Professional Documents
Culture Documents
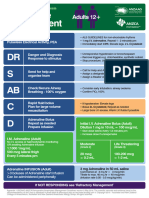
Refractory Anaphylaxis Algorithm 2021
Uploaded by
ay254Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Refractory Anaphylaxis Algorithm 2021
Uploaded by
ay254Copyright:
Available Formats
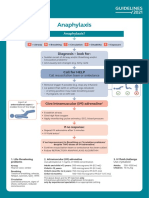
Refractory anaphylaxis A = Airway
Partial upper airway obstruction/stridor:
Nebulised adrenaline (5mL of 1mg/mL)
No improvement in respiratory or cardiovascular symptoms Total upper airway obstruction:
despite 2 appropriate doses of intramuscular adrenaline Expert help needed, follow difficult airway algorithm
B = Breathing
Establish dedicated Seek expert1 help early
Oxygenation is more important than intubation
peripheral IV or IO access Critical care support is essential
If apnoeic:
• Bag mask ventilation
• Consider tracheal intubation
Give rapid IV fluid bolus Start adrenaline infusion Severe/persistent bronchospasm:
e.g. 0.9% sodium chloride
& Adrenaline is essential for treating
• Nebulised salbutamol and ipratropium with oxygen
• Consider IV bolus and/or infusion of salbutamol or
all aspects of anaphylaxis
aminophylline
• Inhalational anaesthesia
Give IM* adrenaline Follow local protocol
every 5 minutes until adrenaline C = Circulation
infusion has been started OR
Peripheral low-dose IV adrenaline infusion: Give further fluid boluses and titrate to response:
*IV boluses of adrenaline are
• 1 mg (1 mL of 1 mg/mL [1:1000]) adrenaline in Child 10 mL/kg per bolus
not recommended, but may be
100 mL of 0.9% sodium chloride Adult 500–1000 mL per bolus
appropriate in some specialist
• Use glucose-free crystalloid
settings (e.g. peri-operative) while • Prime and connect with an infusion pump via a
dedicated line (e.g. Hartmann’s Solution, Plasma-Lyte®)
an infusion is set up
Large volumes may be required (e.g. 3–5 L in adults)
DO NOT ‘piggy back’ on to another infusion line
Place arterial cannula for continuous BP monitoring
DO NOT infuse on the same side as a BP cuff as this will
interfere with the infusion and risk extravasation Establish central venous access
Give high flow oxygen
Titrate to SpO2 94–98% • In both adults and children, start at 0.5–1.0 mL/kg/hour, IF REFRACTORY TO ADRENALINE INFUSION
and titrate according to clinical response Consider adding a second vasopressor in addition
• Continuous monitoring and observation is mandatory to adrenaline infusion:
• ↑↑ BP is likely to indicate adrenaline overdose • Noradrenaline, vasopressin or metaraminol
Monitor HR, BP, pulse oximetry • In patients on beta-blockers, consider glucagon
and ECG for cardiac arrhythmia Consider extracorporeal life support
Take blood sample
for mast cell tryptase Continue adrenaline infusion
and treat ABC symptoms Cardiac arrest – follow ALS ALGORITHM
• Start chest compressions early
Titrate according to clinical response
• Use IV or IO adrenaline bolus (cardiac arrest protocol)
• Aggressive fluid resuscitation
Intravenous adrenaline for anaphylaxis to be given only by experienced specialists in an appropriate setting.
