Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sci7 Unitb Vocabwords
Uploaded by
api-453560453Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sci7 Unitb Vocabwords
Uploaded by
api-453560453Copyright:
Available Formats
Name: ____________________
Vocabulary Sheet
Unit B: Plants for Food and Fibre
Word Definition Example
Section 1.0
1. seed plants plants that make ________.
2. stems conducts ________, ___________,
and _______ to other parts of the
plant; it may also ________ food.
3. flowers/fruits Flower – reproductive _______ of
the _____________ plant. Fruit –
_______-bearing structure
(produced by the ovary of
flowering plant).
4. cones _________ the reproductive organs
of certain ______flowering plants.
5. seeds contains an _________ that will
form a ______ plant.
6. leaves __________ site of photosynthesis,
which helps nourish and sustain
life.
7. roots found underground and functions
by ___________water and
dissolved __________ in soil.
8. transpiration the plant process that ______
water ____ from the _______.
9. capillary action movement of _________ up a
__________ tube; happens when
____________ of liquid particles to
each other is _____ than their
____________ to the _____ of the
tube.
10. osmosis in cells, the _____________ of
water ________ the cell
_____________.
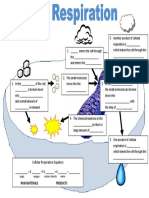
11. photosynthesis process by which plants use light
energy, carbon dioxide, and water
to make their own food.
12. chloroplasts the ____________ in plant cells
that _________ ______
photosynthesis.
13. cellular respiration the process in which cells
breakdown sugar particles into
carbon dioxide, water, and energy.
14. pores tiny ___________ in the cell
____________ of plants; allows
certain substances to _______ in
and out of the cell.
15. diffusion the ___________ of ____________
from an area of ______
concentration to an area with a
______ concentration.
16. concentration the __________ of ___________ of
one substance in a certain
_________ of another substance.
17. active transport the process in which __________
particles ________ the cell
membrane; active transport
requires ________.
18. gas exchange the process by which ________
____________ and oxygen _______
in and out of the plant.
19. life cycle the _______ that an organism Ex. life cycle of a seed…
passes through in going from one *draw*
_____________ to the _______.
20. pollination the process in which ______ and
__________ parts of a plant join to
_________ a seed.
21. pollen the ______ part of a seed plant
that ________ with the female part
to produce a seed; pollen is
produced by either __________ or
male ________.
22. ovary a _____________ structure on a
seed plant that contains the
_______; ovaries are often in the
_________ of a flower or on a
female cone.
23. ovule the __________ part of a seed
plant that joins with the male part
to produce a seed; ovals are usually
found __________ an ovary.
24. pollinator an ____________ that ________
pollen from one flower to another.
25. vegetative reproduction of ________ plants
reproduction. that does _____ involve the
production of seeds.
26. runners long _________ that ______ along
the ______ of the surface and
produce new plants.
27. rhizomes stems that grow __________ stems
and produce new plants.
28. suckers _____ plants that are produced
from the roots of the __________
plant.
29. cutting A cut piece of a _________ that is
used to ______________ that
plant; cuttings usually have a part
of the stem and a few leaves.
30. grafting a _______________ to reproduce
plants that involve _____________
part of one plant to a second plant.
31. nutrients components of food that supplies
energy or building material to a
living thing.
Section 2.0
32. erosion the __________ that _______ soil
from one place to another.
33. organisms
34. shelter plants __________ other
____________ from the weather
and from predators.
35. fibre a material composed of ______ and Ex. Plant fibre
continuous __________.
36. living resources living things that can be used to
meet human ________.
Section 3.0
37. soil _________ material composed of
_______ particles and decaying
____________ matter.
38. mineral particles particles in ______ that come from
rock that has been ________ down.
39. organic particles ___________ in soil that come
from plants and animals that have
______: __________ is composed
of organic particles.
40. humus partly ______________ material
from plants and animals that were
once ___________.
41. irrigation
42. plowing/ploughin the practice of ___________ into
g ______ and turning its _____ layer
________.
43. crop rotation the practice of planting a
__________ crop in a particular
field each _______.
Section 4.0
44. yield the ____________ of __________
plant material produced per
_________, or per _______ planted
in a particular crop.
45. hydroponics a technology for __________ plants
in which the plant _______ are
placed ___ a nutrient solution
___________ of soil.
46. selective breeding a technology for producing ______
varieties of an organism that
involves ___________ parents with
desired _______ in order to
produce ____________ with these
traits.
47. species living things of the same kind that
can reproduce.
48. variety a ________ of organisms of the
same species that has __________
characteristics that can distinguish
it from other varieties of that
species.
49. traits
50. genetic process in which _________ genes
engineering are added to a plant's ___________
material.
51. (a) gene ______ piece of material in a cell's
nucleus; each _______ in a cell is
responsible for the inheritance of
certain traits or characteristics.
