Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Circulatory System Explained
Uploaded by
Cookies Andcream0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
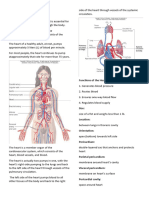
3 views2 pagesThe circulatory system consists of the heart, arteries, veins, and blood vessels that form a network throughout the body. The heart pumps oxygenated blood received from the lungs throughout the body via arteries, and the deoxygenated blood is returned to the heart by veins to be reoxygenated and pumped back out. The main functions are to supply oxygen and nutrients to cells and remove wastes. Key parts include the four chambers of the heart, valves that ensure one-way blood flow, and major vessels like the vena cava, aorta and pulmonary artery.
Original Description:
Original Title
Circulatory system
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe circulatory system consists of the heart, arteries, veins, and blood vessels that form a network throughout the body. The heart pumps oxygenated blood received from the lungs throughout the body via arteries, and the deoxygenated blood is returned to the heart by veins to be reoxygenated and pumped back out. The main functions are to supply oxygen and nutrients to cells and remove wastes. Key parts include the four chambers of the heart, valves that ensure one-way blood flow, and major vessels like the vena cava, aorta and pulmonary artery.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesCirculatory System Explained
Uploaded by
Cookies AndcreamThe circulatory system consists of the heart, arteries, veins, and blood vessels that form a network throughout the body. The heart pumps oxygenated blood received from the lungs throughout the body via arteries, and the deoxygenated blood is returned to the heart by veins to be reoxygenated and pumped back out. The main functions are to supply oxygen and nutrients to cells and remove wastes. Key parts include the four chambers of the heart, valves that ensure one-way blood flow, and major vessels like the vena cava, aorta and pulmonary artery.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
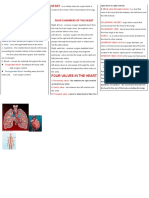
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
What is the circulatory system?
a network of vessels—the arteries, veins, - zeroes in on “bringing back to life” the heart
and capillaries—and a pump, the heart. and the lungs; the Latin word cardio refers to
Needs oxygen from lungs to pump blood, the heart, while pulmo refers to the lungs.
then sends oxygenated blood throughout the
rest of our body.
brings supplies to cells and carries away
wastes
separates oxygen-poor and oxygen-rich
blood
it’s 4 main parts consist of the heart, arteries,
veins, and blood.
Circulatory system vocabulary:
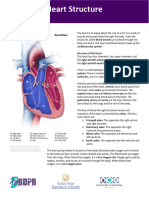
1. Heart
muscular organ that pumps bloods
located in middle of chest cavity w/ tip
pointed to left.
Sized as one’s fist Parts of the heart
2. Blood
Circulating fluid providing body w/ nutrients, 1. 4 interior chambers which refers to the
oxygen, and waste removal. Consists of 4 divisions of the heart where blood flows:
parts: right atrium - receiving chamber, receives
Red blood cells = carries oxygen blood that is deoxygenated (oxygen
White blood cells = part of immune system concentration is low)
that protects body left atrium - receiving chamber, receives
Platelets = needed for clotting blood that is oxygenated (oxygen
Plasma = blood cells, nutrients, and wastes concentration is high)
float in this liquid right ventricle - pumping chamber, pumps
3. Blood vessels: blood to the lungs
Arteries = carries oxygenated blood away left ventricle - pumping chamber, pumps
from heart blood to different parts of the body
Veins = carries de-oxygenated blood to heart
Capillaries = smallest vessel, where nutrients 2. 4 valves which allow blood to flow in only
and gases diffuse one direction through the heart chambers:
tricuspid valve – divides the right side of the
heart
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation pulmonary semilunar valve – the passage to
the pulmonary artery
- Also commonly known as “CPR” bicuspid (mitral) valve – divides the left side
- an emergency technique that has been of the heart
developed to allow trained individuals to aortic valve - the passage to the aorta
revive patients or victims who are close to
dying or have lost consciousness.
