Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GA2 M9 07 Present Continuous
Uploaded by
DeliaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
GA2 M9 07 Present Continuous
Uploaded by
DeliaCopyright:
Available Formats
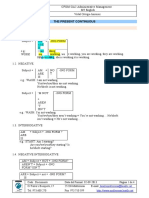
CFGM GA2 Administrative Management
M9 English
Vidal Ortega-Jiménez
THE PRESENT CONTINUOUS
1) FORM
1.1. AFFIRMATIVE
Subject + AM + -ING FORM
ARE
IS
e.g.: WORK: I am working.
You are working, we are working, you are working, they are working.
He is working, she is working it is working.
1.2. NEGATIVE
Subject + AM + NOT -ING FORM
ARE
IS
e.g.: WASH: I am not washing.
You/we/you/they are not washing.
He/she/it is not washing.
Subject + ‘M NOT + -ING FORM
AREN’T
ISN’T
e.g.: WASH: I’m not washing.
You/we/you/they aren’t washing = You’re not washing…
He/she/it isn’t washing = He’s not washing…
1.3. INTERROGATIVE
AM + Subject + -ING FORM ?
ARE
IS
e.g.: START: Am I starting?
Are you/we/you/they starting?
Is he/she/it starting?
1.4. NEGATIVE INTERROGATIVE
AM + Subject + NOT + -ING FORM?
AREN’T + Subject + -ING FORM?
ISN’T
ARE + Subject + not + -ING FORM?
IS
e.g.: PLAY: Am I not playing?
Aren’t you playing?
Codi: Documents Data del Format: 02-09-2013 Pàgina 1 de 4
C/ Ferrer i Busquets, 17 25230-Mollerussa E-mail: lasallemollerussa@lasalle.cat
Tel. 973 600 270 Fax 973 710 599 http://www.mollerussa.lasalle.cat
CFGM GA2 Administrative Management
M9 English
Vidal Ortega-Jiménez
2) FORM OF THE –ING FORM
-ING FORM = INFINITIVE + ING
e.g.: WORK: working.
Except:
a) Verbs ending in –E (not verbs ending in –EE).
-ING FORM = INFINITIVE (without E) + ING
e.g.: TAKE: taking.
but SEE: seeing, AGREE: agreeing.
b) Verbs ending in -IE
-ING FORM = INFINITIVE (without IE) + YING
e.g.: LIE: lying.
c) Verbs ending in one vowel + one consonant double the consonant
-ING FORM = INFINITIVE + consonant + ING
e.g.: STOP: stopping.
CLEAN: cleaning.
HELP: helping.
NB: Verbs with 2 or more syllables only double the consonant if it is an acute word (except
those ending in –L, which always double in British English):
e.g.: PREFER: preferring ≠ VISIT: visiting.
TRAVEL: (Br.E.) travelling, (Am.E.) traveling.
3) USE
3.1. Actions that are happening at the time of speaking (now, at the moment).
e.g.: Peter is going to the supermarket now.
3.2. Temporary (not permanent) actions which happening about this time, but not necessarily
now. They last for a short period.
e.g.: I live in Miralcamp, but I am living in Cambrils this summer.
I am taking lessons in driving this summer (but now I’m picking apples).
3.3. With always (or constantly, continually and forever), to express annoyance or
criticism. Irritating actions.
e.g.: He is always telling lies!
3.4. Future, planned actions. Definite = fixed arrangements in the near future. Diary. The time
of the action (not now) is stated or understood (we say the time adverbial: tomorrow, next
week, next Saturday, in one month’s time, in two weeks’ time, in a few days’ time…).
e.g.: I’m buying a car tomorrow.
I’m flying to London next week (It’s all arranged. I’ve already bought the tickets).
3.5. Changing situations.
e.g.: The world’s population is increasing very quickly.
