Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Change The % Into Grams (23% Na - 23g Na) : Grams of An Element Total Moles
Uploaded by
Aliance Mary AdorioOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Change The % Into Grams (23% Na - 23g Na) : Grams of An Element Total Moles
Uploaded by
Aliance Mary AdorioCopyright:
Available Formats
GENCHEM FORMULAS Change the % into grams (23% Na – 23g Na)
Celsius to Kelvin 1 mol
grams of an element= ( ) = total moles;
molar mass
K= C + 273.15
total moles
= Empirical mass
Kelvin to Celsius smallest total moles
o
C= K – 273.15 Molecular Formula
Celsius to Fahrenheit Execute the formula of Empirical formula, as you get the
Empirical mass,
9o
F= ( C) + 32
5 molar mass of an element
=
empirical mass
Fahrenheit to Celsius
multiply the quotient to the subscript to get the total
o o 5
C= ( F – 32) molecular mass.
9
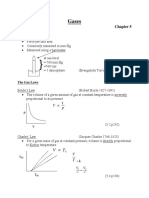
GAS LAWS FORMULAS
Stoichiometry/ Quantitative Composition of Compounds
Note:
Note:
Ideal gas: Standard pressure= 1 atm, Standard
1 mole= 6.02x1023 molecules
temperature= 273.15 K or 273K, Standard Volume=
Atomic mass(amu)= total number of atomic weight of 22.4L
an element
Boyle’s Law
Formula weight (FW)= Molecular weight (MW)= molar
P1V1 = P2V2
mass
P2V 2 P2V 2 P1V 1 P1V 1
Finding FW/MW/Molar Mass P1 = ; V1 = ; P2 = ; V2=
V1 P1 V2 P2
{sum of all atomic weight of elements}
Charles Law
Grams to Moles
V1T2= V2T1
1 mol
grams ( )= mol V 2T 1 V 2T 1 V 1T 2 V 1T 2
grams V1 = ; T2= ; V2= ; T1=
T2 V1 T1 V2
Moles to Grams
Gay-Lussac Law
g /mol
mol ( )= grams P1T2= P2T1
1 mol
P2T 1 P2T 1 P1T 2 P1T 2
Moles to Particles P1 = ; T2= ; P2= ; T1=
T2 P1 T1 P2
6.02 x 1023 molec ules Combined Gas Law
Moles ( )= molecules
1mol
P1V1T2 = P2V2T1
Percentage Composition
P 2 V 2T 1 P 2 V 2T 1 P 2 V 2T 1
atomic mass P1 =
V 1T 2
; V1 =
P 1T 2
; T2=
P1V 1
;
Mass % of Element = X 100
molar mass
P1V 1T 2 P1V 1T 2 P1V 1T 2
(if you get all the % of all the given elements, if they all added up, P2 = ; V2= ; T1=
they all should be equal to 100) V 2T 1 P 2T 1 P2V 2
Empirical Formula Avogadro’s Law
V1n2 = V2n1 Mass to Number of Particles
V 2n1 V 2n1 V 1n2 V 1n2
V1= n 2 ; n2= V 1 ; V2= n 1 ; n1= V 2
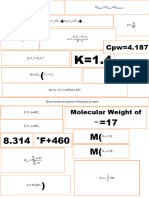
Ideal Gas Law
L . atm
PV=nRT {R= 0.0821 } constant
mol . K
nRT nRT PV PV PV
P= V ; V= P ; n= RT ; R= nT ; T= nR
Percent Yield
Molecular weight? (Ideal Gas Law) Actual yield
Percent yield = x 100
{W= mass in grams} Theoretical yield
W RT
M=
PV
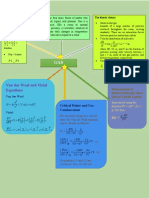
Additional formulas for Gas Law
Boyle’s Law
1 K
Pα ; P=
V V
Ideal Gas Law
PMW
PVMW=mRT ; D=
RT
Aqueous Reactions and Solutions
Concentration
(subscript of an element) x (given M) =
mol Coefficient
Or = =
1 L solvent 1 mol
Molarity Formula
moles of solute mol
M= ; M=
Liters∈solvent L
mol
moles= (M)(L); L=
Molarity
Dilution Formula
M1V1= M2V2
M 2V 2 M 2V 2
M1= ; V1=
V1 M1
M 1V 1 M 1V 1
M2= ; V2=
V2 M2
Stoichiometry
You might also like
- Solution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsFrom EverandSolution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Supersonic ReviewerDocument36 pagesSupersonic ReviewerBerns Dulam100% (1)
