Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anatomy & Physiology: The Digestive System
Uploaded by
Eliezer Nuenay0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views1 pageOriginal Title
Digestive System
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views1 pageAnatomy & Physiology: The Digestive System
Uploaded by
Eliezer NuenayCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Anatomy & Physiology:
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
The digestive system breaks food down into proteins: synthesize DNA, transport materials, provide fibrous
structure, produce enzymes
usable components and expels waste.
rectum: organ located at the end of the large intestine where
solid waste is stored before excretion
Terms
saliva: fluid released in the mouth during mastication
accessory organs: provide additional functions to aid the
(chewing) with enzymes that begin breaking down food
digestive tract in the digestion and absorption of nutrients
small intestine: organ where the majority of digestion and
anus: opening of the rectum through which solid waste leaves
absorption occurs
the body
villi: structures with multiple folds that line the small intestine,
bile: substance that breaks down fat macronutrients
allowing maximum absorption of nutrients
bolus: the mass of partially digested food as it travels through
the esophagus into the stomach
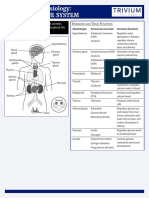
Parts of the Digestive System
carbohydrates: provide energy to cells, form cell structures
chemical digestion: the alteration of food into different
substances Pharynx
chyme: the mixture of food and digestive juices that moves
from the stomach to the small intestine
colon: the longest part of the intestine, where water is Mouth
reabsorbed
defecation: the excretion of solid waste through the anus Tongue
digestion: the process of diffusing nutrients digested from the
food throughout the body for use in cellular respiration and
energy production Esophagus
digestive tract: the central tube through which food travels
esophagus: transports food from the throat to the stomach Liver
extracellular digestion: ingesting food at the mouth and
excreting it at the anus Gallbladder
Stomach
gallbladder: stores and concentrates bile to break down fat
macronutrients
ingestion: the process of taking in food Large
large intestine: organ where remaining water and nutrients intestine
Small
are absorbed; compacts and stores remaining waste material
intestine
until excretion
lipids: provide long-term storage, provide energy to cells
liver: produces bile; detoxifies digested toxins; extracts Rectum
nutrients from blood before it moves to other parts of the body
Anus
mechanical digestion: the physical breaking down of food
pancreas: produces chemicals to decrease small intestine
acidity and to break down fats, proteins, and carbohydrates
peristalsis: muscular contractions that produce waves to move
food from one point to another
pharynx (throat): moves food from the mouth to the
esophagus during swallowing
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- ButterflyDocument13 pagesButterflyashisb444No ratings yet
- Edexcel Biology AS Level Unit 2 Sample NotesDocument4 pagesEdexcel Biology AS Level Unit 2 Sample NotesMariam AhmedNo ratings yet
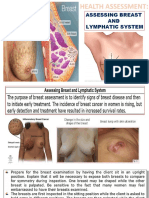
- Musculoskeletal System: Health AssessmentDocument43 pagesMusculoskeletal System: Health AssessmentEliezer Nuenay100% (1)
- Think Mink!: Mammalian Dissection With MinkDocument38 pagesThink Mink!: Mammalian Dissection With MinkMark Penticuff100% (1)
- As - Swine ProductionDocument8 pagesAs - Swine Productionlemuel d. antipordaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology (Chapter 17 - Nutrition, Metabolism, & Body Temperature Regulation)Document17 pagesAnatomy & Physiology (Chapter 17 - Nutrition, Metabolism, & Body Temperature Regulation)Eliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Ha-Assessing Breast and Lymphatic-NgoDocument29 pagesHa-Assessing Breast and Lymphatic-NgoEliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment OBEDocument12 pagesHealth Assessment OBEEliezer Nuenay100% (1)
