Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Short and Sweet DA by LAB 1
Uploaded by
Jon VOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Short and Sweet DA by LAB 1
Uploaded by
Jon VCopyright:
Available Formats
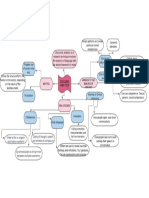
PRINCIPAL SUMMARY of Discourse Analysis by LAB
Main authors Ideas Ideas
Interactional John Gumperz -Essay: Discourse Strategies Irving -physical co presence
Sociolinguistics -real time processes in face to Goffman -interaction order (setting,
Based on relationships face interactions
-cognition and language are form, conduct)
between language,
culture and society and affected by social and cultural -FACE (positive social value a
has its roots in forces person has claimed for himself by the
Anthropology, Sociology -contextualization cues: any line other s assume he has taken
and Linguistics. through a particular
feature of language that
It´s multidisciplinary. contributes to signaling context),FRAME (way which social
Language, context and actors organize their experiences in
contextual
the interaction of self terms of recognizable activities-
and other. presuppositions:(intonation,
people use them to structure
Discourse is a social prosodic choices, conversational code
switching, lexical or syntactic choices, experience), FOOTING (shifting
interaction.
accent, style switching and alignments in relation to the events at
Situational meaning
facial/gestural signs). They function hand: figure, principal, author,
-Brown and Levison´s
indexically but are not lexical animator).
Politeness (On/Off
record) based. Problems arise when -Theory of Politeness is
people don´t recognize them….. based on Goffman´s idea of
face.
Conversational Harold Ethnomethodology: -Adjacent pairs and turn taking
Analysis Garfinkel knowledge is neither (TPR)
-originated in Sociology -preference organization
autonomous nor (preferred and dispreferred of
-interaction is structurally
organized (patterns) decontextualized, avoids response)
-CA explores sequential idealization, categories repair (self or other initiated)
structures of social continuously adjusted pre-sequences (summons, pre-
activities invitation, pre-closing, pre-
request
overall organization (opening,
main body, closing and topic
slots).
Insertion sequence (question
within a question)
-backchannels (well, um, yeah)
they show the listener is paying
attention.
Variation Analysis William Labov - Orderly heterogeneity - Concerned with the variation
-based solely on -probability theory and changes observed along
-materialistic approach different speech communities
Linguistics -constraint: overall structure (group of people that share the
restrains its parts same norms and expectations
-vernacular: variety acquired in pre- regarding the use of language).
adolescent years, spoken when not -focus on different types of
paying attention to they way they
analysis
speak.
Observer´s Paradox: how to observe -differences among text types
vernacular if they only use it w/
people of own variety? Use
sociolinguistic interviews where they
narrative personal events.
Narrative Analysis Labov and -based on VA -Based on narrative clauses
Waletzky -studied Afro-American (temporally ordered)
vernacular: -Structure of a narrative:
Vernacular: variety acquired abstract-orientation-complicating
in pre-adolescence and only used action-evaluation-resolution-coda
when not paying attention to -reportability
their language -Narratives are important in
constructing identity.
Functional -Danes -analyses in function of the Communicative dynamism:
Sentence (Communicative info they contain rates levels of contribution to
Perspective dynamism) -thematic structure (theme, development of the
communication. (theme and
-language as social -Mathesius rheme). Themes can be rheme) Firbas
interaction -Firbas absolute (not connected Themes (Speaker orientated,
-based on the (Functional syntactically to the clause) their point of departure) can be
Linguistic School of Sentence or dislocated (right or left) experiential (subject, verb,
complement….=topic) or non
Prague Perspective) or multiple. experiential (interpersonal:
-speakers have a Thematizing: linear vocatives, markers of attention
communicative organization of sentences and stance) or textual:
purpose and texts (staging, more connectors)
general) Information structure:
End focus: Info focus goes from Given
New (obligatory)and Given
to New. Focus usually falls on last
lexical item of clause (optional, retrievable by
hearer)
Post Structuralist -Foucault -shares some ideas -reality is
Theory (discourse and power. w/Structuralism but stands fragmented/diverse/culture
-The world of material
Discourse cannot be studied specific. Local contextualization is
objectively) against “absolutism” and important.
objects and social space -Bakhtin (language
are discursive in nature their “totalizing” ideas. -symbolic capital: you have
is dialogic.
