Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anatomy & Physiology: The Muscular System
Uploaded by
Eliezer Nuenay0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views1 pageThe muscular system consists of three types of muscles that work together to move the body. Skeletal muscles are voluntarily controlled and attach to bones to allow movement. They are made up of bundles of fibers called myofibrils containing proteins actin and myosin that slide past each other to contract the muscle. Cardiac muscles are only found in the heart and smooth muscles line organs and blood vessels. Some major skeletal muscles include the trapezius, deltoids, pectorals, and quadriceps that work with bones to perform tasks like lifting arms and legs.
Original Description:
Original Title
Muscular System
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe muscular system consists of three types of muscles that work together to move the body. Skeletal muscles are voluntarily controlled and attach to bones to allow movement. They are made up of bundles of fibers called myofibrils containing proteins actin and myosin that slide past each other to contract the muscle. Cardiac muscles are only found in the heart and smooth muscles line organs and blood vessels. Some major skeletal muscles include the trapezius, deltoids, pectorals, and quadriceps that work with bones to perform tasks like lifting arms and legs.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views1 pageAnatomy & Physiology: The Muscular System
Uploaded by
Eliezer NuenayThe muscular system consists of three types of muscles that work together to move the body. Skeletal muscles are voluntarily controlled and attach to bones to allow movement. They are made up of bundles of fibers called myofibrils containing proteins actin and myosin that slide past each other to contract the muscle. Cardiac muscles are only found in the heart and smooth muscles line organs and blood vessels. Some major skeletal muscles include the trapezius, deltoids, pectorals, and quadriceps that work with bones to perform tasks like lifting arms and legs.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
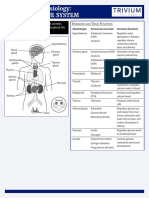
Anatomy & Physiology:
THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM
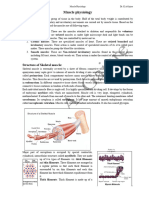
The muscular system moves the body, Structure of Skeletal Muscle
circulates blood, and moves other substances
Muscle
through the body.
Fascia Blood
vessels
Terms Sarcomere
actin (thin filament): a protein that makes up the muscle
and works with myosin to move it
Muscle Actin
cardiac muscles: involuntary muscles found only in the fibers
heart
Myofibril
contract: when the muscle receives a signal from a
motor neuron, the actin and myosin slide past each Myosin
other to shorten (contract) the muscle
myofibrils: muscle fibers
Major Muscles of the Human Body
myosin (thick filament): a protein that makes up the
Trapezius
muscle and works with actin to move it
muscles: move the body, support bodily functions, and Deltoids
circulate blood
Pectorals
relax: when the actin and myosin return to their resting Biceps
position after contracting, the muscle is relaxed
Rectus abdominus
sarcomeres: building blocks of muscle fibers; consist of
actin and myosin Obliques
skeletal muscles: voluntarily controlled; attach to the
skeleton to allow movement in the body Quadriceps
smooth muscles: involuntary; found in organs and
structures like the esophagus, bronchi, and blood vessels
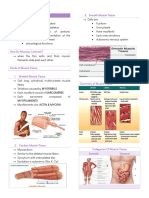
Actin and Myosin
Muscle Fiber or Cell Trapezius
Deltoids
Z Line Z Line Triceps
Sarcomere
Latissimus dorsi
Erector spinae
Obliques
H Zone Gluteus maximus
Myofibril M Line Z Line
Hamstrings
I Band H Band I Band H Band Gastrocnemius
Thick Filament
Thin Filament
You might also like
- MuscleDocument24 pagesMuscleAsmita BhattNo ratings yet
- L6. Muscular System (2021-22)Document32 pagesL6. Muscular System (2021-22)Ahmed AfashNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7: Muscular System: Movement: PSYN 103: Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument67 pagesChapter 7: Muscular System: Movement: PSYN 103: Human Anatomy and PhysiologyWindy LavarientosNo ratings yet
