Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ultrasonic Sensor Fundamentals
Uploaded by
Вячеслав ГлушакOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ultrasonic Sensor Fundamentals
Uploaded by
Вячеслав ГлушакCopyright:
Available Formats
"Sensor Fundamentals"
5th Session: Ultrasonic Sensor
In this session, the ultrasonic sensor will be introduced.
1 OUTLINE
The ultrasonic sensor detects vehicles, obstructions, etc. in front of and
behind the vehicle by transmitting and receiving ultrasonic waves.
Ultrasonic sensors are installed in the front and rear bumpers, and are used
in the back and clearance sonar systems.
There are two types of ultrasonic sensors: 1) a mid-range distance (under
1.0 m) sensor used to detect obstructions behind the vehicle, and 2) a short-
range distance (under 0.5 m) sensor used to detect obstructions at the
bumper corners.
2 CONSTRUCTION
Ultrasonic sensors have a built-in microphone to transmit/receive ultrasonic waves, as well as a built-in
circuit to calculate the distance to obstructions. The microphone consists of a Piezoelectric element attached
to the case (diaphragm). In addition, the calculation circuit features a silicon filled, waterproof construction.
<Short-Range Distance (Under 0.5 m)> <Mid-Range Distance (Under 1.0 m)>
Microphone Microphone
Circuit Circuit
3 OPERATION
When Alternating Current (AC) at a frequency of several tens of kHz is applied to the Piezoelectric element
inside the microphone, the diaphragm vibrates according to the frequency (inverse Piezoelectric effect),
emitting ultrasonic waves into the air. Conversely, when ultrasonic waves (reflected waves) are received and
the Piezoelectric element vibrates, an AC voltage frequency is generated (Piezoelectric effect) according to
the vibration of the ultrasonic waves. Using the built-in distance calculation circuit, the distance to
obstructions can be detected from the time (T) taking for ultrasonic waves to be emitted and then received.
Ultrasonic Waves
Detection Object
Reception Pulse
Transmission Pulse
(Reflected Waves)
Reflection
Transmission Pulse Reception Pulse
T Time
Distance Calculation
13 SERVICE TECH Vol.489 07-4
You might also like
- Mechatronics Notes22Document23 pagesMechatronics Notes22Arun KumarNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Distance Measurement Using Pulse Echo TechniqueDocument35 pagesUltrasonic Distance Measurement Using Pulse Echo TechniqueAmarjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Design an Ultrasonic Motion DetectorDocument13 pagesDesign an Ultrasonic Motion DetectorKatamba RogersNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic SensorsDocument19 pagesUltrasonic Sensorskrish0690100% (1)
- Footboard Travel Alert SystemDocument40 pagesFootboard Travel Alert SystemSaravanan Viswakarma100% (2)
- Ultrasonic Transducer FundamentalsDocument12 pagesUltrasonic Transducer FundamentalsClaudia Ioana100% (2)
- Buried Bodies Detection Using Ground Penetrating RADARDocument6 pagesBuried Bodies Detection Using Ground Penetrating RADARMuhammad Usman RanaNo ratings yet
- Wave Propogation EffectDocument4 pagesWave Propogation EffectPrashanth ChikkannanavarNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic DetectionDocument8 pagesUltrasonic DetectionSaravanan ViswakarmaNo ratings yet
- Design and Development of Microcontroller Based Ultrasonic Flaw DetectorDocument7 pagesDesign and Development of Microcontroller Based Ultrasonic Flaw DetectorBagusElokNo ratings yet
- Haptic Feedback: Rationale and Source of Our Project IdeaDocument25 pagesHaptic Feedback: Rationale and Source of Our Project IdeasrujanNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic/Optical Sensor Precise DistanceDocument4 pagesUltrasonic/Optical Sensor Precise DistancePonpon KujapyNo ratings yet
- HC sr04Document4 pagesHC sr04Abdullah ZafarNo ratings yet
- Sensors and RTOS: Prof. Chung-Ta KingDocument41 pagesSensors and RTOS: Prof. Chung-Ta Kingymcm2010No ratings yet
- A Life-Detection System For Special Rescuing RobotsDocument5 pagesA Life-Detection System For Special Rescuing RobotsAkshyaNo ratings yet
