Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Compilation of Fat-Soluble Vitamins
Uploaded by
Yhannie PendangOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Compilation of Fat-Soluble Vitamins
Uploaded by
Yhannie PendangCopyright:
Available Formats
Pendang, Yhannie D.
Block DDD
November 21, 2020
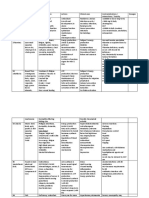
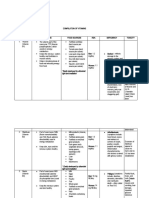
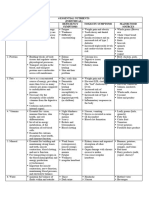
COMPILATION OF VITAMINS
FAT-SOLUBLE VITAMINS
VITAMINS FUNCTIONS FOOD SOURCES RDA DEFICIENCY TOXICITY
1. Vitamin A Promoting Retinol:
vision, Fortified milk Hypovitaminosis A – Hypervitaminosis A –
maintenance of Cheese deficiency disease toxicity disease
cornea Cream
Participating in Butter Men: 900 μg Manifestations: Chronic Toxicity
protein Fortified RAE/day Night blindness, corneal Manifestations:
synthesis and margarine drying (xerosis), Increased activity of
cell Eggs Triangular gray spots on osteoclasts causing
differentiation, eye (Bitot’s spots) reduced bone density;
Liver
thereby Women: 700 μg Softening of the cornea liver abnormalities;
maintaining the RAE/day (keratomalacia), birth defects
Beta-carotene:
health of Spinach and Corneal degeneration and
epithelial other dark leafy blindness (xerophthalmia)
tissues and greens Impaired immunity
skin (infectious diseases) Acute Toxicity
Broccoli Manifestations:
Supporting Plugging of hair follicles
Deep orange
reproduction with keratin, forming white
fruits (apricots, Blurred vision
and growth lumps (hyperkeratosis))
cantaloupe) and
Beta-carotene Nausea
Vegetables
(vitamin A Vomiting
(squash, carrots,
precursor) acts Vertigo
sweet potatoes,
as an
pumpkin) Increase of
antioxidant pressure
Immunity inside skull
mimicking
brain tumor
Headaches
Muscle
incoordination
2. Vitamin D
Mineralization Synthesized in the body Rickets in Children – Hypervitaminosis D –
of bones with the help of: 1997 Adequate deficiency disease toxicity disease
(raises blood Sunlight Intake (AI)
calcium and Fortified milk Adults: Manifestations: Manifestations:
phosphorus by Margarine 5 Inadequate Elevated
increasing Butter μg/day calcification, blood calcium
absorption from Juice, (19–50 resulting in Calcification
digestive tract Cereals, and yr) misshapen bones of soft tissues
Withdrawing chocolate mixes (bowing of legs); (blood
calcium from Veal 10 enlargement of vessels,
bones, Beef μg/day ends of long bones kidneys,
Stimulating Egg yolks
(51–70 (knees, wrists) heart, lungs,
retention by yr) Deformities of ribs tissues
Liver
kidneys) (bowed, with around joints)
Fatty fish
15 beads or knobs)
(herring, salmon,
μg/day delayed closing of
sardines) and
(>70 fontanel, resulting
their oils
yr) in rapid
enlargement of
head
Lax muscles
resulting in
protrusion of
abdomen; muscle
spasms
Osteomalacia or
Osteoporosis in Adults –
deficiency disease
Manifestations:
Loss of calcium, resulting in
soft, flexible, brittle, and
deformed bones;
progressive weakness; pain
in pelvis, lower back, and
legs
3. Vitamin E
(Alpha
Tocopher
ol) Antioxidant Polyunsaturated Red blood cell breakage Augments the effects
(stabilization of plant oils Nerve damage of anti-clotting
cell membranes (margarine, salad Adults: 15 medication
Regulation of dressings, mg/day
oxidation shortenings)
reactions Leafy green
Protection of vegetables
polyunsaturate (spinach, turnip
d fatty acids greens, collard
[PUFA] and greens, broccoli)
vitamin A Wheat germ
Whole grains
Liver
Egg yolks
Nuts
Seeds
Fatty meats
* Easily destroyed by heat
and oxygen
4. Vitamin K
Synthesis of Bacterial Men: 120
blood-clotting synthesis in the μg/day
proteins and digestive tract Hemorrhaging None known
bone proteins Liver
Leafy green Women: 90