-The meaning of texts
Heteroglossic and
-there is nothing outside power if you control discourse
vary according to the the text (all meaning is Habitus: individual differences
speech genres)
reader´s identity relating to practical linguistic
-Relativism underlies all/ -Bourdieu textual and intertextual). competence. Players who put
truth/rationality crisis (symbolic capital, Texts exist in relation to
habitus and bodily language to use. Learn through
-reality is mediated by
ideology and cultural hexis) others. trail and error.
codes Heteroglossia: collection of Bodily hexis: linguistic practices
all forms of social speech or are deeply rooted to bodily
dispositions. Language is a body
rhetorical modes used technique that expresses our
daily. Many voices are social relationship to the world.
usually seen in texts (and
not just the obvious ones)
Centripetal/Centrifugal
Genres: connect and push
forward the history of
society and language
Social Theory -Foucault SEE Post Structuralism
-Bakhtin
-Bourdieu
Critical Discourse -Van Dijk social dominance: power, Focuses on
Analysis -Fairclough dominance, hegemony, -power
-from UK and Australia (discourse is 3 -domination
ideology, gender, race and -social inequality
- analysis of text or dimensional)
discourse (not discrimination. Ideology: social systems
decontextualized -Access to specific forms of discourse
(political, media, science) is itself a
and mental representations
sentences)
-multidisciplinary power resource (which are the basis of
-based on Halliday´s -Power influences people´s minds and social cognition). Link
systemic/functional gram. therefore indirectly their actions.
-The groups that control most between society and
-grammar is an ideological
instrument to classify and influential discourse, have the chance discourse.
categorize what happens to control minds and actions of others Power belongs to some and
in the world, based on -macrolevel (power and dominance)
Sapir/Whorf hypothesis and microlevel (discourse, not to others (depends on socio-
communication, verbal interaction) economic status, gender, ethnic
Social power=control identity…..)
Hegemony: when a group abuses Power elites have special
their power
access to discourse and
therefore symbolic power
Positive Discourse -need to concentrate on -want constructive
Analysis the positive aspects of discourse research
-a recent approach to AD power (not negative) -they want to engage in
-needs to develop
methodology and tools -focus on community (how “heartening accounts of
for analysis people get together and progress” not in repression.
-it has strong foundations make room for themselves (what is done well)
(grounded in Systemic
Functional Linguistics and in the world, redistributing
based on positive values power, w/o struggling
and intentions)
against it)
Mediated Scollon Mediated action: basic unit for Principle of social action:
Discourse Analysis analysis, focus on the acting of discourse is not perceived as a
social actors. It´s a sum of the system of representation, thought
-focuses on social social actors, the action and the or values, but as a matter of social
action means they are using. actions.
-texts have social Site of engagement: social space Giosemiotics: meaning of all
consequences where mediated action takes language is based on the material,
place concrete and physical placement
Mediational means: material of that language in the world.
means (body dress, movement) (Indexicality). Language depends
through which mediated action is on when and where it is (signs
carried out. and symbols).
Practice: mediated action is only Icons, indexes, symbols.
interpretable through practice Social actor: moves in physical
Nexus of Practice: different types world
of practice (discursive or non) are Interaction order: set of social
interrelated and linked to form relationships we take up and
nexus of practice. (all the maintain with those in our
practices involved together) presence.
Visual semiotics: visual frame of
social action. How placement of
visual symbols affect meaning.
Place semiotics: action takes
place in the universe. Semiotic
spaces (where we find signs) and
non semiotic places (signs
forbidden) are taken into account.