- Anatomy & Physiology (Chapter 11 - Blood)Document22 pagesAnatomy & Physiology (Chapter 11 - Blood)Eliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Structure of A Flower and 6.2: Development of Pollen Grain and Embryo SacDocument36 pages6.1 Structure of A Flower and 6.2: Development of Pollen Grain and Embryo Sacwickedbiology101No ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology: The Immune SystemDocument1 pageAnatomy & Physiology: The Immune SystemEliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology: The Endocrine SystemDocument1 pageAnatomy & Physiology: The Endocrine SystemEliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology: The Muscular SystemDocument1 pageAnatomy & Physiology: The Muscular SystemEliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument1 pageCardiovascular SystemEliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology: The Nervous SystemDocument1 pageAnatomy & Physiology: The Nervous SystemEliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Lab Values Tips and TricksDocument2 pagesLab Values Tips and TricksEliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology (Chapter 18 - Urinary System)Document12 pagesAnatomy & Physiology (Chapter 18 - Urinary System)Eliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology (Chapter 13 - Blood Vessels)Document26 pagesAnatomy & Physiology (Chapter 13 - Blood Vessels)Eliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology (Chapter 14 - Lymphatic System)Document18 pagesAnatomy & Physiology (Chapter 14 - Lymphatic System)Eliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Research ArticleDocument32 pagesResearch ArticleEliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Definition of Terms EthicsDocument18 pagesDefinition of Terms EthicsEliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Intro 05-B Analysis UVDocument7 pagesIntro 05-B Analysis UVEliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Definition of Terms EthicsDocument18 pagesDefinition of Terms EthicsEliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Intro 05-A Analysis UVDocument7 pagesIntro 05-A Analysis UVEliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- What Is The Skeletal System?Document21 pagesWhat Is The Skeletal System?Ezekiel A. NavarroNo ratings yet
- 4-4-89-878 Distribucion TabanidaeDocument9 pages4-4-89-878 Distribucion TabanidaeASESORA DE PROYECTOS RT, CANo ratings yet
- Periodical Test Q2 Science 4 Melc BasedDocument7 pagesPeriodical Test Q2 Science 4 Melc BasedEM GinaNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Anatomy of Flowering Plants NotesDocument8 pagesClass 11 Anatomy of Flowering Plants NotesPriyansh PatelNo ratings yet
- ArtExaminingInterpreting HystologyDocument104 pagesArtExaminingInterpreting HystologyalmutazimNo ratings yet
- 1 Nature Scope of BiologyDocument15 pages1 Nature Scope of BiologyRAHUL SHARMANo ratings yet
- Science - Levels of OrganizationDocument4 pagesScience - Levels of OrganizationAlexNo ratings yet
- Lecture 16 Feb 19 Trematode-1Document29 pagesLecture 16 Feb 19 Trematode-1Rajkumar MandalNo ratings yet
- Study of Animal Type CockroachDocument34 pagesStudy of Animal Type CockroachDivya ShivkumarNo ratings yet
- Pex 02 01 PDFDocument7 pagesPex 02 01 PDFbbpcutieNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise4 Tissues Hb-1 GalangDocument4 pagesLab Exercise4 Tissues Hb-1 GalangLihza May Alliah GalangNo ratings yet
- National University: Syllabus Department of PsychologyDocument11 pagesNational University: Syllabus Department of PsychologyMd Rafiul IslamNo ratings yet
- Origin and Development of Organ Systems NotesDocument4 pagesOrigin and Development of Organ Systems NotesimnasNo ratings yet
- Reproductive HealthDocument21 pagesReproductive HealthRosalie Valdez EspirituNo ratings yet
- 9 Behaviour & Home Range PDFDocument22 pages9 Behaviour & Home Range PDFaufaaNo ratings yet
- Molluscan Studies: Journal ofDocument19 pagesMolluscan Studies: Journal ofWidi SetyogatiNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Classifying Plants and AnimalsDocument6 pagesClass 7 Classifying Plants and AnimalsAreeb SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- ZOO 211 - A ClassDocument11 pagesZOO 211 - A Classmusanafisat593No ratings yet
- Hsslive Xi Zoology Rev Test 2 Key by Zta Malappuram - 230212 - 105554Document4 pagesHsslive Xi Zoology Rev Test 2 Key by Zta Malappuram - 230212 - 105554എസ്സാർപി ഊരുചുറ്റൽ തുടരുന്നുNo ratings yet
- 31.2 The Central Nervous SystemDocument28 pages31.2 The Central Nervous Systemmoniaguayo980% (1)
- Orthoptera, DictyopteraDocument35 pagesOrthoptera, DictyopterapurbaliNo ratings yet
- NullDocument22 pagesNullSHANZA KHANUMNo ratings yet
- Phylum Chordata FishesDocument92 pagesPhylum Chordata FishesSoumen ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- English Task About Description of AnimalsDocument6 pagesEnglish Task About Description of AnimalsIkhwan IkhsanNo ratings yet
- Reptiles - Snakes - Python Fact SheetDocument2 pagesReptiles - Snakes - Python Fact SheetUwaisNo ratings yet