- What Ultrasonic Waves Are, and How They PropagateDocument17 pagesWhat Ultrasonic Waves Are, and How They PropagateZahir Rayhan JhonNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic SensorsDocument21 pagesUltrasonic Sensorsbatvengeance2355No ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Range Finder Project ReportDocument56 pagesUltrasonic Range Finder Project ReportNishit Chittora47% (15)
- Ultrasonic Sensor CircuitDocument5 pagesUltrasonic Sensor CircuitRajeev Dey100% (1)
- Phase and Group Velocity of Ultrasonics in Liquids PDFDocument5 pagesPhase and Group Velocity of Ultrasonics in Liquids PDFJose GalvanNo ratings yet
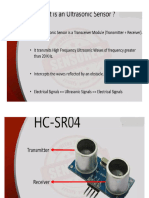
- Guide to Using HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Distance SensorDocument6 pagesGuide to Using HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Distance SensorSreejith Skr100% (1)
- Ultrasonic Sensor (HC-SR04)Document1 pageUltrasonic Sensor (HC-SR04)Dawit BirhanNo ratings yet
- Mate Testing Wei22Document1 pageMate Testing Wei22Hanin ShamillNo ratings yet
- Sonar Signal ProcessingDocument12 pagesSonar Signal ProcessingRamkumar ThiruvenkadamNo ratings yet
- We Already DiscussedDocument71 pagesWe Already Discussedvyshnavi nallaNo ratings yet
- Using Coded Signals To Benefit From Ultrasonic Sensor Crosstalk in Mobile Robot Obstacle AvoidanceDocument6 pagesUsing Coded Signals To Benefit From Ultrasonic Sensor Crosstalk in Mobile Robot Obstacle AvoidancesudharsanankNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound - sensor-HC - SR04Document2 pagesUltrasound - sensor-HC - SR04Geo BabuNo ratings yet
- 2 Intro - To - Ultrasonics 03092013 OKDocument43 pages2 Intro - To - Ultrasonics 03092013 OKferyNo ratings yet
- Marine Radar OverviewDocument25 pagesMarine Radar OverviewNjabulo XimbaNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Distance Meter Embedded System Project Explains About Developing NewDocument63 pagesUltrasonic Distance Meter Embedded System Project Explains About Developing NewSahil SethiNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Motion DetectorDocument9 pagesUltrasonic Motion DetectorMarium AliNo ratings yet
- UNIT 6 Ultrasonic and Infrared SensorsDocument27 pagesUNIT 6 Ultrasonic and Infrared SensorsDương Bá LinhNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonund 012Document35 pagesUltrasonund 012hatemlakherNo ratings yet
- IOT Project POSTERDocument1 pageIOT Project POSTERFemilNo ratings yet
- Ut AscanDocument7 pagesUt AscanEngr Arfan Ali DhamrahoNo ratings yet
- Optoelectronic Devices: Fabrizio BonaniDocument41 pagesOptoelectronic Devices: Fabrizio BonaniBilal Haider TanoliNo ratings yet
- Edp 4 PartDocument4 pagesEdp 4 PartShehreyar MahboobNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic sensor guideDocument4 pagesUltrasonic sensor guidecostpopNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Ultrasonic Testing TechniqueDocument52 pagesIntroduction To Ultrasonic Testing TechniqueDr. Akshay JainNo ratings yet
- Echo CancellationDocument14 pagesEcho CancellationRahul EkhandeNo ratings yet
- C08 Rme PPT1 21221Document45 pagesC08 Rme PPT1 21221DHANANJAY VIJAYKUMAR BILENo ratings yet
- Microwave Sensor Technology HFE0407 - PolivkaDocument8 pagesMicrowave Sensor Technology HFE0407 - Polivkatecnolectronica890No ratings yet
- UT SlidesDocument58 pagesUT SlidesY ShameyaNo ratings yet
- Wall Following Robot Obstacle Avoiding RobotDocument9 pagesWall Following Robot Obstacle Avoiding RobotMuhammad FaisalNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound Distance Measurement and Ultrasonic Doppler EffectDocument4 pagesUltrasound Distance Measurement and Ultrasonic Doppler EffectA N ArunkumarNo ratings yet
- Sonar System: By: Nikhil ShiavdeDocument5 pagesSonar System: By: Nikhil ShiavdeYogesh KedarNo ratings yet
- Sonar - Is Formed As An Abbreviation For Sound Navigation and RangingDocument2 pagesSonar - Is Formed As An Abbreviation For Sound Navigation and RangingLuelsonCordovaDeclaradorNo ratings yet
- Operation of a Pulse RadarDocument2 pagesOperation of a Pulse RadarVaibhav VyasNo ratings yet
