Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Table 1-1 The Geologic Time Scale
Uploaded by
Geo CUKOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Table 1-1 The Geologic Time Scale
Uploaded by
Geo CUKCopyright:
Available Formats
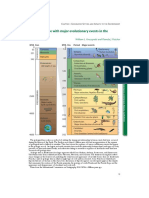
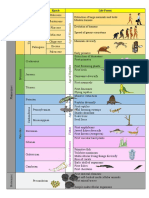
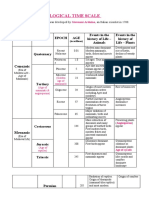
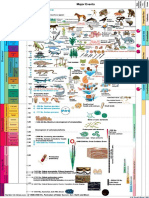
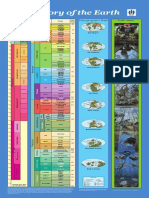
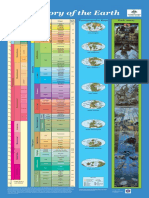
Table 1–1 • THE GEOLOGIC TIME SCALE
TIME UNITS OF THE GEOLOGIC TIME SCALE
Eon Era Period Epoch DISTINCTIVE PLANTS AND ANIMALS
Recent or Humans
Holocene
Quaternary 0.011
“Age of Mammals”
Pleistocene
2.58
Cenozoic Era
Pliocene
Neogene 5.3
Miocene Mammals develop
23 and become dominant
Tertiar
Oligocene
40
Paleogene Eocene
(Phaneros ⫽ “evident”; Zoon ⫽ “life”)
56 Extinction of dinosaurs and
Paleocene many other species
66
First flowering plants, greatest
Cretaceous
Mesozoic Era
Phanerozoic Eon
development of dinosaurs
Reptiles”
145
“Age of
First birds and mammals,
Jurassic abundant dinosaurs
201
Triassic First dinosaurs
252
Extinction of trilobites and many
Permian
Amphibians”
other marine animals3
300
“Age of
Carboniferous
Great coal forests; abundant
Pennsylvanian insects, first reptiles
323
Paleozoic Era
Mississippian Large primitive trees
359
“Age of
Fishes”
Devonian First amphibians
419
Silurian First land plant fossils
443
Invertebrates”
Ordovician First fish
“Age of
485
Marine
First organisms with shells,
Cambrian trilobites dominant
541
First multicelled organisms
First one-celled organisms
Approximate age of oldest rocks
Hadean Origin of the Earth
4600⫾
Time is given in millions of years (for example, 1000 stands for 1000 million, which is one billion). The
table is not drawn to scale. We know relatively little about events that occurred during the early part of the
Earth’s history. Therefore, the first four billion years are given relatively little space on this chart, while the
more recent Phanerozoic Eon, which spans only 538 million years, receives proportionally more space.
You might also like
- Dinosaurs, with Special Reference to the American Museum CollectionsFrom EverandDinosaurs, with Special Reference to the American Museum CollectionsNo ratings yet
- Practical 1 Geological Time Scale and Block DiagramDocument6 pagesPractical 1 Geological Time Scale and Block Diagramसुनिल त्रिपाठीNo ratings yet
- Geologic Time Scale in 40 CharactersDocument1 pageGeologic Time Scale in 40 CharactersdsNo ratings yet
- Geological Time With Major Evolutionary Events in The Fossil RecordDocument1 pageGeological Time With Major Evolutionary Events in The Fossil RecordMubarun100% (1)
- Geologic Time ScaleDocument1 pageGeologic Time Scaleanon_114803412No ratings yet
- Geological Time Scale Output GuideDocument8 pagesGeological Time Scale Output GuideAya Shine MagistradoNo ratings yet
- Geological Time-Scale ExplainedDocument30 pagesGeological Time-Scale ExplainedTitat Placedes Taniog100% (1)
- Eon Era Period Epoch Life FormsDocument2 pagesEon Era Period Epoch Life FormsChristine Joy SulibNo ratings yet
- Geologic TimeDocument1 pageGeologic TimeJesus BolivarNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 Week 2Document16 pagesGeneral Biology 2 Week 2Danikyl Villamonte LukbanNo ratings yet
- Geologycal Time ScaleDocument1 pageGeologycal Time ScaleElvara PriyankaNo ratings yet
- GEOLOGY Lecture 5Document11 pagesGEOLOGY Lecture 5education1354No ratings yet
- Earth Sci 2 SG Unit 4 PDFDocument24 pagesEarth Sci 2 SG Unit 4 PDFbaileyNo ratings yet
