Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TM161 Pendulums Datasheet
Uploaded by
Francisco Garcia del OrbeCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TM161 Pendulums Datasheet
Uploaded by
Francisco Garcia del OrbeCopyright:
Available Formats
theory of machines
T M 161
Simple and Compound Pendulums
Experiment for studying simple harmonic motion and the factors that affect
the period of oscillation of pendulums. Fits on to the Free Vibrations test frame.
K ey f e at u res
• One of a series of modular experiments that explore free vibrations in simple systems
• Quick, safe, and easy for students to use - needing minimal laboratory supervision
• Two modules - a simple pendulum and a compound pendulum for a range of experiments
• Back panels with referenced scales and sliding indicators for accurate positioning of pendulum parts
• The simple pendulum has unique quick-change spheres and adjustable cord length to save time
• The compound pendulum includes extra parts to work as a Kater’s pendulum
• Contains all parts needed for the experiments – including a stopwatch and tools
TecQuipment Ltd, Bonsall Street, long eaton, Nottingham NG10 2AN, UK
tecqu ipment. c o m +4 4 115 972 2611 sales@tecquipment.com
DB/ad 1119 Page 1 of 3
T M 161
Simple and Compound Pendulums
Description Standard Features
This product is part of a range that explores free vibrations • Supplied with lecturer guide and student guide
in simple ‘one degree of freedom’ systems.
• Five-year warranty
It introduces students to key scientific terms such as:
• Manufactured in accordance with the latest European
• Simple harmonic motion (SHM) and period of Union directives
oscillation
• ISO9001 certified manufacturer
• Mass moment of inertia
• Radius of gyration Learning Outcomes
• Cord length and period of a simple pendulum
• Routh’s rule
• Mass and period of a simple pendulum
This product fits to the sturdy test frame (TM160) for study
or demonstration. • Using a simple pendulum to find the acceleration due
to gravity
This product includes a simple pendulum and a
compound pendulum. Both pendulums swing through • Centre of gravity and period of a compound pendulum
small angles, showing the principles and use of simple • How an adjustable mass affects the period of a
harmonic motion using the small angle approximation. compound pendulum
The simple pendulum uses a cord which may be • Using a Kater’s pendulum to find the acceleration due
considered as ‘light’ so you can ignore its mass, leaving to gravity
only the sphere and cord length as the important
variables.
Essential Base U nit
The compound or ‘physical’ pendulum uses a ‘heavy’ solid • Free Vibrations Test Frame (TM160)
rod which has reasonable mass, so you must allow for it in
theoretical equations.
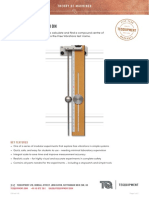
Each pendulum has a back panel that fixes separately
to the test frame. The back panel of each pendulum has
an accurate scale and indicator, referenced to pendulum
pivot or centre of mass points. This improves measurement
accuracy - essential for good results.
The simple pendulum has a choice of two spheres
suspended by a cord. An adjustable indicator also acts
as the pendulum pivot point - allowing you to adjust the
cord length in seconds. This can also provide a quick visual
demonstration of the effect of cord length on period.
Each sphere has a different mass for comparison and
an internal spring retainer so you can easily swap them
between experiments.
The compound pendulum has a solid rod that pivots on a
hardened steel knife edge on the upper surface of a steel
platform. This pendulum includes an additional spherical
mass that fixes at any position along the rod. It also
includes an extra pivot and disc-shaped mass so you can
convert it for use as a Kater’s pendulum.
The Kater’s pendulum works as a reversible and
adjustable compound pendulum. Students adjust the
relative positions of its parts until they have equal time
periods in both its standard and reversed arrangements. It
then works as an accurate gravimeter.
Students test different pendulums to see how different
factors, such as mass or pendulum length affect simple
harmonic motion and the period of oscillation. The theory
shows how to predict the period of oscillation of a given The Simple Pendulum Module in use, Shown fitted to the Test
pendulum for comparison with actual results. It also shows F r a m e (T M 1 6 0)
how pendulums can produce an approximate value of the
acceleration due to gravity.
TecQuipment Ltd, Bonsall Street, long eaton, Nottingham NG10 2AN, UK
tecqu ipment. c o m +4 4 115 972 2611 sales@tecquipment.com
DB/ad 1119 Page 2 of 3
T M 161
Simple and Compound Pendulums
O p e rat i n g C on di ti ons Specifications
O per at ing env iro nme n t: TecQuipment is committed to a programme of continuous
Laboratory improvement; hence we reserve the right to alter the
design and product specification without prior notice.
