Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ata 47 Obiggs-L1
Uploaded by
svyat_kOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ata 47 Obiggs-L1
Uploaded by
svyat_kCopyright:
Available Formats
SJI TRAINING CENTER
ATA 47
OBIGGS
SJ100 - GENERAL FAMILIARIZATION ATA 47 ONBOARD INERTING SYSTEM
Technical Training Manual
SJI TRAINING CENTER
THIS DOCUMENT MUST BE USED FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY
UNDER NO CIRCUMSTANCES SHOULD THIS DOCUMENT BE USED AS A REFERENCE
IT WILL NOT BE UPDATED
SJ100 - GENERAL FAMILIARIZATION ATA 47 ONBOARD INERTING SYSTEM
Technical Training Manual 2
SJI TRAINING CENTER
REVISION 2.0 (Jan 2011)
ATA 47 - OnBoard Inert Gas Generating System (OBIGGS)
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SUBJECT PAGE
General 4
NEA Generating System 6
NEA Distribution 8
Components 10
SJ100 - GENERAL FAMILIARIZATION ATA 47 ONBOARD INERTING SYSTEM
Technical Training Manual 3
SJI TRAINING CENTER
ONBOARD INERT GAS GENERATING SYSTEM (OBIGGS)
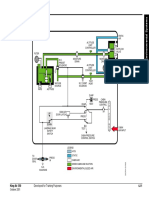
GENERAL OBIGGS SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE
The OBIGGS provides protection against fuel tank fire and explosion The RRJ OBIGGS is comprised of two subsystems which work
by creating inert (non flammable) conditions within the ullage (air) together to convert high temperature engine bleed air, derived from
space of the fuel tanks. This is achieved by using a chemically the Integrated Air Management System (IAMS), to a relatively cool,
unreactive gas (Nitrogen) to displace the oxygen in the tank ullages Nitrogen Enriched Air (NEA) gas stream for delivery to and
such that the average oxygen concentration by volume per tank is distribution within the fuel tank ullage volume.
12% or less.
The OBIGGS architecture consists of the NEA Generation System
The inerting system supplies and maintains a layer of Nitrogen and NEA Distribution System. OBIGGS supply air is tapped from the
Enriched Air (NEA) in each of the tanks ullage spaces. Nitrogen is Integrated Air Management System (IAMS) after it has been pre-
suitable for inerting since it does not support the hydrocarbon cooled.
combustion reaction, is non-reactive with the materials used in fuel
system components and equipment and can be obtained from air.
The OBIGGS is based on a continuous flow principle. This type of
system produces NEA from conditioned engine bleed air by gas
separation and distributes it into the fuel tank ullage spaces. Engine
bleed air is cooled and filtered by the OBIGGS and sent to the Air
Separation Module (ASM). The ASM separates oxygen from the
bleed air, thus creating Nitrogen Enriched Air (NEA).
SJ100 - GENERAL FAMILIARIZATION ATA 47 ONBOARD INERTING SYSTEM
Technical Training Manual 4
SJI TRAINING CENTER
ONBOARD INERT GAS GENERATING SYSTEM (OBIGGS)
SJ100 - GENERAL FAMILIARIZATION ATA 47 ONBOARD INERTING SYSTEM
Technical Training Manual 5
SJI TRAINING CENTER
ONBOARD INERT GAS GENERATING SYSTEM (OBIGGS)
NEA GENERATION SYSTEM COMPONENTS NEA GENERATION SYSTEM OPERATION
The main system components of the NEA generation System are the The OBIGGS remains on and in the low-flow mode during takeoff,
Electronic Control Unit (ECU) and the Air Separation Module (ASM). climb and cruise. During this time period the OBIGGS is filling the
The controller provides for automatic control of the OBIGGS without increasing ullage space created by fuel consumption, diluting the
pilot interaction. Primary ECU functions include: oxygen evolving from fuel, and driving the ullage oxygen
► monitoring LRU health concentration to its lowest possible level at the end of cruise.
► providing ASM temperature control
► switching from low to high flow during descent In cruise, the OBIGGS will enter a health monitoring interval. The
► over-temperature and over-pressure protection. health monitoring interval is performed each flight when the OBIGGS
is fully warm and system operating parameters are stable. ASM’s
require at least 20 minutes to warm up which takes place during the
climb phase.
