Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Thermal Physics: CORE Questions
Thermal Physics: CORE Questions
Uploaded by
raja_tanukuOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Thermal Physics: CORE Questions
Thermal Physics: CORE Questions
Uploaded by
raja_tanukuCopyright:
Available Formats
64
Thermal physics
CORE questions
Core 1
(a) Complete the following sentence.
“The temperature of a body rises when the .............................................. energy of its
molecules is increased.” [1]
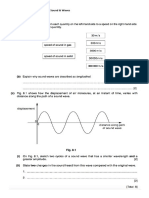
(b) Fig. 1 gives details about an empty beaker and the same beaker with different
substances in it.
Fig. 1
(i) Which of the arrangements has the highest thermal capacity?
......................................................................................................................................
(ii) 1. What is the mass of the water? ..................... g
2. What is the mass of the sand? ..................... g
3. How much energy is needed to raise the temperature of the water by 1 °C?
..................... J
4. How much energy is needed to raise the temperature of the sand by 1 °C?
..................... J
5. Use your answers above to suggest why, on a sunny day, the temperature of
the sand on a beach rises faster than the temperature of the sea.
...............................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................[6]
Core 2
v1 4Y11 Cambridge IGCSE Physics – past paper questions and answers
65
(a) Some students are asked to write down what they know about evaporation of a liquid.
Here are their statements, some of which are correct and some incorrect.
Put a tick alongside those statements which are correct.
A “Evaporation occurs at any temperature.”
B “Evaporation only occurs at the boiling point.”
C “Evaporation occurs where the liquid touches the bottom of the container.”
D “Evaporation occurs at the surface of the liquid.”
E “It is the higher energy molecules which escape”
F “The molecules gain energy as they escape.”
G “The liquid temperature always rises when evaporation occurs.”
H “Rapid evaporation produces cooling.”
[4]
(b) Sometimes after shaving, men splash a liquid, called an aftershave, over their faces.
This makes their faces feel fresher as the aftershave evaporates.
(i) Which of the statements in part (a) explains why the aftershave, even though it is at
room temperature, cools the skin.
statement ...............
(ii) Suggest why the aftershave cools the skin better than water at room temperature.
......................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................
[2]
v1 4Y11 Cambridge IGCSE Physics – past paper questions and answers
66
Core 3
Some smoke is mixed with the air in a glass box. The box is lit brightly from the side and its
contents studied from above through a microscope.
Fig. 2
(a) Bright specks are seen moving in continuous and jerky random movement.
(i) What are the bright specks? Tick one box.
air molecules
smoke molecules
smoke particles
v1 4Y11 Cambridge IGCSE Physics – past paper questions and answers
67
Core 3
(ii) What is the explanation for the jerky random movement? Tick one box.
The air molecules bombard each other.
The smoke particles bombard each other.
The air molecules bombard the smoke particles.
The air molecules bombard the glass.
The smoke particles bombard the glass.
(b) The contents of the glass box exert a pressure on the glass walls.
Tick any of the following sentences which might help explain this pressure.
The air molecules bombard each other.
The smoke particles bombard each other.
The air molecules bombard the smoke particles.
The air molecules bombard the glass.
The smoke particles bombard the glass.
v1 4Y11 Cambridge IGCSE Physics – past paper questions and answers
68
ALTERNATIVE TO PRACTICAL questions
Alternative to Practical 1
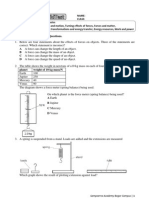
The apparatus shown in Fig. 3 is used in a heat experiment.
Fig. 3
A piece of metal at the boiling temperature of water is transferred to a mass of cold water.
Initially, the cold water is at a temperature of TC. The hot metal raises the temperature of this
water to TH. The rise in temperature, θ, is determined from the relation θ = TH – TC. The
experiment is repeated so as to obtain five sets of readings for different masses of cold water.
(a) Draw up a table, for use in your laboratory notebook, in which you can record
m, the mass of cold water used,
TC, the temperature of the cold water,
TH, the maximum temperature reached by the cold water,
θ, the rise in temperature of the cold water.
[3]
(b) Fig. 4 on page 6 is a graph showing how θ varies with m, the mass of cold water used.
(i) Why has a smooth line been drawn through the points?