- Muscular System ReviewerDocument21 pagesMuscular System ReviewerChloe Mikaela MonsantoNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument8 pagesMuscular SystemCHRISTIANNE DENISE EBREONo ratings yet
- Anatomy 5-6Document10 pagesAnatomy 5-6Gladys Mae S. BañesNo ratings yet
- Reading Assignment 4Document17 pagesReading Assignment 4John Chris LuminangNo ratings yet
- 8 - Muscular System: Taft College Human PhysiologyDocument24 pages8 - Muscular System: Taft College Human PhysiologyMel VinNo ratings yet
- Bones and Muscles Activity 2 and 3Document5 pagesBones and Muscles Activity 2 and 3Marinette Valencia MedranoNo ratings yet
- Day 2 Notes (HAP)Document7 pagesDay 2 Notes (HAP)Psyche Daclag TumandaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 (Muscular System Lecture 2)Document43 pagesLecture 8 (Muscular System Lecture 2)Husnain WattoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 ANAPHY Muscular SystemDocument4 pagesChapter 7 ANAPHY Muscular Systemrobh0026No ratings yet
- Human Anatomy Study Guide: Chapter 10: Muscle Tissue and OrganizationDocument5 pagesHuman Anatomy Study Guide: Chapter 10: Muscle Tissue and OrganizationSuperjunior8No ratings yet
- System: Musculo Muscle Tissue:: A&P Muscle Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument23 pagesSystem: Musculo Muscle Tissue:: A&P Muscle Anatomy & PhysiologyjhnnolanNo ratings yet
- Biosci Chap6 (Muscular System Notes)Document3 pagesBiosci Chap6 (Muscular System Notes)Man DejeloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Muscular SystemDocument2 pagesChapter 6 Muscular SystemEdralyn EgaelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 19Document5 pagesLecture 19vinnie0905No ratings yet
- 589bc774 Df1d 47c6 Bc97 B5fd73030ca6muscle PhysiologyDocument3 pages589bc774 Df1d 47c6 Bc97 B5fd73030ca6muscle PhysiologyMalti SharmaNo ratings yet
- Muscular System TransesDocument7 pagesMuscular System Transesadrielvamos28No ratings yet
- Skeletal Muscle Sarcomere FinalDocument32 pagesSkeletal Muscle Sarcomere FinalCamille MagdirilaNo ratings yet
- Muscular System ReviewDocument12 pagesMuscular System Reviewmaggie :DNo ratings yet
- Joints and Muscle Movement FinalDocument10 pagesJoints and Muscle Movement FinalNevandi ThenuwaraNo ratings yet
- The Muscular System: Myo and Mys - Muscle Sarco - FleshDocument4 pagesThe Muscular System: Myo and Mys - Muscle Sarco - FleshDCRUZNo ratings yet
- MedmuscleDocument38 pagesMedmuscleTesfanew SeteNo ratings yet
- Secondary 5 Musclular SystemDocument3 pagesSecondary 5 Musclular SystemyunnNo ratings yet
- Ally Rose - Muscular SystemDocument4 pagesAlly Rose - Muscular SystemGogo El-HawNo ratings yet
- 2.2. Muscle Physiology - Muscle Structure 2023Document27 pages2.2. Muscle Physiology - Muscle Structure 20236f5d6b5r6tNo ratings yet
- 6.0 Muscular SystemDocument76 pages6.0 Muscular System[R2A] Khadijah AzlanNo ratings yet
- Zoology PPT Muscular SystemDocument68 pagesZoology PPT Muscular SystemDian O. Velasquez100% (1)
- Anaphy Reviewer Muscular SystemDocument4 pagesAnaphy Reviewer Muscular SystemJoyce Kathreen Ebio LopezNo ratings yet
- Human Muscular System: Types of Movement in Human BeingDocument4 pagesHuman Muscular System: Types of Movement in Human Beingaadeshthite476No ratings yet
- MuscularDocument61 pagesMuscularFranz DiazNo ratings yet
- Anatomy CHP 6 NotesDocument5 pagesAnatomy CHP 6 NotesIsland RaeNo ratings yet
- Exposicion MorfologiaDocument28 pagesExposicion MorfologiaCaTePeñaNo ratings yet
- TriChapter27 09 Muscular SystemDocument18 pagesTriChapter27 09 Muscular Systembao.nguyenthienadamsNo ratings yet
- 3c. Muscle 22893Document15 pages3c. Muscle 22893Musharaf RehmanNo ratings yet
- Musclular SystemDocument69 pagesMusclular SystemYahya JuneydiNo ratings yet
- The Muscle Tissue ReviewerDocument5 pagesThe Muscle Tissue ReviewerSasukeNo ratings yet
- Locomotion & Movement (Muscles)Document41 pagesLocomotion & Movement (Muscles)DEEPANKAR SAHANo ratings yet
- Bahan Logam Non FerroDocument26 pagesBahan Logam Non FerroAhmad FadlanNo ratings yet