Storage temperature range:
Net t dimensio ns a nd weight:
–25°C to +55°C (when packed for transport)
Assembled: 2 x 580 mm high x 220 mm wide x 100 mm
O per at ing t emper at ur e r a n ge : front to back
+5°C to +40°C
10 kg total
O per at ing r el at iv e hum i d i ty r a n ge :
Approximate packed vo lume and weight:
80% at temperatures < 31°C decreasing linearly to 50% at
0.1 m3 and 15 kg
40°C
Other pa rts included:
• Hexagon tool
• Stopwatch
• Rule
• 2 x simple pendulum spheres of different mass
TecQuipment Ltd, Bonsall Street, long eaton, Nottingham NG10 2AN, UK
tecqu ipment. c o m +4 4 115 972 2611 sales@tecquipment.com
DB/ad 1119 Page 3 of 3
You might also like
- TM163 Centre Percussion Datasheet PDFDocument2 pagesTM163 Centre Percussion Datasheet PDFABHISHEKNo ratings yet
- TM163 Centre Percussion DatasheetDocument2 pagesTM163 Centre Percussion DatasheetC. ZaragozaNo ratings yet
- STS12 Euler Buckling of Struts DatasheetDocument3 pagesSTS12 Euler Buckling of Struts DatasheetOmar KetfiNo ratings yet
- STS12 Euler Buckling of Struts DatasheetDocument3 pagesSTS12 Euler Buckling of Struts DatasheetOmar KetfiNo ratings yet
- STS2 Bending Moments in A Beam DatasheetDocument3 pagesSTS2 Bending Moments in A Beam DatasheetAsef ShahriarNo ratings yet
- STS12 Euler Buckling of Struts DatasheetDocument3 pagesSTS12 Euler Buckling of Struts DatasheetLeandro Silva SantosNo ratings yet
- STS5 Bending Stress in A Beam DatasheetDocument3 pagesSTS5 Bending Stress in A Beam DatasheetLeandro Silva SantosNo ratings yet
- H3a Calibration Pressure Gauge DatasheetDocument2 pagesH3a Calibration Pressure Gauge DatasheetFardeen KhanNo ratings yet
- TM163 1015 Centre of PercusionDocument2 pagesTM163 1015 Centre of Percusiongurudev001No ratings yet
- STF5 Equilibrium Beam DatasheetDocument2 pagesSTF5 Equilibrium Beam DatasheetGerardo Alberto Navarro LopezNo ratings yet
- STS6 Torsion of Circular Sections DatasheetDocument3 pagesSTS6 Torsion of Circular Sections DatasheetLeandro Silva SantosNo ratings yet
- TM25 Journal Bearing DatasheetDocument2 pagesTM25 Journal Bearing Datasheet3059 SUNARAM HANSDAHNo ratings yet
- STF4 Equilibrium Forces DatasheetDocument2 pagesSTF4 Equilibrium Forces DatasheetGerardo Alberto Navarro LopezNo ratings yet
- H410 Viscosity DatasheetDocument2 pagesH410 Viscosity DatasheetRicardo Javier Huayapa PumaNo ratings yet
- H3a Calibration Pressure Gauge DatasheetDocument2 pagesH3a Calibration Pressure Gauge DatasheetRyadh HaddadNo ratings yet
- STS3 Shear Force in A Beam DatasheetDocument3 pagesSTS3 Shear Force in A Beam DatasheetAyanwale-cole pelumi AkeemNo ratings yet
- Euler Buckling of A Column: StructuresDocument3 pagesEuler Buckling of A Column: StructuresOmar KetfiNo ratings yet
- Continuous and Indeterminate Beams: StructuresDocument2 pagesContinuous and Indeterminate Beams: StructuresBright KnightNo ratings yet
- Modular Air Flow Bench: AerodynamicsDocument2 pagesModular Air Flow Bench: AerodynamicsTaha BaigNo ratings yet
- Stability of A Floating Body: Fluid MechanicsDocument2 pagesStability of A Floating Body: Fluid MechanicsDr.Anmar Hamid AliNo ratings yet
- TE38 Solar Collector DatasheetDocument2 pagesTE38 Solar Collector Datasheetניסן בורוכובNo ratings yet
- Boudary LayetDocument2 pagesBoudary LayetTaha BaigNo ratings yet
- STR1 1115Document2 pagesSTR1 1115Vainilla HernandezNo ratings yet
- H30 Pressure Measurement DatasheetDocument2 pagesH30 Pressure Measurement DatasheetgregorychuanNo ratings yet
- AF10 Air Flow DatasheetDocument2 pagesAF10 Air Flow DatasheetaminemohamedjobNo ratings yet
- 3 Ed 4Document2 pages3 Ed 4muhammad ZailaniNo ratings yet
- CE106 Ball and Beam DatasheetDocument2 pagesCE106 Ball and Beam DatasheetMansoor RatherNo ratings yet
- ES3 Moments DatasheetDocument2 pagesES3 Moments DatasheetGerardo Alberto Navarro LopezNo ratings yet