vegetables, μg/day
cabbage-type
vegetables
Milk
You might also like
- Fat Soluble VitaminsDocument3 pagesFat Soluble VitaminsRan And SanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - The VitaminsDocument3 pagesChapter 8 - The VitaminsYcell Latido100% (1)
- Keratomalacia in Eyes: Xerophthalmia, Bitot's SpotsDocument3 pagesKeratomalacia in Eyes: Xerophthalmia, Bitot's SpotsNimish BajareNo ratings yet
- Vitamins Table FormDocument7 pagesVitamins Table FormR-Chian Jose GermanpNo ratings yet
- Study Notes of Vitamins: (A) - Fat Soluble Vitamins: Vitamins (Name) Rich Food Source Functions Deficiency DiseasesDocument3 pagesStudy Notes of Vitamins: (A) - Fat Soluble Vitamins: Vitamins (Name) Rich Food Source Functions Deficiency DiseasesWaseemNo ratings yet
- Study Notes of Vitamins: (A) - Fat Soluble Vitamins: Vitamins (Name) Rich Food Source Functions Deficiency DiseasesDocument3 pagesStudy Notes of Vitamins: (A) - Fat Soluble Vitamins: Vitamins (Name) Rich Food Source Functions Deficiency DiseasesAnugrah MNo ratings yet
- BCH 211 Lecture NoteDocument13 pagesBCH 211 Lecture NotemanomistephenNo ratings yet
- Vitamin Active Form Function Deficiency Disease Precursor Hypervitamin Osis SourcesDocument3 pagesVitamin Active Form Function Deficiency Disease Precursor Hypervitamin Osis Sourceshatem alsrour100% (4)
- VitaminsDocument8 pagesVitaminsecho tiongcoNo ratings yet
- Vitamins and NutritionDocument10 pagesVitamins and NutritionAnurag KumarNo ratings yet
- Vitamin and Mineral ChartDocument4 pagesVitamin and Mineral ChartJagan LogaiyaNo ratings yet
- Vitamin NotesDocument3 pagesVitamin NotesKamran ZaheerNo ratings yet
- Micronutrients - VitaminsDocument9 pagesMicronutrients - VitaminsKate SantosNo ratings yet
- Phle Reviewer - Minerals VitaminsDocument2 pagesPhle Reviewer - Minerals VitaminsStudy HabitNo ratings yet
- Vitamin and Mineral ChartDocument5 pagesVitamin and Mineral ChartKaye Tubungbanua MatunogNo ratings yet
- Vitamins and Minerals TableDocument7 pagesVitamins and Minerals TableDHANUSRI K 1840747100% (1)
- VitaminsDocument2 pagesVitaminsShivrajNo ratings yet
- Cielo, Divina Gracia V. BSM-1 Vitamins Function RDA Sources Effects of Deficiency Symptoms of Excess ADocument10 pagesCielo, Divina Gracia V. BSM-1 Vitamins Function RDA Sources Effects of Deficiency Symptoms of Excess ADivina Gracia Vibal CieloNo ratings yet
- 5th Vitamins & MineralsDocument5 pages5th Vitamins & MineralsKennedy HouseNo ratings yet
- Vitamens in TabuleDocument7 pagesVitamens in TabuleOzgan SüleymanNo ratings yet
- जीवनसत्वे (VIDARBH IAS) -Document2 pagesजीवनसत्वे (VIDARBH IAS) -adityasjadhav2505No ratings yet
- Nutrients TableDocument1 pageNutrients TableNelson LongsworthNo ratings yet
- Vitamins NotesDocument8 pagesVitamins NotesEllyNo ratings yet
- Notes of VitaminsDocument8 pagesNotes of VitaminsEllyNo ratings yet
- Definition of VitaminsDocument2 pagesDefinition of VitaminsShalini PalrajNo ratings yet
- Water-Soluble VitaminsDocument5 pagesWater-Soluble VitaminsJustin AncogNo ratings yet
- Foods I Vitamins and MineralsDocument25 pagesFoods I Vitamins and MineralsEve TinirnacNo ratings yet
- VitaminDocument2 pagesVitamindaroshamchaudhary1237No ratings yet
- Vitamin Summary SheetDocument8 pagesVitamin Summary Sheetglenn johnstonNo ratings yet
- Vitamins and Minerals - Vitamin ChartDocument5 pagesVitamins and Minerals - Vitamin Chartraz_939No ratings yet
- Vitamins SummaryDocument5 pagesVitamins SummaryDanny LeeNo ratings yet
- CC VitaminsDocument3 pagesCC VitaminsDaphne HernaezNo ratings yet
