Professional Documents
Culture Documents
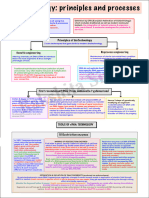
Biotechnology: Principles and Processes
Uploaded by
Rishi Rao AOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biotechnology: Principles and Processes
Uploaded by
Rishi Rao ACopyright:
Available Formats
Biotechnology : Principles and Processes
Biotechnology is the field of molecular biology dealing with the techniques of using live
microorganisms to produce products that are useful to humankind.
Genetic engineering
It is a technique used by scientists for manipulating genetic material of living organisms.
It involves artificial synthesis, isolation, modification and transfer of genetic material into a
host organism to alter its phenotype.
DNA cloning/Gene cloning: It is the method of making multiple identical copies of a single
gene.
Plasmid: It is a small, circular, extra-chromosomal genetic material that is capable of self
replication.
Characteristics of plasmid –
o Has an origin of replication
o Has a selectable marker
o One or few cloning sites
Recombinant DNA technology
It is a set of techniques for altering DNA. It includes the recognition and cloning of genes,
the study of the expression of cloned genes and the production of a large number of gene
products.
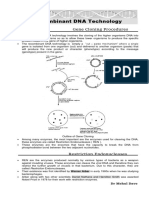
Construction of a Recombinant DNA
Plasmid (autonomously replicating, circular, extra-chromosomal DNA) is isolated.
Plasmid DNA is cut with a specific restriction enzyme at specific locations.
The DNA of interest (to be inserted) is also cut with the same restriction enzyme.
The DNA of interest is hybridised with the plasmid with the help of DNA ligase to form
a Recombinant DNA.
Recombinant DNA is then transferred into host for cloning.
i. Tools of recombinant DNA technology –
i. They are also known as molecular scissors.
o There are two types of restriction enzymes –
o Endonuclease: It removes the nucleotide from DNA fragments at specific positions within
the DNA.
o Exonuclease: It makes a cut at the 5’ or the 3’ end of DNA.
o Naming of restriction endonuclease enzyme (for example, in EcoRI)
o First letter represents the genus of bacteria
o The next two letters represent the species from which the enzyme is isolated.
o The second capital letter represents the name of the strain.
o The roman number indicates the order in which the enzyme is isolated.
Restriction endonuclease recognises a particular sequence known as palindromic
sequence.
o Palindrome is a sequence of base pairs that reads the same on the forward strand and the
reverse strand.
o Action of the restriction endonuclease enzyme
o The recognition sequence for the restriction enzyme EcoRI is
o EcoRI recognises this particular palindromic sequence and makes a cut between the
adjacent guanine and adenine nucleotides, thereby producing overhanging, single-stranded
pieces called sticky ends.
o The generated sticky ends can be joined by DNA ligase to form recombinant DNA molecule.
o Gel electrophoresis: It is a technique used for separating and isolating the DNA fragments
generated by the action of the endonuclease enzyme.
o Electric field is applied to the electrophrosis matrix (commonly agarose gel) and negatively
charged DNA moves towards anode.
o Fragments get separated according to their size.
Cloning vectors: Examples include plasmids and bacteriophage. Cloning vectors consist of
origin of replication (ori), selectable marker and one or few cloning sites.
o Insertional inactivation: It is a technique to select recombinant DNA on the basis of their
ability to produce colour in the presence of chromogenic substrate.
o Agrobacterium tumifaciens acts as a vector for cloning genes in plants.
o Retroviruses can be disarmed and used as cloning vectors in animals.
(iii) Transformation: It is the method of uptaking foreign DNA particle into a bacterial
cell. The following methods are used for transformation.
o Microinjection: It involves the injecting of recombinant DNA directly into the host cell
using micropipettes.
o Biolistics or gene gun: It involves the bombardment of gold or tungsten particles coated
with DNA into a plant cell.
Steps involved in recombinant DNA technology –
Isolation of genetic material: This is the method of obtaining purified DNA. It is achieved
by lysozyme in bacteria, by cellulase in plant cell and by chitinase in fungus.
Cutting of DNA at specific location: It is performed by using restriction endonuclease
and then separating the DNA fragments using agarose gel electrophoresis.
Amplification of gene: The gene is amplified using polymerase chain reaction.
o Polymerase chain reaction is a method of amplifying specific regions of DNA strand. It
involves three steps – denaturation, annealing and extension.
o This technique requires a set of primers and the thermostable DNA polymerase enzyme.
o The thermostable DNA polymerase enzyme is isolated from the bacterium called Thermus
aquaticus. The enzyme is resistant to denaturation by heat treatment.
Ligation of DNA fragments into the vector for cloning
Insertion of recombinant DNA into recipient cells
o It is done by making the cell competent to take up DNA from its surroundings. This method
is known as transformation.