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
3. 4 blood vessels that provide a pathway for 8. Aorta distributes blood to body
the entire circulation to proceed:
vena cava (superior and inferior) – pathway
of blood as it enters the heart
aorta - pathway of blood as it leaves the
heart
pulmonary artery –pathway of blood as it
goes from the heart to the lungs
pulmonary veins –pathway of blood from the
lungs as it goes back to the hear
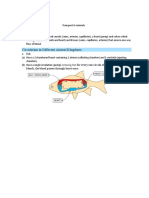
Blood Pathway through the Heart
Process of blood flow through the heart:
De-oxygenated blood:
1. Deoxygenated blood enters right atrium through
Superior (upper) and Inferior Vena Cava (lower)
2. Blood enters right ventricle through tricuspid valve
3. Blood exits right ventricle through pulmonary valve
and enters pulmonary artery
4. Left and right pulmonary arteries send blood to
lungs, where gas exchange occurs
Oxygenated blood:
5. Oxygenated blood returns to heart via the
pulmonary veins then enters left atrium
6. Blood enters left ventricle through mitral valve
7. Blood exits left ventricle through aortic semilunar
valve to enter aorta
You might also like
- Circulatory System ExplainedDocument3 pagesCirculatory System ExplainedJjongNo ratings yet
- Beating with Precision: The Science of Cardiology: Understand the Intricacies of the Human HeartFrom EverandBeating with Precision: The Science of Cardiology: Understand the Intricacies of the Human HeartNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System NotesDocument3 pagesCirculatory System Noteshannah peloniaNo ratings yet
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Vascular System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionFrom EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Vascular System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System - LectureDocument2 pagesCirculatory System - Lecturebay de jesusNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesThe Circulatory SystemBrettnia Angela AradoNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument10 pagesCirculatory Systemletangletty07No ratings yet
- Quarter1 Week2 Lesson2Blood and Gas ExchangeDocument24 pagesQuarter1 Week2 Lesson2Blood and Gas ExchangeRicky RickyNo ratings yet
- Topic 2.2 - Human Circulatory SystemDocument30 pagesTopic 2.2 - Human Circulatory Systembienfrancis.reyes.jhsNo ratings yet
- Blood Circulation and TransportDocument23 pagesBlood Circulation and TransportcikzafirahNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument6 pagesCardiovascular Systemapi-297526590No ratings yet
- HeartDocument1 pageHeartswati singhNo ratings yet
- Transports Nutrients and Water Transports Gases Like Oxygen Transports Hormones Heals and Fight InfectionsDocument46 pagesTransports Nutrients and Water Transports Gases Like Oxygen Transports Hormones Heals and Fight InfectionsElla LlamasNo ratings yet
- The 4-Chamber Heart and Circulatory-Respiratory SystemDocument1 pageThe 4-Chamber Heart and Circulatory-Respiratory SystemPauline InocenteNo ratings yet
- Transport in AnimalsDocument43 pagesTransport in AnimalsEdwins MaranduNo ratings yet
- Medical Science Part 2Document21 pagesMedical Science Part 2Gauge FalkNo ratings yet
- 5-Structure and Function of The Body Systems 2Document29 pages5-Structure and Function of The Body Systems 2uxdan154No ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument8 pagesThe Circulatory SystembysshelarbyNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System Lesson Plan Explains Heart & Blood FlowDocument6 pagesCirculatory System Lesson Plan Explains Heart & Blood FlowYenny YenNo ratings yet
- 024-Premedical Circulatory SystemDocument31 pages024-Premedical Circulatory Systemchealzea asuncsionNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument30 pagesCirculatory SystemIra Lavigne De VillaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Up Your Cardiovascular System. Yourheart Works As ADocument6 pagesCardiovascular System: Up Your Cardiovascular System. Yourheart Works As AMalaquias VallejosNo ratings yet
- The Heart and The Pathway of BloodDocument21 pagesThe Heart and The Pathway of BloodSaadNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System Sci 6Document26 pagesCirculatory System Sci 6Regin BaguioNo ratings yet