52. herbicides A ___________ that ______
unwanted __________.
53. pesticides ___________ that are
_____________ to __________.
54. biological control a technology for controlling
_______ in which the natural
_____________ of the pests are
introduced into an environment to
_________ their population _____.
55. unintended results of an action that were not
consequences predicted or planned.
56. environmental the process of _____________ the
management ______ of humans with the
_______ of the environment.
57. monoculture the practice of growing only _____
type of _______ in a __________
area.
58. biodiversity the number of __________ species
in an ________________.
59. sustainable can be _____________ or
(sustained) _____________; capable of being
used indefinitely, often referring to
the _____ of resources.
You might also like
- 12th Biology NCERT Microassignments All Chapters - FinalDocument38 pages12th Biology NCERT Microassignments All Chapters - Finalasdwaad0% (2)
- Revision For Mid Term Test 2.: Module: C - Importance of PlantsDocument10 pagesRevision For Mid Term Test 2.: Module: C - Importance of Plantsvenice tranNo ratings yet
- ReproductionDocument21 pagesReproductionSahrulRashidNo ratings yet
- Active Recall WorksheetDocument9 pagesActive Recall Worksheetanweshaasingh22No ratings yet
- Name: - GR & Sec: - A. Answer The Following QuestionsDocument2 pagesName: - GR & Sec: - A. Answer The Following QuestionsLorena DizonNo ratings yet
- SC Form 1Document4 pagesSC Form 1Nurul NadiaNo ratings yet
- Science 5 QuizDocument3 pagesScience 5 Quizmarife galecioNo ratings yet
- Primary 5 Science Unit 2 Adaptation of PlantsDocument2 pagesPrimary 5 Science Unit 2 Adaptation of PlantsMonika DamanikNo ratings yet
- Latihan Chap 7 f4Document3 pagesLatihan Chap 7 f4Faizal PejerNo ratings yet
- Cell NotesDocument12 pagesCell NotesP1No ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom Unit TestDocument7 pagesPlant Kingdom Unit TestrileysandersjakeNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Plants - Revision QuestionsDocument2 pagesReproduction in Plants - Revision Questionsradhika fomraNo ratings yet
- 11th Biology NCERT Microassignments All Chapters - FinalDocument58 pages11th Biology NCERT Microassignments All Chapters - FinalKayu KayathriNo ratings yet
- Science QuizDocument2 pagesScience QuizAlexandra Pauline DimayugaNo ratings yet
- Grain PHT QuetionairesDocument5 pagesGrain PHT QuetionairesLoushh OcampoNo ratings yet
- Propagation Powerpoint StudentDocument18 pagesPropagation Powerpoint StudentAnnabelle Matat-enNo ratings yet
- Science Grade 4 Q1 Revision Sheet Dalia El-Hawey-2-1Document6 pagesScience Grade 4 Q1 Revision Sheet Dalia El-Hawey-2-1Ruwina AymanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Ecosystem NewDocument38 pagesChapter 2 - Ecosystem NewZubair HUssainNo ratings yet
- Sex Fill in The BlanksDocument2 pagesSex Fill in The BlanksFabriV9No ratings yet
- Intro To PlantsDocument15 pagesIntro To PlantsJanelle BerkemeierNo ratings yet
- Botany QuizzzDocument17 pagesBotany QuizzzApichayaNo ratings yet
- Cell: The Unit of LifeDocument6 pagesCell: The Unit of LifeSamyakNo ratings yet
- Unit 1-Basic NeedsDocument3 pagesUnit 1-Basic NeedsKeroltakeshi KaneshiroNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Plants VIIDocument2 pagesReproduction in Plants VIISantoshPathakNo ratings yet
- Pre-Test in Sciq2Document1 pagePre-Test in Sciq2Erwin San JoseNo ratings yet
- Biology: Chapter 24: Sexual Rep. in Flow. PlantDocument21 pagesBiology: Chapter 24: Sexual Rep. in Flow. PlantAditya ManeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Study Guide Study Guide Section 1 A Protist Belongs ToDocument2 pagesChapter 11 Study Guide Study Guide Section 1 A Protist Belongs ToAbrar HussamNo ratings yet
- Botany-Morphology-Fill in The BlanksDocument10 pagesBotany-Morphology-Fill in The BlanksSK M Basha100% (2)
- 2019 Grade Three WorksheetDocument14 pages2019 Grade Three Worksheetmon pereNo ratings yet
- Biology: 1. CellDocument8 pagesBiology: 1. CellAtiqueNo ratings yet
- Soal Ipa Kelas 6 SDDocument1 pageSoal Ipa Kelas 6 SDana novita liaNo ratings yet
- Science TutionDocument2 pagesScience TutionMonal ShastriNo ratings yet
- Exercise Science Form 1Document1 pageExercise Science Form 1Komalata Manokaran50% (2)
