Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Standard Scores
Uploaded by
Jayson PasiaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Standard Scores
Uploaded by
Jayson PasiaCopyright:
Available Formats
Standard Scores
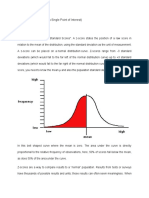
In particular, a score can be interpreted more meaningfully if we know the mean and variabilityof the
other scores where that single score belongs. Knowing this, a raw score can be converted into standard
scores.
Z-score. There are many kinds of standard scores. The most useful is the z-score, which is often used
to express a raw score in relation to the mean and standard deviation. This relationship is expressed
in the following formula:
x−x
z=
S
Recall that x – x is a deviation score. With this difference, we are able to know whether your test
score, say, x is above or below the average score. However, you cannot say whether your test score or grade
is better or worse than the average score. Again, the importance of knowing the standard deviation is
highlighted here.
The standard deviation helps you locate the relative position of the score in a distribution.
The equation above gives you the z-score, which can indicate the number of standard deviations the
score is above or below the mean. A z-score is called a standard score, simply because it is a deviation
score expressed in standard deviation units.
T-score. A z-score may also be a repeating, or non-repeating decimal, which may not be comfortable
for others. One option is to convert a z-score into a T-score, which is a transformed standard
score. To do this, there is scaling in which a mean of 0 in a z-score is transformed into a mean of 50,
and the standard deviation in z-score is multiplied by 10. The corresponding equation is:
T-score = 50 +10z
For example, a z-score of -2 is equivalent to a T-score of 30. That is:
T-score = 50 + 10(-2)
= 50 – 20
= 30
Stanine Scores. Another standard score is stanine, shortened from standard nine. With nine in its
name, the scores are on a nine-point scale.
In a z-score distribution, the mean is 0, and the standard deviation is 1. In this scale, the mean is 5,
and the standard deviation is 1. In this scale, the mean is 5, and the standard deviation is 2. Each stanine is
one-half standard deviation-wide. Like the T-score, stanine score can be calculated from the z-score by
multiplying the z-score by 2 and adding 5. That is,
Stanine = 2z + 5
You might also like
- Sample Size for Analytical Surveys, Using a Pretest-Posttest-Comparison-Group DesignFrom EverandSample Size for Analytical Surveys, Using a Pretest-Posttest-Comparison-Group DesignNo ratings yet
- Measures of DispersionDocument11 pagesMeasures of DispersionKristen Imie Dungog LacapagNo ratings yet
- Standard ScoresDocument2 pagesStandard ScoresDr. Nisanth.P.MNo ratings yet
- GCSE Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Aklan State University College of Industrial Technology: Kalibo, A KlanDocument3 pagesAklan State University College of Industrial Technology: Kalibo, A KlanGuien GemotoNo ratings yet
- Z - ScoreDocument12 pagesZ - ScoreSam SamNo ratings yet
- Fulgar - 9040 Standard Normal DistributionDocument29 pagesFulgar - 9040 Standard Normal Distributioneugene louie ibarraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 PDFDocument5 pagesLesson 6 PDFaggieNo ratings yet
- Z-Score: Definition, Calculation and InterpretationDocument5 pagesZ-Score: Definition, Calculation and Interpretationppkuldeep4No ratings yet
- Z ScoreDocument7 pagesZ ScoreakshayNo ratings yet
- Stats Chapter 5 Z Scores Stand DistDocument20 pagesStats Chapter 5 Z Scores Stand DistMadison HartfieldNo ratings yet
- 13 ZscoresDocument13 pages13 ZscoresMhelvyn RamiscalNo ratings yet