- CVS IDocument7 pagesCVS Itemple samNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument28 pagesCirculatory SystemMaria Theresa DemeterioNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesRespiratory SystemMarnel DincolNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System +Document14 pagesCardiovascular System +Yasin AbassNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To The Cardiovascular SystemDocument4 pagesAn Introduction To The Cardiovascular SystemLili M.No ratings yet
- Circulatory System GuideDocument10 pagesCirculatory System GuidenaviNo ratings yet
- Heart Cardiovascular SystemDocument2 pagesHeart Cardiovascular SystemKim Nae A. MasucolNo ratings yet
- Parts and Function of Heart: Group 5 9 - ActsDocument47 pagesParts and Function of Heart: Group 5 9 - ActsJasmin GarciaNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and Physiology AssignmentDocument8 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology AssignmentSiti Sumari HarahapNo ratings yet
- NOTES IN CIRCULATORY SYSTEMDocument3 pagesNOTES IN CIRCULATORY SYSTEMVianney CamachoNo ratings yet
- 1 Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument25 pages1 Anatomy and PhysiologyMichelle Dona MirallesNo ratings yet
- Handouts Science and Health VI The HeartDocument3 pagesHandouts Science and Health VI The HeartjairaestrellaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Human Cardiovascular SystemDocument19 pagesHuman Cardiovascular SystemLenka ZáveckáNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System Notes IgcseDocument19 pagesCirculatory System Notes IgcseWork WiseNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System ZooDocument9 pagesThe Circulatory System Zoopierre TritzNo ratings yet
- Ron Seraph Anjello Javier - Q1 Sci. 9 FA No.1Document4 pagesRon Seraph Anjello Javier - Q1 Sci. 9 FA No.1Mute GuerreroNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory and Circulatory Systems Working With Othe Organs in The SystemDocument29 pagesThe Respiratory and Circulatory Systems Working With Othe Organs in The SystemAngela VirayNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary CirculationDocument5 pagesPulmonary CirculationGPearce204No ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument28 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyeliseudesafateNo ratings yet
- HLT51612 Diploma in Nursing - Cardiovascular SystemDocument20 pagesHLT51612 Diploma in Nursing - Cardiovascular SystemPrince YoungNo ratings yet
- CVS 1 (Physiological Anatomy) .PDF AfraaDocument36 pagesCVS 1 (Physiological Anatomy) .PDF AfraaEra NewNo ratings yet
- HEARTDocument8 pagesHEARTSJane FeriaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: 6 GradeDocument42 pagesCirculatory System: 6 Grademayonaissedelight smoothieNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To The Cardiovascular SystemDocument4 pagesAn Introduction To The Cardiovascular SystemLili M.No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System LectureDocument5 pagesCardiovascular System LectureMarci MunirNo ratings yet
- BookDocument8 pagesBookmohamed aweys abuukarNo ratings yet
- The Heart: Basis of Life .?Document94 pagesThe Heart: Basis of Life .?Diksha AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 KSSM FORM 4 BIODocument12 pagesChapter 10 KSSM FORM 4 BIOYEO MING HUI MoeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology - Circulatory System - The HeartDocument14 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - Circulatory System - The Heartxuxi dulNo ratings yet
- Sistem Peredaran Darah ResumeDocument10 pagesSistem Peredaran Darah Resumeilham ramNo ratings yet
- Respiratory and Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesRespiratory and Circulatory SystemJovie Erma AtonNo ratings yet
- GastroschisisDocument2 pagesGastroschisisCarlos Caipo CardosoNo ratings yet
- Term 4Document40 pagesTerm 4thatolebelo9No ratings yet
- Course of circulation through the human heartDocument4 pagesCourse of circulation through the human heartvishal pundirNo ratings yet
- Movement Disorders - 2022 - Lange - Nomenclature of Genetic Movement Disorders Recommendations of The InternationalDocument38 pagesMovement Disorders - 2022 - Lange - Nomenclature of Genetic Movement Disorders Recommendations of The InternationalAgnes IacobNo ratings yet
- BTS 2018 New BrochureDocument10 pagesBTS 2018 New BrochureMinhquang NgoNo ratings yet
- MicrobesDocument1 pageMicrobesHartford CourantNo ratings yet
- PASTURE MANAGEMENT - Final PDFDocument101 pagesPASTURE MANAGEMENT - Final PDFDexter Andrew Lyken100% (1)
