and
sodium is more desirable and why.
10. Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of Lithium, Bismuth and sodium as coolants
ww
for nuclear reactors.
UNIT – 4: GAS AND DIESEL POWER PLANTS
w.E
1. What are the main advantages of a combined cycle system in the present power picture
of the world?
2. Draw the line diagrams of repowering system using steam turbine only and boiler only.
asy
Discuss the merits and demerits also.
3. What is the gasification of coal and explain in detail.
En
4. What are the merits and demerits of using air or O2 in a gasification plant when the
gasification plant is integrated with closed cycle?
gin
5. What do you understand by PFBC, Explain in detail?
6. Draw the line diagrams of two different PFBC systems which are commonly used and
discuss their merits and demerits.
ee rin
7. What are the main difficulties faced in developing the combined cycles with PFBC.
8. Why and when organic fluid is preferred over water in the bottoming cycle. What are its
advantages?
g.n
9. Discuss the part behavior of combined cycle plant and compare with conventional gas
turbine plant of the same capacity.
10. What future developments are expected in combined cycle plants?
UNIT – 5: NON-CONVENTIONAL POWER GENERATION
et
1. What are the non-conventional sources of energy and why are they seriously thought
throughout the world.
2. What are the different sources of geothermal energy?
3. Discuss the different systems used for generating the power using geo-thermal energy.
4. What are the specific environmental effects if the geothermal source of energy is used for
power generation?
5. What factors are considered for selecting a suitable site for tidal power plants?
6. Differentiate with neat sketches the difference between single basin and double basin
systems.
85
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
7. List out the advantages of tidal power plants over the conventional hydel power plants.
8. What are the basic requirements for locating a wind power plant? What factors affect
them?
9. What methods are used to overcome the fluctuating power generation of a wind mill?
10. Explain the working of a fuel cell and list out its advantages over other non-
conventional systems of power generation.
ww V.S.B ENGINEERING COLLEGE, KARUR
DEPARTMENT OFELECTRICALAND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING
II YEAR / III SEMESTER
w.E DIGITAL LOGICCIRCUITS TWO MARK QUESTION AND ANSWER
UNIT I
asy
NUMBER SYSTEMS AND DIGITAL LOGIC FAMILIES
1. What is meant by parity bit?
En
A parity bit is an extra bit included with a message to make the total number of 1’s
gin
either even or odd. Consider the following two characters and their even and odd parity:
with even parity with odd parity.
ee
ASCII A = 1000001 01000001 11000001
ASCII T = 1010100 11010100 01010100
rin
In each case we add an extra bit in the left most position of the code to produce an
even number of 1’s in the character for even parity or an odd number of 1’s in the character
g.n
for odd parity. The parity bit is helpful in detecting errors during the transmission of
information from one location to another.
2. What are registers?
et
Register is a group of binary cells. A register with n cells can store any discrete
quantity of information that contains n bits. The state of a register is an n-tuple number of
1’s and 0’s, with each bit designating the state of one cell in the register.
3. Define binary logic?
Binary logic consists of binary variables and logical operations. The variables are
designated by the alphabets such as A, B, C, x, y, z, etc., with each variable having only
two distinct values: 1 and 0. There are three basic logic operations: AND, OR, and NOT.
