Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EE1000 DC Networks Problem Set
Uploaded by
Amit DipankarCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EE1000 DC Networks Problem Set
Uploaded by
Amit DipankarCopyright:
Available Formats
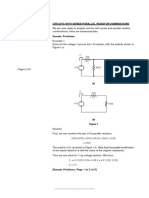
DC Networks - Problem Set
Basic Electrical Engineering (Code: EE-1000) January 15, 2022
Department of EE, NIT Rourkela
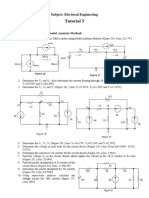
1. For the circuit shown in Fig. 1, find the potential differences between points C, E (VCE ) and
A, G (VAG ). [ 8.5 V, 30.5 V ]
A B E F
5Ω 2Ω
5Ω
12 V 7Ω 4Ω 20 V
20 V
D C H G
12 Ω 4Ω
Figure 1: Q1.
2. In the circuits with dependent voltage and current sources, find
(a) the currents i1 and i2 in the circuit shown in Fig. 2(a),
(b) the voltage v in the circuit shown in Fig. 2(b),
(c) the voltage v in the circuit shown in Fig. 2(c),
(d) i1 and i2 in the circuit shown in Fig. 2(d). [ (a) 3.59 A, 4.47 A, (b) 3 V, (c) 3.73 V, (d) 6 A, 1 A ]
i1 11 Ω i2 3Ω
v -
2Ω +
4A 5Ω 3Ω 5A 2Ω 3v 23 V
+
6i1
-
(a) Current dependent voltage source. (b) Voltage dependent current source.
-
+
2Ω i1 i2
5v
-
+
v
4Ω
24 V 3Ω 10 A 1Ω 3i2 6Ω
2Ω
(c) Voltage dependent voltage source. (d) Current dependent current source.
Figure 2: Q2.
3. Find Vab in the circuit shown in Fig. 3.
Please go on to the next page. . .
EE-13111 Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering Page 2 of 7
10 V
a
1Ω +
i1 5i1 -
+ V1
+
20 V V1 10 A Vab
- 10 V
-b
Figure 3: Q3.
Sol: i1 = 10 A, V1 = (5i1 -i1 ) - 20 = 60 V. Vab ⇒ Va - 10 + V1 - 10 = Vb . [-40 V]
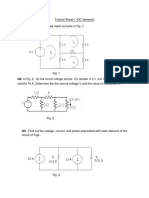
4. Determine the currents i1 , i2 and i3 of the network shown in Fig. 4 using Mesh analysis. []
5Ω 1Ω
20 V
12 Ω i3 25 V
25 V i1 i2 10 V
12 Ω 2Ω 5Ω 5Ω
6Ω 11 Ω
10 V i1 5Ω i2 4A
i3
25 Ω 7Ω
(a) i1 , i2 , i3 = 0.85 A, 1.02 A, 0.39 A. (b) i1 , i2 , i3 = 2.78 A, 4 A, 0.68 A.
Figure 4: Q4 - Mesh analysis.
5. Source conversion technique.
(a) By subsequent source conversions, find the current i in the circuit shown in Fig. 5 (a).
(b) Use source conversion technique to find the current flowing through the 2 Ω resistor present
in the circuit shown in Fig. 5 (b). [ (a) -32/19 A, (b) 5 A ]
6. Find the node voltages V1 and V2 in the circuits shown in Fig. 6 using Nodal analysis. []
7. Superposition technique.
(a) With the help of superposition theorem, compute the current flowing through the branch
ab in the circuit shown in Fig. 7 (a).
(b) Using superposition theorem, find the current flowing through the 10 Ω resistor in the
circuit shown in Fig. 7 (b). [(a) -3 A, (b) 10/13 A]
8. Using superposition theorem, find the voltage V in the circuit shown in Fig. 8. [12 V]
Please go on to the next page. . .
EE-13111 Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering Page 3 of 7
3Ω 2Ω 5Ω i 2Ω
i
12 V 6Ω 10 A 7A 5Ω 10 Ω 5A
10 Ω
(a) (b)
Figure 5: Source conversion technique.