- Water Soluble VitaminsDocument6 pagesWater Soluble VitaminsRan And SanNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Name: Miriam Harriott Grade: 10 Mignott Subject: Foods and Nutrition Teacher: Mrs. ThomasDocument22 pagesAssignment: Name: Miriam Harriott Grade: 10 Mignott Subject: Foods and Nutrition Teacher: Mrs. Thomasmiriam harriottNo ratings yet
- Vitamins and Minerals: Name: Mahajan, Deepika Sardar Student No: 16-2-21988 Section: BDocument8 pagesVitamins and Minerals: Name: Mahajan, Deepika Sardar Student No: 16-2-21988 Section: BDeepika MahajanNo ratings yet
- Vitamins TableDocument3 pagesVitamins Tableapi-512416839No ratings yet
- Nutrition VITAMIN TABLE CompletedDocument2 pagesNutrition VITAMIN TABLE CompletedGeneralRipphookNo ratings yet
- VitaminDocument5 pagesVitaminVanessa AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Fat Soluble VitDocument1 pageFat Soluble VitUmi Khalsom BajuriNo ratings yet
- Pendang-Compilation of Water-Soluble Vitamins (Resubmission)Document5 pagesPendang-Compilation of Water-Soluble Vitamins (Resubmission)Yhannie PendangNo ratings yet
- Kwashiorkor: The Function of Fat IncludeDocument3 pagesKwashiorkor: The Function of Fat IncludeJASHINEE A/P BASKARAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Retinol in Animal Food: Milk,: Vitamin ADocument2 pagesRetinol in Animal Food: Milk,: Vitamin AsashellNo ratings yet
- 6 Essential NutrientsDocument5 pages6 Essential NutrientsRussel Kate SulangNo ratings yet
- Reaction of Glucose: CarbohydratesDocument4 pagesReaction of Glucose: CarbohydratesADITYA TIWARINo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument1 pageVitaminsZayan HaiderNo ratings yet
- Classes of Food Source Functions Effects of Deficiency CarbohydratesDocument1 pageClasses of Food Source Functions Effects of Deficiency CarbohydratesUlya YeeaaNo ratings yet
- Christine P. Salimbagat: BSN262 Nutrition and Diet TherapyDocument5 pagesChristine P. Salimbagat: BSN262 Nutrition and Diet TherapyChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics: FGLM Success Is Not Final Failure Is Not FatalDocument16 pagesPediatrics: FGLM Success Is Not Final Failure Is Not FatalkrishNo ratings yet
- Vitamins ChartDocument2 pagesVitamins Chartautumn15_7No ratings yet
- 6.2 - Concept of Balanced DietDocument27 pages6.2 - Concept of Balanced DietNigel Subhash BakkerNo ratings yet
- Inorg Jingle FinalDocument1 pageInorg Jingle FinalZenen DaranNo ratings yet
- Other Names: Retinol, Retinal, Retinoic Acid Precursors Are Carotenoids Such As Beta-Carotene)Document3 pagesOther Names: Retinol, Retinal, Retinoic Acid Precursors Are Carotenoids Such As Beta-Carotene)Justin AncogNo ratings yet
- A Few Minutes Series: VitaminsDocument3 pagesA Few Minutes Series: VitaminsPriti MishraNo ratings yet
- Minerals and Vitamins NotesDocument1 pageMinerals and Vitamins NotesI.HONo ratings yet
- Vitamins and Oligoelements Abstract Cristhian Camilo Lozano FernandezDocument5 pagesVitamins and Oligoelements Abstract Cristhian Camilo Lozano FernandezCristhian LozanoNo ratings yet
- Vitamin's Name Function Deficiency Requirements: Retinal RetinolDocument4 pagesVitamin's Name Function Deficiency Requirements: Retinal RetinolAsem AlmeerabiNo ratings yet
- Online Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreDocument23 pagesOnline Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreYoAmoNYCNo ratings yet
- Balanced DietDocument13 pagesBalanced DietOffice AccountNo ratings yet
- Vitamin and Mineral ChartDocument4 pagesVitamin and Mineral ChartGerarld Immanuel KairupanNo ratings yet
- Gold Exp B1P WB AudioscriptDocument9 pagesGold Exp B1P WB AudioscriptHamedHashemian100% (1)
- Anna TleDocument22 pagesAnna TleReigne AngcayaNo ratings yet
- BUENOS AIRES City Guide 2023Document33 pagesBUENOS AIRES City Guide 2023Cecilia ReyNo ratings yet