After cruise the airplane begins descent and the OBIGGS is switched
to the high flow mode. The high-flow mode maximizes the volume of
NEA entering the fuel tank, which curbs the amount of vent inflow.
During descent the ambient pressure continuously increases, which
causes the vent pressure to increase and outside air to enter the fuel
tanks. Increasing the NEA flow rate reduces the amount of outside air
entering the tank and also increases the NEA oxygen concentration.
The goal is to optimize the balance between the NEA oxygen
concentration, NEA flow rate, and the amount of outside air entering
the tank so that at the end of descent, the average fuel tank oxygen
concentration is near or below 12%.
SJ100 - GENERAL FAMILIARIZATION ATA 47 ONBOARD INERTING SYSTEM
Technical Training Manual 6
SJI TRAINING CENTER
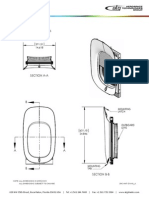
AIR SEPARATION MODULE
NEA GENERATION SYSTEM
SJ100 - GENERAL FAMILIARIZATION ATA 47 ONBOARD INERTING SYSTEM
Technical Training Manual 7
SJI TRAINING CENTER
ONBOARD INERT GAS GENERATING SYSTEM (OBIGGS)
NEA (NITROGEN ENRICHED AIR) DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM
This NEA is distributed into the ullage spaces of the fuel tank through
transport tubing routed from the NEA Generation System to the
discharge points within the fuel tanks. The system is protected from
fuel ingress by individual check valves as well as a common check
valve in the main NEA supply line.
SJ100 - GENERAL FAMILIARIZATION ATA 47 ONBOARD INERTING SYSTEM
Technical Training Manual 8
SJI TRAINING CENTER
NEA DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM
SJ100 - GENERAL FAMILIARIZATION ATA 47 ONBOARD INERTING SYSTEM
Technical Training Manual 9
SJI TRAINING CENTER
ONBOARD INERT GAS GENERATING SYSTEM (OBIGGS)
COMPONENT LOCATION
The NEA generation components are located in the RH forward
wing-to-body fairing and the Electronic Control Unit (ECU) is located
in the middle avionics rack.
SJ100 - GENERAL FAMILIARIZATION ATA 47 ONBOARD INERTING SYSTEM
Technical Training Manual 10
SJI TRAINING CENTER
ELECTRONIC
CONTROL UNIT
OBIGGS COMPONENTS
SJ100 - GENERAL FAMILIARIZATION ATA 47 ONBOARD INERTING SYSTEM
Technical Training Manual 11
SJI TRAINING CENTER
THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK
SJ100 - GENERAL FAMILIARIZATION ATA 47 ONBOARD INERTING SYSTEM
Technical Training Manual 12
You might also like
- The Crash of an Alaska Airlines Boeing 727 Juneau, Alaska September 4, 1971From EverandThe Crash of an Alaska Airlines Boeing 727 Juneau, Alaska September 4, 1971No ratings yet
- 47 Fuel InertingDocument28 pages47 Fuel InertingTamara AntonyNo ratings yet
- Ewis Job CardDocument4 pagesEwis Job CardNikolaos KechagiasNo ratings yet
- 35 OxygenDocument142 pages35 OxygenduythienddtNo ratings yet
- Ac A380 20161201Document326 pagesAc A380 20161201Javier GleiserNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Systems No. 1 or No. 2 - Fill With Hydraulic FluidDocument12 pagesHydraulic Systems No. 1 or No. 2 - Fill With Hydraulic FluidaliNo ratings yet
- 28 FuelDocument19 pages28 Fueleng.mohamedmansour84No ratings yet
- As332L Bristow Tiger: Technical Notes For AircrewDocument22 pagesAs332L Bristow Tiger: Technical Notes For AircrewrobbertmdNo ratings yet
- Windshield Protection PDFDocument3 pagesWindshield Protection PDFJasonNo ratings yet