......................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................
v1 4Y11 Cambridge IGCSE Physics – past paper questions and answers
69
Alternative to Practical 1
Fig. 4
(ii) The graph point that is labelled A does not lie on the graph line. (You can assume
that the graph line is correctly drawn.) Complete the following statements about the
value of θ and of m at the point A.
1. If the value of θ were .................... °C smaller, the point A would lie on the line.
2. If the value of m were .................... g smaller, the point A would lie on the line.
(iii) In (ii) above which is the most likely reason, 1 or 2, for the point A not being on the
line? Give a reason for your choice.
choice: Tick one box.
1.
2.
reason:
......................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................[4]
v1 4Y11 Cambridge IGCSE Physics – past paper questions and answers
70
EXTENSION questions
Extension 1
Fig. 5 shows a student's design for a thermometer. The student stated that the material
labelled M could be a copper rod, alcohol or nitrogen gas.
Fig. 5
(a) Explain what is meant by the term sensitivity of the thermometer.
..............................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................[1]
(b) (i) State which of the three suggested materials would give a thermometer of greatest
sensitivity.
......................................................................................................................................
(ii) Explain your answer.
......................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................
[2]
(c) (i) State which of the three materials would allow the thermometer to measure the
largest range of temperature.
......................................................................................................................................
(ii) Explain your answer.
......................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................
[2]
(d) The student found that the temperature scale of this thermometer was non-linear.
Explain what this means.
..............................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................[2]
v1 4Y11 Cambridge IGCSE Physics – past paper questions and answers
71
Extension 2
Fig. 6 shows a sealed box containing only dry air. At a particular instant, one of the air
molecules in the box is situated at P and it is moving towards face ABCD along the direction
shown by the arrow.
Fig. 6
(a) Describe and explain a possible path of the molecule within the box.
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................[2]
(b) Explain how this molecule
(i) helps to cause a pressure on the side ABCD,
......................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................
(ii) helps to cause an equal pressure on all the sides.
......................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................[2]
v1 4Y11 Cambridge IGCSE Physics – past paper questions and answers
72
Extension 2
(c) The box is squashed but no air leaks out. By calculation, complete the table below.
volume of box pressure temperature
3
/m / Pa / °C
1.0 × 10
5
before squashing 0.09 20
after squashing 0.04 20
[2]
Extension 3
In an experiment to find the specific latent heat of fusion of ice, an electric heater, of power
200 W, is used.
The following readings are taken.
mass of ice at 0 °C, before heating started, 0.54 kg
mass of ice at 0 °C, after 300 s of heating, 0.36 kg
(a) Calculate a value of the specific latent heat of fusion of ice.
specific latent heat of fusion of ice = .................... [4]
(b) Explain, in molecular terms, how heat is transferred from the surface of a block of ice to
its centre.
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................[2]
v1 4Y11 Cambridge IGCSE Physics – past paper questions and answers
73
Thermal physics – answers
Core 1
(a) internal / thermal / kinetic / heat / motion / movement
b (i) the beaker and water
(ii) 1 250 g
2 250 g
3 1050 J
4 200 J
5 sand requires less energy to raise its temperature
or the temperature of sand rises more for the same energy input
or the reverse argument for water
or water has a bigger specific heat capacity
Core 2
(a) correct answers ADEH
(b) (i) either E or H
(ii) evaporates more rapidly / easily
Core 3
(a) (i) correct answer smoke particles
(ii) correct answer air molecules bombard the smoke particles
(b) correct answer air molecules bombard the glass
smoke particles bombard the glass
Alternative to Practical 1
(a) a suitable table showing units for both mass and temperature
(b) (i) it is a way of taking an average
it is a way of showing up unexpected results
(ii) 1 0.8 °C
2 3g
(iii) correct answer box 1
reason difficult to measure temperature to 1 °C
or heat losses involved
or easy to measure mass to better than 1 g
v1 4Y11 Cambridge IGCSE Physics – past paper questions and answers
74
Extension 1
(a) change in property / length / volume per degree
(b) (i) nitrogen
(ii) gases expand more / most
(c) (i) copper
(ii) a small increase in length per degree / high melting point etc.