Codi: Documents Data del Format: 02-09-2013 Pàgina 2 de 4
C/ Ferrer i Busquets, 17 25230-Mollerussa E-mail: lasallemollerussa@lasalle.cat
Tel. 973 600 270 Fax 973 710 599 http://www.mollerussa.lasalle.cat
CFGM GA2 Administrative Management
M9 English
Vidal Ortega-Jiménez
DIAGRAM OF THE USE:
1. Now, at the moment.
2. Short period.
3. Irritating actions (always).
4. Future, planned. Definite arrangements. Diary (time adverbial).
5. Changing situations.
4) NON-CONTINUOUS VERBS
There are some verbs that are not usually used in the continuous or progressive tenses, and
others that are not used in the progressive tenses in certain of their meanings. These verbs
are often called STATIVE VERBS (as opposed to dynamic verbs, which can normally have
continuous tenses). The most important ones are:
a) SENSATIONS (unwilling actions): feel, see, hear, smell (=give out a smell), taste (=have a
flavour), notice, observe (=notice), sound.
Exception: When feel is followed by an adjective indicating the subject’s emotions or physical
or mental condition (well/ill, hot/cold, tense/relaxed, happy/sad, nervous/confident,
anxious/relieved, angry/pleased), it can also be used in the Present Continuous.
e.g.: How do you feel? (= How are you feeling?).
I feel better now (= I’m feeling better now).
He feels much happier now (=He is feeling much happier now).
b) EMOTIONS: adore, appreciate (=value), care about (=feel interest), care for (=like), care to
(=want), desire, detest, dislike, fear, hate, like, loathe (=hate), love, mind, prefer, value, want,
wish.
c) MENTAL ACTIVITIES: agree, appreciate (=understand), believe, doubt, expect (=think),
feel (=think, have an opinion), feel sure, feel certain, forget, forgive, guess, imagine, know,
mean, perceive, realize, recall, recognize, recollect (=remember), refuse, remember, see
(=understand), see through somebody / something (=not be deceived by somebody /
something), suppose, think (=have an opinion), trust (=believe), understand.
d) INHERENT PROPERTIES (permanent qualities): appear (=seem), be, consist of, contain,
have, hold (=contain), look, measure (=have length, etc), seem, resemble, weigh (=have
weight).
e) POSSESSION: belong to, have, owe, own, possess.
Codi: Documents Data del Format: 02-09-2013 Pàgina 3 de 4
C/ Ferrer i Busquets, 17 25230-Mollerussa E-mail: lasallemollerussa@lasalle.cat
Tel. 973 600 270 Fax 973 710 599 http://www.mollerussa.lasalle.cat
CFGM GA2 Administrative Management
M9 English
Vidal Ortega-Jiménez
f) MODAL AUXILIARIES: can / could, may / might, must, need, will / would, shall / should,
ought to, dare, used to.
g) OTHER VERBS: appear (=seem), apply to (=refer to), astonish, concern, consist of, cost,
depend on, deserve, equal, fit, hold (=contain), impress, include, involve, keep (=continue),
lack, matter, need, please, remain, satisfy, seem, signify, surprise.
EXCEPTIONS:
However, some of these verbs can be used in continuous tenses when they express an
ACTIVITY or a WILLING (=deliberate) ACTION (rather than a state).
a) be (as the auxiliary of a passive tense).
e.g.: The house opposite our college is being pulled down.
b) be (=behave temporarily).
e.g.: Tom is being foolish (=Tom is acting or talking foolishly now).
c) expect (=await).
e.g.: I expect that he will not come.
I’m expecting a telephone call from France.
d) feel (=touch).
e.g.: Can you feel the bump on my head?
e) have (except when it expresses possession or obligation).
e.g.: Don’t disturb her, she’s having a bath.
I’m having a tooth taken out tomorrow.
We’re having breakfast now.
We’re having a wonderful time (=enjoying ourselves).
f) hear (=listen formally to).
e.g.: The court is hearing evidence this afternoon.
g) like (=enjoy).
e.g.: How are you liking this hot weather?
h) see (=meet somebody).
e.g.: I’m seeing John tonight (=meeting).
i) smell (=sniff at).
e.g.: I smell gas. There must be a leak somewhere.
Why are you smelling the fish? Has it gone bad?
j) think (when it doesn’t refer to an opinion).
e.g.: I think that you are right (=have an opinion).
Be quiet while I’m thinking (=considering).
He’s thinking of going to France.