- Muscular TissueDocument37 pagesMuscular Tissueمؤمل عدنان الشمخيNo ratings yet
- Group B1 General Anatomy: Submitted byDocument15 pagesGroup B1 General Anatomy: Submitted byMigz BolivarNo ratings yet
- Muscle 1Document29 pagesMuscle 1drpankaj28No ratings yet
- Locomotion and MovementDocument58 pagesLocomotion and MovementdddNo ratings yet
- The Muscular System Powerpoint 1227697713114530 8Document44 pagesThe Muscular System Powerpoint 1227697713114530 8ninya puella100% (1)
- Chapter 7 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGYDocument10 pagesChapter 7 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGYAngela Mae MeriñoNo ratings yet
- Muscle, Structure, and FunctionDocument59 pagesMuscle, Structure, and FunctionJesus AbgNo ratings yet
- 11.2 Movement: Essential Idea: The Roles ofDocument20 pages11.2 Movement: Essential Idea: The Roles ofReshma DookarranNo ratings yet
- Histology of Muscle: Lecturer Anatomy DepartmentDocument19 pagesHistology of Muscle: Lecturer Anatomy DepartmentSUMAN GHOSHNo ratings yet
- Lec5 TransesDocument10 pagesLec5 Transes4xwqm42hyrNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY - Muscular SystemDocument11 pagesANAPHY - Muscular SystemSoleil RiegoNo ratings yet
- Muscles Bones VocabDocument2 pagesMuscles Bones VocabKiana AlguardNo ratings yet
- #2 Muscular SystemDocument12 pages#2 Muscular SystemLapitan Jared Anne S.No ratings yet
- Eme 1Document20 pagesEme 1Tara LingatingNo ratings yet
- The Muscular SystemDocument50 pagesThe Muscular SystemArina GainaNo ratings yet
- Anfis Ke 4Document60 pagesAnfis Ke 4Adeputra WijayaNo ratings yet
- 2-Skeletal Muscles Team441Document17 pages2-Skeletal Muscles Team441Bujeng BardaNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument3 pagesMuscular Systemmartinezkylene1124No ratings yet
- HAP Lesson 3 (Muscular System)Document33 pagesHAP Lesson 3 (Muscular System)rodolfogallineroNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology: The Immune SystemDocument1 pageAnatomy & Physiology: The Immune SystemEliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology: The Endocrine SystemDocument1 pageAnatomy & Physiology: The Endocrine SystemEliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment OBEDocument12 pagesHealth Assessment OBEEliezer Nuenay100% (1)
- Lab Values Tips and TricksDocument2 pagesLab Values Tips and TricksEliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology (Chapter 13 - Blood Vessels)Document26 pagesAnatomy & Physiology (Chapter 13 - Blood Vessels)Eliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument1 pageCardiovascular SystemEliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology: The Nervous SystemDocument1 pageAnatomy & Physiology: The Nervous SystemEliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology (Chapter 11 - Blood)Document22 pagesAnatomy & Physiology (Chapter 11 - Blood)Eliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology (Chapter 17 - Nutrition, Metabolism, & Body Temperature Regulation)Document17 pagesAnatomy & Physiology (Chapter 17 - Nutrition, Metabolism, & Body Temperature Regulation)Eliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology (Chapter 18 - Urinary System)Document12 pagesAnatomy & Physiology (Chapter 18 - Urinary System)Eliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Research ArticleDocument32 pagesResearch ArticleEliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology (Chapter 14 - Lymphatic System)Document18 pagesAnatomy & Physiology (Chapter 14 - Lymphatic System)Eliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Intro 05-B Analysis UVDocument7 pagesIntro 05-B Analysis UVEliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Intro 05-A Analysis UVDocument7 pagesIntro 05-A Analysis UVEliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Definition of Terms EthicsDocument18 pagesDefinition of Terms EthicsEliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal System: Health AssessmentDocument43 pagesMusculoskeletal System: Health AssessmentEliezer Nuenay100% (1)
