Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Report On Neutralisation
Report On Neutralisation
Uploaded by
Sandesh Lawand0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views3 pagesNeutralization reactions occur when an acid and base react quantitatively to form a salt and water. There are four types of neutralization reactions: 1) strong acid and strong base, which react completely to form products with no excess reactants, 2) strong acid and weak base, which produces an acidic solution due to excess hydrogen ions, 3) weak acid and strong base, which produces a basic solution due to excess hydroxide ions, and 4) weak acid and weak base, which does not fully neutralize due to incomplete dissociation of both reactants. Neutralization is used in paint industry to adjust pH for latex stabilization.
Original Description:
Original Title
Report on Neutralisation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentNeutralization reactions occur when an acid and base react quantitatively to form a salt and water. There are four types of neutralization reactions: 1) strong acid and strong base, which react completely to form products with no excess reactants, 2) strong acid and weak base, which produces an acidic solution due to excess hydrogen ions, 3) weak acid and strong base, which produces a basic solution due to excess hydroxide ions, and 4) weak acid and weak base, which does not fully neutralize due to incomplete dissociation of both reactants. Neutralization is used in paint industry to adjust pH for latex stabilization.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views3 pagesReport On Neutralisation
Report On Neutralisation
Uploaded by
Sandesh LawandNeutralization reactions occur when an acid and base react quantitatively to form a salt and water. There are four types of neutralization reactions: 1) strong acid and strong base, which react completely to form products with no excess reactants, 2) strong acid and weak base, which produces an acidic solution due to excess hydrogen ions, 3) weak acid and strong base, which produces a basic solution due to excess hydroxide ions, and 4) weak acid and weak base, which does not fully neutralize due to incomplete dissociation of both reactants. Neutralization is used in paint industry to adjust pH for latex stabilization.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
NEUTRALISATION
What is Neutralization Reaction?
1. Chemical reaction in which an acid and base quantitatively react together to form a salt and
water as products.
2. In this reaction there is combination of the H+ & OH- ions which forms water.
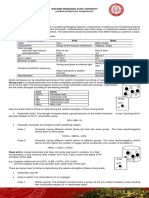
ACID + BASE = H+OH- + SALT
3. This reactions are usually exothermic in nature. In exothermic reactions bonds are made and
energy is released to the surroundings.
Types of the Neutralization Reaction: -
1. Strong Acid & Strong Base.
2. Strong Acid & Weak Base.
3. Weak Acid & Strong Base
4. Weak Acid & Weak Base.
1. Strong Acid & Strong Base:
SA & SB dissociate entirely in aqueous solution. There are no any surplus ions present in the
resultant solution.
e.g.- SA- HCL, H2SO4 & SB - NAOH, KOH.
2. Strong Acid & Weak Base.
Weak base dissociates to a very less extent only 5 – 10 %, here amount of the OH- ions is very
less compared to the H+ ions available. Resultant solution is acidic (3-6).
e.g.- WB- Mg (OH)2, Ca (OH)2 etc.
3. Weak Acid & Strong Base:
OH- ion concentration is much higher than the H+ ions. Weak acid does not dissociate much in
the aqueous conditions. Resultant solution is basic (8-11).
e.g. – WA - Acetic acid & all other organic acids.
5. Weak Acid & Weak Base.
Here both acid & base both are weak so neither of them dissociates completely & so
neutralization does not occur.
Applications:
In Paint industry the neutralization reaction is used for adjustment of the pH necessary in order
to stabilize the latex.
You might also like
- Chem 2 Q2 Week 3 BRONSTED ACID BASE For StudentsDocument13 pagesChem 2 Q2 Week 3 BRONSTED ACID BASE For StudentsVince Niño M. TuldaNo ratings yet
- Acids & Bases OL NotesDocument5 pagesAcids & Bases OL NotesHooria AminNo ratings yet
- Acids 2Document4 pagesAcids 2Syed AyaanNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Experiment No. 8 Advanced Acid-BaseDocument4 pagesLaboratory Experiment No. 8 Advanced Acid-BaseShayne Angelique CongsonNo ratings yet
- Chem Module Acid BaseDocument12 pagesChem Module Acid BaseRANJEET SHARMANo ratings yet
- Comparison of Acids and BasesDocument5 pagesComparison of Acids and BasesSANDEEP SINGH100% (1)
- Acids, Bases and OxidesDocument64 pagesAcids, Bases and OxidesThe ExistingNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases SaltsDocument13 pagesAcids Bases SaltsChito JarciaNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases and Salts NotesDocument22 pagesAcids Bases and Salts NotesHaneefah AhmedNo ratings yet
- Basic Pharmaceutical Chemistry 15Document108 pagesBasic Pharmaceutical Chemistry 15Gideon AntwiNo ratings yet
- PH and pOHDocument16 pagesPH and pOHAngelo PunzalanNo ratings yet
- Cours Acide-Base en English PDFDocument22 pagesCours Acide-Base en English PDFالغزيزال الحسن EL GHZIZAL HassaneNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry The Chemistry of Acids and Bases: Acid-Base TheoriesDocument22 pagesAP Chemistry The Chemistry of Acids and Bases: Acid-Base TheoriesJohn TranNo ratings yet
- 2.acids, Bases and SaltsDocument9 pages2.acids, Bases and SaltsayanNo ratings yet