1 2 1 2
1Ω 2Ω 5Ω
2Ω 3Ω 4Ω 7Ω
1A 2Ω 1Ω 2A
10 V 25 V
0 0
(a) V1 = 10/3 V, V2 = 8/3 V (b) V1 = 6.42 V, V2 = 8.19 V
7Ω
2Ω
1 1
3 2 2
2Ω 2i
12 A i
7.5 A 11 Ω 1Ω 10 A 7Ω 3Ω
0 0
(c) V1 = 25.14 V, V2 = -9.78 V (d) V1 = 21.9 V, V2 = 20.6 V
Figure 6: Nodal analysis.
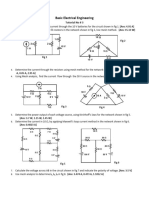
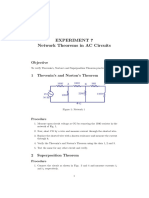
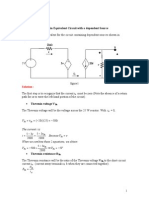
9. Find the Thevenin’s and Norton’s equivalent circuits across the Load of the networks shown
in Fig. 9.
10. Find the Thevenin’s and Norton’s equivalent circuits across the Load of the networks with
dependent voltage and current sources shown in Fig. 10.
11. For the network shown in Fig. 11, find the value of RL for maximum power transfer condition
and find the maximum power transfer to RL .
Question 11 continues on the next page. . .
EE-13111 Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering Page 4 of 7
a b
2Ω
15 V 2Ω
10 V 5A
5V
6A 7Ω 12 Ω 7A 10 Ω
7Ω
2A
3Ω
(a) (b)
Figure 7: Superposition technique.
6Ω 2Ω
20 V
+
30 V 5A V 3Ω V/3 +
-
-
Figure 8: Superposition technique.
Question 11 continues on the next page. . .
EE-13111 Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering Page 5 of 7
5Ω 2Ω
Load
1Ω
Load
3Ω 4Ω
2A
10 Ω 4Ω
15 V 3Ω 2Ω
0.5 Ω
12 V
(a) (b)
5V
3A
6A
6Ω
Load 1.5 Ω 6Ω
Load
2.5 A 10 Ω 1Ω 12 Ω 2Ω 5Ω
2.5 A
2Ω
(c) (d)
Figure 9: Q9 - Networks with independent voltage and current sources.
Question 11 continues on the next page. . .
EE-13111 Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering Page 6 of 7
V -
+
-
+
3Ω 6i i 6Ω 8Ω 1Ω
3Ω
Load Load
10 V 3Ω 1Ω 5V 2.5 Ω
+
V/3 -
(a) (b)
10 V
2Ω 7Ω Load
Load i 5Ω
+ 2Ω
2V 10 Ω V 3A 8 Ω 11 Ω 3.5i 3Ω
-
7V
(c) (d)
Figure 10: Q10 - Circuits with independent and dependent voltage and current sources.
Question 11 continues on the next page. . .
EE-13111 Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering Page 7 of 7
3Ω 9Ω
5A 10 Ω 10 A 10 Ω RL RL
12 24 V
(a) (b)
3Ω 0.5 Ω
3Ω
10 A 10 Ω RL 15 V 3Ω 2Ω RL
12
(c) (d)
2Ω
5i 5Ω RL
10
(e)
Figure 11: Q11 - Maximum power transfer theorem.