(d) the pointer movement is not the same for all degrees
or the effect is different at different parts of the scale
Extension 2
(a) any two from
random path lengths
collides with or bounces off sides
hits or bounces off other molecules
(b) (i) it hits / bounces off ABCD at some time
(ii) it hits / bounces off all sides at some time / the chance of hitting all sides is equal
(c) pressure × volume = constant
pressure = 0.09 / 0.04 × 10
5
= 2.3 × 10 Pa
5
Extension3
(a) specific latent heat of fusion of ice = heat supplied / mass melted
= 60 000 / 0.18 J / kg
= 330 000 J / kg
(b) any two from
molecules vibrate
pass energy from molecule to molecule
process is conduction
v1 4Y11 Cambridge IGCSE Physics – past paper questions and answers
You might also like
- Pacific Antenna 20 and 40M Lightweight Dipole Kit: Diagram Showing Configuration and Approximate LengthsDocument6 pagesPacific Antenna 20 and 40M Lightweight Dipole Kit: Diagram Showing Configuration and Approximate LengthsedosviracNo ratings yet
- 22 - The Nuclear AtomDocument10 pages22 - The Nuclear AtomEdgardo LeysaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1.2 Precise MeasurementDocument1 pageWorksheet 1.2 Precise Measurementgdsuta60% (5)
- Complete Igcse Physics PPT CompilationDocument185 pagesComplete Igcse Physics PPT CompilationKareem Elhag100% (4)
- ROB Design 35 Deg Skew - SuperstructureDocument25 pagesROB Design 35 Deg Skew - SuperstructureAnonymous sfkedkymNo ratings yet
- Vector QuestionsDocument3 pagesVector QuestionsNudrat100% (4)
- 12 - LightDocument25 pages12 - LightEdgardo LeysaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 6 IG I Physics (1) Adding ForcesDocument3 pagesWorksheet 6 IG I Physics (1) Adding ForcesRaj Malkan100% (1)
- Physics Practical Skills (IGCSE)Document175 pagesPhysics Practical Skills (IGCSE)Mabrur Quaderi100% (1)
- IGCSE - Physics - MCQ 12 - Light WavesDocument4 pagesIGCSE - Physics - MCQ 12 - Light WavesHAMAD NoorNo ratings yet
- Basic Electricity Questions IGCSEDocument11 pagesBasic Electricity Questions IGCSEFan Xin Foo100% (1)
- KS3 Physics: Worksheet TwoDocument4 pagesKS3 Physics: Worksheet TwoAsif AyazNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Grade 6 PhysicsDocument5 pagesIGCSE Grade 6 PhysicsSathya MarieNo ratings yet
- Waves Questions For 10 IGCSE Physics Formal ExamsDocument10 pagesWaves Questions For 10 IGCSE Physics Formal Examspixelhobo80% (5)
- IGCSE Light WorksheetDocument45 pagesIGCSE Light WorksheetAref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- Pressure Questions For IGCSE PhysicsDocument14 pagesPressure Questions For IGCSE PhysicsLai Kee Kong100% (2)
- 83 Revision Questions For IGCSE Questions Solutions PDFDocument5 pages83 Revision Questions For IGCSE Questions Solutions PDFChui Wai100% (4)
- OracleDocument1 pageOracle山口 記世0% (1)
- Moments QuestionsDocument12 pagesMoments Questionsmuxadey100% (1)
- Current-Electricity (Edexcel Igcse) WorksheetDocument27 pagesCurrent-Electricity (Edexcel Igcse) Worksheetertugoz100% (2)
- Motion Speed-Time Graphs Classified Past Paper 2 Solved IGCSE GCSE O Level Physics 0625Document11 pagesMotion Speed-Time Graphs Classified Past Paper 2 Solved IGCSE GCSE O Level Physics 0625IGCSE Physics & Chemistry100% (1)
- Physics Important Definitions and Formulae Light and WavesDocument4 pagesPhysics Important Definitions and Formulae Light and WavesVernon67% (3)
- 2019.09.03 - EST & SCHED - r.2 - Combined OverviewDocument1 page2019.09.03 - EST & SCHED - r.2 - Combined OverviewSriNo ratings yet
- Alan Watts-Instant Wind Forecasting - Adlard Coles (2010)Document119 pagesAlan Watts-Instant Wind Forecasting - Adlard Coles (2010)Wee WeeNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Practice Electromagnetism QuestionsDocument20 pagesIGCSE Physics Practice Electromagnetism QuestionsFahim Ahmed67% (6)