Obtaining the gene product
o It involves culturing host cells in a medium and then extracting the desired product.
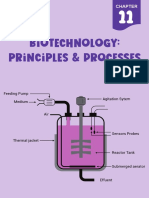
o Bioreactors: Used for large scale production of desired protein; two types of bioreactors
used –
o Simple stirred-tank bioreactor
o Sparged stirred-tank bioreactor
Downstream processing: It is the process of separation and purification of recombinant
protein so that product is ready for marketing.
Diagrammatic representation of recombinant DNA technology
You might also like
- Biology Project On Dna FingerprintingDocument21 pagesBiology Project On Dna Fingerprintingrichard74% (68)
- DNA Structure & Replication Quiz ReviewDocument4 pagesDNA Structure & Replication Quiz ReviewAlvin Pabores100% (1)
- The Double Helix: Film Activity Student HandoutDocument4 pagesThe Double Helix: Film Activity Student HandoutMatthew Spencer HoNo ratings yet
- DNA Review PacketDocument6 pagesDNA Review Packeteric wyatt100% (1)
- Rajkumar Biology Unit - 9 by RajatDocument12 pagesRajkumar Biology Unit - 9 by RajatprasannandaNo ratings yet
- Biotech Principles: Genetic Engineering & Microbial GrowthDocument6 pagesBiotech Principles: Genetic Engineering & Microbial GrowthIndrajith MjNo ratings yet
- II ME NRP B SS 27. Biotechnology-Principles and Processes, Biotechnology - ApplicationsDocument8 pagesII ME NRP B SS 27. Biotechnology-Principles and Processes, Biotechnology - ApplicationsAmit RavindhraNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology I (Lecture Note)Document8 pagesBiotechnology I (Lecture Note)Pranav ShinojNo ratings yet
- BIOTECHNOLOGYDocument9 pagesBIOTECHNOLOGYtamalbio7No ratings yet
- BiotechDocument5 pagesBiotechkaiaNo ratings yet
- Notebook Q & ADocument11 pagesNotebook Q & Aumamahfarooq75No ratings yet
- Biotechnology Principles and Processes - NotesDocument8 pagesBiotechnology Principles and Processes - NotesSquad 4 GamingNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY XII Study Material 2022-23 Chapter Wise PrepDocument29 pagesBIOLOGY XII Study Material 2022-23 Chapter Wise PrepashwinkumarcoimatoreNo ratings yet
- XII Biology Biotechnology: Principles and Pro0Cesses: Recombinant DNA TechnologyDocument8 pagesXII Biology Biotechnology: Principles and Pro0Cesses: Recombinant DNA TechnologyNobisuke NobiNo ratings yet
- Contents:: Project Report 1. Introduction To Recombinant DNA TechnologyDocument15 pagesContents:: Project Report 1. Introduction To Recombinant DNA TechnologyShivraj GundayyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-11 BiotechnologyDocument7 pagesChapter-11 BiotechnologyJay RoyNo ratings yet
- Hsslive XII Botany CH 11 Minhad NewDocument4 pagesHsslive XII Botany CH 11 Minhad NewAKUULLLNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Principles and Processes Revision Notes Cbse Class 12 BiologyDocument7 pagesBiotechnology Principles and Processes Revision Notes Cbse Class 12 Biologyak9268509No ratings yet
- Genetic EngineeringDocument38 pagesGenetic EngineeringNaila Izzaty KarimahNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Principles & ProcessesDocument3 pagesBiotechnology Principles & ProcessesKambaska Kumar BeheraNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology - Principles and Processes - Notes - June 2023Document15 pagesBiotechnology - Principles and Processes - Notes - June 2023Tahsinul islamNo ratings yet
- 11.1: Principles of BiotechnologyDocument10 pages11.1: Principles of BiotechnologyMauz KhanNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Principles and Processes NotesDocument9 pagesBiotechnology Principles and Processes NotessameemNo ratings yet
- PDF DocumentDocument10 pagesPDF Documentlisale2441No ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principle and ProcessDocument50 pagesChapter 11 Biotechnology Principle and ProcessMkisneymar Meymar100% (1)
- Biotechnology Principles and Processes: DNA Isolation and ManipulationDocument13 pagesBiotechnology Principles and Processes: DNA Isolation and Manipulationranvir madaviNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology NotesDocument11 pagesBiotechnology NotesExporting WarriorNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNA TechnologyDocument10 pagesRecombinant DNA TechnologySonam SharmaNo ratings yet