- Statistics (Z-Scores) : Burak Doğruyol Associate Professor of PsychologyDocument32 pagesStatistics (Z-Scores) : Burak Doğruyol Associate Professor of Psychologysimi savasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Standard Scores in Normal DistributionDocument8 pagesLesson 5 - Standard Scores in Normal DistributionEmyren ApuyaNo ratings yet
- The Standard Normal Distribution Transcript (With Images)Document6 pagesThe Standard Normal Distribution Transcript (With Images)Peter HuangNo ratings yet
- 05 Interpretation of Assessment ResultsDocument40 pages05 Interpretation of Assessment ResultsJim Boy BumalinNo ratings yet
- Statistik UjiDocument21 pagesStatistik UjiAlya Nabilah AzzahraNo ratings yet
- Psych Stats Notes in Normal DistributionDocument4 pagesPsych Stats Notes in Normal DistributionLIEZEL ANN ORDINANNo ratings yet
- 13 Zscores PDFDocument13 pages13 Zscores PDFAna ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document20 pagesChapter 5FatimaIjazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document20 pagesChapter 5Huseyin OztoprakNo ratings yet
- Statistical Analysis With Software Application: Module No. 5Document9 pagesStatistical Analysis With Software Application: Module No. 5Vanessa UbaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document20 pagesChapter 5Nimfa PlazaNo ratings yet
- Assessment in Learning 1 Standard Scores I. ObjectivesDocument3 pagesAssessment in Learning 1 Standard Scores I. ObjectivesSymon FeolinoNo ratings yet
- 2 Z-Scores (English)Document10 pages2 Z-Scores (English)marco sponzielloNo ratings yet
- Converting Z ScoresDocument14 pagesConverting Z ScoresMary Jane Duma-ogNo ratings yet
- Written Report Z-ScoresDocument3 pagesWritten Report Z-ScoresEilishNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Z-ScoresDocument14 pagesUnderstanding The Z-ScoresJaneth MarcelinoNo ratings yet
- Z-Scores, The Normal Curve, & Standard Error of The MeanDocument33 pagesZ-Scores, The Normal Curve, & Standard Error of The MeanDåvê D. BãçølōtNo ratings yet
- Ijsrmjournal, Journal Manager, 17 IjsrmDocument4 pagesIjsrmjournal, Journal Manager, 17 Ijsrmdana chuaNo ratings yet
- Report Educl-MeasurementDocument21 pagesReport Educl-MeasurementLorna Dollisen Labrada - MiguelaNo ratings yet
- Standard Normal DistributionDocument28 pagesStandard Normal DistributionMae Angela BautistaNo ratings yet
- 5 Z&NormalDocument33 pages5 Z&NormalRosemarie GasparNo ratings yet
- Unit II Lesson 2 Understanding The Z-ScoresDocument14 pagesUnit II Lesson 2 Understanding The Z-ScoresBernadette Remigio - JovellanosNo ratings yet
- Z ScoresDocument27 pagesZ ScoresSoma San JoseNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Understanding The Z-ScoresDocument16 pagesLesson 6 Understanding The Z-ScoresKenneth JeminoNo ratings yet
- Zscores HANDOUT PDFDocument56 pagesZscores HANDOUT PDFikhwanghazaliNo ratings yet
- Day 7 - Z-ScoresDocument4 pagesDay 7 - Z-ScoresLianne SedurifaNo ratings yet
- 1.07 Z-ScoresDocument2 pages1.07 Z-ScoresAisha ChohanNo ratings yet
- BS-chapter3-2021-Z - Score or STD ScoreDocument17 pagesBS-chapter3-2021-Z - Score or STD ScorefarwaNo ratings yet
- (Assignment) (Business) (International Analysis)Document4 pages(Assignment) (Business) (International Analysis)Sheraz Aslam SherazNo ratings yet
- Annotated SINGLE VARIABLE NotesDocument19 pagesAnnotated SINGLE VARIABLE Notesprimalp6105No ratings yet
- Week 05Document23 pagesWeek 05Javeria EhteshamNo ratings yet
- What Is A Z ScoreDocument2 pagesWhat Is A Z ScoreDeseree Mae ApenasNo ratings yet
- CH 6Document33 pagesCH 6kavinbhatia777No ratings yet
- Standard Scores and The Normal Curve: Report Presentation byDocument38 pagesStandard Scores and The Normal Curve: Report Presentation byEmmanuel AbadNo ratings yet
- Notes No. 5 For 11 e Understanding Z ScoresDocument5 pagesNotes No. 5 For 11 e Understanding Z Scoresnikkigabanto.24No ratings yet
