Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cause of Mental Problem of Humanistic Theory
Uploaded by
kibrom mekonen0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views3 pagesHumanistic theory was founded by Abraham Maslow, who proposed a hierarchy of needs including physiological, safety, love, esteem, and self-actualization needs. Humanistic psychology assumes people have free will and personal agency to make choices. According to humanistic theory, mental problems stem from an interrupted development process and immaturity. The goals of humanistic therapy are to promote social/emotional maturity and growth by helping clients develop a stronger sense of self and understand their feelings to gain a sense of meaning in life. Therapists use techniques like congruence, empathetic understanding, reflective listening, and unconditional positive regard to support self-awareness and directing one's own behavior rather than solving specific problems.
Original Description:
Original Title
kebrarawu 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentHumanistic theory was founded by Abraham Maslow, who proposed a hierarchy of needs including physiological, safety, love, esteem, and self-actualization needs. Humanistic psychology assumes people have free will and personal agency to make choices. According to humanistic theory, mental problems stem from an interrupted development process and immaturity. The goals of humanistic therapy are to promote social/emotional maturity and growth by helping clients develop a stronger sense of self and understand their feelings to gain a sense of meaning in life. Therapists use techniques like congruence, empathetic understanding, reflective listening, and unconditional positive regard to support self-awareness and directing one's own behavior rather than solving specific problems.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views3 pagesCause of Mental Problem of Humanistic Theory
Uploaded by
kibrom mekonenHumanistic theory was founded by Abraham Maslow, who proposed a hierarchy of needs including physiological, safety, love, esteem, and self-actualization needs. Humanistic psychology assumes people have free will and personal agency to make choices. According to humanistic theory, mental problems stem from an interrupted development process and immaturity. The goals of humanistic therapy are to promote social/emotional maturity and growth by helping clients develop a stronger sense of self and understand their feelings to gain a sense of meaning in life. Therapists use techniques like congruence, empathetic understanding, reflective listening, and unconditional positive regard to support self-awareness and directing one's own behavior rather than solving specific problems.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
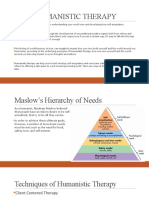
Who founded humanistic theory?
The American psychologist Abraham Maslow, considered one of the leading architects of humanistic
psychology, proposed a hierarchy of needs or drives in order of decreasing priority or potency but
increasing sophistication: physiological needs, safety, belongingness and love, esteem, and self-
actualization.
Basic Assumptions
Humanistic psychology begins with the existential assumption
that people have free will:
Personal agency is the humanistic term for the exercise of free will. Personal
agency refers to the choices we make in life, the paths we go down and their
consequences.
Cause of mental problem of humanistic theory
In the humanistic vision, human dysfunctions are caused by a faulty or
interrupted development process; essentially human problems are due
to immaturity, generally of the social/emotional variety. The goal of a
humanistic therapy is thus to promote social/emotional maturity and growth.
Goals of Humanistic Therapy
The aim of humanistic therapy is to help the client develop a
stronger, healthier sense of self, as well as access and
understand their feelings to help gain a sense of meaning in
life.
Techniques
Humanistic therapists use a number of techniques that are
designed to support people as they work toward change. Some
of the main techniques that are frequently used include:3
Congruence: This technique is essential to humanistic therapy
and involves the therapist being authentic, open, and genuine
as they interact with the individual who is in therapy.
Empathetic understanding: This involves the therapist not only
understanding what the client is feeling and saying, but also
communicating that understanding to the client. The individual
should feel heard, seen, and understood.4
Reflective listening: This involves actively listening to the
individual and then summarizing what the client has said in
their own words. This strategy can help reinforce what the
client is saying, allow them to reflect back on their own words,
and clear up potential misunderstandings.5
Unconditional positive regard: This technique involves the
therapist accepting the individual without judgment. It is
characterized by a caring attitude that plays an important role
in fostering self-worth, personal growth, and self-awareness.6
Because humanistic therapy is focused on the present, it may
also utilize a practice known as mindfulness to help people
become more aware of themselves and their environment.