- rDNA PDFDocument11 pagesrDNA PDFbroken reedNo ratings yet
- Notes CH-11 Biotechnology and Its PrinciplesDocument6 pagesNotes CH-11 Biotechnology and Its Principles16739No ratings yet
- Genetic Engineering: Aliyu, HabibuDocument32 pagesGenetic Engineering: Aliyu, HabibuAkinsanmi TaiwoNo ratings yet
- Manipul. of Gene Expression in ProkaryotesDocument34 pagesManipul. of Gene Expression in ProkaryotesLeviathan ValleyNo ratings yet
- CBSE Biology Class XII Principles and Processes of BiotechnologyDocument7 pagesCBSE Biology Class XII Principles and Processes of BiotechnologyAkshat JainNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Principles & Processes PDFDocument3 pagesBiotechnology Principles & Processes PDFMEGHA KRISHNANNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document25 pagesModule 4Saalif RahmanNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology NotesDocument18 pagesBiotechnology NotesAmmar ZahidNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Principles and ProcessesDocument43 pagesBiotechnology Principles and ProcessesAnushka LimbuNo ratings yet
- BiotechnologyDocument6 pagesBiotechnologyRabiya ShaanNo ratings yet
- BiotechnologyDocument31 pagesBiotechnologyJijendarNo ratings yet
- Dr. V. P. Wankhade: Vidyabharti College of Pharmacy, AmravatiDocument31 pagesDr. V. P. Wankhade: Vidyabharti College of Pharmacy, AmravatiNikita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Bio TechnologyDocument51 pagesBio Technologylalithadithya85No ratings yet
- Useful To Human. Analogues For Products and Services: BIOTECHNOLOGY - Principles and ProcessesDocument10 pagesUseful To Human. Analogues For Products and Services: BIOTECHNOLOGY - Principles and ProcessesKorou LaikhaNo ratings yet
- Add A Little Bit of Body TextDocument9 pagesAdd A Little Bit of Body Textaayushparmar361No ratings yet
- Unit 9Document12 pagesUnit 9Rohan sharmaNo ratings yet
- CH 11Document11 pagesCH 11SakthivelNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 11: Quick Revision Notes Biotechnology - Principle and Processes Important TermsDocument4 pagesChapter - 11: Quick Revision Notes Biotechnology - Principle and Processes Important TermsShaharukh NadafNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Notes-1Document6 pagesBiotechnology Notes-1Exporting WarriorNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNA Technology - OurvleDocument30 pagesRecombinant DNA Technology - Ourvledpkf6dj725No ratings yet
- Aula BMol 2Document35 pagesAula BMol 2Diogo MadalenoNo ratings yet
- Genetic Engineering and RDNA TechnologyDocument83 pagesGenetic Engineering and RDNA TechnologyvaldezjesebyNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology: Presented by M QasimDocument15 pagesBiotechnology: Presented by M QasimFaiza RashidNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Principles and ProcessesDocument22 pagesBiotechnology Principles and Processesshreya sardesaiNo ratings yet
- GENETICSDocument56 pagesGENETICSKeziah Tayco100% (1)
- Recombinant DNA TechnologyDocument34 pagesRecombinant DNA TechnologyDr. M. Prasad NaiduNo ratings yet
- rDNA Technol Tools Chapter12Document15 pagesrDNA Technol Tools Chapter12Rajeev KalyanNo ratings yet
- 11 Biotechnology-Principles N Processes-Notes - ToDocument4 pages11 Biotechnology-Principles N Processes-Notes - ToArjun GowdaNo ratings yet
- Gene Cloning Procedures ExplainedDocument17 pagesGene Cloning Procedures ExplainedDRMEHUL DAVENo ratings yet
- Genetic Engineering (Recombinant DNA Technology)Document4 pagesGenetic Engineering (Recombinant DNA Technology)Geo NalobNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNA TechnologyDocument39 pagesRecombinant DNA TechnologyDr-Dalya ShakirNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNA TechnologyDocument80 pagesRecombinant DNA TechnologyRaizza Mae CorderoNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Comp Unit in One Shot Mindmaps by Rakshita SinghDocument7 pagesBiotechnology Comp Unit in One Shot Mindmaps by Rakshita Singhkchahar886No ratings yet
- GCMBDocument5 pagesGCMBHarshita SinhaNo ratings yet
- Strategies For Enhancement in Food ProductionDocument4 pagesStrategies For Enhancement in Food ProductionRishi Rao ANo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Organisms: Hydra and Yeast Chlamydomonas PenicilliumDocument4 pagesReproduction in Organisms: Hydra and Yeast Chlamydomonas PenicilliumRishi Rao ANo ratings yet