- Dinosaurs Knowledge Organiser v3Document1 pageDinosaurs Knowledge Organiser v3RyanNo ratings yet
- Geoti̇me TableDocument1 pageGeoti̇me TableiakkNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science: Quarter 1 - Week 6Document15 pagesEarth and Life Science: Quarter 1 - Week 6Lucy Jhamaicka Maruquin IliNo ratings yet
- Time ScaleDocument1 pageTime ScaleAdi HarjaNo ratings yet
- 2018 Task 3Document1 page2018 Task 3api-222503660No ratings yet
- P-27 Geological Time ScaleDocument2 pagesP-27 Geological Time ScaleFelix Joshua.B 10 BNo ratings yet
- How do we know Earth's ageDocument7 pagesHow do we know Earth's ageruukiNo ratings yet
- NP - General Biology 2 11 & 12 - Q3 - W2 BDocument9 pagesNP - General Biology 2 11 & 12 - Q3 - W2 BIrrah Sheene De VegaNo ratings yet
- Geologic Time ScaleDocument22 pagesGeologic Time ScaleJuby Ann EnconadoNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument31 pagesUntitledFeliks Albert RitaNo ratings yet
- Eras and Periods ERA Period Millions of Years. Animals DaysDocument1 pageEras and Periods ERA Period Millions of Years. Animals DaysDani UwUNo ratings yet
- History of LifeDocument41 pagesHistory of LifeMaria Zeny OrtegaNo ratings yet
- The Origin of PetroleumDocument46 pagesThe Origin of PetroleumWaldy Nur Patria100% (1)
- General Biology 2 Quarter 3: Week 2 - Module 2: Evolution and Origin of BiodiversityDocument24 pagesGeneral Biology 2 Quarter 3: Week 2 - Module 2: Evolution and Origin of Biodiversitycristina maquinto0% (1)
- Geologic Time ScaleDocument1 pageGeologic Time ScaleBeya BagsaoNo ratings yet
- Time ScaleDocument2 pagesTime ScaleStarNo ratings yet
- Report BioDocument5 pagesReport BiosharkNo ratings yet
- Geologic Time Scale: EON ERA Period Epoch Major Biological EventsDocument2 pagesGeologic Time Scale: EON ERA Period Epoch Major Biological EventsednakNo ratings yet
- Biology 2 Las 2 Maria Carmina R Martin Version 4Document4 pagesBiology 2 Las 2 Maria Carmina R Martin Version 4FEMALE Dawal LaizaNo ratings yet
- Geo Assignment No.1Document2 pagesGeo Assignment No.1Angelika HernandezNo ratings yet
- Geology of Ontario 8/5/2005Document28 pagesGeology of Ontario 8/5/2005Mathilda TerusNo ratings yet
- GENBIO2Document16 pagesGENBIO2Jhude JosephNo ratings yet
- Geological Ages-1Document1 pageGeological Ages-1AisyalathifaNo ratings yet
- History of The Earth-Tower of TimeDocument1 pageHistory of The Earth-Tower of Timecatacata001100% (1)
- Tower PDFDocument1 pageTower PDFasdNo ratings yet
- Kavish Geography 26 7 2023Document1 pageKavish Geography 26 7 2023rabia buttNo ratings yet
- Time ScaleDocument2 pagesTime ScaleKitty AlipioNo ratings yet
- The Geological Time Scale-2015Document9 pagesThe Geological Time Scale-2015StanliNo ratings yet
- Geologic Time: Earth'S Historical Past Divisons and Summary of EventsDocument2 pagesGeologic Time: Earth'S Historical Past Divisons and Summary of EventsKatrina SooNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Els Earths History GTDocument31 pagesWeek 6 Els Earths History GTChristine CastilloNo ratings yet
- Geological TimescaleDocument33 pagesGeological TimescaleCian KangleonNo ratings yet
- Geological Applications To Petroleum ReservoirDocument76 pagesGeological Applications To Petroleum Reservoiriqbal maratamaNo ratings yet
- Stratigraphic Chronological Chart History-of-the-Earth-posterDocument1 pageStratigraphic Chronological Chart History-of-the-Earth-posterUdit KumarNo ratings yet
- Geologic Timeline: Earth and Life Science Maricar M. Paladan 11-HUMSSDocument4 pagesGeologic Timeline: Earth and Life Science Maricar M. Paladan 11-HUMSSMaryjoy PaladanNo ratings yet