You might also like
- John Dewey and the Artful Life: Pragmatism, Aesthetics, and MoralityFrom EverandJohn Dewey and the Artful Life: Pragmatism, Aesthetics, and MoralityNo ratings yet
- Overview - AL Semester 1 - 2022Document117 pagesOverview - AL Semester 1 - 2022Proem VersionNo ratings yet
- COMUNICATIVE LEARNING HOMEWORK 1 Unidad 2 - en GrupoDocument3 pagesCOMUNICATIVE LEARNING HOMEWORK 1 Unidad 2 - en Grupovictoria puycan romeroNo ratings yet
- Session 7 - 8Document62 pagesSession 7 - 8SaturnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Language, Learning, and Teaching: @ming - EngtDocument37 pagesChapter 1 Language, Learning, and Teaching: @ming - Engt이주영No ratings yet
- Semantic Pragmatic-Speech ActDocument26 pagesSemantic Pragmatic-Speech ActDiah Retno WidowatiNo ratings yet
- Sociolinguistic ModelsDocument1 pageSociolinguistic ModelsFer RíosNo ratings yet
- 1995 With Thomas Luckmann ReconstructivDocument12 pages1995 With Thomas Luckmann ReconstructivAdriana HikawczukNo ratings yet
- Discourse and Translation: Presented byDocument13 pagesDiscourse and Translation: Presented byAbu M AyaNo ratings yet
- Stylistics: Prepared By: MBLDocument13 pagesStylistics: Prepared By: MBLMaricris BlgtsNo ratings yet
- Discurse AnalysisDocument1 pageDiscurse AnalysisLluvia lluviasNo ratings yet
- MergedDocument7 pagesMergeddANANo ratings yet
- Major in English NotesDocument6 pagesMajor in English NotesDhem Paul Nikko A. PeñalosaNo ratings yet
- SLIDES Inglese 2Document8 pagesSLIDES Inglese 2Barbara ConcuNo ratings yet
- Adjectives and AdverbsDocument9 pagesAdjectives and Adverbsirabatueva5689No ratings yet
- Lingua Inglese II - CP H-Z: Aoife Beville Abeville@unior - ItDocument22 pagesLingua Inglese II - CP H-Z: Aoife Beville Abeville@unior - ItL LawlietNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To LinguisticsDocument2 pagesAn Introduction To LinguisticsDelluza, Kylene JorgeNo ratings yet
- Banaat Ain Shams November 2018 (Prof. Bahaa Mazeed)Document99 pagesBanaat Ain Shams November 2018 (Prof. Bahaa Mazeed)Omnia N. Elkholy100% (4)
- (Second) Language Acquisition: Student's Name/ ID Vivian 9722609 Betty 9722609 Yuri 9722616 Date Sep. 29th, 2008Document23 pages(Second) Language Acquisition: Student's Name/ ID Vivian 9722609 Betty 9722609 Yuri 9722616 Date Sep. 29th, 2008katak_puru1989780No ratings yet
- Discourse Analysis and Pragmatics LessonDocument57 pagesDiscourse Analysis and Pragmatics LessonPatrickXavierNo ratings yet
- Systemic Functional Linguistics TheoryDocument29 pagesSystemic Functional Linguistics TheoryNoor KhanNo ratings yet
- Journal of PersonalityDocument14 pagesJournal of PersonalitySammel SevillaNo ratings yet
- Handouts For Report DiscourseDocument2 pagesHandouts For Report DiscourseMary Joyce BautistaNo ratings yet
- T N E C Communication: HE Ature AND Lements OF OmmunicationDocument21 pagesT N E C Communication: HE Ature AND Lements OF OmmunicationMakai CunananNo ratings yet
- Theories of Language DescriptionDocument7 pagesTheories of Language DescriptionShahid Ali RaiNo ratings yet
- Cogs Final Writing Assignment Module ThreeDocument3 pagesCogs Final Writing Assignment Module ThreeLisbon AndersonNo ratings yet
- General Linguistics1 2Document37 pagesGeneral Linguistics1 2nancyzhyklnNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document9 pagesLecture 1hayleyng05No ratings yet
- Discourse Analysis HANDOUTSDocument4 pagesDiscourse Analysis HANDOUTSAlain Delon Lim SerinoNo ratings yet