- Cas 67A Tcas Ii System Installation ManualDocument6 pagesCas 67A Tcas Ii System Installation ManualАлександр КорякинNo ratings yet
- A320 Family Fuel SystemDocument304 pagesA320 Family Fuel SystemBahador100% (1)
- 71 IAE Trouble ShootDocument22 pages71 IAE Trouble ShootMarc Covas MartorellNo ratings yet
- Form-Fit Ads-B Compliant Mode S Transponders: The Nextgen TransponderDocument2 pagesForm-Fit Ads-B Compliant Mode S Transponders: The Nextgen Transponderjoel alvaradoNo ratings yet
- 71-00-00-710-004-B - Engine Manual StartDocument9 pages71-00-00-710-004-B - Engine Manual StartEder LucianoNo ratings yet
- LEAP Weekly Issue 01 Rev 03Document22 pagesLEAP Weekly Issue 01 Rev 03Ankit KaushikNo ratings yet
- Air Conditionning System: CB - List - 330 200.xls Sheet1Document29 pagesAir Conditionning System: CB - List - 330 200.xls Sheet1Sergio SouzaNo ratings yet
- Bro ATR42MP 2012 PDFDocument16 pagesBro ATR42MP 2012 PDFfranz_zero2No ratings yet
- HandbookOnRTIAct2005 - Latest (Sep 18) PDFDocument93 pagesHandbookOnRTIAct2005 - Latest (Sep 18) PDFPsycho Soldier100% (1)
- 24 Electrical PowerDocument164 pages24 Electrical PowermarkNo ratings yet
- EASA TCDS A.110 Airbus A380Document17 pagesEASA TCDS A.110 Airbus A380kiecard33% (3)
- NFF Units Safety RiskDocument6 pagesNFF Units Safety RiskpannNo ratings yet
- Obogs System Training: Life SupportDocument30 pagesObogs System Training: Life SupportKim GomezNo ratings yet
- Exterior Inspection B737-800Document14 pagesExterior Inspection B737-800Me KeenNo ratings yet
- Checklist EC145 PDFDocument276 pagesChecklist EC145 PDFBruno BertozziNo ratings yet
- Section 12 - Lighting PDFDocument10 pagesSection 12 - Lighting PDFrobbertmdNo ratings yet
- Mega Ac25Document93 pagesMega Ac25Nariaki SumiNo ratings yet
- Aeroflot A318 - 319 - 320 - 321 FCOM Vol3 - Flight Operations (Rev 39) PDFDocument1,348 pagesAeroflot A318 - 319 - 320 - 321 FCOM Vol3 - Flight Operations (Rev 39) PDFAli GardeziNo ratings yet
- B737 Hydraulic Systems OverviewDocument32 pagesB737 Hydraulic Systems OverviewzeblaouarNo ratings yet
- Afm Embraer 170 General 1385 003 Faa Section01Document12 pagesAfm Embraer 170 General 1385 003 Faa Section01Lg123_4No ratings yet
- Easa TCDS A.084 - Atr - 42 - Atr - 72 03 17102012Document35 pagesEasa TCDS A.084 - Atr - 42 - Atr - 72 03 17102012mpusNo ratings yet
- Afm Atr 76 - RN 15 - Feb 12Document406 pagesAfm Atr 76 - RN 15 - Feb 12Andrei NecuţăNo ratings yet
- A318/A319/A320/A321: Service BulletinDocument22 pagesA318/A319/A320/A321: Service BulletinPradeep K sNo ratings yet
- Thales Ife Amm 44-27-26-Rev. 02Document756 pagesThales Ife Amm 44-27-26-Rev. 02joartus100% (1)
- Type Ratings FaaDocument14 pagesType Ratings FaaricardotorresNo ratings yet
- BT139394EDocument23 pagesBT139394Ehin wongyai100% (1)
- Airbus - A320 Engine StartDocument15 pagesAirbus - A320 Engine StartNutapol thungpaoNo ratings yet
- Vapor Cycle System (VCS) : Effectivity:AllDocument16 pagesVapor Cycle System (VCS) : Effectivity:AllclebersjcNo ratings yet
- Cl600 Easa-Mmel Rev01 2Document198 pagesCl600 Easa-Mmel Rev01 2Philippe TORNENo ratings yet
- DASSAULT FALCON 000DX-EX-Hydraulic System PDFDocument36 pagesDASSAULT FALCON 000DX-EX-Hydraulic System PDFjjaavvmmNo ratings yet