End
You might also like
- George Salvan Architectural Utilities 2 Electrical and Mechanical Equipment PDFDocument434 pagesGeorge Salvan Architectural Utilities 2 Electrical and Mechanical Equipment PDFclainNo ratings yet
- JB - Gupta Objective PDFDocument840 pagesJB - Gupta Objective PDFSiva Prakash100% (1)
- CSS Selector Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesCSS Selector Cheat SheetRodrigo-5553974No ratings yet
- Electrician job hazard analysisDocument1 pageElectrician job hazard analysisZaul tatingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04 Sedra Solutions PDFDocument50 pagesChapter 04 Sedra Solutions PDFMaryam Sana83% (6)
- Compressor Tech May 2013Document89 pagesCompressor Tech May 2013H.a. UlicesNo ratings yet
- Method Statement (RC Slab)Document3 pagesMethod Statement (RC Slab)group2sd131486% (7)
- Teaching Guide 2Document172 pagesTeaching Guide 2Floura Sparks100% (1)
- Pulp and Paper IndustryDocument6 pagesPulp and Paper IndustrySaad AhmedNo ratings yet
- Code of Practice On Environmental Health (COPEH) 1998Document24 pagesCode of Practice On Environmental Health (COPEH) 1998Trang NgoNo ratings yet
- # 1 (7 Problems)Document8 pages# 1 (7 Problems)wl0o0dyNo ratings yet
- Assignment1 Ele411Document2 pagesAssignment1 Ele411Fatin Nur Syahirah AzharNo ratings yet
- MCQ Gate by RK KanodiaecDocument440 pagesMCQ Gate by RK KanodiaecViswakarma ChakravarthyNo ratings yet
- EEE-201 Circuits Theory I Homework #2Document2 pagesEEE-201 Circuits Theory I Homework #2lillyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1satya prakashNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Cap05Document8 pagesEjercicios Cap05Miguel LiceagaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits For Engineers (EC1000) : Lecture-4 Network TheoremsDocument11 pagesElectrical Circuits For Engineers (EC1000) : Lecture-4 Network TheoremsnithishNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 Nodal AnalysisDocument2 pagesTutorial 5 Nodal AnalysisKailash ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Solution Assignment 5Document8 pagesSolution Assignment 5Ahmed JamalNo ratings yet
- Mert Terzi 150718061 LabReport1Document5 pagesMert Terzi 150718061 LabReport1Mert TerziNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 1 DC NetworkDocument4 pagesTutorial Sheet 1 DC NetworkAbhijeet100% (2)
- Shree VEDA GATE Institutions: NW Crpt-1Document7 pagesShree VEDA GATE Institutions: NW Crpt-1Jimmygadu007No ratings yet
- Kirchhoff's Laws circuit problemsDocument2 pagesKirchhoff's Laws circuit problemsSajan MaharjanNo ratings yet
- Node and Supernode Final 2Document10 pagesNode and Supernode Final 2Ellen Kay CacatianNo ratings yet
- Solutions of Homework ProblemsDocument21 pagesSolutions of Homework ProblemsHusni MustafaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document2 pagesTutorial 3dareludumNo ratings yet
- Determine The Voltage at Each Labelled Node and The Current Through Each Resistor. (Answer: V 3.333 V, V 2.333 V, I 0.667 A, I 0.333 A, I 0.333 A)Document7 pagesDetermine The Voltage at Each Labelled Node and The Current Through Each Resistor. (Answer: V 3.333 V, V 2.333 V, I 0.667 A, I 0.333 A, I 0.333 A)TJ20 042WAN NUR'AINUN 'AFIFAHNo ratings yet
- EE101 Assignment Waveforms, Circuits (40chDocument3 pagesEE101 Assignment Waveforms, Circuits (40chBikash SahNo ratings yet
- DC Circuit TheoremsDocument75 pagesDC Circuit TheoremsRohit SinghNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits Chapter 4 Node Voltage Method ProblemsDocument32 pagesElectrical Circuits Chapter 4 Node Voltage Method ProblemsHorn Kim HanNo ratings yet
- EE 1100 Assignment 1 circuit analysis and calculationsDocument3 pagesEE 1100 Assignment 1 circuit analysis and calculationsShivani ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Short Test I 2019 PDFDocument5 pagesShort Test I 2019 PDFNaiker KaveetNo ratings yet
- National Institute of Technology Karnataka, Surathkal: NITK-Surathkal EE DeptDocument2 pagesNational Institute of Technology Karnataka, Surathkal: NITK-Surathkal EE DeptAndrewNo ratings yet
