Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cardiovascular System
Uploaded by
Eliezer NuenayOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cardiovascular System
Uploaded by
Eliezer NuenayCopyright:
Available Formats
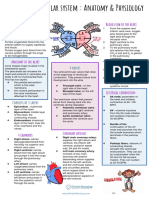
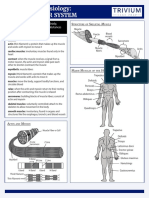
Anatomy & Physiology:
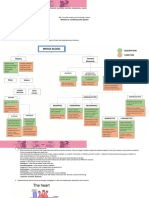
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
The circulatory system carries nutrients, gases, Terms
and hormones in blood throughout the body. aorta: artery from which oxygenated blood is pumped from
the heart to the rest of the body
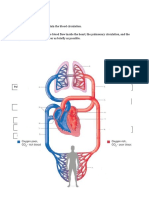
The Circulatory System arteries: large, firm vessels that transport oxygenated blood
throughout the body from the heart
Deoxygenated
Upper body blood atria: chambers of the heart that receive the blood
Superior
vena cava Oxygenated blood: fluid composed of plasma, red blood cells, white blood
blood cells, and other molecules; delivers nutrients and gases to body
Pulmonary arteries locations and removes waste
blood pressure: pressure exerted on the vessels of the
Right
lung Aorta cardiovascular system as the heart pumps blood throughout
the body
Left
lung capillaries: small vessels where oxygen, nutrients, and other
materials are exchanged with tissue
diastole phase: period of ventricle relaxation
Pulmonary veins Liver
heart: muscular organ that continuously pumps oxygenated
Portal vein blood throughout the body
Digestive
Inferior system left atrium: chamber of the heart that receives oxygenated
vena cava blood from the lungs
Lower body left ventricle: chamber of the heart that pumps oxygenated
blood to the rest of the body
mitral valve: separates left atrium from left ventricle
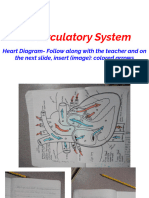
The Human Heart
plasma: fluid that transports red and white blood cells as well
Superior vena
as other molecules in the blood
cava from upper To upper body
body pulmonary circuit: term for blood flow from the lungs to the
To lower body heart
red blood cells (hemoglobin): transport oxygen in the blood
Pulmonary artery Aorta
ery Pulmonary artery right atrium: chamber of the heart that receives oxygen-poor
to right lung ry art
Pulmona to left lung
blood from throughout the body
Pulmonary veins
right ventricle: chamber of the heart that receives oxygen-
from left lung
Pulmonary veins Left poor blood from the right atrium and pumps it out to the lungs
atrium
from Right Mitral valve
right lung atrium
systemic circuit: term for blood flow from the heart to the rest
of the body
Pulmonic valve Aortic valve
Left systole phase: period of ventricle contraction
ventricle
tricuspid valve: separates right atrium from right ventricle
Tricuspid valve
Right
ventricle valves: prevent blood from flowing backwards from the
ventricle to the atrium
veins: vessels that carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart
from the rest of the body
Inferior
vena cava from Aorta to lower ventricles: chambers of the heart that pump blood to the body
body
lower body and lungs
You might also like
- F3 3.2Document41 pagesF3 3.2amalina rohaizanNo ratings yet
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Vascular System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionFrom EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Vascular System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNo ratings yet
- Care of Mother and Child at Risk or With ProblemsDocument87 pagesCare of Mother and Child at Risk or With ProblemsQueen Jyil100% (1)
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Circulatory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionFrom EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Circulatory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNo ratings yet
- Heart Organ and Its FunctionDocument1 pageHeart Organ and Its FunctionSofia Eunice TurlaNo ratings yet
- ANAPHYDocument12 pagesANAPHYchrstiannNo ratings yet
- Cardiac PhysiologyDocument8 pagesCardiac PhysiologyPo-Lin HsuNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument10 pagesCirculatory Systemletangletty07No ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument2 pagesCirculatory SystemCookies AndcreamNo ratings yet
- B4 - Organising Animals and PlantsDocument4 pagesB4 - Organising Animals and PlantsozmanNo ratings yet
- Lect 8. Cardiovascular SystemDocument35 pagesLect 8. Cardiovascular Systemrukhsanatariq299No ratings yet
- Circulatory / Transport System: For 1O Grade Igcse Semesta Bilingual Boarding SchoolDocument52 pagesCirculatory / Transport System: For 1O Grade Igcse Semesta Bilingual Boarding SchoolThe Deep Sea IdNo ratings yet