- SM1001 Torsion Testing DatasheetDocument3 pagesSM1001 Torsion Testing DatasheetChriv SokundavannNo ratings yet
- H215 Osborne Reynolds Apparatus DatasheetDocument2 pagesH215 Osborne Reynolds Apparatus DatasheetSebastian GomezNo ratings yet
- TM160 1015 Free VibrationsDocument2 pagesTM160 1015 Free Vibrationsgurudev001No ratings yet
- STS17 Redundant Truss DatasheetDocument3 pagesSTS17 Redundant Truss DatasheetLeandro Silva SantosNo ratings yet
- HartnellDocument2 pagesHartnellAmit AherwarNo ratings yet
- SM1007 Thin Cylinder DatasheetDocument3 pagesSM1007 Thin Cylinder Datasheetmmoojjttaabbaa1112No ratings yet
- H2MkII Metacentric Height DatasheetDocument2 pagesH2MkII Metacentric Height DatasheetDavid Iparraguirre ChavezNo ratings yet
- Umar Lab ReportDocument24 pagesUmar Lab ReportMia HussainNo ratings yet
- Torque Measuremen T: MQC SeminarDocument17 pagesTorque Measuremen T: MQC SeminarVaibhavNo ratings yet
- Dillon Orbis PDFDocument2 pagesDillon Orbis PDFed_maltosNo ratings yet
- TE4a Solar Light Bank DatasheetDocument2 pagesTE4a Solar Light Bank Datasheetניסן בורוכובNo ratings yet
- Francis Turbine: Fluid MechanicsDocument2 pagesFrancis Turbine: Fluid Mechanicsshabi049No ratings yet
- SM1011 Thick Cylinder DatasheetDocument3 pagesSM1011 Thick Cylinder Datasheethansdavid.aquino2004No ratings yet
- KOM Lab ManualDocument24 pagesKOM Lab ManualMithra SNo ratings yet
- Unit 3-1Document153 pagesUnit 3-1Muket AgmasNo ratings yet
- 01 Introduction To MetrologyDocument138 pages01 Introduction To MetrologyShivanand ArwatNo ratings yet
- Standards of MeasurementDocument12 pagesStandards of MeasurementShubham KheraNo ratings yet
- GearsDocument13 pagesGearsMohsin Iftikhar Lab EngineerNo ratings yet
- Experiment On Torsion of Bars (Repaired)Document26 pagesExperiment On Torsion of Bars (Repaired)Bhunjun Vandana100% (1)
- Test Chain Instruction ManualDocument14 pagesTest Chain Instruction ManualTo TianNo ratings yet
- L7 Dynamics - Simple PendulumDocument4 pagesL7 Dynamics - Simple PendulumRandy ClarckNo ratings yet
- IntroductiontometrologyDocument120 pagesIntroductiontometrologyVishal PatilNo ratings yet
- Barkatullah University Institute of Technology: Presentation OnDocument20 pagesBarkatullah University Institute of Technology: Presentation OnSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Pipework Energy Losses: Fluid MechanicsDocument4 pagesPipework Energy Losses: Fluid MechanicsHelmer Edgardo Monroy GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Fundementals of Torque CalibrationDocument137 pagesFundementals of Torque CalibrationMiguel Alfonso Ruiz MendezNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document55 pagesCH 2Hoheyat BerhanuNo ratings yet
- ES Spares and Consumables: Engineering ScienceDocument2 pagesES Spares and Consumables: Engineering SciencePRONOBNo ratings yet
- Alineador LaserDocument104 pagesAlineador LaserVilla Rios del SurNo ratings yet
- The Utility of A System To Measure and Monitor The Tension of The Spoke Cables of The Wheel Originates From The Following ReasonsDocument13 pagesThe Utility of A System To Measure and Monitor The Tension of The Spoke Cables of The Wheel Originates From The Following ReasonsXanthi Georgia BartsotaNo ratings yet
- Pendulum Impact Tester E LowDocument29 pagesPendulum Impact Tester E LowEmre GuneyNo ratings yet
- CouplingsDocument60 pagesCouplingsSUKhanNo ratings yet
- Tig and Plasma Welding: Process Techniques, Recommended Practices and ApplicationsFrom EverandTig and Plasma Welding: Process Techniques, Recommended Practices and ApplicationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Integrales ImpropiasDocument26 pagesIntegrales ImpropiasPatricia Gutiérrez MoralesNo ratings yet
- 5335ec864b3945b78e263ac0f1eb7598Document1 page5335ec864b3945b78e263ac0f1eb7598Francisco Garcia del OrbeNo ratings yet