- Assignments 5Document4 pagesAssignments 5Ahmed Jamal100% (1)
- Analog Crash Course Workbook GaDocument54 pagesAnalog Crash Course Workbook GaAbhishek RajNo ratings yet
- EENG223/INFE221 Final Exam Circuit Theory I/Electric CircuitsDocument7 pagesEENG223/INFE221 Final Exam Circuit Theory I/Electric Circuitskwakwa4No ratings yet
- © All Rights Reserved by Gateforum Educational Services Pvt. Ltd. No Part of This Booklet May Be Reproduced or Utilized in Any Form Without TheDocument18 pages© All Rights Reserved by Gateforum Educational Services Pvt. Ltd. No Part of This Booklet May Be Reproduced or Utilized in Any Form Without Theakhtar_140No ratings yet
- Major 1 Previous From (2018-2021) PDFDocument48 pagesMajor 1 Previous From (2018-2021) PDFfatima alyammahyNo ratings yet
- ESE Questions Bank EE NetworkDocument12 pagesESE Questions Bank EE NetworkgregNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering Tutorial 2Document5 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering Tutorial 2RajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document20 pagesChapter 2badrilaminNo ratings yet
- Bölüm Soruları - 5th-EditionDocument14 pagesBölüm Soruları - 5th-EditionBee MiteNo ratings yet
- Exercise Problems #1: + V + 2 V 4 V + 3 A 2 ADocument1 pageExercise Problems #1: + V + 2 V 4 V + 3 A 2 ADavid WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Test 1 Eee121 Jun2020Document4 pagesTest 1 Eee121 Jun2020Nabil ZamriNo ratings yet
- Sheet 4-1Document4 pagesSheet 4-1bodesaid2002No ratings yet
- Assignment 1: BasicDocument3 pagesAssignment 1: Basicits me RaviNo ratings yet
- ESc201A HA1 02 - 08 19 PDFDocument2 pagesESc201A HA1 02 - 08 19 PDFraj sahuNo ratings yet
- RK Kanodia Ece McqsDocument400 pagesRK Kanodia Ece Mcqsprince krNo ratings yet
- 101 Milestone Problems On Electronics CommunicationDocument31 pages101 Milestone Problems On Electronics CommunicationAmandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Elec-275 Final Examination April 2012Document4 pagesElec-275 Final Examination April 2012YoussoufAdelekeNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5Document8 pagesTutorial 5Muhammad FauziNo ratings yet
- ESC201 Assignment 1Document3 pagesESC201 Assignment 1garud2221No ratings yet
- Buku DiodaDocument8 pagesBuku Diodanaru_chan1003No ratings yet
- EE8251-Circuit Theory AT I QN Bank New FormatDocument15 pagesEE8251-Circuit Theory AT I QN Bank New FormatKeerthiSahaNo ratings yet
- ESC201 Assignment 2Document3 pagesESC201 Assignment 2garud2221No ratings yet
- Expt 6Document2 pagesExpt 6HARSH RAINo ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering E E E D: E 223 Circuit Theory I I 221 - Electrical Circuits Midterm Exam Spring 2009-10Document6 pagesFaculty of Engineering E E E D: E 223 Circuit Theory I I 221 - Electrical Circuits Midterm Exam Spring 2009-10JOSE LUIS LEON RUBIANONo ratings yet
- 2.tutorial 2Document4 pages2.tutorial 2Harsh SameerNo ratings yet
- Example 4 1 Circuits IntroductionDocument4 pagesExample 4 1 Circuits IntroductionDiego Escobar MoncadaNo ratings yet
- Thevenin Equivalent Circuit With A Dependent Source ExampleDocument6 pagesThevenin Equivalent Circuit With A Dependent Source ExampleMohammed IsmailNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Session 16 Circuit Series-Parallel Resistor CombinationsDocument3 pagesWeek 6 Session 16 Circuit Series-Parallel Resistor CombinationsJhan Jovyn CuestaNo ratings yet
- ExCap5 PDFDocument9 pagesExCap5 PDFChorrinha ChorraNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law and Circuit Analysis ProblemsDocument11 pagesOhm's Law and Circuit Analysis ProblemsVladimir KijimaNo ratings yet
- 1.tutorial 1Document3 pages1.tutorial 1Harsh SameerNo ratings yet
- Revision Exercise DiodesDocument4 pagesRevision Exercise DiodesAlvin TanNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit Theory NotesDocument3 pagesElectric Circuit Theory Notesezrah ogoriNo ratings yet