- Flora & Fiona: Earth's Eras and PeriodsDocument1 pageFlora & Fiona: Earth's Eras and PeriodsYseea OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Phanerozoic: Etymology of The Term Proterozoic-Phanerozoic Boundary Eras of The PhanerozoicDocument12 pagesPhanerozoic: Etymology of The Term Proterozoic-Phanerozoic Boundary Eras of The PhanerozoicTheodore PetreaNo ratings yet
- 02 Rise in The TriassicDocument41 pages02 Rise in The TriassicMadelyn MackintoshNo ratings yet
- Period: A Division of Geologic History With Spans of No More Than 100 Million YearsDocument5 pagesPeriod: A Division of Geologic History With Spans of No More Than 100 Million YearsStain KingNo ratings yet
- 02 Origin of PetroleumDocument46 pages02 Origin of PetroleumNuri Tri HerikaNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Activity SheetDocument5 pagesEarth Science Activity SheetRham Jay SaladoNo ratings yet
- Geologic-Time-Scale (1)Document2 pagesGeologic-Time-Scale (1)Jaymark HisonaNo ratings yet
- WS 3Document5 pagesWS 3SANDYNo ratings yet
- Geologic Time ScaleDocument4 pagesGeologic Time ScaleNika MatammuNo ratings yet
- GTSDocument14 pagesGTSMariel LolincoNo ratings yet
- Evolution, 4th EditionDocument1 pageEvolution, 4th EditionEbooks Cart100% (1)
- Evolutionary History, Molecular Systematics and Evolutionary Ecology of Canidae (Wang Et Al., 2006) PDFDocument18 pagesEvolutionary History, Molecular Systematics and Evolutionary Ecology of Canidae (Wang Et Al., 2006) PDFFrancisco J. OvalleNo ratings yet
- Ground Water2Document11 pagesGround Water2Geo CUKNo ratings yet
- Solar SystemDocument22 pagesSolar SystemGeo CUKNo ratings yet
- Aeration1 I: 1.8.4. Hydrolog1Cal CycleDocument2 pagesAeration1 I: 1.8.4. Hydrolog1Cal CycleGeo CUKNo ratings yet
- King's Model of Geomorphic EvolutionDocument5 pagesKing's Model of Geomorphic EvolutionGeo CUKNo ratings yet
- Inside This Chapter: Earthquakes Engineering Earthquake in IndiaDocument13 pagesInside This Chapter: Earthquakes Engineering Earthquake in IndiaGeo CUKNo ratings yet
- Origin of Indo-Gangetic PlainDocument7 pagesOrigin of Indo-Gangetic PlainGeo CUKNo ratings yet
- EarthDocument26 pagesEarthGeo CUKNo ratings yet
- Insights into Glacial Geology and MorphologyDocument12 pagesInsights into Glacial Geology and MorphologyGeo CUKNo ratings yet
- Origin of Himalayas (Extra Peninsula) 2Document3 pagesOrigin of Himalayas (Extra Peninsula) 2Geo CUKNo ratings yet
- Geology of the Himalayan Mountain RangeDocument5 pagesGeology of the Himalayan Mountain RangeGeo CUKNo ratings yet
- Karst LandformsDocument2 pagesKarst LandformsGeo CUKNo ratings yet
- Origin of Indo-Gangetic PlainsDocument1 pageOrigin of Indo-Gangetic PlainsGeo CUKNo ratings yet
- Wind Shaped Landforms Under 40 CharactersDocument6 pagesWind Shaped Landforms Under 40 CharactersGeo CUKNo ratings yet
- Origin of Indo-Gangetic PlainsDocument1 pageOrigin of Indo-Gangetic PlainsGeo CUKNo ratings yet
- Morphometric Analysis of A Drainage Basin Using Geographical Information System: A Case StudyDocument6 pagesMorphometric Analysis of A Drainage Basin Using Geographical Information System: A Case StudyNugraha WijanarkoNo ratings yet
- Neotectonics 2Document4 pagesNeotectonics 2Geo CUKNo ratings yet
- NeotectonicsDocument4 pagesNeotectonicsGeo CUKNo ratings yet
- NeotectonicsDocument4 pagesNeotectonicsGeo CUKNo ratings yet
- Neotectonics 2Document4 pagesNeotectonics 2Geo CUKNo ratings yet
- Principle of CatastrophismDocument1 pagePrinciple of CatastrophismGeo CUKNo ratings yet