4. Convert (4021.2)5 to its equivalent decimal.
(4021.2)5 = 4 x 53 + 0 x 52 + 2 x 51 + 1 x 50 + 2 x 5-1
= (511.4)10
86
Downloaded From : www.EasyEngineering.net
You might also like
- Elementary Reactor Physics: The Commonwealth and International Library: Nuclear Engineering DivisionFrom EverandElementary Reactor Physics: The Commonwealth and International Library: Nuclear Engineering DivisionNo ratings yet
- The Development of Mini Air-Core Based Turbine Generator in Design CircuitDocument6 pagesThe Development of Mini Air-Core Based Turbine Generator in Design CircuitAhmad Aimi SafuanNo ratings yet
- New Methods For Detecting Unintentional IslandingDocument9 pagesNew Methods For Detecting Unintentional IslandingjlcegarraNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Thermoelectric Solar RefrigeratorDocument7 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Thermoelectric Solar RefrigeratorHumberto Manuel Joao CinturaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Module 5Document7 pagesEngineering Module 5cc7895486No ratings yet
- Geothermal Energy: From Theoretical Models to Exploration and DevelopmentFrom EverandGeothermal Energy: From Theoretical Models to Exploration and DevelopmentNo ratings yet
- Chemical EngineDocument20 pagesChemical EngineDejan DjokićNo ratings yet
- Experimental Investigation of A Hermetic Scroll ExDocument8 pagesExperimental Investigation of A Hermetic Scroll ExKarthikeyanKarunNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: Power System Operational PlanningDocument14 pagesChapter One: Power System Operational PlanningHassan ShahidNo ratings yet
- Flow and Heat Transfer in Geothermal Systems: Basic Equations for Describing and Modeling Geothermal Phenomena and TechnologiesFrom EverandFlow and Heat Transfer in Geothermal Systems: Basic Equations for Describing and Modeling Geothermal Phenomena and TechnologiesNo ratings yet
- Hindusthan College of Engineering and Technology Department of Aeronautical EngineeringDocument15 pagesHindusthan College of Engineering and Technology Department of Aeronautical EngineeringCurious ManNo ratings yet
- GovernorDocument93 pagesGovernorLê Trung DũngNo ratings yet
- Wind Turbine Efficiency and Grid Code Requirements: Dr. Arshad Ali Assistant ProfessorDocument35 pagesWind Turbine Efficiency and Grid Code Requirements: Dr. Arshad Ali Assistant ProfessorIbn e Adam100% (1)
- Solved Sample Question PaperDocument18 pagesSolved Sample Question PaperPrathamesh DabadeNo ratings yet
- Towards The Optimal Operation of An Organic Rankine Cycle Unit by Means of Model Predictive ControlDocument10 pagesTowards The Optimal Operation of An Organic Rankine Cycle Unit by Means of Model Predictive ControlAndres HernandezNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics by S K Mondal 1Document95 pagesThermodynamics by S K Mondal 1Mostafa MohamedNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0360319913010379 MainDocument9 pages1 s2.0 S0360319913010379 MainveepekayNo ratings yet
- VibrationDocument15 pagesVibrationZac IriberriNo ratings yet
- Econd Law of Thermodynamics: DirectionDocument12 pagesEcond Law of Thermodynamics: DirectionSyed Muhammad TaqiNo ratings yet
- = (cos (θ) sin (θ) 1 cos 2 x 3 sin 2 x 3 1 cos 2 x 3 sin 2 x 3 1Document9 pages= (cos (θ) sin (θ) 1 cos 2 x 3 sin 2 x 3 1 cos 2 x 3 sin 2 x 3 1smonimalaNo ratings yet
- The Second Law of Thermodynamics: Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachDocument31 pagesThe Second Law of Thermodynamics: Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachmechgokulNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS5704685Document29 pagesChapter 6 THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS5704685bensonNo ratings yet
- The Second Law of Thermodynamics: Mehmet KanogluDocument29 pagesThe Second Law of Thermodynamics: Mehmet KanogluMalav PurohitNo ratings yet