1 • Consider prolonged resuscitation/extracorporeal CPR
You might also like
- Values May Vary Between Laboratories: Normal Lab Values (Partial List)Document2 pagesValues May Vary Between Laboratories: Normal Lab Values (Partial List)gladz25No ratings yet
- Dengue CaseDocument4 pagesDengue CaseHo Yong WaiNo ratings yet
- Module 5A: Dental Management of Patients With Asthma: Prepared By: Dr. Maria Luisa Ramos - ClementeDocument27 pagesModule 5A: Dental Management of Patients With Asthma: Prepared By: Dr. Maria Luisa Ramos - Clementeelaine100% (1)
- Anaphylaxis Algorithm 2021Document1 pageAnaphylaxis Algorithm 2021Shawn Gaurav JhaNo ratings yet
- Anaphylaxis Algorithm 2021Document1 pageAnaphylaxis Algorithm 2021Shawn Gaurav JhaNo ratings yet
- Muscle Origins and InsertionsDocument9 pagesMuscle Origins and Insertionsnoisytaost92% (12)
- Anatomy of The SkinDocument28 pagesAnatomy of The Skinay254No ratings yet
- Restrictive Lung DiseaseDocument32 pagesRestrictive Lung DiseaseSalman Khan100% (1)
- Overview of Fluid and Electrolyte MaintenanceDocument54 pagesOverview of Fluid and Electrolyte MaintenanceIan WongNo ratings yet
- Iron Deficiency Anemia GuideDocument54 pagesIron Deficiency Anemia GuideRamsha ZafarNo ratings yet
- Airway AdjunctsDocument17 pagesAirway AdjunctsChannelGNo ratings yet
- Clinical Aspects of PneumothoraxDocument3 pagesClinical Aspects of PneumothoraxelisabethNo ratings yet
- Indoor Air Quality TraneDocument45 pagesIndoor Air Quality TraneMuhammad Faheem ShahbazNo ratings yet
- 2016 PAD ACC+AHA SlidesDocument74 pages2016 PAD ACC+AHA SlidesPonpimol Odee BongkeawNo ratings yet
- OJT PORTFOLIO REDCROSS4A - RoveliDocument52 pagesOJT PORTFOLIO REDCROSS4A - RoveliRaffy Liwan Kalinga ChapterNo ratings yet
- Lung Metabolism: Proteolysis and Antioproteolysis Biochemical Pharmacology Handling of Bioactive SubstancesFrom EverandLung Metabolism: Proteolysis and Antioproteolysis Biochemical Pharmacology Handling of Bioactive SubstancesAlain JunodNo ratings yet
- Radiology Emergency: Cranial, Chest, and AbdomenDocument69 pagesRadiology Emergency: Cranial, Chest, and AbdomenDani Kartika SariNo ratings yet
- Refrat Obat Anestesi RilaDocument69 pagesRefrat Obat Anestesi RilaRila RivandaNo ratings yet
- IntussusceptionDocument10 pagesIntussusceptionPatrick DycocoNo ratings yet
- Gambaran Patologi Anatomik Kelainan Sistem PernapasanDocument49 pagesGambaran Patologi Anatomik Kelainan Sistem PernapasanWahyunitadotokaNo ratings yet
- Monitoring Intra Operatif: Mindi Widayani NRP 122.022.1115 FK UPN "Veteran" JakartaDocument21 pagesMonitoring Intra Operatif: Mindi Widayani NRP 122.022.1115 FK UPN "Veteran" Jakartaputri wulandariNo ratings yet
- Management of Local Anaesthetic Toxicity Update 2009Document6 pagesManagement of Local Anaesthetic Toxicity Update 2009leviosagalNo ratings yet
- The Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory SyndromeDocument7 pagesThe Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory SyndromeAlexandra PaunNo ratings yet
- Aetiology: Obe, FFCM, F.FQMDocument5 pagesAetiology: Obe, FFCM, F.FQMYusfi RydokaNo ratings yet
- Hanifin and Rajka Diagnostic Criteria For Atopic DermatitisDocument3 pagesHanifin and Rajka Diagnostic Criteria For Atopic DermatitisAlief LeisyahNo ratings yet
- PBL ObstreticsDocument7 pagesPBL ObstreticsMako ManuelNo ratings yet
- AspergillomaDocument20 pagesAspergillomaFatur ReyhanNo ratings yet
- Larynx InfectionsDocument28 pagesLarynx InfectionsMuskan GogiaNo ratings yet
- Toxic GasesDocument21 pagesToxic GasesBestariNugrahiniNo ratings yet
- Difficult AirwayDocument38 pagesDifficult AirwaybrojeemNo ratings yet
- Lutembacher's Syndrome at KolonodaleDocument7 pagesLutembacher's Syndrome at KolonodaleWayan GunawanNo ratings yet
- Shock Types and Treatments GuideDocument14 pagesShock Types and Treatments GuidenataliaNo ratings yet
- BronkiektasisDocument7 pagesBronkiektasisirenaNo ratings yet
- Bilas LambungDocument12 pagesBilas LambungNthie UnguNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia.Document5 pagesBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia.Mas HaqiNo ratings yet
- Verview: Scoliosisopen Pop-Up Dialog BoxDocument6 pagesVerview: Scoliosisopen Pop-Up Dialog BoxAnton DeeNo ratings yet