- Eon Era Period Epoch Life FormsDocument2 pagesEon Era Period Epoch Life FormsChristine Joy SulibNo ratings yet
- Earth's Geologic Time Scale: A Brief History of Life and EventsDocument20 pagesEarth's Geologic Time Scale: A Brief History of Life and EventsMaria Cielo Lucino100% (4)
- E Science Cenozoic EraDocument1 pageE Science Cenozoic EraDaphney JaralveNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument64 pagesReportTrần Minh HuyNo ratings yet
- Periods of The Paleozoic Era: Cambrian PeriodDocument8 pagesPeriods of The Paleozoic Era: Cambrian PeriodChinatsu HayashidaNo ratings yet
- Geology PDFDocument76 pagesGeology PDFducatiss900No ratings yet
- GenBio2 - Q3 Module 2 For Grade 12 MendelDocument16 pagesGenBio2 - Q3 Module 2 For Grade 12 MendelFranshua Esbra LibronNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science: Geological EventsDocument8 pagesEarth and Life Science: Geological EventsJoseffia MedranoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7 Major Divisions of Geologic Time (Including Index Fossil)Document7 pagesCHAPTER 7 Major Divisions of Geologic Time (Including Index Fossil)Julius MacaballugNo ratings yet
- International Chronostratigraphic Chart 2016Document1 pageInternational Chronostratigraphic Chart 2016Diego Ardila100% (1)
- NegOr Q3 GenBio2 SLKWeek2 v2 FINALDocument29 pagesNegOr Q3 GenBio2 SLKWeek2 v2 FINALmacgigaonlinestoreNo ratings yet
- Fossil of Permian Trilobites (001-110)Document32 pagesFossil of Permian Trilobites (001-110)williams100% (1)
- DemonstratingGeologicTime WithCards PDFDocument31 pagesDemonstratingGeologicTime WithCards PDFJESON SANTIAGONo ratings yet
- Development of The Planet EarthDocument14 pagesDevelopment of The Planet EarthHana CpnplnNo ratings yet
- Decorative Stones of AlbaniaDocument6 pagesDecorative Stones of AlbaniaPatricia BrownNo ratings yet
- Permian Basin Stratigraphic Column ComparisonDocument1 pagePermian Basin Stratigraphic Column ComparisonrafaelNo ratings yet
- Earth'S History and It'S Geologic Time ScaleDocument40 pagesEarth'S History and It'S Geologic Time ScaleNela RainNo ratings yet
- Mesozoic Era: Age of ReptilesDocument41 pagesMesozoic Era: Age of ReptilesMhel PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- Bio2 11 - 12 Q3 0301 PF FDDocument40 pagesBio2 11 - 12 Q3 0301 PF FDdanarturo18No ratings yet
- Guide to the Proterozoic EonDocument13 pagesGuide to the Proterozoic EonSofia AzoresNo ratings yet
- Geologic Time ScaleDocument8 pagesGeologic Time ScaleFran SidetteNo ratings yet
- Geologic Time Scale IndonesiaDocument1 pageGeologic Time Scale IndonesiasyariefiqbalNo ratings yet
- Geological-Time-Scale Grade 11 LessonDocument43 pagesGeological-Time-Scale Grade 11 LessonWilson CadienteNo ratings yet
- Mapa Geologico HuacaretaDocument1 pageMapa Geologico Huacaretavanesa100% (1)
- How The Planet Earth Evolved - 120114Document43 pagesHow The Planet Earth Evolved - 120114vrbatitangNo ratings yet
- Lesson 12: Geologic Time Scale: Relative and Absolute DatingDocument18 pagesLesson 12: Geologic Time Scale: Relative and Absolute DatingMargarita EcaldreNo ratings yet
- Stratigraphic Column For Gulf of Suez, Western Desert and Nile Delta, Egypt-M.M.badawyDocument1 pageStratigraphic Column For Gulf of Suez, Western Desert and Nile Delta, Egypt-M.M.badawyOmarMokhtarZayed100% (1)
- Compilation of Phanerozoic Sea-Level ChangeDocument3 pagesCompilation of Phanerozoic Sea-Level ChangeFrancisco JavierNo ratings yet
- Geological Eras-TableDocument1 pageGeological Eras-Tablemonika hronecováNo ratings yet
- Album ForaminiferaDocument12 pagesAlbum ForaminiferagilangNo ratings yet