- Language & Language LearningDocument77 pagesLanguage & Language LearningAurelio CameroNo ratings yet
- Framework Model For Intercultural CompetencesDocument4 pagesFramework Model For Intercultural CompetencesLylia MezNo ratings yet
- DA - Week 1 - Worksheet - 0922Document3 pagesDA - Week 1 - Worksheet - 0922Trung NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Lense Iv Iii:: What Is Linguistics?Document5 pagesLense Iv Iii:: What Is Linguistics?Matt SalvaNo ratings yet
- SYmbolic GesturesDocument6 pagesSYmbolic GesturesMary-ElizabethClintonNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Theoretical and Applied LinguisticsDocument8 pagesComparison of Theoretical and Applied LinguisticsSabrina BadalovaNo ratings yet
- Teaching English ChallengesDocument4 pagesTeaching English ChallengesbaltacNo ratings yet
- Schools of Thought - PPPDocument16 pagesSchools of Thought - PPPAlonso GaxiolaNo ratings yet
- Extra-musical world influencesDocument1 pageExtra-musical world influencesJunior CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- LingwistykaDocument1 pageLingwistykaAnia SiminskaNo ratings yet
- Mapping Into Meaning: What's Behind Language?Document5 pagesMapping Into Meaning: What's Behind Language?Teresa RoqueNo ratings yet
- The Baboonandthe BeeDocument27 pagesThe Baboonandthe Beeakindele02muchNo ratings yet
- Gravano15 InterspeechDocument5 pagesGravano15 InterspeechMariano CannavoNo ratings yet
- European Structuralism: A Concise DefinitionDocument5 pagesEuropean Structuralism: A Concise DefinitionMARIA DANIELANo ratings yet
- Social Relation, Concept of Time, Concept of Space, GesturesDocument1 pageSocial Relation, Concept of Time, Concept of Space, GesturesVincent EmilioNo ratings yet
- Nonverbal Communication - Rubric: Intercultural Competence - Global Citizenship Program - LibGuides at Webster UniversityDocument6 pagesNonverbal Communication - Rubric: Intercultural Competence - Global Citizenship Program - LibGuides at Webster UniversityabologjNo ratings yet
- Annual Teaching Plan FirstDocument6 pagesAnnual Teaching Plan FirstGabriela CarrilloNo ratings yet
- DA Analysis of DiscourseDocument28 pagesDA Analysis of DiscoursedeviNo ratings yet
- Discourse Analysis: Topics in Applied Linguistics Widhiaistuti@staff - Unnes.ac - IdDocument28 pagesDiscourse Analysis: Topics in Applied Linguistics Widhiaistuti@staff - Unnes.ac - IdMuhammad ArdianNo ratings yet
- Didactic Sequence Tales From The Jungle. Horacio Quiroga.Document33 pagesDidactic Sequence Tales From The Jungle. Horacio Quiroga.ScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- 2006 Storkel Et Al Phonotactic Probability Neighborhood Density Word LearningDocument18 pages2006 Storkel Et Al Phonotactic Probability Neighborhood Density Word LearningSebaco BossNo ratings yet
- Discourse AnalysisDocument28 pagesDiscourse Analysisgunawan.abwNo ratings yet
- Prags 1Document4 pagesPrags 1letiserranoNo ratings yet
- Reading 9Document4 pagesReading 9Martin HauserNo ratings yet
- PRELIMDocument3 pagesPRELIMTemptations MnlNo ratings yet
- Neverbalna 1.kolokvijDocument15 pagesNeverbalna 1.kolokvijKatarina MileticNo ratings yet
- Phonology and Additional Language Learners - JVDL 16Document6 pagesPhonology and Additional Language Learners - JVDL 16Signup LettersNo ratings yet
- Language and Language LearningDocument62 pagesLanguage and Language LearningChristyNo ratings yet
- Drama Integration Grade 4 (U3)Document2 pagesDrama Integration Grade 4 (U3)innaNo ratings yet