- Management of ACS Complicated With Acute Heart Failure DR BudianaDocument27 pagesManagement of ACS Complicated With Acute Heart Failure DR BudianaLuh Leni AriniNo ratings yet
- Asthma: Khadejah Stewart May 2021 Pediatric RotationDocument14 pagesAsthma: Khadejah Stewart May 2021 Pediatric RotationRujay BlackwoodNo ratings yet
- Methacholine1 21Document21 pagesMethacholine1 21Mihaela Dudau100% (1)
- Patofisiologi AritmiaDocument27 pagesPatofisiologi AritmiaVedora Angelia GultomNo ratings yet
- Eisenmenger SyndromeDocument2 pagesEisenmenger Syndromecarlo_nonNo ratings yet
- Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar StateDocument17 pagesHyperglycemic Hyperosmolar StateAqila Mumtaz50% (2)
- Pleural Effusion Causes and DiagnosisDocument69 pagesPleural Effusion Causes and DiagnosisUswatun Hasanah RINo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About DyspneaDocument34 pagesEverything You Need to Know About DyspneaAlvin BrilianNo ratings yet
- Tatalaksana Pada Luka BakarDocument55 pagesTatalaksana Pada Luka Bakarmagdalena sriNo ratings yet
- Modern View of AsthmaDocument27 pagesModern View of AsthmaraisaNo ratings yet
- Hypoxic SpellsDocument3 pagesHypoxic SpellsMemo LoezaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Announcement JakNews 2024Document19 pages2nd Announcement JakNews 2024Nando EllaNo ratings yet
- Critical Limb IschemiaDocument11 pagesCritical Limb Ischemianurliah armandNo ratings yet
- CWP Background: Causes, Types, and Pathophysiology of Coal Worker's PneumoconiosisDocument10 pagesCWP Background: Causes, Types, and Pathophysiology of Coal Worker's Pneumoconiosisdrmohamed2017No ratings yet
- Final 2nd Announcement Konas Perdatin Perdici 2019 - WebsiteDocument65 pagesFinal 2nd Announcement Konas Perdatin Perdici 2019 - Websitetia_drNo ratings yet
- Trauma Kapitis RevisiDocument54 pagesTrauma Kapitis RevisiRatika Ayu PiliangNo ratings yet
- Subcutaneous: EmphysemaDocument70 pagesSubcutaneous: EmphysemaWer TeumeNo ratings yet
- Air Way Management (ABCDE of Trauma)Document25 pagesAir Way Management (ABCDE of Trauma)makmmkaNo ratings yet
- HDDocument23 pagesHDSardjitoNo ratings yet
- PVC Stoelting Coex 1Document29 pagesPVC Stoelting Coex 1Rudy SiahaanNo ratings yet
- Bronchiolitis Guideline RecommendationsDocument10 pagesBronchiolitis Guideline RecommendationsAmi WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Causes and Treatment of ChylothoraxDocument8 pagesCauses and Treatment of ChylothoraxMaral Bimanti FebrilinaNo ratings yet
- Patch Test ROAT PDFDocument9 pagesPatch Test ROAT PDFrochmandrg dokter gigiNo ratings yet
- Referat - Spondilitis TB (RSAL)Document35 pagesReferat - Spondilitis TB (RSAL)Angga Yogi LaksmanaNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis dan Tatalaksana Awal Stroke dan SAH di IGDDocument26 pagesDiagnosis dan Tatalaksana Awal Stroke dan SAH di IGDekaNo ratings yet
- Airway ManagementDocument41 pagesAirway ManagementKharisma RatihNo ratings yet
- Death Case Dr. MeikoDocument49 pagesDeath Case Dr. MeikoMohamad ZulfikarNo ratings yet
- Refractory Anaphylaxis Algorithm 2021Document1 pageRefractory Anaphylaxis Algorithm 2021Joana JohnNo ratings yet
- Adult CardDocument1 pageAdult CardIvan MoralesNo ratings yet
- Anaphylaxis - DR Dina MDocument31 pagesAnaphylaxis - DR Dina MimamNo ratings yet
- Emergency Treatment of Anaphylaxis May 2021 - 0Document61 pagesEmergency Treatment of Anaphylaxis May 2021 - 0Glades AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Quality Standards Primary Care Equipment and Drug ListsDocument10 pagesQuality Standards Primary Care Equipment and Drug Listsay254No ratings yet
- Quality Standards for Primary Care Resuscitation TrainingDocument10 pagesQuality Standards for Primary Care Resuscitation Trainingay254No ratings yet
- Key Recommendations For Clinical Practice: Airway And/or Breathing And/or Circulation ProblemsDocument5 pagesKey Recommendations For Clinical Practice: Airway And/or Breathing And/or Circulation ProblemsShawn Gaurav JhaNo ratings yet
- Local Anaesthetic Systemic Toxicity V6Document10 pagesLocal Anaesthetic Systemic Toxicity V6ay254No ratings yet
- Emergency Medicines - PHA 59 - April 2017Document31 pagesEmergency Medicines - PHA 59 - April 2017ay254No ratings yet