- Chapt 04Document14 pagesChapt 04SakibNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- Four Probe MethodDocument6 pagesFour Probe MethodAmit DipankarNo ratings yet
- EE1000 Problem Set RMS Avg FFDocument1 pageEE1000 Problem Set RMS Avg FFAmit DipankarNo ratings yet
- EE1000 Problem Set RMS Avg FFDocument1 pageEE1000 Problem Set RMS Avg FFAmit DipankarNo ratings yet
- EE1000 Problem Single Phase AC CircuitsDocument4 pagesEE1000 Problem Single Phase AC CircuitsAmit DipankarNo ratings yet
- Bar PendulumDocument7 pagesBar PendulumAmit DipankarNo ratings yet
- Diode CharactersticsDocument9 pagesDiode CharactersticsAmit DipankarNo ratings yet
- Newton RingDocument4 pagesNewton RingAmit DipankarNo ratings yet
- Diffraction GartingDocument8 pagesDiffraction GartingAmit DipankarNo ratings yet
- Lee DiskDocument4 pagesLee DiskAmit DipankarNo ratings yet
- COMPARING MAGNETIC MOMENTS OF TWO MAGNETSDocument11 pagesCOMPARING MAGNETIC MOMENTS OF TWO MAGNETSAmit DipankarNo ratings yet
- Example For Writing Records Experiment 4Document5 pagesExample For Writing Records Experiment 4Amit DipankarNo ratings yet
- Newton RingDocument4 pagesNewton RingAmit DipankarNo ratings yet
- List of ExperimentDocument1 pageList of ExperimentAmit DipankarNo ratings yet
- Four Probe MethodDocument6 pagesFour Probe MethodAmit DipankarNo ratings yet
- COMPARING MAGNETIC MOMENTS OF TWO MAGNETSDocument11 pagesCOMPARING MAGNETIC MOMENTS OF TWO MAGNETSAmit DipankarNo ratings yet
- 121ee0664 - Assignment 1 Math (Vaddi Karthik)Document4 pages121ee0664 - Assignment 1 Math (Vaddi Karthik)Amit DipankarNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1, 121CH0104Document2 pagesAssignment 1, 121CH0104Amit DipankarNo ratings yet
- 121CS0232-Maths AssignmentDocument2 pages121CS0232-Maths AssignmentAmit DipankarNo ratings yet
- Propeller Tolerances and Inspection - John Carlton PDFDocument17 pagesPropeller Tolerances and Inspection - John Carlton PDFhenryNo ratings yet
- DebugDocument295 pagesDebugkarthikNo ratings yet
- Wire Size Chart NEC 2011Document1 pageWire Size Chart NEC 2011Gustavo TovarNo ratings yet
- Dual Output Ac Current - Voltage TransducerDocument7 pagesDual Output Ac Current - Voltage TransducerMagendran SurulivelNo ratings yet
- 36 Insp Pad Plate A OriDocument2 pages36 Insp Pad Plate A OriHastagnya Jangan LupaNo ratings yet
- Melab1 Exp3Document11 pagesMelab1 Exp3John Ferben Sallena DepnagNo ratings yet
- Four Probe ExperimentDocument2 pagesFour Probe ExperimentAryan VijayNo ratings yet
- V 0 S 2 P 5Document78 pagesV 0 S 2 P 5DELIAL-ABABNo ratings yet
- Pedestal Column For Tower-Usd: Ast (MM 2) Ab (MM 2)Document18 pagesPedestal Column For Tower-Usd: Ast (MM 2) Ab (MM 2)Joy lauriaNo ratings yet
- Experiment #8 - Slender MemberDocument4 pagesExperiment #8 - Slender MemberLuís Alberto Tang YorisNo ratings yet
- Unit I Acoustics Planning For Noise, STC, NRCDocument9 pagesUnit I Acoustics Planning For Noise, STC, NRCKavya DesaiNo ratings yet
- 123 ChemDocument4 pages123 Chemoperator daazNo ratings yet
- PMAS-Arid Agriculture University RawalpindiDocument3 pagesPMAS-Arid Agriculture University RawalpindiAli AzanNo ratings yet
- Safety PrecautionDocument1 pageSafety PrecautionSJ Chua100% (1)
- Tremie SealsDocument12 pagesTremie SealsWalid MghazliNo ratings yet
- Park Residence BrochureDocument86 pagesPark Residence Brochureahmed ahmedNo ratings yet
- Surge Protection Device - Product Selection GuideDocument36 pagesSurge Protection Device - Product Selection GuideRahul DevaNo ratings yet
- AdjustmentDocument48 pagesAdjustmentesther jaimeNo ratings yet
- Technical Bulletin: Control Joint Placement in Gypsum Board AssembliesDocument5 pagesTechnical Bulletin: Control Joint Placement in Gypsum Board AssembliesAllen liuNo ratings yet
- CV - Teguh Agung Kusuma - COC I - Chief Mate - AHTS, Survey, AWBDocument7 pagesCV - Teguh Agung Kusuma - COC I - Chief Mate - AHTS, Survey, AWBTeguh Agung KusumaNo ratings yet
- Check Valve VickersDocument15 pagesCheck Valve Vickersعلي عائشة100% (1)
- LinkDocument2 pagesLinkFresh aliveNo ratings yet