- UltrasoundDocument78 pagesUltrasoundAmeer MattaNo ratings yet
- EF03085-HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Module User Guide PDFDocument6 pagesEF03085-HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Module User Guide PDF1000kyNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic SensorTraining MaterialDocument15 pagesUltrasonic SensorTraining MaterialToan PhamNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic SensorTraining MaterialDocument15 pagesUltrasonic SensorTraining MaterialToan PhamNo ratings yet
- ACOUSTIC EMISSION MONITORINGDocument47 pagesACOUSTIC EMISSION MONITORINGSaravana Kumar MNo ratings yet
- Life Detection System Based on L-S Band MicrowavesDocument24 pagesLife Detection System Based on L-S Band MicrowavesRahul KmNo ratings yet
- VRhistoryAppfuture (TMazuryk - Etal) 19 30Document12 pagesVRhistoryAppfuture (TMazuryk - Etal) 19 30sebastian sotoNo ratings yet
- Acoustic Doppler EffectDocument9 pagesAcoustic Doppler EffectJose GalvanNo ratings yet
- UT NotesDocument8 pagesUT NotesAbhijith ChandranNo ratings yet
- SONAR - NavigationDocument25 pagesSONAR - NavigationKarlaColinaNo ratings yet
- PL2303CheckChipVersion ReadMeDocument1 pagePL2303CheckChipVersion ReadMezeenhaddadNo ratings yet
- C Make ListsDocument3 pagesC Make ListspiptendoNo ratings yet
- Read - Me - 17 10 2019Document65 pagesRead - Me - 17 10 2019Вячеслав ГлушакNo ratings yet
- Passenger Presence SensorDocument1 pagePassenger Presence SensorВячеслав ГлушакNo ratings yet
- Service Manual R721 TYPE GOVERNORDocument48 pagesService Manual R721 TYPE GOVERNORВячеслав ГлушакNo ratings yet
- Determining The Injection TimingDocument4 pagesDetermining The Injection TimingВячеслав ГлушакNo ratings yet
- Knock SensorDocument1 pageKnock SensorTommy TribbianiNo ratings yet
- PL2303 DriverInstallerv1.8.0 ReleaseNoteDocument4 pagesPL2303 DriverInstallerv1.8.0 ReleaseNoteas12e34No ratings yet
- Composition and Construction of ECD-V3 Pump SystemDocument4 pagesComposition and Construction of ECD-V3 Pump SystemВячеслав ГлушакNo ratings yet
- Service Manual RSV GovernorDocument33 pagesService Manual RSV GovernorВячеслав Глушак100% (1)
- ECD Sensors OperationDocument4 pagesECD Sensors OperationВячеслав ГлушакNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Mounted Multiplex Communication and Controller Area NetworkDocument4 pagesVehicle Mounted Multiplex Communication and Controller Area NetworkВячеслав ГлушакNo ratings yet
- Types of Systems in ECD-V SeriesDocument4 pagesTypes of Systems in ECD-V SeriesВячеслав ГлушакNo ratings yet
- Fuel Injection Pump Technical Hint for Land CruiserDocument45 pagesFuel Injection Pump Technical Hint for Land CruiserВячеслав ГлушакNo ratings yet
- Intake Restriction ControlDocument4 pagesIntake Restriction ControlВячеслав ГлушакNo ratings yet
- 8th Session Injector Construction and OperationDocument4 pages8th Session Injector Construction and OperationВячеслав ГлушакNo ratings yet
- El Sistema Egr en Common Rail PDFDocument4 pagesEl Sistema Egr en Common Rail PDFJuan Carlos Neyra BlasNo ratings yet
- Vehicle CAN Communication BasicsDocument4 pagesVehicle CAN Communication BasicsВячеслав ГлушакNo ratings yet
- HTTP Contents2.Ss - Denso.co - JP Sics Tsics5 Secu Edemo - Asp Docpic Doc5 PDF 5 52900064EDocument91 pagesHTTP Contents2.Ss - Denso.co - JP Sics Tsics5 Secu Edemo - Asp Docpic Doc5 PDF 5 52900064EВячеслав ГлушакNo ratings yet
- Communication Protocol and FramesDocument4 pagesCommunication Protocol and FramesВячеслав ГлушакNo ratings yet
- Car Air Conditioning Operation GuideDocument68 pagesCar Air Conditioning Operation GuideВячеслав ГлушакNo ratings yet
- HTTP Contents2.ss - Denso.co - JP Sics Tsics5 Secu Edemo - Asp Docpic Doc5 PDF 5 50400217EDocument125 pagesHTTP Contents2.ss - Denso.co - JP Sics Tsics5 Secu Edemo - Asp Docpic Doc5 PDF 5 50400217EВячеслав ГлушакNo ratings yet
- EMV (Electro-Multi Vision) : General EditionDocument43 pagesEMV (Electro-Multi Vision) : General EditionВячеслав ГлушакNo ratings yet