- Ha-Assessing Breast and Lymphatic-NgoDocument29 pagesHa-Assessing Breast and Lymphatic-NgoEliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Definition of Terms EthicsDocument18 pagesDefinition of Terms EthicsEliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Carcinoma BreastDocument47 pagesCarcinoma BreastMayank YadavNo ratings yet
- Some Important ENT PointsDocument3 pagesSome Important ENT PointsfrabziNo ratings yet
- Management of Peripheral Nerve Injuries: Basic Principles of Microneurosurgical RepairDocument11 pagesManagement of Peripheral Nerve Injuries: Basic Principles of Microneurosurgical RepairPrasad AilamNo ratings yet
- Reinhard L. Friede M.D. (Auth.) - Developmental Neuropathology-Springer Vienna (1975) PDFDocument535 pagesReinhard L. Friede M.D. (Auth.) - Developmental Neuropathology-Springer Vienna (1975) PDFMuhammad HabiburrahmanNo ratings yet
- Safran 2018Document11 pagesSafran 2018Freddy ChurataNo ratings yet
- 2010 Muscle Activity During The Active Straight Leg Raise (ASLR), and The Effects of A Pelvic Belt On The ASLR and On Treadmill WalkingDocument8 pages2010 Muscle Activity During The Active Straight Leg Raise (ASLR), and The Effects of A Pelvic Belt On The ASLR and On Treadmill WalkingFrancisco Antonó Castro WeithNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy An Illustrated Colour Text Crossman 6 Ed 2020 PDFDocument185 pagesNeuroanatomy An Illustrated Colour Text Crossman 6 Ed 2020 PDFKatrin CoolChe100% (3)
- ArnoldDocument3 pagesArnoldGiambattista Mastrapasqua100% (1)
- Management of Maxillofacial Trauma in Emergency An Update of Challenges and ControversiesDocument17 pagesManagement of Maxillofacial Trauma in Emergency An Update of Challenges and ControversiesHelna AmeliaNo ratings yet
- Ben Pakulski's 6 Essentials of Exercise ExecutionDocument10 pagesBen Pakulski's 6 Essentials of Exercise ExecutionDiego Poveda67% (3)
- PATHFit 2 Final Requirement Fitness Plan 1Document6 pagesPATHFit 2 Final Requirement Fitness Plan 1Yerro, Rhone Julienne May C.No ratings yet
- The YMCA Bench Press Test.10Document4 pagesThe YMCA Bench Press Test.10katerinaNo ratings yet
- Orthodontic Treatment of A Severe Combined Anterior and Posterior Open Bite Case, Involving AnkylosisDocument8 pagesOrthodontic Treatment of A Severe Combined Anterior and Posterior Open Bite Case, Involving Ankylosisgifar ihsanNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Surface Anatomy and Surface Landmarks For Thoracic SurgeryDocument13 pages1.1 Surface Anatomy and Surface Landmarks For Thoracic SurgeryResidentes CirugíaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Muscular Analysis of Upper Extremity ExercisesDocument20 pagesChapter 8 Muscular Analysis of Upper Extremity ExercisesAya AmerNo ratings yet
- MeningiomaDocument7 pagesMeningiomadrhendyjuniorNo ratings yet
- 33 DPP of Biology PDFDocument38 pages33 DPP of Biology PDFashaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Review HeartDocument6 pagesAnatomy Review HeartfailinNo ratings yet
- Cranial NervesDocument2 pagesCranial Nervesmp_329100% (1)
- Report Text The Brainy BodyDocument3 pagesReport Text The Brainy BodyHana alkhairaNo ratings yet
- Pupillary Light ReflexDocument2 pagesPupillary Light ReflexJohn OsborneNo ratings yet
- Maglaqui - Skeletal SystemDocument5 pagesMaglaqui - Skeletal SystemNICOLE MAGLAQUINo ratings yet
- Taste and SmellDocument22 pagesTaste and SmellabdirizakNo ratings yet
- Female CatheterizationDocument64 pagesFemale CatheterizationLara Marie MACALINTALNo ratings yet
- Sheiko 4 Day ProgramDocument20 pagesSheiko 4 Day ProgramGiovan Maria Catalan BelmonteNo ratings yet
- Cephalic Vein: OriginDocument25 pagesCephalic Vein: OriginsquidblitzNo ratings yet
- Static Stretching ExercisesDocument6 pagesStatic Stretching ExercisesJai SengNo ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument4 pagesChapter TwoIris NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Animal Physiology: Review For Licensure Exam in AgricultureDocument152 pagesAnimal Physiology: Review For Licensure Exam in AgricultureJayson BasiagNo ratings yet
- Skeletal Muscle Practice Exam #1Document46 pagesSkeletal Muscle Practice Exam #1Sayang TalagaNo ratings yet