- British Standards of Hair RestorationDocument10 pagesBritish Standards of Hair Restorationay254No ratings yet
- Hair Loss v0.5 PathwayDocument1 pageHair Loss v0.5 PathwayAdi PurnomoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Functions of the Digestive TractDocument27 pagesAnatomy and Functions of the Digestive Tractay254No ratings yet
- Adverse Effects of Blood TransfusionDocument3 pagesAdverse Effects of Blood Transfusionay254No ratings yet
- PAE STAGE 2 EXAM PRACTICE With Answer Key and TapescriptDocument39 pagesPAE STAGE 2 EXAM PRACTICE With Answer Key and TapescriptaagNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 Nursing As A ProfessionDocument3 pagesCHAPTER 1 Nursing As A ProfessionKarl ZacariasNo ratings yet
- Mba HRM 3 AprDocument13 pagesMba HRM 3 AprFarhaNo ratings yet
- LanoLip Power Point PresentationDocument12 pagesLanoLip Power Point PresentationWalter Sanchez EscobarNo ratings yet
- Identification of Aerobic Pathogenic Bacteria Isolated From Ready-to-Eat Cakes Sold in Traditional Markets in Manado CityDocument3 pagesIdentification of Aerobic Pathogenic Bacteria Isolated From Ready-to-Eat Cakes Sold in Traditional Markets in Manado CityVenita NapitNo ratings yet
- DM PhysecDocument237 pagesDM PhysecnormoNo ratings yet
- Rainier-Andal A11-02 GT6Document1 pageRainier-Andal A11-02 GT6Rosalie AndalNo ratings yet
- Apostila 04Document112 pagesApostila 04fazziobeatrizNo ratings yet
- Week 4 English 9: Judging The Validity of The Evidence From A TextDocument4 pagesWeek 4 English 9: Judging The Validity of The Evidence From A TextMaria Carmela ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Ecl SW Iso45001Document92 pagesEcl SW Iso45001Meghanath LalemmaNo ratings yet
- 4.health 8 Law Q2 21 22 PDFDocument8 pages4.health 8 Law Q2 21 22 PDFwensleyarcillaNo ratings yet
- Basketball Court Construction SampleDocument17 pagesBasketball Court Construction Sampleashenafi girmaNo ratings yet
- Clearance PDFDocument1 pageClearance PDFJane DeckerNo ratings yet
- Konsep Dasar ErgonomiDocument19 pagesKonsep Dasar Ergonomimugi prajeniNo ratings yet
- Long-Term Mortality After The Blood Pressure and Lipid-Lowering Treatment in Hypertensive Patients: 16-Year Follow-Up of The ASCOT Legacy StudyDocument22 pagesLong-Term Mortality After The Blood Pressure and Lipid-Lowering Treatment in Hypertensive Patients: 16-Year Follow-Up of The ASCOT Legacy StudyFlore HountondjiNo ratings yet
- Understanding Perceptual Sensitivity and Decision CriteriaDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Perceptual Sensitivity and Decision CriteriaHarshit ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Head To Toe AssessmentDocument2 pagesHead To Toe AssessmentMichelle Myca Rosauro100% (1)
- Straumann Dental Implant System Listino PrezziDocument24 pagesStraumann Dental Implant System Listino PrezziNatalia Music LiveNo ratings yet
- Profiles in Diversity Journal - Sep/Oct 2007Document201 pagesProfiles in Diversity Journal - Sep/Oct 2007Profiles in Diversity JournalNo ratings yet
- Plagarisim ReportDocument39 pagesPlagarisim ReportNila VeerapathiranNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Cashew Nut. Doc Phuoc Long 24-SepDocument6 pages1.3 Cashew Nut. Doc Phuoc Long 24-SepPhuong NguyenNo ratings yet
- Đề 1Document16 pagesĐề 1Tri DangNo ratings yet
- Figure of Speech QuizDocument1 pageFigure of Speech QuizManal SalamehNo ratings yet
- Daily Diary Stress and Mood Variation/TITLEDocument103 pagesDaily Diary Stress and Mood Variation/TITLEFilsa Putri AnwarNo ratings yet
- Depression Associated With Dementia With Lewy Bodies (DLB) and The Effect of SomatotherapyDocument6 pagesDepression Associated With Dementia With Lewy Bodies (DLB) and The Effect of SomatotherapyRaluca ElenaNo ratings yet
- RhetoricDocument32 pagesRhetoricDian ValerieNo ratings yet
- Triethanolamine Safety ReportDocument6 pagesTriethanolamine Safety ReportMaria Inês HarrisNo ratings yet
- Human Monkeypox 2022 Virus Machine Learning Prediction Model Outbreak Forecasting Visualization With Time-Series Exploratory Data AnalysisDocument6 pagesHuman Monkeypox 2022 Virus Machine Learning Prediction Model Outbreak Forecasting Visualization With Time-Series Exploratory Data AnalysisNeelima DudaNo ratings yet