Codi: Documents Data del Format: 02-09-2013 Pàgina 4 de 4
C/ Ferrer i Busquets, 17 25230-Mollerussa E-mail: lasallemollerussa@lasalle.cat
Tel. 973 600 270 Fax 973 710 599 http://www.mollerussa.lasalle.cat
You might also like
- English Grammar ExplanationsDocument13 pagesEnglish Grammar ExplanationsНикола Каранфиловски100% (3)
- Verbs With PrepositionsDocument6 pagesVerbs With PrepositionsLê Mai Huyền LinhNo ratings yet
- Run-On Sentences: ProblemDocument2 pagesRun-On Sentences: ProblemNorielee GlayzeNo ratings yet
- Exercises with Phrasal Verbs #2: For Intermediate Students of English: Exercises with Phrasal Verbs, #2From EverandExercises with Phrasal Verbs #2: For Intermediate Students of English: Exercises with Phrasal Verbs, #2Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (2)
- Learn SanskritDocument52 pagesLearn SanskritLuis Hurtado100% (7)
- First Conditional Review (Business Version)Document4 pagesFirst Conditional Review (Business Version)JaumeNo ratings yet
- UTN-FRA Inglés 3 Introducing Yourself-Present TensesDocument23 pagesUTN-FRA Inglés 3 Introducing Yourself-Present TensesMarcus Natael FernándezNo ratings yet
- 150 Really Useful English Phrases: Book 1.: 150 Really Useful English PhrasesFrom Everand150 Really Useful English Phrases: Book 1.: 150 Really Useful English PhrasesRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (6)
- The English Tenses - The Big FourDocument3 pagesThe English Tenses - The Big FourClaire Hart100% (4)
- Idiom Bahasa InggrisDocument4 pagesIdiom Bahasa InggrisWiki NasrullahNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH Verb Tenses (Table For ALL)Document5 pagesENGLISH Verb Tenses (Table For ALL)elasu85100% (1)
- GA2 M9 07 Present ContinuousDocument6 pagesGA2 M9 07 Present ContinuousDeliaNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 - Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument10 pagesUnit 6 - Gerunds and InfinitivesCarmen Marcos VicancosNo ratings yet
- 4 Tenses-HTD, HTTD, HTHT, QKDDocument6 pages4 Tenses-HTD, HTTD, HTHT, QKDNguyễn Ngọc Thanh ThanhNo ratings yet
- SV - English 2 - Unit 1 - Welcome To Our CompanyDocument59 pagesSV - English 2 - Unit 1 - Welcome To Our CompanyPhương UyênNo ratings yet
- SV - English 2 - Unit 1 - Welcome To Our CompanyDocument59 pagesSV - English 2 - Unit 1 - Welcome To Our CompanyPhương Uyên100% (2)
- Cultural Diversity: Unit 2Document9 pagesCultural Diversity: Unit 216Trương Thảo Nhi12A12No ratings yet
- Times EnglishDocument6 pagesTimes EnglishAngelina HarabagiuNo ratings yet
- Date of Teaching: 22/9/ 2020: Unit 1: The Generation Gap Listening A. ObjectivesDocument8 pagesDate of Teaching: 22/9/ 2020: Unit 1: The Generation Gap Listening A. Objectivesnhianh2512No ratings yet
- Tiểu Luận môn Ngữ pháp PRESENTDocument13 pagesTiểu Luận môn Ngữ pháp PRESENTKim Anh HàNo ratings yet
- Bai Tap Ngu Phap Tieng Anh 10 HK I - Nang Cao - GV Le Ngoc ThachDocument35 pagesBai Tap Ngu Phap Tieng Anh 10 HK I - Nang Cao - GV Le Ngoc ThachwindgiagiaNo ratings yet
- Dory TOEIC 3 - Grammar - TensesDocument20 pagesDory TOEIC 3 - Grammar - TensesHuyền Trinh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Makalah Grammar 2-BenerDocument10 pagesMakalah Grammar 2-Benermultimedia. smkicNo ratings yet
- Gerund and InfinitiveDocument4 pagesGerund and InfinitiveRaul CosminNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes LT1Document204 pagesLecture Notes LT1Nguyễn UyênNo ratings yet