- Answers To IGCSE Physics WORKSHEET ElectromagnetismDocument8 pagesAnswers To IGCSE Physics WORKSHEET ElectromagnetismFahim AhmedNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Sound and Waves QP MSDocument5 pagesIGCSE Physics Sound and Waves QP MShasnizaaziz39No ratings yet
- Pressure Questions For IGCSE PhysicsDocument14 pagesPressure Questions For IGCSE PhysicsMohamed Jameel77% (31)
- Cambridge IGCSE ANSWERS Physics Study and Revision Guide Third EditionDocument8 pagesCambridge IGCSE ANSWERS Physics Study and Revision Guide Third EditionNermine Abdel GelilNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Paper 1Document182 pagesIGCSE Physics Paper 1Hakim Abbas Ali Phalasiya100% (24)
- IGCSE Biology Workbook Answers: 1 Characteristics and Classification of Living ThingsDocument28 pagesIGCSE Biology Workbook Answers: 1 Characteristics and Classification of Living ThingsJessica SamanthaNo ratings yet
- (GR) Answers To Questions Within The ChapterDocument24 pages(GR) Answers To Questions Within The ChapterNau KiwiNo ratings yet
- Mid-Term IGCSE PhysicsDocument4 pagesMid-Term IGCSE Physicsgdsuta89% (9)
- Physics-Worksheet 1-Thermal Physics-Grade 8Document9 pagesPhysics-Worksheet 1-Thermal Physics-Grade 8dhureyaaNo ratings yet
- Multilink's Installation & Construction CatalogDocument110 pagesMultilink's Installation & Construction CatalognajeebrafiqNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/42Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/42Summer ShuanNo ratings yet
- Cambridge iGCSE Physics Formula Sheet - Teaching Resources PDFDocument6 pagesCambridge iGCSE Physics Formula Sheet - Teaching Resources PDFMalak Mqq100% (2)
- IGCSE Physics Mark Scheme 3 Summer 2009Document13 pagesIGCSE Physics Mark Scheme 3 Summer 2009Adi Sut Wijananto0% (1)
- IGCSE Physics MCQDocument11 pagesIGCSE Physics MCQSriram ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Space PhysicsDocument38 pagesSpace PhysicsAminah ShahzadNo ratings yet
- CIE IGCSE Physics (0625) Pressure NotesDocument22 pagesCIE IGCSE Physics (0625) Pressure Notes9322483% (53)
- RadioactivityDocument16 pagesRadioactivityEdgardo Leysa100% (1)
- Strategy: Choices and Change MN6003 Session 17 Strategic Change Context Lecturer: XXXXXXDocument29 pagesStrategy: Choices and Change MN6003 Session 17 Strategic Change Context Lecturer: XXXXXXVladimir LosenkovNo ratings yet
- KInetic Model of Matter WorksheetDocument7 pagesKInetic Model of Matter WorksheetNudrat50% (2)
- 0620 Chemistry Example Candidate Responses Booklet 2012Document158 pages0620 Chemistry Example Candidate Responses Booklet 2012sookchin100% (2)
- IGCSE Physics NotesDocument6 pagesIGCSE Physics Noteslhngu0% (1)
- All IGCSE Physics Practicals 2015Document79 pagesAll IGCSE Physics Practicals 2015NicholasChong75% (4)
- IGCSE Physics - Section 1 - Forces and Motion - Practice Exam Questions. Question 1Document20 pagesIGCSE Physics - Section 1 - Forces and Motion - Practice Exam Questions. Question 1Gajendra50% (2)
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 3.3Document1 pageIGCSE Physics Worksheet 3.3Alex DatsyukNo ratings yet
- Brochure SIMRAD Ecdis E5024 SystemDocument2 pagesBrochure SIMRAD Ecdis E5024 SystemwandersonNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate IGCSE Physics GuideDocument40 pagesThe Ultimate IGCSE Physics GuideMaaz Rashid100% (3)
- IGCSE (Complete Physics) Chapter 1Document16 pagesIGCSE (Complete Physics) Chapter 1Hubbak Khan100% (26)
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 12.1Document2 pagesIGCSE Physics Worksheet 12.1Alex DatsyukNo ratings yet