- Standard ScoresDocument10 pagesStandard ScoresDr. Nisanth.P.M100% (2)
- Lesson 2.2 Z-ScoresDocument8 pagesLesson 2.2 Z-ScoresAldous FranciscoNo ratings yet
- How Well Did Sarah Perform in Her English Literature Coursework Compared To The Other 50 Students?Document2 pagesHow Well Did Sarah Perform in Her English Literature Coursework Compared To The Other 50 Students?Sangeeta JhunjhunwalaNo ratings yet
- Understading Z ScoresDocument2 pagesUnderstading Z ScoresJhun francis BisaNo ratings yet
- Standard ScoresDocument3 pagesStandard ScoresElle RoxasNo ratings yet
- Stat ch2Document12 pagesStat ch2Solomon MeleseNo ratings yet
- Part 6 - Week 07 Students TDocument13 pagesPart 6 - Week 07 Students TJane DoeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.2 - Understanding The Z-ScoreDocument24 pagesLesson 2.2 - Understanding The Z-ScoreHayashida KunNo ratings yet
- Nordis FinalDocument6 pagesNordis FinalSamuel GoyoNo ratings yet
- Z-Score TableDocument8 pagesZ-Score TableThy Trương PhươngNo ratings yet
- Z Scores & Correlation: Greg C ElversDocument21 pagesZ Scores & Correlation: Greg C ElversFrancisco MenesesNo ratings yet
- Jayson Pasia-Special-QuizDocument4 pagesJayson Pasia-Special-QuizJayson PasiaNo ratings yet
- Short Answer TestDocument2 pagesShort Answer TestJayson PasiaNo ratings yet
- President Ramon Magsaysay State University: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument1 pagePresident Ramon Magsaysay State University: Republic of The PhilippinesJayson PasiaNo ratings yet
- President Ramon Magsaysay State University: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument1 pagePresident Ramon Magsaysay State University: Republic of The PhilippinesJayson PasiaNo ratings yet
- GROUP 3medialiteracy Written ReportDocument8 pagesGROUP 3medialiteracy Written ReportJayson PasiaNo ratings yet
- President Ramon Magsaysay State University: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument1 pagePresident Ramon Magsaysay State University: Republic of The PhilippinesJayson PasiaNo ratings yet
- Jayson Pasia-Special-QuizDocument4 pagesJayson Pasia-Special-QuizJayson PasiaNo ratings yet
- Citation 343976009Document1 pageCitation 343976009Jayson PasiaNo ratings yet
- PRINCIPE Written Repost in Assessment in LearningDocument4 pagesPRINCIPE Written Repost in Assessment in LearningJayson PasiaNo ratings yet
- President Ramon Magsaysay State UniversityDocument1 pagePresident Ramon Magsaysay State UniversityJayson PasiaNo ratings yet
- President Ramon Magsaysay State University: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument1 pagePresident Ramon Magsaysay State University: Republic of The PhilippinesJayson PasiaNo ratings yet
- World War II - UNIT PLAN PDFDocument20 pagesWorld War II - UNIT PLAN PDFJayson PasiaNo ratings yet
- EEM 225 - Complex Numbers Functions - Oct 2021 - HTEDocument23 pagesEEM 225 - Complex Numbers Functions - Oct 2021 - HTEİsmail ŞahinNo ratings yet
- Combinatorial Geometry - Reid Barton - MOP 2005Document4 pagesCombinatorial Geometry - Reid Barton - MOP 2005Ayush AryanNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium Temperature DistributionsDocument14 pagesEquilibrium Temperature DistributionsAlejo PirakokNo ratings yet
- 1 - 10 Mean Median ModeDocument2 pages1 - 10 Mean Median Modecristina gomezNo ratings yet
- Internal Order in Crystals1Document35 pagesInternal Order in Crystals1Kripa KattelNo ratings yet
- MATH 1142 - Assign #6Document2 pagesMATH 1142 - Assign #6arlandoNo ratings yet
- Seton Test 1 AlgebraDocument4 pagesSeton Test 1 AlgebraGabrielle DiazonNo ratings yet
- MA1506TUT11Document2 pagesMA1506TUT11Wong JiayangNo ratings yet
- CVDocument12 pagesCVPrincespragti PatilNo ratings yet
- Maths English G.2 ThailandDocument8 pagesMaths English G.2 ThailandDookkuu Pirapon PotiNo ratings yet