- SCIENCE4 QUARTERLY4 Jen1Document2 pagesSCIENCE4 QUARTERLY4 Jen1Yn DelNo ratings yet
- The Great Plant EscapeDocument5 pagesThe Great Plant EscapeLynn DeLeon100% (2)
- std.5 - Science Vacation Worksheet - 2023 PDFDocument8 pagesstd.5 - Science Vacation Worksheet - 2023 PDFTheMoneyMitraNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Reviewer in ScienceDocument1 page2nd Quarter Reviewer in ScienceLuna LedezmaNo ratings yet
- Plant Structure and Function: Interpreting DiagramsDocument4 pagesPlant Structure and Function: Interpreting DiagramsWayne CasanovaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration FlowchartDocument1 pageCellular Respiration FlowchartHaley OsbornNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction QUIZ: - Life ScienceDocument1 pagePlant Reproduction QUIZ: - Life Sciencesmitha raoNo ratings yet
- Zoology EcosystemDocument5 pagesZoology EcosystemHadiya FatimaNo ratings yet
- Science Workbook - 5thG - MercedesZamDocument80 pagesScience Workbook - 5thG - MercedesZamdaniela dueñasNo ratings yet
- EALS Perpetuation of LifeDocument1 pageEALS Perpetuation of LifeClaudene GellaNo ratings yet
- 6th Class 2nd Term Quick Revision WorksheetDocument4 pages6th Class 2nd Term Quick Revision WorksheetMazhar FarooqNo ratings yet
- Worksheet: © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private LimitedDocument7 pagesWorksheet: © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private LimitedKaung Myat SanNo ratings yet
- Science No.24 PDFDocument9 pagesScience No.24 PDFPanida Mhew SukkasemNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument39 pagesPlant Kingdompreethikarnam35No ratings yet
- Botany Lesson 1 Study Guide StudentDocument2 pagesBotany Lesson 1 Study Guide StudentjessieNo ratings yet
- Q1. Choose The Correct Answer:: Elpro International School Worksheet 2020-21Document2 pagesQ1. Choose The Correct Answer:: Elpro International School Worksheet 2020-21FoundationNo ratings yet
- 4th Grade Science Vocabulary Blanks 12-13Document4 pages4th Grade Science Vocabulary Blanks 12-13Ana Raymundo VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Cell - The Unit of Life Line-By-Line NcertDocument14 pagesCell - The Unit of Life Line-By-Line Ncertchandumenswear3No ratings yet
- Evaluacion U2Document5 pagesEvaluacion U2CAROLINA ANDREA SOTO CORREANo ratings yet
- Understanding Reinforcement Exercise Sains SPM BacteriaDocument5 pagesUnderstanding Reinforcement Exercise Sains SPM BacteriaEric ChongNo ratings yet
- Grade 2 2nd Q ScienceDocument6 pagesGrade 2 2nd Q Scienceflower.power11233986No ratings yet
- SOL Review Answer SheetDocument15 pagesSOL Review Answer Sheetbrandonaniah7No ratings yet
- Class 11 Neet Cell - The Unit of LifeDocument14 pagesClass 11 Neet Cell - The Unit of LifeViswaNo ratings yet
- G7 FR U6L1-Bacteria-Class WorksheetDocument6 pagesG7 FR U6L1-Bacteria-Class Worksheetweijun wuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Nutrition in Plants: Fill in The BlanksDocument1 pageChapter 1: Nutrition in Plants: Fill in The BlanksTulasi NarayanamNo ratings yet
- Professional insect rearing: Strategical points and management methodFrom EverandProfessional insect rearing: Strategical points and management methodNo ratings yet
- ps3 PipDocument11 pagesps3 Pipapi-453560453No ratings yet
- Science7 Interact Eco Unitplan AmandayostDocument19 pagesScience7 Interact Eco Unitplan Amandayostapi-453560453No ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Understanding Percent Section 4.1 - Representing PercentsDocument9 pagesChapter 4: Understanding Percent Section 4.1 - Representing Percentsapi-453560453No ratings yet
- Longrangeplan Science7 AmandayostDocument5 pagesLongrangeplan Science7 Amandayostapi-453560453No ratings yet
- Smart Goals ps3Document3 pagesSmart Goals ps3api-453560453No ratings yet
- gr7 Planetearth Finalproject YostDocument7 pagesgr7 Planetearth Finalproject Yostapi-453560453No ratings yet
- Annual Professional Growth Plan Incorporating ReflectionDocument4 pagesAnnual Professional Growth Plan Incorporating Reflectionapi-453560453No ratings yet
- Micro TeachDocument2 pagesMicro Teachapi-453560453No ratings yet