- Fuel rail components and operationDocument4 pagesFuel rail components and operationВячеслав ГлушакNo ratings yet
- Communication Protocol and FramesDocument4 pagesCommunication Protocol and FramesВячеслав ГлушакNo ratings yet
- HTTP Contents2.ss - Denso.co - JP Sics Tsics5 Secu Edemo - Asp Docpic Doc5 PDF 0 00500196EDocument58 pagesHTTP Contents2.ss - Denso.co - JP Sics Tsics5 Secu Edemo - Asp Docpic Doc5 PDF 0 00500196EВячеслав Глушак100% (1)
- Repair Car AC and Prevent Climate ChangeDocument68 pagesRepair Car AC and Prevent Climate ChangeВячеслав ГлушакNo ratings yet
- Operation: Air ConditioningDocument26 pagesOperation: Air ConditioningВячеслав ГлушакNo ratings yet
- CAN Features and Access MethodsDocument4 pagesCAN Features and Access MethodsВячеслав ГлушакNo ratings yet
- Infrasound StalkerDocument9 pagesInfrasound StalkerAneek ThaparNo ratings yet
- Solucionario Music I UT01 PDFDocument9 pagesSolucionario Music I UT01 PDFClara VírsedaNo ratings yet
- Sokolova M A Teoreticheskaya Fonetika Angliiskogo Yazyka PDFDocument97 pagesSokolova M A Teoreticheskaya Fonetika Angliiskogo Yazyka PDFDamirZhukenovNo ratings yet
- Speech Recognition Using Ic HM2007Document31 pagesSpeech Recognition Using Ic HM2007Nitin Rawat100% (4)
- Hfe JBL Loudspeaker Systems 1973 enDocument24 pagesHfe JBL Loudspeaker Systems 1973 enfrbNo ratings yet
- Hfe Onkyo ht-r758 Service enDocument99 pagesHfe Onkyo ht-r758 Service enRobson LuizNo ratings yet
- Amca 300Document37 pagesAmca 300Erwin MaldoNo ratings yet
- Thesis CompleteDocument107 pagesThesis CompleteJac MeNo ratings yet
- Tori SphericalDocument62 pagesTori SphericalWebsoft Tech-HydNo ratings yet
- In The Place of SoundDocument23 pagesIn The Place of Soundrodrigoguaba0% (1)
- Rules For Proper Gain Structure: Rule #1 Rule #2 Rule #3Document2 pagesRules For Proper Gain Structure: Rule #1 Rule #2 Rule #3Alfonso Santimone100% (3)
- FileDocument20 pagesFiledragoon963No ratings yet
- Explore DSP effects on vocalsDocument3 pagesExplore DSP effects on vocalsJanFrancoGlancNo ratings yet
- Beam Behavior in Nearfield of Vibrating PistonDocument12 pagesBeam Behavior in Nearfield of Vibrating PistonNothing ConnoisseurNo ratings yet
- Control and Optimization of Directional Audible Sound Beams Using Ultrasonic TransducersDocument6 pagesControl and Optimization of Directional Audible Sound Beams Using Ultrasonic TransducerslakisNo ratings yet
- 2017 NSV G Eng (Vers Blue)Document142 pages2017 NSV G Eng (Vers Blue)Saprudin -No ratings yet
- Physics Does Recording Studio DimensionsDocument7 pagesPhysics Does Recording Studio Dimensionsziggie_lenzNo ratings yet
- Cox Dantonio ReviewDocument3 pagesCox Dantonio ReviewLavkeshKumarNo ratings yet
- Sound Waves Practice Problems SolvedDocument16 pagesSound Waves Practice Problems SolvedAlexa AquinoNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Piezoelectric TransducersDocument50 pagesCharacteristics of Piezoelectric Transducersextremo1No ratings yet
- EPICON MANUAL - Setup Guide for DALI EPICON LoudspeakersDocument26 pagesEPICON MANUAL - Setup Guide for DALI EPICON Loudspeakersmark_ferdinand_2No ratings yet
- Cavitation Monitoring in Hydraulic TurbinesDocument9 pagesCavitation Monitoring in Hydraulic TurbinesEd Gar YundaNo ratings yet
- Appreciating The Art of Music and DancingDocument45 pagesAppreciating The Art of Music and DancingLuna MoonNo ratings yet
- Olson 1957 IDocument737 pagesOlson 1957 IAdamadios Vasilis KaliabetsosNo ratings yet
- International Standard: Test Code For Machine Tools - Determination of The Noise EmissionDocument11 pagesInternational Standard: Test Code For Machine Tools - Determination of The Noise EmissionAnonymous 2SQDbt2No ratings yet
- Laws of Reflection OfsoundDocument17 pagesLaws of Reflection OfsoundCharukesh SNo ratings yet
- Mixing For God PDFDocument196 pagesMixing For God PDFPautaNo ratings yet
- Acoustic DesignDocument44 pagesAcoustic DesignDennis Mari Justiniano67% (3)
- Atomic AmpliFire Manual V1.0.0Document44 pagesAtomic AmpliFire Manual V1.0.0neckhumbuckerNo ratings yet
- Sound Question BankDocument3 pagesSound Question BankAgam PiperseniaNo ratings yet