Therapists utilize these techniques to support people as they
develop greater self-awareness. These techniques are focused
on solving specific problems; instead, their goal is to encourage
people to view themselves as capable of directing their own
behavior and achieving their unique goals.
You might also like
- Psycho Therapy: Therapy Practices for the Mind, Body and EmotionsFrom EverandPsycho Therapy: Therapy Practices for the Mind, Body and EmotionsNo ratings yet
- 3 ParadigmsDocument9 pages3 Paradigmsasmita sainiNo ratings yet
- Gestalt therapy explained to everyone: Understanding and exploring the here and nowFrom EverandGestalt therapy explained to everyone: Understanding and exploring the here and nowNo ratings yet
- PresentationDocument10 pagesPresentationMaryamkashifNo ratings yet
- BoundlessDocument7 pagesBoundlessFahmi ArdianNo ratings yet
- PDF-6 Humanistic - Exixential ModelDocument23 pagesPDF-6 Humanistic - Exixential ModelChinmayi C SNo ratings yet
- Teori̇ Özetleri̇Document4 pagesTeori̇ Özetleri̇Begüm TopalNo ratings yet
- Methods of TherapyDocument6 pagesMethods of TherapyRomeliza Ann Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Humanistic TherapyDocument27 pagesHumanistic Therapyfabiha anjum100% (2)
- C-Self-Reflection Paper (Peter 2)Document9 pagesC-Self-Reflection Paper (Peter 2)Ras Jemoh100% (1)
- Welcome To The Online Classroom: Disciplines and Ideas in The Applied Social SciencesDocument47 pagesWelcome To The Online Classroom: Disciplines and Ideas in The Applied Social Sciencesdonny riveroNo ratings yet
- GC Unit-II, III, IV, V FULLDocument65 pagesGC Unit-II, III, IV, V FULLAlyna FathimaNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Perspectives in CounselingDocument28 pagesTheoretical Perspectives in CounselingGargi BishtNo ratings yet
- Adiba Final Activity CousellingDocument29 pagesAdiba Final Activity Cousellingadiba KhanNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals To Clinical PsychologyDocument6 pagesFundamentals To Clinical PsychologySurabhi RanjanNo ratings yet
- Clinical CounselingDocument9 pagesClinical CounselingAshna Mei100% (3)
- PsychoanalysisDocument13 pagesPsychoanalysisRENLIE OMADLENo ratings yet
- Client Centered TherapyDocument8 pagesClient Centered TherapyIqbal BaryarNo ratings yet
- Counselling Approaches - A Brief OverviewDocument3 pagesCounselling Approaches - A Brief OverviewknoakesNo ratings yet
- Person-Centred TherapyDocument27 pagesPerson-Centred TherapyShreyasi S100% (1)
- Journal Critique 2Document8 pagesJournal Critique 2ROSVIE APPLE BUENAVENTURANo ratings yet
- Therapeutic ModalitiesDocument11 pagesTherapeutic ModalitiesPamplona FireStation CagayanNo ratings yet
- Theory Critique PaperDocument7 pagesTheory Critique PaperKylie AnneNo ratings yet
- Existential, Gestalt, Behavioral, Cognitive Behavioral and Person Centered Therapy ActivitiesDocument6 pagesExistential, Gestalt, Behavioral, Cognitive Behavioral and Person Centered Therapy ActivitiesBriones, Jesse Abegael ManalansanNo ratings yet
- The Settings, Processes, Methods, and Tools of CounselingDocument2 pagesThe Settings, Processes, Methods, and Tools of Counselingnoel joaquin100% (1)
- CounsellingDocument28 pagesCounsellinggopika100% (1)
- HUMANISMDocument36 pagesHUMANISMAshim SharmaNo ratings yet
- Client Centred TherapyDocument7 pagesClient Centred TherapyMahrukhNo ratings yet
- Individual PsychotherapyDocument9 pagesIndividual PsychotherapyNikita Nelson67% (3)