- Microbes in Human WelfareDocument2 pagesMicrobes in Human WelfareRishi Rao ANo ratings yet
- All The Best: Kannada English Physics Chemistry Biology MathsDocument1 pageAll The Best: Kannada English Physics Chemistry Biology MathsRishi Rao ANo ratings yet
- EcosystemDocument4 pagesEcosystemRishi Rao ANo ratings yet
- Enhancing Youth Political Participation Throughout The Electoral Cycle PDFDocument76 pagesEnhancing Youth Political Participation Throughout The Electoral Cycle PDFMuhammad Moshiur RahmanNo ratings yet
- College Student Registration Report 16370240639558Document4 pagesCollege Student Registration Report 16370240639558Rishi Rao ANo ratings yet
- S3 ZW 1 e 5 A7 HT INPYBczhhDocument2 pagesS3 ZW 1 e 5 A7 HT INPYBczhhRishi Rao ANo ratings yet
- S3 ZW 1 e 5 A7 HT INPYBczhhDocument2 pagesS3 ZW 1 e 5 A7 HT INPYBczhhRishi Rao ANo ratings yet
- S3 ZW 1 e 5 A7 HT INPYBczhhDocument2 pagesS3 ZW 1 e 5 A7 HT INPYBczhhRishi Rao ANo ratings yet
- DNA RepairDocument35 pagesDNA RepairAbid Al RezaNo ratings yet
- HnRNA ProcessingDocument38 pagesHnRNA ProcessingM.PRASAD NAIDUNo ratings yet
- Virtual LabDocument5 pagesVirtual LabNicole PunzalanNo ratings yet
- DNA Protein Synthesis Crime SceneDocument2 pagesDNA Protein Synthesis Crime SceneJaneNo ratings yet
- Genomic Tools For Crop ImprovementDocument41 pagesGenomic Tools For Crop ImprovementNeeru RedhuNo ratings yet
- Brochure amaROne Rev - 2019.05Document2 pagesBrochure amaROne Rev - 2019.05Nguyễn Khắc DuNo ratings yet
- From Gene To ProteinDocument42 pagesFrom Gene To ProteinNathan AdornadoNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles and Components of PCRDocument30 pagesBasic Principles and Components of PCRDiahNo ratings yet
- CloneJET PCR Cloning KitDocument9 pagesCloneJET PCR Cloning Kitodile1987No ratings yet
- Nucleic acids: DNA, RNA and protein synthesisDocument10 pagesNucleic acids: DNA, RNA and protein synthesisLeila BeyyoudhNo ratings yet
- Ph7gwiwg2 (I)Document2 pagesPh7gwiwg2 (I)xprakashNo ratings yet
- PCR, DNA Sequencing and in Vitro Mutagensis: Chapter 6Document29 pagesPCR, DNA Sequencing and in Vitro Mutagensis: Chapter 6trandoanngoc100% (2)
- DNA to Proteins Practice: From DNA to Protein MutationDocument2 pagesDNA to Proteins Practice: From DNA to Protein MutationpaulakaczNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry, Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument4 pagesBiochemistry, Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfsasaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid - WikipediaDocument1 pageNucleic Acid - WikipediaElton ViannaNo ratings yet
- Illustrated DIY CRISPR - Freeze Dried DH5a Liquid PlasmidsDocument19 pagesIllustrated DIY CRISPR - Freeze Dried DH5a Liquid PlasmidsKevin LimNo ratings yet
- Molecular BiologyDocument20 pagesMolecular BiologyDaphne CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- Biology STD 12: Biology MCQ: Section A //X Choose Correct Answer From The Given Options. (Each Carries 1 Mark)Document10 pagesBiology STD 12: Biology MCQ: Section A //X Choose Correct Answer From The Given Options. (Each Carries 1 Mark)Darshil MakwanaNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic DNA Replication OriginsDocument81 pagesEukaryotic DNA Replication OriginsBintang PundhraNo ratings yet
- Transcription and Translation Practice WorksheetDocument4 pagesTranscription and Translation Practice Worksheetsmith joeNo ratings yet
- Day 29 - Daily MCQ Workout - 40 Revision MCQsDocument5 pagesDay 29 - Daily MCQ Workout - 40 Revision MCQsnorah araujoNo ratings yet
- RNA Structure and TypesDocument39 pagesRNA Structure and Typesshubham sachdeva100% (1)
- IG. Primer-Blast Results MARFAN NM - 000138.5Document11 pagesIG. Primer-Blast Results MARFAN NM - 000138.5Josue BarralNo ratings yet
- Carter Et Al.2023. Estimating Phylogenetics From GenomesDocument13 pagesCarter Et Al.2023. Estimating Phylogenetics From GenomesLAURA SOFIA AVILA CANTORNo ratings yet
- A Beginners Guide To RT PCR QPCRDocument6 pagesA Beginners Guide To RT PCR QPCRTom WrightNo ratings yet
- 4-Molecular Basis of HeredityDocument4 pages4-Molecular Basis of HereditylarraNo ratings yet