- Journal of Energy Storage: J.P. Rouse, S.D. Garvey, B. Cárdenas, T.R. Davenne TDocument15 pagesJournal of Energy Storage: J.P. Rouse, S.D. Garvey, B. Cárdenas, T.R. Davenne TDanang AjiNo ratings yet
- Contact Hours/week:lecture:3, Tutorial:1, Practical:0::Department Core (DC)Document21 pagesContact Hours/week:lecture:3, Tutorial:1, Practical:0::Department Core (DC)AMAN GAUTAMNo ratings yet
- Instrument Ation, Control and Management of Batch Reactors Using Distributed ControlsDocument4 pagesInstrument Ation, Control and Management of Batch Reactors Using Distributed ControlsVytha MarmoetNo ratings yet
- People Oriented Innovation and DevelopmentDocument28 pagesPeople Oriented Innovation and DevelopmentshivaNo ratings yet
- Bme Question Bank PDFDocument41 pagesBme Question Bank PDFnagarajan224No ratings yet
- Lecture 16Document13 pagesLecture 16sanyamjain51150No ratings yet
- Unit 1-Introduction To Renewable EnergyDocument13 pagesUnit 1-Introduction To Renewable EnergyhoorparvaizfNo ratings yet
- Steam Power Plant - Part 1.1 HeatEngine - 2nd LawDocument17 pagesSteam Power Plant - Part 1.1 HeatEngine - 2nd LawMaznan JaafarNo ratings yet
- Power Plants: CH 6 Economics of Power Plants: Amer Al-AniDocument15 pagesPower Plants: CH 6 Economics of Power Plants: Amer Al-Anitarikayehu amanuelNo ratings yet
- Short-Term Frequency Stability Regulation For Power System With Large-Scale Wind Energy Penetration Using PID ControllerDocument5 pagesShort-Term Frequency Stability Regulation For Power System With Large-Scale Wind Energy Penetration Using PID ControllerEngr GM SialNo ratings yet
- Thermo Chapter - 8 - Lecture PDFDocument23 pagesThermo Chapter - 8 - Lecture PDFFattihiEkhmalNo ratings yet
- Captive Power PlantDocument6 pagesCaptive Power PlantAman SauravNo ratings yet
- Vapor Compression Refrigeration Cycle FoDocument11 pagesVapor Compression Refrigeration Cycle FoWilliam BassoliNo ratings yet
- PV TegDocument22 pagesPV TegPiyush Kumar SahooNo ratings yet
- Circuit Analysis, Theory and Practice 2nd EditionDocument22 pagesCircuit Analysis, Theory and Practice 2nd EditionsasikalasivakumarNo ratings yet
- Q.No. Part A Marks Unit IDocument36 pagesQ.No. Part A Marks Unit IThe car geek CargeekNo ratings yet
- Tem AguaDocument11 pagesTem AguaHugo MirandaNo ratings yet
- Power Plants: CH 6 Economics of Power Plants: Amer Al-AniDocument15 pagesPower Plants: CH 6 Economics of Power Plants: Amer Al-Anijuchaca36No ratings yet
- An Introduction to the Neutron Kinetics of Nuclear Power Reactors: Nuclear Engineering DivisionFrom EverandAn Introduction to the Neutron Kinetics of Nuclear Power Reactors: Nuclear Engineering DivisionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Bme Digital NotesDocument88 pagesBme Digital NotesAkshay KharmateNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument53 pagesUntitledASHWIN MUNo ratings yet
- 8269Document20 pages8269Vishnupriya VaradarajanNo ratings yet
- 3 s2.0 B9780128197233001256 MainDocument13 pages3 s2.0 B9780128197233001256 Mainmi IzuNo ratings yet
- Energies 16 07506Document18 pagesEnergies 16 07506smrasteg12No ratings yet
- Exp-1. Evacuative Tube ConcentratorDocument8 pagesExp-1. Evacuative Tube ConcentratorWaseem Nawaz MohammedNo ratings yet
- Wind Hydro 2Document6 pagesWind Hydro 2Vani TiwariNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 0029549393900439 MainDocument17 pages1 s2.0 0029549393900439 MainLyes AbbassenNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Heat and Mass TransferDocument11 pagesInternational Journal of Heat and Mass TransferFrancisco OppsNo ratings yet
- Energy Conversion and Management: A. Marni Sandid, M. Bassyouni, Driss Nehari, Y. ElhenawyDocument14 pagesEnergy Conversion and Management: A. Marni Sandid, M. Bassyouni, Driss Nehari, Y. Elhenawymahmoud hassanNo ratings yet