- Chemical Technician Review GasesDocument53 pagesChemical Technician Review GasesJasonTenebrosoNo ratings yet
- Vacuum Engineering Calculations, Formulas, and Solved ExercisesFrom EverandVacuum Engineering Calculations, Formulas, and Solved ExercisesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Pages From Glencoe - Chemistry - Matter and Change (Mcgraw 2008) ch10Document46 pagesPages From Glencoe - Chemistry - Matter and Change (Mcgraw 2008) ch10api-261034721No ratings yet
- Genchem FormulasDocument2 pagesGenchem FormulasAliance Mary AdorioNo ratings yet
- All Formulas Revision in One Shot For JEE Main 2021 Feb Attempt (21-02-2021)Document85 pagesAll Formulas Revision in One Shot For JEE Main 2021 Feb Attempt (21-02-2021)Kampili akashNo ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument6 pagesGas LawskimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 GasesDocument8 pagesChapter 5 GasessamNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Gas LawsDocument3 pagesStudy Guide Gas LawsAdamNo ratings yet
- Chem0861 GasLawProblemsDocument3 pagesChem0861 GasLawProblemsHavenNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics CH 5Document32 pagesThermodynamics CH 5WILYNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 560982adad40bDocument5 pagesChapter 3 560982adad40bJimson MasculinoNo ratings yet
- Chapter09 Kinetic Theory of Gases SDocument10 pagesChapter09 Kinetic Theory of Gases SeltytanNo ratings yet
- 2.gaseous State PDFDocument13 pages2.gaseous State PDFP. E. I. AcademicsNo ratings yet
- Gaseous State Worksheet PDFDocument10 pagesGaseous State Worksheet PDFHarsh Agarwal100% (1)
- Gas Laws Cheat SheetDocument1 pageGas Laws Cheat SheetJohn Cailen Barceñas IINo ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument2 pagesGas Lawskimtaemin1997.stageNo ratings yet
- Gas LawDocument14 pagesGas LawRoszelan Majid100% (1)
- General Chemistry 1: NRT P Atm Mol KDocument2 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1: NRT P Atm Mol KViannix GameplayNo ratings yet
- Problem 2725Document29 pagesProblem 2725Clyde SuerteNo ratings yet
- 5.0 STATES OF MATTER - NOTES & TUTORIAL Q'sDocument27 pages5.0 STATES OF MATTER - NOTES & TUTORIAL Q'sFida KhaidzirNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Problems1-100Document5 pagesThermodynamics Problems1-100Monique OrugaNo ratings yet
- 6 - ch5 Aa 0Document49 pages6 - ch5 Aa 0Edlyn RamirezNo ratings yet
- Investigative Activity of Ideal Gas LawDocument7 pagesInvestigative Activity of Ideal Gas LawShaina AdralesNo ratings yet
- GUIDE Group Exercise #17: This Study Resource WasDocument2 pagesGUIDE Group Exercise #17: This Study Resource WasnicoleNo ratings yet
- Gaseous StateDocument3 pagesGaseous StateSiya ThakkarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 GasesDocument30 pagesChapter 13 GasesGwen100% (1)
- State of Matter Gases and Liquids - Short Notes - Arjuna NEET 2024Document2 pagesState of Matter Gases and Liquids - Short Notes - Arjuna NEET 2024shraddha2572sharmaNo ratings yet
- ChapterII - GasesDocument40 pagesChapterII - Gasesjumanahelmy12No ratings yet
- CHPT 06Document6 pagesCHPT 06Joshua ZikuNo ratings yet