- Foundation of CounselingDocument5 pagesFoundation of CounselingSushmitaNo ratings yet
- Existential and Humanistic Therapies: Lekshmi Priya.K.B 1 MSC PsychologyDocument39 pagesExistential and Humanistic Therapies: Lekshmi Priya.K.B 1 MSC PsychologyALISHA ARORANo ratings yet
- Different Schools of PsychotherapyDocument10 pagesDifferent Schools of PsychotherapysanaNo ratings yet
- Grp4 Person CenteredDocument16 pagesGrp4 Person CenteredJasper AndalNo ratings yet
- What Is Humanistic CounsellingDocument9 pagesWhat Is Humanistic CounsellingSankalp JainNo ratings yet
- Brief Humanistic and Existential TherapiesDocument17 pagesBrief Humanistic and Existential TherapiesSanchez Roman100% (1)
- PsychotherapiesDocument26 pagesPsychotherapiesLiviaNo ratings yet
- Name Edouard NoemieDocument9 pagesName Edouard NoemienoemieedwardsNo ratings yet
- Psykoterapeut OsloDocument2 pagesPsykoterapeut OsloPsykolog TjenesterNo ratings yet
- Gestalt & Behavioral TherapyDocument4 pagesGestalt & Behavioral TherapyZaib RehmanNo ratings yet
- Dexter ReportDocument6 pagesDexter ReportDarwin Lacson GabrielNo ratings yet
- Application Counseling ApproachesDocument6 pagesApplication Counseling ApproachesWinnie TunayNo ratings yet
- Client Centered TherapyDocument6 pagesClient Centered TherapyMahrukh100% (1)
- Brief Humanistic and Existential TherapyDocument16 pagesBrief Humanistic and Existential TherapyKrishnapriya T SNo ratings yet
- Client Centered TherapyDocument3 pagesClient Centered TherapyDavender VashistNo ratings yet
- Motivational Therapy (Or MT) Is A Combination ofDocument2 pagesMotivational Therapy (Or MT) Is A Combination ofRumana AliNo ratings yet
- Sana AfzalDocument5 pagesSana AfzalMishi BajwaNo ratings yet
- Theories of CounsellingDocument35 pagesTheories of Counsellingkariuki90406978No ratings yet
- 2: Aim and Goals of Counseling PsychologyDocument9 pages2: Aim and Goals of Counseling PsychologyNayyer ShahNo ratings yet
- Intervention Systems Internal ExaminationDocument4 pagesIntervention Systems Internal ExaminationTejas JadhavNo ratings yet
- Counselling ApprochesDocument8 pagesCounselling Approchesamitrawal0100% (1)
- Methods in CounselingDocument25 pagesMethods in CounselingMaryJoyceRamosNo ratings yet
- Rogers Person Centred TheoryDocument18 pagesRogers Person Centred TheoryCourage Chigerwe100% (1)
- Psychotherapy ReportDocument7 pagesPsychotherapy ReportEileen Medina CostoNo ratings yet
- DefinitionDocument5 pagesDefinitionEmma TaylorNo ratings yet
- I. Proponent: Tendency, Which Refers To A Person's Basic Instinct To Succeed at His or Her Highest PossibleDocument5 pagesI. Proponent: Tendency, Which Refers To A Person's Basic Instinct To Succeed at His or Her Highest PossibleJenine CarpioNo ratings yet
- Humanistic Approaches in Counselling andDocument6 pagesHumanistic Approaches in Counselling andمالك مناصرةNo ratings yet
- Existential-Humanistic ApproachDocument21 pagesExistential-Humanistic ApproachGianna MinochaNo ratings yet
- Humanistic Humanistic Therapy Therapy: Group 4Document23 pagesHumanistic Humanistic Therapy Therapy: Group 4Kyra Jane F. DellosaNo ratings yet
- What Is Psychotherapy?Document11 pagesWhat Is Psychotherapy?swathy sudheerNo ratings yet
- Internal Family SystemsDocument3 pagesInternal Family Systemsmarian arguelles100% (10)