- Gcse Physics: Boyle's Law QuestionsDocument3 pagesGcse Physics: Boyle's Law Questionsamvijayagopal50% (2)
- 15 - Electrical QuantitiesDocument20 pages15 - Electrical QuantitiesEdgardo LeysaNo ratings yet
- CBC-Event Management Services NC III - Modules of Instruction - CoreDocument39 pagesCBC-Event Management Services NC III - Modules of Instruction - CoreJhainne Yome FulgencioNo ratings yet
- Refraction WorksheetDocument2 pagesRefraction WorksheetRicardo Johnson0% (1)
- Physics 1 - Length and TimeDocument43 pagesPhysics 1 - Length and TimeHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- Physics Atp TipsDocument2 pagesPhysics Atp TipsFehmeed Alchemy78% (9)
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 9.1Document2 pagesIGCSE Physics Worksheet 9.1Alex DatsyukNo ratings yet
- RefractionDocument12 pagesRefractionJustin MadrisitaNo ratings yet
- Thesis (Editing) (Autosaved) (Repaired)Document167 pagesThesis (Editing) (Autosaved) (Repaired)jc PHNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence in Education - A ReviewDocument6 pagesArtificial Intelligence in Education - A ReviewyasmineNo ratings yet
- Financial Literacy Kim RedgwellDocument1 pageFinancial Literacy Kim Redgwellapi-527336218No ratings yet
- Indonesian As A Meaning of Cultural CrossDocument16 pagesIndonesian As A Meaning of Cultural CrossMarsya Cha RichaNo ratings yet
- 802.11 ArchitectureDocument10 pages802.11 ArchitectureSarath KsNo ratings yet
- Aashish Malik 057 Information Technology Management LabDocument52 pagesAashish Malik 057 Information Technology Management LabRajeev TripathiNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument7 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesJenny Himor BalitaNo ratings yet
- 01 MEM40105 Multiple Choice Assignment PDFDocument93 pages01 MEM40105 Multiple Choice Assignment PDFMohammad Saidul Islam ShantoNo ratings yet
- Technical Data MotorDocument12 pagesTechnical Data Motordaoquan222222No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Engineering Economic Analysis, 2nd Canadian EditionDocument46 pagesChapter 7 - Engineering Economic Analysis, 2nd Canadian EditionSamNo ratings yet
- Timetable 22-23 14 Juli 2022Document18 pagesTimetable 22-23 14 Juli 2022Luhut GultomNo ratings yet
- PPT II Plastics Materials and Its Applications II 20 221Document1 pagePPT II Plastics Materials and Its Applications II 20 221Raj ThakurNo ratings yet
- RMS Value MeasurementDocument3 pagesRMS Value MeasurementGiovanni GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Middlebrook S Extra Element TheoremDocument10 pagesMiddlebrook S Extra Element TheoremAnushree SaranNo ratings yet
- 2020-Tymstra Et Al-Wildfire Management in Canada Review, Challenges and OpportunitiesDocument10 pages2020-Tymstra Et Al-Wildfire Management in Canada Review, Challenges and Opportunitiesmajid 1993No ratings yet
- Enterprise Solutions: Smart Office - Energy Management - LED Lighting Solution - Infrastructure ManagementDocument9 pagesEnterprise Solutions: Smart Office - Energy Management - LED Lighting Solution - Infrastructure ManagementpradeeshNo ratings yet
- CMP1025 Tutorial 2Document2 pagesCMP1025 Tutorial 2Leia MichaelsonNo ratings yet
- Answers For Electricity In-Text and Book ExerciseDocument16 pagesAnswers For Electricity In-Text and Book ExerciseLorith Plays SMPNo ratings yet
- 07 - The Behavioral Investor by Daniel CrosbyDocument7 pages07 - The Behavioral Investor by Daniel CrosbyZulfan ArifNo ratings yet
- Bettis - Line Break Detection - Lineguard2100Document6 pagesBettis - Line Break Detection - Lineguard2100andy175No ratings yet
- ABB OVRH SPD Catalog 090417 RebrandDocument20 pagesABB OVRH SPD Catalog 090417 RebrandIvan HerreraNo ratings yet