- LP in Properties of MultiplicationDocument15 pagesLP in Properties of MultiplicationJohn Mark CubarNo ratings yet
- Prac 1 ControlDocument37 pagesPrac 1 ControlJack ClarksonNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Further Mathematics 9231/21Document16 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Further Mathematics 9231/21윤소리No ratings yet
- Strategic Practice and Homework 5Document14 pagesStrategic Practice and Homework 5yip90100% (1)
- Notas de Aula Álgebra 1 - Oliver Lorscheid - IMPA PDFDocument26 pagesNotas de Aula Álgebra 1 - Oliver Lorscheid - IMPA PDFNoeme MatosNo ratings yet
- Cape Unit 1 Pure Math p3 2019Document20 pagesCape Unit 1 Pure Math p3 2019Unkown WetlordNo ratings yet
- Floating Point ExampleDocument2 pagesFloating Point Exampleanukriti meenaNo ratings yet
- Regularization and Feature Selection: Big Data For Economic ApplicationsDocument39 pagesRegularization and Feature Selection: Big Data For Economic ApplicationsValerio ZarrelliNo ratings yet
- 04 - Logic Gates and Boolean AlgebraDocument44 pages04 - Logic Gates and Boolean AlgebraGirishNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Mathematics 0580/23Document8 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Mathematics 0580/23muroojghazalyNo ratings yet
- Lecture Time Domain Analysis of Control SystemsDocument15 pagesLecture Time Domain Analysis of Control SystemsFahadKhNo ratings yet
- Type 2 ANFISDocument2 pagesType 2 ANFISBALASUNDAR CNo ratings yet
- A Stereo ProjectionDocument16 pagesA Stereo ProjectionMary Grace Magpayo LanwangNo ratings yet
- History of GeometryDocument42 pagesHistory of GeometryChie ChieNo ratings yet
- Cs502 Final Term Solved Mcqs by JunaidDocument103 pagesCs502 Final Term Solved Mcqs by JunaidKhadija Afzal100% (1)
- HKMO2016heatans PDFDocument22 pagesHKMO2016heatans PDFChai Usajai UsajaiNo ratings yet
- The Reference Frame - Nice Try But I Am Now 99% Confident That Atiyah's Proof of RH Is Wrong, HopelessDocument5 pagesThe Reference Frame - Nice Try But I Am Now 99% Confident That Atiyah's Proof of RH Is Wrong, Hopelesssurjit4123No ratings yet
- 11 09 2020 PPT CIA Revision IIDocument13 pages11 09 2020 PPT CIA Revision IIjaisri RNo ratings yet
- Polynomial Farm 2023Document11 pagesPolynomial Farm 2023Sophia JimenezNo ratings yet
- f5 c8 Probability Distribution NewDocument7 pagesf5 c8 Probability Distribution NewYoga NathanNo ratings yet
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsFrom EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.From EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormFrom EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Calculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandCalculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Mathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingFrom EverandMathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Mental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorFrom EverandMental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Who Tells the Truth?: Collection of Logical Puzzles to Make You ThinkFrom EverandWho Tells the Truth?: Collection of Logical Puzzles to Make You ThinkRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Fluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldFrom EverandFluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (79)
- Assessment Prep for Common Core Mathematics, Grade 6From EverandAssessment Prep for Common Core Mathematics, Grade 6Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)From EverandMental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)No ratings yet
- Strategies for Problem Solving: Equip Kids to Solve Math Problems With ConfidenceFrom EverandStrategies for Problem Solving: Equip Kids to Solve Math Problems With ConfidenceNo ratings yet