- Heart Cardiovascular SystemDocument2 pagesHeart Cardiovascular SystemKim Nae A. MasucolNo ratings yet
- Major Part of The Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesMajor Part of The Circulatory SystemBrettnia Angela AradoNo ratings yet
- MY CLASS NOTES - BIOLOGY Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesMY CLASS NOTES - BIOLOGY Circulatory SystemJjongNo ratings yet
- Ron Seraph Anjello Javier - Q1 Sci. 9 FA No.1Document4 pagesRon Seraph Anjello Javier - Q1 Sci. 9 FA No.1Mute GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Ppt-Grade 9 - Blood CirculationDocument7 pagesPpt-Grade 9 - Blood CirculationEdralyn Panes VillacrucisNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 5 - The Human HeartDocument35 pagesBiology Form 5 - The Human HeartKimAyra100% (1)
- Blood Flow: Right AtriumDocument2 pagesBlood Flow: Right AtriumDaffodelle AnneNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: Chapter 13-Blood VesselsDocument8 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: Chapter 13-Blood VesselsRonnie De Vera IINo ratings yet
- GastroschisisDocument2 pagesGastroschisisCarlos Caipo CardosoNo ratings yet
- Sci9Q1M1 - Rev-Bait-it 2Document4 pagesSci9Q1M1 - Rev-Bait-it 2Realyn Delana OguisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13: Blood Vessels and CirculationDocument6 pagesChapter 13: Blood Vessels and CirculationPrecious Faith RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: The Body's Transport SystemDocument17 pagesCirculatory System: The Body's Transport SystemShania DavidsonNo ratings yet
- The Heart and Blood VesselsDocument1 pageThe Heart and Blood VesselsozmanNo ratings yet
- Quarter1 Week2 Lesson2Blood and Gas ExchangeDocument24 pagesQuarter1 Week2 Lesson2Blood and Gas ExchangeRicky RickyNo ratings yet
- TEAM3 BSN1-J Anatomy Lec Module 10 Cardiovascular SystemDocument6 pagesTEAM3 BSN1-J Anatomy Lec Module 10 Cardiovascular SystemElisha Fleur Cambas GachoNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: The Body's Transport SystemDocument17 pagesCirculatory System: The Body's Transport SystemnoviNo ratings yet
- Superior Vena Cava: Right AtriumDocument3 pagesSuperior Vena Cava: Right AtriumMary SimbulanNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System La PazDocument9 pagesCirculatory System La PazFlori de CâmpNo ratings yet
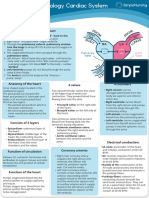
- Anatomy & Physiology Cardiac SystemDocument1 pageAnatomy & Physiology Cardiac SystemTori RolandNo ratings yet
- 024-Premedical Circulatory SystemDocument31 pages024-Premedical Circulatory Systemchealzea asuncsionNo ratings yet
- Systemic and Pulmonary CirculationDocument13 pagesSystemic and Pulmonary CirculationLuis eduardo bolaño vilaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 f3Document101 pagesChapter 3 f3Ghanapathi RamanathanNo ratings yet
- Heart and Neck VesselsDocument11 pagesHeart and Neck Vesselsdiana borromeoNo ratings yet
- How The Heart Works For College StudentsDocument12 pagesHow The Heart Works For College StudentsAshajNo ratings yet
- Human Heart and Circulation 2019Document114 pagesHuman Heart and Circulation 2019Jeff Bryan Arellano Himor100% (1)
- CVS 1 (Physiological Anatomy) .PDF AfraaDocument36 pagesCVS 1 (Physiological Anatomy) .PDF AfraaEra NewNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesRespiratory SystemMarnel DincolNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System Heart DiagramDocument7 pagesCirculatory System Heart DiagramoliviazagerNo ratings yet
- Circolatory SystemDocument2 pagesCircolatory SystemGAIA BACCANINo ratings yet
- Exercise 1: Label and Explain The Blood CirculationDocument2 pagesExercise 1: Label and Explain The Blood CirculationKiana Ramosa100% (1)
- Heart Reviewer 1Document6 pagesHeart Reviewer 1tokzzNo ratings yet
- Transport SystemDocument18 pagesTransport SystemBalqis QisNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument2 pagesCirculatory SystemNathaniel BurgeNo ratings yet
- Patent Ductus ArteriosusDocument9 pagesPatent Ductus ArteriosusAnonymous QOCn5dNo ratings yet
- Ana CardioDocument3 pagesAna CardioFIONA DANE MAURERANo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument10 pagesCardiovascular Systemabdelrhman aboodaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cardiovascular Physiology: Welcome To Block 3! Part IIDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Cardiovascular Physiology: Welcome To Block 3! Part IIwayneNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular SystemDocument3 pagesThe Cardiovascular SystemnvhnygNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 5 Chapter 1 - Transport: 1.2 The Circulatory System - The Human HeartDocument34 pagesBiology Form 5 Chapter 1 - Transport: 1.2 The Circulatory System - The Human HeartkiongocNo ratings yet