- Theories of Speech PerceptionDocument6 pagesTheories of Speech PerceptionBetül Özsoy TanrıkuluNo ratings yet
- Brochure DISCOURS. 2022Document68 pagesBrochure DISCOURS. 2022Camilla PorcellaNo ratings yet
- Mastering Blocking and Stuttering - A Handbook For Gaining Fluency (PDFDrive)Document275 pagesMastering Blocking and Stuttering - A Handbook For Gaining Fluency (PDFDrive)Angelo De La Rama100% (2)
- GOD Is The Greatest ArtistDocument1 pageGOD Is The Greatest ArtistJane Moran100% (1)
- Rainbows in English - 6 PDFDocument176 pagesRainbows in English - 6 PDFJexter Magpantay100% (3)
- Education 2030 Article AnalysisDocument4 pagesEducation 2030 Article AnalysisNESTOR SANDOVALNo ratings yet
- DLL in TLE 8Document4 pagesDLL in TLE 8arlene yusonNo ratings yet
- Overcoming "Ifs and ButsDocument16 pagesOvercoming "Ifs and ButsPratigya Gupta50% (2)
- Framing in Political CommunicationDocument13 pagesFraming in Political CommunicationdusanxxNo ratings yet
- Mba Mysore SyllabusDocument2 pagesMba Mysore SyllabusJimmy MuthukattilNo ratings yet
- Communication Skills in MedicineDocument5 pagesCommunication Skills in MedicineSGD blima semlimanamNo ratings yet
- The Key To IELTS Success Complete Book UPDATED April 18Document138 pagesThe Key To IELTS Success Complete Book UPDATED April 18Nam Nguyen100% (11)
- MARIA LUISA A. BELTRAN, MANDocument8 pagesMARIA LUISA A. BELTRAN, MANNovelyn PuaNo ratings yet
- The Psychology of Chess - Fernand GobetDocument140 pagesThe Psychology of Chess - Fernand GobetbeemoviekoalaNo ratings yet
- Human Resource PlanningDocument37 pagesHuman Resource PlanningCRESTINE JOYCE DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Simmons Case Study Eed225Document7 pagesSimmons Case Study Eed225api-280357644No ratings yet
- Stats - Mean, Median and ModeDocument5 pagesStats - Mean, Median and Modetoy sanghaNo ratings yet
- MELC Eng 7 - 062407Document2 pagesMELC Eng 7 - 062407Nelissa Pearl ColomaNo ratings yet
- Learning Delivery Modalities Course (Ldm2) : Most Essential Learning Competencies (Melcs)Document10 pagesLearning Delivery Modalities Course (Ldm2) : Most Essential Learning Competencies (Melcs)Roy P. JaudalsoNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Contextual Meaning in Maherzain's Song LyricsDocument87 pagesAnalyzing Contextual Meaning in Maherzain's Song Lyricskeynatalia siahaanNo ratings yet
- Reading ReferenceDocument4 pagesReading ReferenceRaffy CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Zhang 2014Document20 pagesZhang 2014Gaina SulieNo ratings yet
- MFAT assessment results summaryDocument3 pagesMFAT assessment results summaryMARVY VILLAMOR100% (1)
- Las Diass Week 1Document13 pagesLas Diass Week 1NamBawan TVNo ratings yet
- Victoria, Lady WelbyDocument4 pagesVictoria, Lady WelbyderenifNo ratings yet
- Winning Strategies For ACT Essay Writing: With 15 Sample PromptsDocument26 pagesWinning Strategies For ACT Essay Writing: With 15 Sample PromptsVibrant PublishersNo ratings yet
- How CBT Effectively Treats DepressionDocument52 pagesHow CBT Effectively Treats DepressionUkhtSameehNo ratings yet
- Persons Behaviors and SituationsDocument7 pagesPersons Behaviors and SituationsRhoma siregarNo ratings yet
- Life Skills by DKDocument98 pagesLife Skills by DKahmet100% (8)
- Toronto Notes 2011 PsychiatryDocument52 pagesToronto Notes 2011 Psychiatrymina000005100% (1)
- Unit 5 SG - ASL1Document4 pagesUnit 5 SG - ASL1Mark Angelo G. OrdonioNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document2 pagesLesson 1Jessuel Larn-eps100% (2)