- EU2-Chap 4Document2 pagesEU2-Chap 4Kevin Mark IlaganNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas Law: PVNRT - Notebook November 02, 2015Document8 pagesIdeal Gas Law: PVNRT - Notebook November 02, 2015Faith AsdfNo ratings yet
- Thermal PropertiesDocument21 pagesThermal PropertiesNIGGERHATErNo ratings yet
- Van Der Waal and Virial Equations: V1 T1 V2 T2 DN N MDocument4 pagesVan Der Waal and Virial Equations: V1 T1 V2 T2 DN N MAyu SuwarniNo ratings yet
- Gases: Course Name: Chemistry 101 Course CodeDocument28 pagesGases: Course Name: Chemistry 101 Course CodeHeartcheNo ratings yet
- ME2121 Thermodynamics: The Psychrometric ChartDocument4 pagesME2121 Thermodynamics: The Psychrometric ChartDesiree LinNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics NotesDocument13 pagesThermodynamics NotesParas ThakurNo ratings yet
- W-4, Chap.3-Properties of Pure Substances-2Document31 pagesW-4, Chap.3-Properties of Pure Substances-2سيمو بشيريNo ratings yet
- E Rathakrishnan Gas Dynamics SolutionsDocument216 pagesE Rathakrishnan Gas Dynamics SolutionsVigneshVickey67% (15)
- Topic 4 States of MatterDocument43 pagesTopic 4 States of MatterJowyn SeetNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry: Pressure and Its Common UnitsDocument15 pagesGeneral Chemistry: Pressure and Its Common UnitsDenver John Caloza LamarcaNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws Ws PDFDocument6 pagesGas Laws Ws PDFJulia Franchesca BorromeoNo ratings yet
- 5.0 States of MatterDocument106 pages5.0 States of MatterTasya KassimNo ratings yet
- Properties of Mixtures Mixture of Perfect GasesDocument7 pagesProperties of Mixtures Mixture of Perfect GasesAudu SanusiNo ratings yet
- Formulario Termodinamica 1Document2 pagesFormulario Termodinamica 1Jesus LyroyNo ratings yet
- THERMO1 Formula SheetDocument7 pagesTHERMO1 Formula SheetNyahaha HahahNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument38 pagesStates of MatterJack LupinoNo ratings yet
- TF Lecture 07Document6 pagesTF Lecture 07chandumamidi18No ratings yet
- CH 5Document50 pagesCH 5Paul ArcillaNo ratings yet
- Mole Concept: Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocument19 pagesMole Concept: Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryNaman AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Ideal GasDocument24 pagesIdeal Gastechno studioNo ratings yet
- BSG 104 Gas LawsDocument35 pagesBSG 104 Gas LawsCJ DRBNo ratings yet
- 1.10 Partial Pressures and KP: Mole FractionDocument3 pages1.10 Partial Pressures and KP: Mole Fractionbazel mukuzeNo ratings yet
- Note Ideal Gas TutorialDocument5 pagesNote Ideal Gas TutorialGnabryNo ratings yet
- E233 - Thermofluids: The Perfect GasDocument16 pagesE233 - Thermofluids: The Perfect GasYingyote LubphooNo ratings yet
- Air Standard CycleDocument54 pagesAir Standard CycleKhurram SherazNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium Constant of PressureDocument2 pagesEquilibrium Constant of PressureMic DropNo ratings yet
- CHM 101 Lecture Note-Gas LawsDocument11 pagesCHM 101 Lecture Note-Gas LawsMichael DanielsNo ratings yet
- Module 11 - The Gas PhaseDocument15 pagesModule 11 - The Gas PhaseAna Maria Millan RinconNo ratings yet
- Main Staar Chemistry Reference MaterialsDocument4 pagesMain Staar Chemistry Reference MaterialsEmma UtterbackNo ratings yet