- REE - Question Bank-2Document1 pageREE - Question Bank-2Arc ReactorNo ratings yet
- Processes: Multi-Tubular Reactor For Hydrogen Production: CFD Thermal Design and Experimental TestingDocument15 pagesProcesses: Multi-Tubular Reactor For Hydrogen Production: CFD Thermal Design and Experimental TestingLaura KaracicNo ratings yet
- Pyro Chem Attendant IIDocument2 pagesPyro Chem Attendant IItrangweicoNo ratings yet
- Advanced Liquid Cooling in HCPVT Systems To Achieve Higher Energy EfficienciesDocument5 pagesAdvanced Liquid Cooling in HCPVT Systems To Achieve Higher Energy EfficienciesFelipeNo ratings yet
- Unit - IDocument39 pagesUnit - IhavejsnjNo ratings yet
- Manual Montaj Cobra 600iDocument130 pagesManual Montaj Cobra 600iDdanaa DanaNo ratings yet
- Spare Parts List E3325338891: Roll Clamp Roll ClampDocument13 pagesSpare Parts List E3325338891: Roll Clamp Roll ClampDmitriy100% (1)
- Analisis Investasi Penyediaan Air Baku Untuk PdamDocument7 pagesAnalisis Investasi Penyediaan Air Baku Untuk PdamsadanNo ratings yet
- Fast Web View PDF TomcatDocument2 pagesFast Web View PDF TomcatEddieNo ratings yet
- IT MAth QuestionsDocument24 pagesIT MAth QuestionsTechnicianccna100% (2)
- Ohm's Law (Lab Report)Document7 pagesOhm's Law (Lab Report)yuta titeNo ratings yet
- BiyDaalt2+OpenMP - Ipynb - ColaboratoryDocument3 pagesBiyDaalt2+OpenMP - Ipynb - ColaboratoryAngarag G.No ratings yet
- Introductory Statistics A Problem Solving Approach - 2nd EditionDocument890 pagesIntroductory Statistics A Problem Solving Approach - 2nd EditionManuel Guardia Araujo100% (2)
- Study of RGB Color Classification Using Fuzzy LogicDocument6 pagesStudy of RGB Color Classification Using Fuzzy LogicBhavin GajjarNo ratings yet
- Catalog Hensoldt 2016Document36 pagesCatalog Hensoldt 2016Panthep PattongNo ratings yet
- Effect of MG Content On Microstructure andDocument12 pagesEffect of MG Content On Microstructure andMohamed RamadanNo ratings yet
- Manual Sitrans Fup1010Document46 pagesManual Sitrans Fup1010cchung147554No ratings yet
- Python Lab 1Document4 pagesPython Lab 1vaskoreNo ratings yet
- Edr IonicsDocument3 pagesEdr IonicsMax JacintoNo ratings yet
- AISF302x en PDFDocument270 pagesAISF302x en PDFvsimongNo ratings yet
- Practica 3Document4 pagesPractica 3Fernxndo BxsxntesNo ratings yet
- Rubrics Vital Signs TakingDocument6 pagesRubrics Vital Signs TakingRichard SluderNo ratings yet
- The Postulates of Quantum Mechanics: Postulate 1Document6 pagesThe Postulates of Quantum Mechanics: Postulate 1sgybleeNo ratings yet
- BRKACI-3503 ACI Multi-SiteDocument67 pagesBRKACI-3503 ACI Multi-SiteronzoNo ratings yet
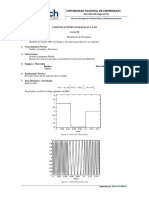
- To Study The Fourier Series and Transform by Using OscilloscopeDocument5 pagesTo Study The Fourier Series and Transform by Using OscilloscopeSagar RawalNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolytes Lecture NotesDocument85 pagesFluid and Electrolytes Lecture NotesVince Peliño De MesaNo ratings yet
- It Skills NotesDocument29 pagesIt Skills Notesjuttahtsham160No ratings yet
- Logistic RegressionDocument10 pagesLogistic RegressionNikhil GandhiNo ratings yet
- Sprint Case - Study IICS - UpdatedDocument3 pagesSprint Case - Study IICS - UpdatedajaybhosalNo ratings yet
- New Plan Ai TS 2022-2023 - Revised As On 17.08.2022Document2 pagesNew Plan Ai TS 2022-2023 - Revised As On 17.08.2022VANo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 Network DesignDocument132 pagesLecture 11 Network Designjon-jon anchetaNo ratings yet
- Turbine Control SystemDocument8 pagesTurbine Control SystemZakariya50% (2)
- Pac3A Sect 600 EarthworksDocument66 pagesPac3A Sect 600 EarthworksazizuddinNo ratings yet
- Assignment AEP 2014Document5 pagesAssignment AEP 2014Sagar MohanNo ratings yet
- HCIP Datacom Advanced RS H12 831 - V1.0 ENUDocument123 pagesHCIP Datacom Advanced RS H12 831 - V1.0 ENUguido.martini100% (2)