- ATA 5-12 Ground Handling & ServicingDocument70 pagesATA 5-12 Ground Handling & Servicingامیر شعاعیNo ratings yet
- Faa A320 TcdsDocument90 pagesFaa A320 Tcdsuanaa hyyNo ratings yet
- A318/A319/A320/A321: Service BulletinDocument58 pagesA318/A319/A320/A321: Service BulletinPradeep K sNo ratings yet
- 3510A Model 377 Series PN 3510A377 CMM 25-25-69 (3510A377) Rev 3Document357 pages3510A Model 377 Series PN 3510A377 CMM 25-25-69 (3510A377) Rev 3mikeNo ratings yet
- WMKK-Charts Related To KL International Sepang Airport PDFDocument69 pagesWMKK-Charts Related To KL International Sepang Airport PDFFiqri ProductionNo ratings yet
- Ata 52 DoorsDocument176 pagesAta 52 DoorsPardNo ratings yet
- Conectores Amphenol PDFDocument38 pagesConectores Amphenol PDFGABRIEL ROJOSNo ratings yet
- Engine Report - AcmsDocument367 pagesEngine Report - AcmsakeelNo ratings yet
- BOEING 747-8i: Cabin Window ShadesDocument2 pagesBOEING 747-8i: Cabin Window ShadesGlenn MillerNo ratings yet
- A320 Modification ListDocument1,336 pagesA320 Modification ListAhsanNo ratings yet
- Kulite Pressure Transducer HandbookDocument76 pagesKulite Pressure Transducer Handbookpmud123No ratings yet
- FOIM 2019 03 Engine-Cool-down-time Issue 2Document8 pagesFOIM 2019 03 Engine-Cool-down-time Issue 2ralfair16No ratings yet
- Procedure For DFDR DataDocument1 pageProcedure For DFDR DataAbhishek Roy100% (1)
- Wiring Instructions For Series It Itb and Its ConnectorsDocument52 pagesWiring Instructions For Series It Itb and Its ConnectorsРоман ДяченкоNo ratings yet
- Environmental Systems PressurizationDocument14 pagesEnvironmental Systems PressurizationJuan Garcia SanchezNo ratings yet
- Ea 767 31-002 Eicas Upgrade Ops6 PDFDocument5 pagesEa 767 31-002 Eicas Upgrade Ops6 PDFjuanf490No ratings yet
- Maint BriefingDocument4 pagesMaint BriefingWellington RamosNo ratings yet
- A320 LG ServicingDocument59 pagesA320 LG ServicingSergej RepenkovNo ratings yet
- ASB 412-14-160B Page 1 of 7 Export Classification C, ECCN EAR99 Approved For Public ReleaseDocument7 pagesASB 412-14-160B Page 1 of 7 Export Classification C, ECCN EAR99 Approved For Public Releasesebastian eduardoNo ratings yet
- Naca-Rm-E51l06 Facilities and Methods Used in Full Scale Airplane Crash Fire InvestigationDocument61 pagesNaca-Rm-E51l06 Facilities and Methods Used in Full Scale Airplane Crash Fire Investigationsvyat_kNo ratings yet
- Naca-Tn-258 A Warning Concerning The Take Off With Heavy LoadDocument9 pagesNaca-Tn-258 A Warning Concerning The Take Off With Heavy Loadsvyat_kNo ratings yet
- DSTO-TR-2850 Guide On The Effective Block Approach For The Fatigue Life Assessment of Metallic StructuresDocument89 pagesDSTO-TR-2850 Guide On The Effective Block Approach For The Fatigue Life Assessment of Metallic Structuressvyat_kNo ratings yet
- Naca Report 1347Document28 pagesNaca Report 1347svyat_kNo ratings yet
- Naca-Report-1133 Mechanism of Start and Development of Aircraft Crash FiresDocument53 pagesNaca-Report-1133 Mechanism of Start and Development of Aircraft Crash Firessvyat_kNo ratings yet
- 3 00 - 09.08.10 - QRH 95004Document322 pages3 00 - 09.08.10 - QRH 95004svyat_kNo ratings yet
- ATA 22 AutoFlight-L1Document28 pagesATA 22 AutoFlight-L1svyat_kNo ratings yet
- Ata 49 Auxiliary Power Unit (Apu)Document34 pagesAta 49 Auxiliary Power Unit (Apu)svyat_k100% (1)