- Individual Student Experience Is The FocusDocument2 pagesIndividual Student Experience Is The Focusapi-453560453No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 ADocument12 pagesChapter 1 ASuha AlgharazNo ratings yet
- Haematology and Biochemistry Reference Values For Sows Kept Under Modern Management ConditionsDocument5 pagesHaematology and Biochemistry Reference Values For Sows Kept Under Modern Management ConditionsDianaNo ratings yet
- Switch From Sexual To Parthenogenetic Reproduction in A Zebra SharkDocument8 pagesSwitch From Sexual To Parthenogenetic Reproduction in A Zebra SharkGIULIA GIULIANINo ratings yet
- Notice Filing Affidavit Leah Larkin Support Defendants 3rd Motion CompelDocument14 pagesNotice Filing Affidavit Leah Larkin Support Defendants 3rd Motion CompelMatt Blac inc.100% (1)
- Hall+Collis Integron Review MolMic1995Document9 pagesHall+Collis Integron Review MolMic1995DrAhmedSalimNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Breathing 2023Document17 pagesPhysiology of Breathing 2023ErickTéquizNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Review of Theories Related To The Learners DevelopmentDocument5 pagesModule 3 Review of Theories Related To The Learners Developmentshiela67% (3)
- Challenges OF Nanotechnology: B Manasa D Tejaswi Naidu MD JavedDocument13 pagesChallenges OF Nanotechnology: B Manasa D Tejaswi Naidu MD JavedManasa BanothNo ratings yet
- Maceration 101 - How To Clean Bones With Water OddArticulations, LLC - HTMLDocument39 pagesMaceration 101 - How To Clean Bones With Water OddArticulations, LLC - HTMLvftytdyu34No ratings yet
- ICMR-National Institute of Virology, Kerala UnitDocument4 pagesICMR-National Institute of Virology, Kerala Unitrt prepNo ratings yet
- The Lac Operon: (BIOT 4006: Genetics and Molecular Biology)Document8 pagesThe Lac Operon: (BIOT 4006: Genetics and Molecular Biology)Alina RafiqueNo ratings yet
- Honors Biology: 21-22 Midterm Exam Review PacketDocument11 pagesHonors Biology: 21-22 Midterm Exam Review PacketaubreymertNo ratings yet
- Clown Knifefish (Chitala Ornata) : Ecological Risk Screening SummaryDocument13 pagesClown Knifefish (Chitala Ornata) : Ecological Risk Screening SummaryAdi PutraNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEM Lec 1 - Introduction To BiochemistryDocument53 pagesBIOCHEM Lec 1 - Introduction To BiochemistryThea Cheruve TomentosNo ratings yet
- Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) Analysis of Exon26 of The MDR1 GeneDocument1 pageFragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) Analysis of Exon26 of The MDR1 GeneVenkata Suryanarayana GorleNo ratings yet
- BASICSCIENCEDocument185 pagesBASICSCIENCENeha Sharma100% (1)
- AP Biology 2009 Free-Response Questions: The College BoardDocument4 pagesAP Biology 2009 Free-Response Questions: The College BoardsophisticatedslutNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetics Transes Topic 17Document7 pagesCytogenetics Transes Topic 17Dianne NolascoNo ratings yet
- Human EyeDocument7 pagesHuman Eyeofmir154No ratings yet
- Unit-1 MMWDocument6 pagesUnit-1 MMWJaizer TimbrezaNo ratings yet
- ZoologyDocument146 pagesZoologyGogull GogullNo ratings yet
- Sea Lycanthropes FinalDocument3 pagesSea Lycanthropes FinalLuiz Fernando SouzaNo ratings yet
- Test On Molecular Biology NEETDocument4 pagesTest On Molecular Biology NEETSadananda KumbhakarNo ratings yet
- Day Starting RM Category Argt Code: Published Room Rate SetupDocument6 pagesDay Starting RM Category Argt Code: Published Room Rate SetupEmeraldtowers ApartementNo ratings yet
- General Biology ModuleDocument16 pagesGeneral Biology ModuleKimberly C. Javier100% (1)
- LawrenceNewton1995 Families and Subfamilies of Coleopteraocr PDFDocument142 pagesLawrenceNewton1995 Families and Subfamilies of Coleopteraocr PDFedliverNo ratings yet
- MAN0012622 PCR Master 2X K0171 UGDocument1 pageMAN0012622 PCR Master 2X K0171 UGRebeca VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Development Evolving - The Origins and Meanings of InstinctDocument10 pagesDevelopment Evolving - The Origins and Meanings of InstinctMangaka DomingosNo ratings yet
- March 2020 Revised Final ProgDocument9 pagesMarch 2020 Revised Final Progkvm nccNo ratings yet
- BBC Science Focus 05.2022Document92 pagesBBC Science Focus 05.2022Ile de France coursNo ratings yet