- Acidic, Basic, and Neutral Salts: Weak Acids and BasesDocument3 pagesAcidic, Basic, and Neutral Salts: Weak Acids and BasesSandeep JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Ref: Introduction To Acids, Bases and Salts: Classification of MatterDocument5 pagesRef: Introduction To Acids, Bases and Salts: Classification of MatterAhmed shakilNo ratings yet
- Ref: Introduction To Acids, Bases and Salts: Classification of MatterDocument5 pagesRef: Introduction To Acids, Bases and Salts: Classification of MatterAhmed shakilNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases and Salts 3Document145 pagesAcids Bases and Salts 3Austin KuoNo ratings yet
- CN 9Document59 pagesCN 9Shaira Jane AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Week 6 8Document10 pagesGeneral Chemistry Week 6 8marjorie branzuelaNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases and SaltsDocument8 pagesAcids Bases and SaltsngaaNo ratings yet
- Organic Acids & Organic BasesDocument20 pagesOrganic Acids & Organic BasesCheng KathyNo ratings yet
- Science Revision All ChaptersDocument9 pagesScience Revision All ChaptersBhavyaa JoshiNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases and Salts For Students To StickDocument4 pagesAcids Bases and Salts For Students To StickARSHAD JAMILNo ratings yet
- Acid and BasesDocument37 pagesAcid and Basesnoor uddinNo ratings yet
- Add ChemDocument22 pagesAdd ChemDaniel PiamonteNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases and SaltsDocument11 pagesAcids Bases and SaltsCollins Obari AdiyeNo ratings yet
- 05 Acid Base and Redox 2009 IncDocument8 pages05 Acid Base and Redox 2009 Incapi-27085921No ratings yet
- Chapter 4-Inorganic ChemDocument27 pagesChapter 4-Inorganic ChemMark Harold GonzalesNo ratings yet
- AcidsbasesandsaltsDocument46 pagesAcidsbasesandsaltsalimelsayehNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Complete CourseDocument32 pagesChemistry Complete Coursewinston loboNo ratings yet
- Acid and Base 5 PDFDocument22 pagesAcid and Base 5 PDFZenonissya GalwanNo ratings yet
- CTSC Matric Masterclasses Acid and Bases 2020-1Document13 pagesCTSC Matric Masterclasses Acid and Bases 2020-1mxolisi mkhumaneNo ratings yet
- Non-Aqueous Acid Base TitrationDocument35 pagesNon-Aqueous Acid Base TitrationApurba Sarker Apu100% (9)
- Acids and Bases: Regents: Chapter 19 P. 586 - 629 Honors: Chapters 20, 21 P. 576 - 643Document103 pagesAcids and Bases: Regents: Chapter 19 P. 586 - 629 Honors: Chapters 20, 21 P. 576 - 643Zaina ZaliraNo ratings yet
- Intended Learning Outcomes: Lecture Notes in Inorganic Chemistry 1 Acids and BasesDocument10 pagesIntended Learning Outcomes: Lecture Notes in Inorganic Chemistry 1 Acids and Basessarah meneseNo ratings yet
- Acid Bases and SaltsDocument9 pagesAcid Bases and SaltsVenusCrazy 550No ratings yet
- Water Chemistry: I-Chemical Constituents of Water (Table 1)Document6 pagesWater Chemistry: I-Chemical Constituents of Water (Table 1)ismailchoughuleNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Acids and Bases Grade 12 Matric 2024Document13 pagesFundamentals of Acids and Bases Grade 12 Matric 2024snothandoxesibe2006No ratings yet
- CN 9Document73 pagesCN 9Shaira Jane AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Module 4 in Gen ChemDocument8 pagesModule 4 in Gen ChemEarl Cris RiggsNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases&Salts NotesDocument12 pagesAcids Bases&Salts NotesAngelic Shine100% (1)
- Introduction To Acids, Bases and Salts: Classification of MatterDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Acids, Bases and Salts: Classification of MatterSumit JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument63 pagesAcids and Basesgarnettdalagan.bascNo ratings yet
- Acid Base and SaltDocument24 pagesAcid Base and Saltmanish100% (1)
- CH 2Document10 pagesCH 2charanNo ratings yet
- Lab1 TeodoroDocument9 pagesLab1 TeodoroJherby TeodoroNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument6 pagesAcids, Bases and Saltsikd playNo ratings yet
- What Happens When You Mix Substances Together?Document19 pagesWhat Happens When You Mix Substances Together?AlyssaNo ratings yet
- Ch-2 Acid Base and SaltDocument40 pagesCh-2 Acid Base and SaltRushikKaretiyaNo ratings yet
- Acid and BasesDocument43 pagesAcid and BasesRobin TimkangNo ratings yet
- Class X Subject: Chemistry Chapter 2: Acids, Bases and Salts Following Notes Till Page No: 25 of Science NCERT BookDocument5 pagesClass X Subject: Chemistry Chapter 2: Acids, Bases and Salts Following Notes Till Page No: 25 of Science NCERT Bookashok pradhanNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument13 pagesAcids and BasesTahmed HasanNo ratings yet
- Solutions Constant of A Weak Acid or BaseDocument8 pagesSolutions Constant of A Weak Acid or BaseJeromeNo ratings yet
- However, Only The First H Is Ever Easily DissociatedDocument4 pagesHowever, Only The First H Is Ever Easily DissociatedVanessa Mirlisenna CastilloNo ratings yet
- The Big Chemistry Book on Solutions - Chemistry for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandThe Big Chemistry Book on Solutions - Chemistry for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Catalysis ReportDocument20 pagesCatalysis ReportSandesh LawandNo ratings yet
- Nitration: An Overview of Recent Developments and ProcessesDocument9 pagesNitration: An Overview of Recent Developments and ProcessesSandesh LawandNo ratings yet
- Cooling& Heating Time CalculationDocument6 pagesCooling& Heating Time CalculationSandesh LawandNo ratings yet
- Insulated Pipe V3Document37 pagesInsulated Pipe V3Sandesh LawandNo ratings yet
- Report On CyclizationDocument2 pagesReport On CyclizationSandesh LawandNo ratings yet