- DSTO-TN-0178 Residual Stress Measurements and Boeing Wedge Durability Data For The Proposed 470 Bulkhead Bonded RepairDocument33 pagesDSTO-TN-0178 Residual Stress Measurements and Boeing Wedge Durability Data For The Proposed 470 Bulkhead Bonded Repairsvyat_kNo ratings yet
- AGATE-WP3.3-033051-095 B-Basis Design Allowables For Epoxy Based Prepreg - Newport Carbon Plain Weave Fabric 3K70P-NB321Document93 pagesAGATE-WP3.3-033051-095 B-Basis Design Allowables For Epoxy Based Prepreg - Newport Carbon Plain Weave Fabric 3K70P-NB321svyat_kNo ratings yet
- ATA 00 General-L1Document63 pagesATA 00 General-L1svyat_kNo ratings yet
- SJI Air Conditioning Training ManualDocument42 pagesSJI Air Conditioning Training Manualsvyat_kNo ratings yet
- AGATE-C-GEN-3451-2 Full Scale Starship Drop TestDocument29 pagesAGATE-C-GEN-3451-2 Full Scale Starship Drop Testsvyat_kNo ratings yet
- Naca-Rm-A7h29 High Speed Aerodynamic Characteristics of Horn and Overhang Balances On A Full Scale ElevatorDocument84 pagesNaca-Rm-A7h29 High Speed Aerodynamic Characteristics of Horn and Overhang Balances On A Full Scale Elevatorsvyat_kNo ratings yet
- AGATE-WP3.3-033051-096 B-Basis Design Allowables For Epoxy Based Prepreg - Newport Graphite Unitape G150 NASS-NCT321Document116 pagesAGATE-WP3.3-033051-096 B-Basis Design Allowables For Epoxy Based Prepreg - Newport Graphite Unitape G150 NASS-NCT321svyat_kNo ratings yet
- AGARD-R-797 An Assessment of Fatique Damage and Crack Growth Prediction TechniquesDocument292 pagesAGARD-R-797 An Assessment of Fatique Damage and Crack Growth Prediction Techniquessvyat_kNo ratings yet
- AGATE-WP3.3-033048-117 B-Basis Design Allowables For 2X2 Biaxially Braided RTM Composite Material Systems - Carbon Braid AS4-6K-GP-PR520Document241 pagesAGATE-WP3.3-033048-117 B-Basis Design Allowables For 2X2 Biaxially Braided RTM Composite Material Systems - Carbon Braid AS4-6K-GP-PR520svyat_kNo ratings yet
- DSTO-TN-0178 Residual Stress Measurements and Boeing Wedge Durability Data For The Proposed 470 Bulkhead Bonded RepairDocument33 pagesDSTO-TN-0178 Residual Stress Measurements and Boeing Wedge Durability Data For The Proposed 470 Bulkhead Bonded Repairsvyat_kNo ratings yet
- AGATE-AP3.1-031200-130 Guide For Low Cost Design and Manufacturing of Composite General Aviation AircraftDocument103 pagesAGATE-AP3.1-031200-130 Guide For Low Cost Design and Manufacturing of Composite General Aviation Aircraftsvyat_kNo ratings yet
- ARC-CP-340 Full Scale Measurement of Impact Loads On A Large Flying Boat (Sunderland Mk. 5) Part III - Data For Impacts On Main StepDocument43 pagesARC-CP-340 Full Scale Measurement of Impact Loads On A Large Flying Boat (Sunderland Mk. 5) Part III - Data For Impacts On Main Stepsvyat_kNo ratings yet
- SSJ-100 Ata 50 Structures GeneralDocument68 pagesSSJ-100 Ata 50 Structures Generalsvyat_k100% (3)
- POF 303 ILI Data Feedback Form - Nov 2021Document4 pagesPOF 303 ILI Data Feedback Form - Nov 2021Satya RaoNo ratings yet
- Al Sadd Complex Fire Strategy Report Rev 1Document16 pagesAl Sadd Complex Fire Strategy Report Rev 1sameh100% (2)
- Eastman Kodak Case QuestionsDocument2 pagesEastman Kodak Case QuestionsPravet Singh KanwarNo ratings yet