- Nursing Simplified SheetsDocument14 pagesNursing Simplified Sheetssao sl78% (9)
- Blood Circulation: Presented By: Samiur Rahim Kazi Roll No.: 19 Section: NeptuneDocument5 pagesBlood Circulation: Presented By: Samiur Rahim Kazi Roll No.: 19 Section: NeptuneSkaredNo ratings yet
- Genzoo Circulatory SystemDocument11 pagesGenzoo Circulatory SystemAbram TicmanNo ratings yet
- Topic 2.2 - Human Circulatory SystemDocument30 pagesTopic 2.2 - Human Circulatory Systembienfrancis.reyes.jhsNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Tutorial 2Document3 pagesGroup 4 Tutorial 2SN1-0622 Khairul Bariah Binti IzaniNo ratings yet
- English Work 4Document4 pagesEnglish Work 4Jaime Ernesto VanegasNo ratings yet
- Pig's Heart Post LabDocument2 pagesPig's Heart Post LabMichaella Jane BugayNo ratings yet
- Multicellular Organisms: Circulatory SystemDocument36 pagesMulticellular Organisms: Circulatory SystemSpidervaitNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology: The Endocrine SystemDocument1 pageAnatomy & Physiology: The Endocrine SystemEliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology: The Immune SystemDocument1 pageAnatomy & Physiology: The Immune SystemEliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment OBEDocument12 pagesHealth Assessment OBEEliezer Nuenay100% (1)
- Anatomy & Physiology: The Muscular SystemDocument1 pageAnatomy & Physiology: The Muscular SystemEliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology: The Nervous SystemDocument1 pageAnatomy & Physiology: The Nervous SystemEliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Lab Values Tips and TricksDocument2 pagesLab Values Tips and TricksEliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology (Chapter 13 - Blood Vessels)Document26 pagesAnatomy & Physiology (Chapter 13 - Blood Vessels)Eliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology (Chapter 11 - Blood)Document22 pagesAnatomy & Physiology (Chapter 11 - Blood)Eliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology (Chapter 14 - Lymphatic System)Document18 pagesAnatomy & Physiology (Chapter 14 - Lymphatic System)Eliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology (Chapter 17 - Nutrition, Metabolism, & Body Temperature Regulation)Document17 pagesAnatomy & Physiology (Chapter 17 - Nutrition, Metabolism, & Body Temperature Regulation)Eliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology (Chapter 18 - Urinary System)Document12 pagesAnatomy & Physiology (Chapter 18 - Urinary System)Eliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Research ArticleDocument32 pagesResearch ArticleEliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Intro 05-B Analysis UVDocument7 pagesIntro 05-B Analysis UVEliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Definition of Terms EthicsDocument18 pagesDefinition of Terms EthicsEliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal System: Health AssessmentDocument43 pagesMusculoskeletal System: Health AssessmentEliezer Nuenay100% (1)
- Intro 05-A Analysis UVDocument7 pagesIntro 05-A Analysis UVEliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Ha-Assessing Breast and Lymphatic-NgoDocument29 pagesHa-Assessing Breast and Lymphatic-NgoEliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Definition of Terms EthicsDocument18 pagesDefinition of Terms EthicsEliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Antianginal DrugsDocument47 pagesAntianginal Drugsmospala285No ratings yet
- Congenital Heart Disease: Kriti Puri, MD Hugh D. Allen, MD Athar M. Qureshi, MDDocument30 pagesCongenital Heart Disease: Kriti Puri, MD Hugh D. Allen, MD Athar M. Qureshi, MDhari ilman toniNo ratings yet
- Takayasu's Arteritis - WikipediaDocument32 pagesTakayasu's Arteritis - WikipediadrnurmayasarisihombingNo ratings yet
- Intercostal ArteriesDocument3 pagesIntercostal ArteriesranshNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Tests in CardiologyDocument38 pagesDiagnostic Tests in CardiologyDea Amelia YolandaNo ratings yet
- PigDocument34 pagesPigaa62893% (14)
- Embolism & InfarctionDocument27 pagesEmbolism & InfarctionAsutosh PradhanNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument8 pagesHypertensioncookie.rajabNo ratings yet
- Mammalian HeartDocument7 pagesMammalian Heartnickmirad2No ratings yet
- Chevannese Ellis - Circ Class WorkDocument3 pagesChevannese Ellis - Circ Class WorkChevannese EllisNo ratings yet