- On Ngu Phap ToeicDocument31 pagesOn Ngu Phap ToeicanvanNo ratings yet
- Support Du Cours Master IT Anglais de La Technologie Et de L'information-1Document14 pagesSupport Du Cours Master IT Anglais de La Technologie Et de L'information-1Abdul Rachid DermanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Indicative TensesDocument8 pagesChapter 1 - Indicative TensesAndreea DascaluNo ratings yet
- Tenses CamilaDocument12 pagesTenses CamilaWanda FernandezNo ratings yet
- PRESENT TENSES Clasa A VII-aDocument2 pagesPRESENT TENSES Clasa A VII-aViviana BursucNo ratings yet
- Tugas Mandiri Mata Kuliah: Bahasa Inggris Teknik: DOSEN: Drs. Ir. Abdul Hakim Butar-Butar, MT, PH.DDocument9 pagesTugas Mandiri Mata Kuliah: Bahasa Inggris Teknik: DOSEN: Drs. Ir. Abdul Hakim Butar-Butar, MT, PH.Dawan anggaraNo ratings yet
- De Cuong - Anh 7Document5 pagesDe Cuong - Anh 7vânNo ratings yet
- Av -Tài Liệu Ôn Thi Ts Cao Học Không Chuyên.2018 - đợt 2Document42 pagesAv -Tài Liệu Ôn Thi Ts Cao Học Không Chuyên.2018 - đợt 2PhuongAnhNo ratings yet
- Đề Cương Ôn Tập Tiếng Anh 9Document48 pagesĐề Cương Ôn Tập Tiếng Anh 9akazumaNo ratings yet
- MAKALAHDocument12 pagesMAKALAHalputrimustikaNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan Ke 10 - Gerunds and InfinitiveDocument3 pagesPertemuan Ke 10 - Gerunds and InfinitiveImam GunawanNo ratings yet
- Sem 4 H - Auxiliaries and Primary VerbsDocument6 pagesSem 4 H - Auxiliaries and Primary VerbsAgnesNo ratings yet
- 2 - Anglais Technique PDFDocument13 pages2 - Anglais Technique PDFHalima BouamraNo ratings yet
- Words Ending in - y (Baby, Carry, Easy Etc.)Document5 pagesWords Ending in - y (Baby, Carry, Easy Etc.)Taras KhaletskyNo ratings yet
- SO THAT Vs SUCH THATDocument7 pagesSO THAT Vs SUCH THATSeydou Sy OBAMANo ratings yet
- Present SimpleDocument41 pagesPresent SimpledaniNo ratings yet
- Paper Group 4 (B Class)Document14 pagesPaper Group 4 (B Class)DellAriyantiNo ratings yet
- InglésDocument41 pagesInglésdaniNo ratings yet
- The Simple Present TenseDocument7 pagesThe Simple Present Tensecuongpham.31211025133No ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Time and TenseDocument30 pagesLecture 2 Time and TenseCosmin LemnaruNo ratings yet
- Present TenseDocument14 pagesPresent TensePramudya WardhaniNo ratings yet
- TheoryDocument52 pagesTheoryPaula Rodríguez Cambra100% (1)
- Present Continuous Team 1Document8 pagesPresent Continuous Team 1Dilan DiasNo ratings yet
- Simple Present and Present ContinuousDocument3 pagesSimple Present and Present ContinuousskniferlyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 - BasicDocument5 pagesLesson 8 - BasicMichael MccormickNo ratings yet
- Tense 1Document18 pagesTense 1shafiullahsh35No ratings yet
- The Quest For The Holy VerbDocument13 pagesThe Quest For The Holy VerbLotte WynantsNo ratings yet
- Inglês - AidaDocument10 pagesInglês - Aidamuchuaneosvaldo4No ratings yet
- Present Continous Tense - WordDocument2 pagesPresent Continous Tense - WordQuý Trần T.No ratings yet
- Present Simple Vs Present ContinuousDocument16 pagesPresent Simple Vs Present ContinuousNisrine Idrissi ChouahdiNo ratings yet
- On Tap Hoc Ki 1 Tieng Anh 11Document9 pagesOn Tap Hoc Ki 1 Tieng Anh 11Hang LeNo ratings yet
- Grammar GridDocument2 pagesGrammar Gride_marn2566No ratings yet
- Grammar Basic ReviewDocument10 pagesGrammar Basic ReviewemmagutizNo ratings yet
- ĐỀ CƯƠNG HK2 Môn Anh-Khối 10-NH 22-23Document25 pagesĐỀ CƯƠNG HK2 Môn Anh-Khối 10-NH 22-23원정초No ratings yet