- Course Title Instructor: Managing Customer Experience and Relationships: A Strategic FrameworkDocument11 pagesCourse Title Instructor: Managing Customer Experience and Relationships: A Strategic FrameworkAyyaz ReshiNo ratings yet
- Thales FMS 220 User GuideDocument346 pagesThales FMS 220 User GuideArefin FerdousNo ratings yet
- The Future of Machine Learning: Supervised, Unsupervised and Reinforcement LearningDocument5 pagesThe Future of Machine Learning: Supervised, Unsupervised and Reinforcement LearningResearch ParkNo ratings yet
- Control PlaneDocument42 pagesControl PlanemakislaskosNo ratings yet
- We Should Not Expect Our Online Activities To Remain PrivateDocument10 pagesWe Should Not Expect Our Online Activities To Remain PrivateDauz YusufNo ratings yet
- Test Report For Asynchronous Motors Plant Rembang Customer ABB Indonesia Customer Ref 1555613Document17 pagesTest Report For Asynchronous Motors Plant Rembang Customer ABB Indonesia Customer Ref 1555613Jauhary HarrysNo ratings yet
- Bose Lifestyle 28 Repair - Schematics PDFDocument32 pagesBose Lifestyle 28 Repair - Schematics PDFAurelio Machado75% (4)
- MRAM-Merchandise Return Authorization Messages - 6.8.-2021 - SPDocument3 pagesMRAM-Merchandise Return Authorization Messages - 6.8.-2021 - SPЗоран ЂурићNo ratings yet
- Web301 - Prelim LessonDocument85 pagesWeb301 - Prelim LessonJessabel DigaoNo ratings yet
- SAP Closing Cockpit Asdddddasd2132Document12 pagesSAP Closing Cockpit Asdddddasd2132JacekNo ratings yet
- 3406 Performance Specification PDFDocument2 pages3406 Performance Specification PDFaliNo ratings yet
- Waze Presentation at TechAviv Founders ClubDocument34 pagesWaze Presentation at TechAviv Founders ClubYaron SamidNo ratings yet
- Laser Driver 06DLD203A ManualDocument44 pagesLaser Driver 06DLD203A Manualgoat100% (1)
- Jenbacher Type-6 EngineDocument24 pagesJenbacher Type-6 EngineAb Hannan chowdhury100% (1)
- VTU B.E CSE Sem 8 Software Testing NotesDocument26 pagesVTU B.E CSE Sem 8 Software Testing NotesAravind RossiNo ratings yet
- Nemo File Format 2.30Document532 pagesNemo File Format 2.30bclarke113No ratings yet
- SUP 3033 - Assignment - 1Document5 pagesSUP 3033 - Assignment - 1Sachin LoboNo ratings yet
- Asterisk Installation On Centos 5Document3 pagesAsterisk Installation On Centos 5kumargupt117No ratings yet
- Device Expert Credentials TutorialDocument12 pagesDevice Expert Credentials TutorialMuhammadNurIqbalNo ratings yet
- CRMDocument5 pagesCRMLieanne EspinosaNo ratings yet
- CCTV CataloqueDocument48 pagesCCTV CataloquesujiNo ratings yet
- PVC Coated Conduit ProtectionDocument1 pagePVC Coated Conduit ProtectionXinoko MosqueiraNo ratings yet
- Internet Linguistics David CrystalDocument25 pagesInternet Linguistics David CrystalTamara Petković67% (3)
- Updated Price ListDocument2 pagesUpdated Price ListbatterymedicsNo ratings yet
- Printer Drivers: Installation GuideDocument44 pagesPrinter Drivers: Installation GuideHONEYWELL VIETNAMNo ratings yet
- Supply & Installation of The Security Services For The Lta Karavi Weighbridge Station at Karavi, Ba, Fiji IslandsDocument32 pagesSupply & Installation of The Security Services For The Lta Karavi Weighbridge Station at Karavi, Ba, Fiji IslandsThaungMyintNo ratings yet
- Convolutional Neural Networks: CMSC 35246: Deep LearningDocument166 pagesConvolutional Neural Networks: CMSC 35246: Deep LearningDiego AntonioNo ratings yet