- Surgery NBME 1 AnswersDocument1 pageSurgery NBME 1 AnswersVikasYellapu89% (18)
- Fetal Circulation (For MBBS)Document50 pagesFetal Circulation (For MBBS)Tashif100% (1)
- Esmr 2Document1 pageEsmr 2Martina FitriaNo ratings yet
- CHD Managemen Withot Surgery Cansy JHC (Prof. Mul) PDFDocument39 pagesCHD Managemen Withot Surgery Cansy JHC (Prof. Mul) PDFFery NurjayantoNo ratings yet
- Portal Hypertension: IntroductionDocument13 pagesPortal Hypertension: IntroductionGaoudam NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Laporan Kasus Kardiovaskuler (Fransiska - C11107156)Document32 pagesLaporan Kasus Kardiovaskuler (Fransiska - C11107156)Fransiska Carmelia SubenoNo ratings yet
- Myocardial Infarction Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramDocument3 pagesMyocardial Infarction Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramAbi Habiling100% (3)
- HM3 in FontonDocument2 pagesHM3 in FontonselvakumarNo ratings yet
- 10th (ICSE) - (BIOLOGY) - Absorption by Roots+Circulatory SystemDocument2 pages10th (ICSE) - (BIOLOGY) - Absorption by Roots+Circulatory SystemDhun100% (2)
- University of Saint Louis Tuguegarao City, Philippines: Maternal and Child Health NursingDocument69 pagesUniversity of Saint Louis Tuguegarao City, Philippines: Maternal and Child Health NursingErica Veluz LuyunNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument3 pagesCoronary Artery DiseaseMarta Luquez RNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument7 pagesLymphatic SystemAsher Eby VargeeseNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing: Anatomy HeartDocument8 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing: Anatomy HeartRoyce Vincent TizonNo ratings yet
- Takayasu S Arter It IsDocument5 pagesTakayasu S Arter It IsButarbutar MelvaNo ratings yet
- Echocardiography in Heart Failure: A Guide For General PracticeDocument6 pagesEchocardiography in Heart Failure: A Guide For General PracticesavitageraNo ratings yet
- Atherosclerosis CompendiumDocument13 pagesAtherosclerosis CompendiumanushanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan No. 1 Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term: Short TermDocument11 pagesNursing Care Plan No. 1 Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term: Short TermYumeko JabamiNo ratings yet
- MCQ On Heart DiseaseDocument10 pagesMCQ On Heart DiseaseSucheta Ghosh ChowdhuriNo ratings yet
- 3Document265 pages3Carlos HernándezNo ratings yet
- RBCDocument3 pagesRBCSupreeth RulesNo ratings yet
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (404)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (82)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (36)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDFrom EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)From EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- The Twentysomething Treatment: A Revolutionary Remedy for an Uncertain AgeFrom EverandThe Twentysomething Treatment: A Revolutionary Remedy for an Uncertain AgeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Manipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesFrom EverandManipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (1412)
- I Shouldn't Feel This Way: Name What’s Hard, Tame Your Guilt, and Transform Self-Sabotage into Brave ActionFrom EverandI Shouldn't Feel This Way: Name What’s Hard, Tame Your Guilt, and Transform Self-Sabotage into Brave ActionNo ratings yet
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Critical Thinking: How to Effectively Reason, Understand Irrationality, and Make Better DecisionsFrom EverandCritical Thinking: How to Effectively Reason, Understand Irrationality, and Make Better DecisionsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (39)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (170)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (46)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (254)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsFrom EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsNo ratings yet
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- Self-Care for Autistic People: 100+ Ways to Recharge, De-Stress, and Unmask!From EverandSelf-Care for Autistic People: 100+ Ways to Recharge, De-Stress, and Unmask!Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (267)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Summary: Thinking, Fast and Slow: by Daniel Kahneman: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: Thinking, Fast and Slow: by Daniel Kahneman: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (61)