- AF1 M6 06 1st Exam RevisionDocument5 pagesAF1 M6 06 1st Exam RevisionDeliaNo ratings yet
- AF1 M6 01b Numbers DiagramsDocument2 pagesAF1 M6 01b Numbers DiagramsDeliaNo ratings yet
- AF1 M6 02 Book 1Document6 pagesAF1 M6 02 Book 1DeliaNo ratings yet
- AF1 M6 01 NumbersDocument8 pagesAF1 M6 01 NumbersDeliaNo ratings yet
- AF1 M6 39 6th Exam RevisionDocument6 pagesAF1 M6 39 6th Exam RevisionDeliaNo ratings yet
- Para Examen 08 - 02 - 23Document1 pagePara Examen 08 - 02 - 23DeliaNo ratings yet
- Task 04Document2 pagesTask 04DeliaNo ratings yet
- Adjective PhrasesDocument5 pagesAdjective PhrasesAFRA PAULNo ratings yet
- Geschlecht Der Substantive Theorie: Noun Gender Der Mann Die Frau Das KindDocument4 pagesGeschlecht Der Substantive Theorie: Noun Gender Der Mann Die Frau Das Kindl1624242No ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: French For Examination From 2020Document24 pagesCambridge IGCSE: French For Examination From 2020Kirthik MathanNo ratings yet
- Teaching The English Modal Verbs in School Ina SurujiuDocument14 pagesTeaching The English Modal Verbs in School Ina SurujiuValentinaNo ratings yet
- Prova Mensal 3º Ano ADocument2 pagesProva Mensal 3º Ano AJane Cristina da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Bottom Up ParsingDocument36 pagesBottom Up Parsingparoo7kNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 Topic 4 Parts of Speech NewDocument2 pagesAssignment 4 Topic 4 Parts of Speech Newayu nilawatiNo ratings yet
- Sentence Structure FinalDocument22 pagesSentence Structure FinalBlacknight GamingNo ratings yet
- Nepal Army Officer Cadet English Exam QuestionDocument6 pagesNepal Army Officer Cadet English Exam QuestionBISHAL CHHETRI100% (1)
- Unit 2Document86 pagesUnit 2abcd efghNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5Document2 pagesAssignment 5Ahlam okashNo ratings yet
- Unit 10 Propositions and IllocutionsDocument3 pagesUnit 10 Propositions and IllocutionsAlif PramonoNo ratings yet
- Clause Types (TSLB3013 Linguistics)Document6 pagesClause Types (TSLB3013 Linguistics)LookAtTheMan 2002No ratings yet
- TLE-Industrial Arts 4 Quarter Week 1Document3 pagesTLE-Industrial Arts 4 Quarter Week 1Bea Claresse100% (1)
- Ingles 5 Phrasal Verbs Units-1-2Document8 pagesIngles 5 Phrasal Verbs Units-1-2Eli GonzálezNo ratings yet
- XXXXXXXXXX 4444444444444444Document8 pagesXXXXXXXXXX 4444444444444444kiszkaNo ratings yet
- A. Complete The Following Sentences Using The Correct Form of The Past Progressive Tense of The Verbs ProvidedDocument2 pagesA. Complete The Following Sentences Using The Correct Form of The Past Progressive Tense of The Verbs ProvidedJafet Ambriz DiazNo ratings yet
- Past Continuous and Past SimpleDocument1 pagePast Continuous and Past SimpleEnemias Perez AlarconNo ratings yet
- Upssc PDFDocument71 pagesUpssc PDFCp singhNo ratings yet
- Semana 4 PDFDocument19 pagesSemana 4 PDFLuis mauricioNo ratings yet
- Adjective Order NADocument2 pagesAdjective Order NAarcoro9783No ratings yet
- Textual Grammar STD 10thDocument2 pagesTextual Grammar STD 10thVipul Vaibhav MahajanNo ratings yet
- Books2 Guardada en Papa PitufoDocument58 pagesBooks2 Guardada en Papa PitufoGerman ReyesNo ratings yet
- So Such ThatDocument3 pagesSo Such Thatagus nurNo ratings yet
- Syl Lab Us Roberto 2Document9 pagesSyl Lab Us Roberto 2Javier Elvira MathezNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Will and Will BeDocument6 pagesDifference Between Will and Will BeJose PerezNo ratings yet