- Mole Concept Sheet - 01 (Exercise-1)Document36 pagesMole Concept Sheet - 01 (Exercise-1)New AccountNo ratings yet
- Student Edexce Moles Workbook Unit 1 PDFDocument112 pagesStudent Edexce Moles Workbook Unit 1 PDFdhawana20% (1)
- Module 4 Polymers & Green FuelsDocument8 pagesModule 4 Polymers & Green Fuelsdeepika seran100% (2)
- 1108apni KakshaDocument10 pages1108apni KakshaOjasNo ratings yet
- MoleDocument30 pagesMoleHelenora Mae LapenaNo ratings yet
- Some Basic DPPDocument11 pagesSome Basic DPPtanishqpawar360No ratings yet
- Soal Dan Jawaban Kimia Dasar Chapter 12Document5 pagesSoal Dan Jawaban Kimia Dasar Chapter 12cacaNo ratings yet
- B 098Document17 pagesB 098Suresh NeeluriNo ratings yet
- SOLUTIONS WorksheetDocument2 pagesSOLUTIONS WorksheetKingsley CalexNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry Challenge - Experiment ReportDocument11 pagesStoichiometry Challenge - Experiment ReportsamansarsarNo ratings yet
- Stoikiometri - Konsep MolDocument41 pagesStoikiometri - Konsep MolElmayaNo ratings yet
- Csec Chemistry Notes 3Document2 pagesCsec Chemistry Notes 3debestieNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Worksheet - Atoms and MoleculesDocument15 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Worksheet - Atoms and Moleculesaaliya raiyaniNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Exam Grade 9Document3 pages2nd Quarter Exam Grade 9Ma. Lourdes CarbonillaNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Chemistry and Chemical Calculations: Unit - 1Document3 pagesBasic Concepts of Chemistry and Chemical Calculations: Unit - 1AfsarNo ratings yet
- IB Chemistry SL ReviewDocument120 pagesIB Chemistry SL ReviewShamwow_12389% (9)
- The Relative Atomic MassDocument42 pagesThe Relative Atomic MassMorris KariukiNo ratings yet
- CHM01 CO4 LESSON1 StoichiometryDocument16 pagesCHM01 CO4 LESSON1 StoichiometryLance Giello DuzonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3. Stoichiometry: Calculations With Chemical Formulas and EquationsDocument14 pagesChapter 3. Stoichiometry: Calculations With Chemical Formulas and Equationssrinivasan01981No ratings yet
- Set 4 DK014Document4 pagesSet 4 DK014faris zainuddinNo ratings yet
- Ch9-Stoichiometry 2Document87 pagesCh9-Stoichiometry 2Jorelyn FriasNo ratings yet
- Mole ConceptDocument32 pagesMole ConceptFatin ComelNo ratings yet
- Mole MoleDocument4 pagesMole Moleshaikha_77No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 1Document74 pagesOrganic Chemistry 1jemimahisraelNo ratings yet
- The Mole Concept and StoichiometryDocument41 pagesThe Mole Concept and StoichiometryAshe BekNo ratings yet
- ISO 23210 2009 Calculation Program EDocument9 pagesISO 23210 2009 Calculation Program ETri SulyonoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 StoichiometryDocument45 pagesLecture 2 StoichiometryKalinda MondeNo ratings yet
- Titration GuideDocument44 pagesTitration GuideMichel M.No ratings yet
- This PDF Is The Sample PDF Taken From Our Comprehensive Study Material For IIT-JEE Main & AdvancedDocument13 pagesThis PDF Is The Sample PDF Taken From Our Comprehensive Study Material For IIT-JEE Main & AdvancedGod is every whereNo ratings yet