- Source Partitioning and Emission Factor of Nitrous Oxide During Warm and Cold Cropping Seasons From An Upland Soil in South KoreaDocument10 pagesSource Partitioning and Emission Factor of Nitrous Oxide During Warm and Cold Cropping Seasons From An Upland Soil in South KoreaIleana CosanzeanaNo ratings yet
- Time 120Document3 pagesTime 120ardhra pNo ratings yet
- Đề Thi Hsg Tiếng Anh Vĩnh Phúc (Lớp 12)Document8 pagesĐề Thi Hsg Tiếng Anh Vĩnh Phúc (Lớp 12)Cù Minh HiếuNo ratings yet
- Notice: Environmental Statements Notice of Intent: U. S. Navy Surveillance Towed Array Sensor System Low Frequency Active Sonar OperationsDocument2 pagesNotice: Environmental Statements Notice of Intent: U. S. Navy Surveillance Towed Array Sensor System Low Frequency Active Sonar OperationsJustia.comNo ratings yet
- Upstream & DownstreamDocument20 pagesUpstream & DownstreamLamtiarma PanjaitanNo ratings yet
- Trace the Genetic Code to Identify Amino AcidsDocument3 pagesTrace the Genetic Code to Identify Amino Acidsrommel rentoria100% (1)
- Statement of Purpose (Stanford)Document2 pagesStatement of Purpose (Stanford)Emily CribasNo ratings yet
- Authors: Ibel Carri, María Marcela Barrio, Morten Nielsen: BackgroundDocument1 pageAuthors: Ibel Carri, María Marcela Barrio, Morten Nielsen: BackgroundrexNo ratings yet
- Los 12 Pilares de La Inteligencia, Adrian Owen PDFDocument6 pagesLos 12 Pilares de La Inteligencia, Adrian Owen PDFYasmina Itzel Murillo LopezNo ratings yet
- Iso 16140 Validation by Afnor On TVC TC and Ec Adria-2 PDFDocument1 pageIso 16140 Validation by Afnor On TVC TC and Ec Adria-2 PDFJuliet RomeroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - General Characteristics of The SpineDocument50 pagesChapter 2 - General Characteristics of The SpineveronicalovirgenNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument17 pagesScienceTambong HailyNo ratings yet
- Potato Spindle Tuber Viroid (PSTVD)Document4 pagesPotato Spindle Tuber Viroid (PSTVD)Leydi Yudith Angarita BautistaNo ratings yet
- High Voltage Galvanic Current Lecture PDFDocument22 pagesHigh Voltage Galvanic Current Lecture PDFdespNo ratings yet
- Sickle Cell AnaemiaDocument10 pagesSickle Cell AnaemiaAhmadNo ratings yet
- A) State and Describe Various Stages of A Biodegradation StudyDocument6 pagesA) State and Describe Various Stages of A Biodegradation StudyAbdulkadir AlbabaNo ratings yet
- Blakemore Frith 2005 The Leaning BrainDocument221 pagesBlakemore Frith 2005 The Leaning BrainVictor MN100% (2)
- iicc// - Aarrttw Woorrkk//Ccrriittiiqquuee: P Poosstt Aa R ReeppllyyDocument21 pagesiicc// - Aarrttw Woorrkk//Ccrriittiiqquuee: P Poosstt Aa R ReeppllyyhisohisoNo ratings yet
- Safety Tests CosmeticsDocument41 pagesSafety Tests CosmeticsPogiri Rambabu100% (1)
- Botany MicrobiologyDocument89 pagesBotany Microbiologytarungupta2001No ratings yet
- Conducting Sediment Toxicity Tests With Polychaetous AnnelidsDocument26 pagesConducting Sediment Toxicity Tests With Polychaetous AnnelidsDavid AriasNo ratings yet
- Renal Physiology Lab ReportDocument5 pagesRenal Physiology Lab Reportpatricia ankarNo ratings yet
- Daftar Harga Alkes & Reagensia Non-CatalogDocument2 pagesDaftar Harga Alkes & Reagensia Non-CatalogPT SNAFANo ratings yet
- M3.1. PTG and Calcium Homeostasis (CC2-LEC)Document5 pagesM3.1. PTG and Calcium Homeostasis (CC2-LEC)Hannah Elizabeth CastroNo ratings yet
- Cladistics PDFDocument4 pagesCladistics PDFmanoj_rkl_07100% (1)
- Tips - Microbiology of Meat and Poultry PDFDocument332 pagesTips - Microbiology of Meat and Poultry PDFFadhili DungaNo ratings yet
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (402)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (14)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (78)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo ratings yet
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementFrom EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (40)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesFrom EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (34)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingFrom EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsFrom EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsNo ratings yet
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (327)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (253)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (33)
- Daniel Kahneman's "Thinking Fast and Slow": A Macat AnalysisFrom EverandDaniel Kahneman's "Thinking Fast and Slow": A Macat AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (130)
- Summary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)