- Revisiting Structural Family TherapyDocument2 pagesRevisiting Structural Family TherapyKim ScottNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Introduction To Learning and Behavior 4th Edition Powell DownloadDocument33 pagesTest Bank For Introduction To Learning and Behavior 4th Edition Powell DownloadTeresaMoorecsrby100% (38)
- Theories in Learning PsychologyDocument8 pagesTheories in Learning PsychologyJam Licupa100% (1)
- E Jurnal REBT PDFDocument18 pagesE Jurnal REBT PDFali azkaNo ratings yet
- Negative Effects of Positive ReinforcementDocument14 pagesNegative Effects of Positive ReinforcementLuciano LobatoNo ratings yet
- Uts Lesson 2Document40 pagesUts Lesson 2Sweetzel SenielNo ratings yet
- Oneself/ Personality As An Interaction of Many FactorsDocument16 pagesOneself/ Personality As An Interaction of Many FactorstianNo ratings yet
- Supportive TherapyDocument9 pagesSupportive Therapyejaz2No ratings yet
- Bandura QUIZDocument3 pagesBandura QUIZJayc SaleraNo ratings yet
- Counseling Theory SlidesDocument169 pagesCounseling Theory SlidesKuan Loong100% (2)
- ABA Workshop SlidesDocument162 pagesABA Workshop SlidesMaria AhmedNo ratings yet
- Behavorisme by Karel Samangun C1A119002Document6 pagesBehavorisme by Karel Samangun C1A119002Chaken SamangunNo ratings yet
- School of Saint Anthony: The Effectiveness of Operants in Lowering Tardiness Frequency Among Grade 12 StudentsDocument78 pagesSchool of Saint Anthony: The Effectiveness of Operants in Lowering Tardiness Frequency Among Grade 12 StudentsAloisia Rem RoxasNo ratings yet
- Ray Belden Eckerman Learning and Conditioning TutorialsDocument81 pagesRay Belden Eckerman Learning and Conditioning TutorialsitscindyguanNo ratings yet
- CBT βιβλίαDocument24 pagesCBT βιβλίαEliza KottikaNo ratings yet
- Equivalence Relations and The Reinforcement ContingencyDocument20 pagesEquivalence Relations and The Reinforcement ContingencyEva SkvarčaNo ratings yet
- D M, Id, Ego, SuperegoDocument3 pagesD M, Id, Ego, SuperegoqurratainiNo ratings yet
- RukajatDocument2 pagesRukajatbalqisNo ratings yet
- Adlerian Counseling Consist of PhasesDocument2 pagesAdlerian Counseling Consist of PhasesFrans Dwi OktarezaNo ratings yet
- Motivational Theory (Theory X and Theory Y Maslow Theory)Document22 pagesMotivational Theory (Theory X and Theory Y Maslow Theory)Anirudh Khaneja2033No ratings yet
- Theories of Personality Pre TestDocument99 pagesTheories of Personality Pre TestCLARISSA VICTORIA LUMAINNo ratings yet
- What Is MOTIVATIONDocument3 pagesWhat Is MOTIVATIONAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Operant ConditioningDocument3 pagesOperant ConditioningMark neil a. GalutNo ratings yet
- (EDES113) : An Introduction To The Study of EducationDocument21 pages(EDES113) : An Introduction To The Study of EducationAfika NtandaNo ratings yet
- Davidson and Nevin 1999Document44 pagesDavidson and Nevin 1999jsaccuzzoNo ratings yet
- 10 Techniques To Increase Motivation and WillpowerDocument2 pages10 Techniques To Increase Motivation and WillpowerAlicia GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Learning and Behavior 5th Edition Powell Test Bank DownloadDocument32 pagesIntroduction To Learning and Behavior 5th Edition Powell Test Bank Downloadmirabeltuyenwzp6f100% (32)
- Pro. Ed 2Document10 pagesPro. Ed 2Reynald MatiasNo ratings yet
- The Functions of Observational Learning in The Learning ProcessesDocument6 pagesThe Functions of Observational Learning in The Learning ProcessesmahahajNo ratings yet