- Which Is A City Where The Mist Remains at Any Time: 1. Before You WatchDocument3 pagesWhich Is A City Where The Mist Remains at Any Time: 1. Before You WatchFrancisco Garcia del OrbeNo ratings yet
- Which Is A City Where The Mist Remains at Any Time: 1. Before You WatchDocument3 pagesWhich Is A City Where The Mist Remains at Any Time: 1. Before You WatchFrancisco Garcia del OrbeNo ratings yet
- Steris Amsco Century v120Document2 pagesSteris Amsco Century v120Juan OrtizNo ratings yet
- Intel Server RoadmapDocument19 pagesIntel Server Roadmapjinish.K.GNo ratings yet
- Add New Question (Download - PHP? SC Mecon&id 50911)Document9 pagesAdd New Question (Download - PHP? SC Mecon&id 50911)AnbarasanNo ratings yet
- Setup LogDocument221 pagesSetup LogCarlos MendezNo ratings yet
- Bali Hai LawsuitDocument14 pagesBali Hai LawsuitLas Vegas Review-JournalNo ratings yet
- Induction-Llgd 2022Document11 pagesInduction-Llgd 2022Phạm Trúc QuỳnhNo ratings yet
- Personal Information: Witec Smaranda 11, A3 Bis, Blvd. Chisinau, Bucharest, Romania 0040722597553Document6 pagesPersonal Information: Witec Smaranda 11, A3 Bis, Blvd. Chisinau, Bucharest, Romania 0040722597553MirelaRoșcaNo ratings yet
- Group Tour Operators in Pune - Best Tours and Travels in PuneDocument10 pagesGroup Tour Operators in Pune - Best Tours and Travels in PuneGargi ToursNo ratings yet
- GGSB MibDocument4 pagesGGSB MibShrey BudhirajaNo ratings yet
- Maverick Research: World Order 2.0: The Birth of Virtual NationsDocument9 pagesMaverick Research: World Order 2.0: The Birth of Virtual NationsСергей КолосовNo ratings yet
- Danais 150 ActuadoresDocument28 pagesDanais 150 Actuadoresedark2009No ratings yet
- Note 2958296 Pre-Implementation Steps: Create Table TypeDocument3 pagesNote 2958296 Pre-Implementation Steps: Create Table Typevishnu900890No ratings yet
- Case Chart Complete (Business Law)Document29 pagesCase Chart Complete (Business Law)LimShuLingNo ratings yet
- Civpro RevDocument102 pagesCivpro RevJocelyn Baliwag-Alicmas Banganan BayubayNo ratings yet
- E14r50p01 800 MhaDocument4 pagesE14r50p01 800 Mha'Theodora GeorgianaNo ratings yet
- Subsistence and Travel FormsDocument3 pagesSubsistence and Travel FormsAnonymous YRLhQY6G6jNo ratings yet
- Transport Phenomena 18.4.CDocument3 pagesTransport Phenomena 18.4.CDelyana RatnasariNo ratings yet
- Transportation Problem VAMDocument16 pagesTransportation Problem VAMLia AmmuNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting The Rate of Chemical Reactions Notes Key 1Document3 pagesFactors Affecting The Rate of Chemical Reactions Notes Key 1api-292000448No ratings yet
- Price Action Trading Strategies - 6 Patterns That Work (Plus Free Video Tutorial)Document22 pagesPrice Action Trading Strategies - 6 Patterns That Work (Plus Free Video Tutorial)kalpesh kathar100% (1)
- HRM OmantelDocument8 pagesHRM OmantelSonia Braham100% (1)
- Upload 1 Document To Download: Ergen DedaDocument3 pagesUpload 1 Document To Download: Ergen DedakNo ratings yet
- RFBT - Law On Sales Cont. Week 11Document1 pageRFBT - Law On Sales Cont. Week 11Jennela VeraNo ratings yet
- Oil Refinery OpsDocument3 pagesOil Refinery OpsPhiPhiNo ratings yet
- Kudla Vs PolandDocument4 pagesKudla Vs PolandTony TopacioNo ratings yet
- Zapanta v. COMELECDocument3 pagesZapanta v. COMELECnrpostreNo ratings yet
- An Analytical Study On Impact of Credit Rating Agencies in India 'S DevelopmentDocument14 pagesAn Analytical Study On Impact of Credit Rating Agencies in India 'S DevelopmentRamneet kaur (Rizzy)No ratings yet
- LG LCD TV 32lp1dc - Al-04ca Service ManualDocument47 pagesLG LCD TV 32lp1dc - Al-04ca Service ManualJavin GallardoNo ratings yet
- BBI2002 SCL 7 WEEK 8 AdamDocument3 pagesBBI2002 SCL 7 WEEK 8 AdamAMIRUL RIDZLAN BIN RUSIHAN / UPMNo ratings yet
- Nxivm: 2nd Superseding IndictmentDocument32 pagesNxivm: 2nd Superseding IndictmentTony Ortega100% (2)