- 30 Day Perfect Pup With Zak GeorgeDocument53 pages30 Day Perfect Pup With Zak GeorgeJedidiah Carl Tan100% (7)
- ES MANUAL Cafetera Bomba Tradicional Espresso EC270 DelonghiDocument17 pagesES MANUAL Cafetera Bomba Tradicional Espresso EC270 Delonghialejandro ferrer0% (1)
- School Adventures at The Harvey N. Trouble Elementary SchoolDocument9 pagesSchool Adventures at The Harvey N. Trouble Elementary SchoolJesha MarianoNo ratings yet
- 8 P's ScriptDocument2 pages8 P's ScriptManasi JamsandekarNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 1: Quarter 1-Module 4: Learning From Others and Reviewing The LiteratureDocument14 pagesPractical Research 1: Quarter 1-Module 4: Learning From Others and Reviewing The LiteratureAlehxis Gglc Fonts RnlptNo ratings yet
- WORKBOOKDocument55 pagesWORKBOOKღAmy NekoღNo ratings yet
- Accomplishment Report Gulayan Sa PaaralanDocument5 pagesAccomplishment Report Gulayan Sa Paaralanbhenz RosarioNo ratings yet
- Ssac 2104Document100 pagesSsac 2104Amrutha amrNo ratings yet
- Tugas BingDocument10 pagesTugas BingVviyaaNo ratings yet
- Essential Oils As Antioxidants: Their Evaluation by DPPH, ABTS, Frap, Cuprac, and B-Carotene Bleaching MethodsDocument9 pagesEssential Oils As Antioxidants: Their Evaluation by DPPH, ABTS, Frap, Cuprac, and B-Carotene Bleaching MethodsVincentius KevinNo ratings yet
- Cheese 101 Cheese 101 Cheese 101 Cheese 101: Cutting Cheese: Cutting Cheese: Cutting Cheese: Cutting CheeseDocument5 pagesCheese 101 Cheese 101 Cheese 101 Cheese 101: Cutting Cheese: Cutting Cheese: Cutting Cheese: Cutting Cheesejorison cardozoNo ratings yet
- 1 SMDocument10 pages1 SMDara aditya NingrumNo ratings yet
- High Quality Melamine Powder Plastic Raw Material For TablewareDocument4 pagesHigh Quality Melamine Powder Plastic Raw Material For TablewareErmiasNo ratings yet
- Project Work Topics English Class 11Document1 pageProject Work Topics English Class 11Kunal SahNo ratings yet
- Caderno 16 1000 Questões de Inglês ESA 2022 Prof Leonardo PontesDocument49 pagesCaderno 16 1000 Questões de Inglês ESA 2022 Prof Leonardo Pontesgabrielmendes2023rjjNo ratings yet
- Design, Development and Performance Evaluation of An Improved Palm Kernel Oil (PKO) ExpellerDocument24 pagesDesign, Development and Performance Evaluation of An Improved Palm Kernel Oil (PKO) ExpellerInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- On Persuading, On Marketing StrategiesDocument4 pagesOn Persuading, On Marketing StrategiesLala BubNo ratings yet
- Business PlanDocument4 pagesBusiness PlanLEAH MAE CANDADONo ratings yet
- Klaus Dragull Jim Henderson Mel C. Ja... 2006 - Hawaiian Awa Views of An Ethnobotanical TreasureDocument103 pagesKlaus Dragull Jim Henderson Mel C. Ja... 2006 - Hawaiian Awa Views of An Ethnobotanical TreasureDouglas Kojo LaRoseNo ratings yet
- Analysis of For MOSH and MOAH in Food and Packaging MaterialsDocument3 pagesAnalysis of For MOSH and MOAH in Food and Packaging MaterialsAbu Althaf100% (1)
- Fruitlite Water Bottle Detox RecipeDocument39 pagesFruitlite Water Bottle Detox RecipeD Chandra SekharNo ratings yet
- Unit 7-1Document2 pagesUnit 7-1Lara MarondaNo ratings yet
- Anglisht ProjektDocument6 pagesAnglisht ProjektKlea XhafaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Life Processes MCQ Practice SolutionsDocument14 pagesCBSE Class 10 Life Processes MCQ Practice SolutionsRAJESH BNo ratings yet
- Cotton FibreDocument26 pagesCotton Fibrekavi RAJ SenNo ratings yet
- SITHCCC002 Assessment 1 Short AnswersDocument12 pagesSITHCCC002 Assessment 1 Short AnswersCallyNo ratings yet
- G11 Bubalus EditedDocument28 pagesG11 Bubalus EditedA - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet