Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Language of Chemistry Test: Marks: 40
Uploaded by
Vaishnavi Rajgopal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views2 pagesThe document is a 13 question chemistry test assessing understanding of key chemistry concepts such as symbols, atomicity, valency, chemical formulas, equations, and reactions. It contains multiple choice and short answer questions testing the meaning of terms like acid radical and basic radical. It also contains questions requiring students to write balanced chemical equations for word equations describing various chemical reactions between substances.
Original Description:
Original Title
Lang of Chem
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document is a 13 question chemistry test assessing understanding of key chemistry concepts such as symbols, atomicity, valency, chemical formulas, equations, and reactions. It contains multiple choice and short answer questions testing the meaning of terms like acid radical and basic radical. It also contains questions requiring students to write balanced chemical equations for word equations describing various chemical reactions between substances.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views2 pagesThe Language of Chemistry Test: Marks: 40
Uploaded by
Vaishnavi RajgopalThe document is a 13 question chemistry test assessing understanding of key chemistry concepts such as symbols, atomicity, valency, chemical formulas, equations, and reactions. It contains multiple choice and short answer questions testing the meaning of terms like acid radical and basic radical. It also contains questions requiring students to write balanced chemical equations for word equations describing various chemical reactions between substances.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
The Language of Chemistry Test
Marks: 40
Q1. What is a symbol? What information does it convey? (2)
Q2. Why is the symbol S for Sulphur, but Na for Sodium and Si for Silicon? (2)
Q3. What do the following symbols stand for? (2)
a) H b) H2 c) 2H d) 2H2
Q4. What is meant by atomicity? Name a diatomic element. (2)
Q5. a) Explain the terms valency and variable valency (2)
b) How are the elements with variable valency named? Explain with an example.
Q6. Give the formula and valency of (2)
a) aluminate
b) chromate
c) aluminium
d) cupric
Q7. a) What is a chemical formula? (2)
b) What is the significance of a formula? Give an illustrate.
Q8. I] What do you understand by the following terms? (8)
A) Acid radical B) Basic radical
II]write the basic and acidic radicals of the following and then write the
chemical formulae of these compounds.
a) Barium sulphate
b) Bismuth nitrate
c) calcium bromide
d) Ferrous sulphide
e) Chromium sulphate
f) Calcium silicate
g) Stannic oxide
h) Sodium Zincate
i) Magnesium phosphate
j) Sodium thiosulphate
k) Nickel-bi-sulphate
l) Potassium manganate
Q9. Write the chemical formulae of sulphates of Aluminium, Ammonium and
Zinc. (2)
Q10. What is a chemical equation? Why is it necessary to balance it? (2)
Q11. State the information conveyed by the following equation. (2)
Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq)→ ZnCl2 (aq) + H2
What is the limitation of reaction given above.
Q12. Give Balanced Reaction for the following by particle equation method (2)
I] Reaction of excess ammonia with chlorine- Ammonia as a reducing agent
II] Oxidation of Lead [II] Sulphide by ozone
Q13. Write the balanced equation of the following word equations. (10)
1. Potassium Bicarbonate + Sulphuric Acid → Potassium Sulphate + Carbon
Di oxide + Water
2. Iron + Sulphuric acid →Ferrous Sulphate + hydrogen
3. Silver Nitrate → Silver + Nitrogen di oxide + Oxygen
4. Copper + Nitric acid → Copper nitrate + Nitric oxide + water
5. Ammonia + Oxygen → nitric oxide + water
6. Barium Chloride + Sulphuric acid → Barium sulphate + Hydrochloric acid
7. Zinc Sulphide + Oxygen → Zinc oxide + sulphur di oxide
8. Potassium Dichromate + sulphuric acid → potassium sulphate + chromium
Chromium sulphate + water +oxygen
9. Sodium hydroxide + sulphuric acid → sodium sulphate + water
10. Sulphur + nitric acid → Sulphuric acid + nitrogen dioxide + water
You might also like
- Electrochemistry: Chemistry 30 WorksheetsDocument49 pagesElectrochemistry: Chemistry 30 Worksheetsdan anna stylesNo ratings yet
- Water Proofing MaterialsDocument53 pagesWater Proofing MaterialsDarshit ShahNo ratings yet
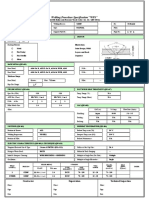
- WPSDocument2 pagesWPSAlam MD Sazid100% (1)
- 10th Chemistry Revision Assignments - All Chapters CombinedDocument11 pages10th Chemistry Revision Assignments - All Chapters CombinedYash KapoorNo ratings yet
- Wa0020.Document3 pagesWa0020.Guddi SinghNo ratings yet
- DPP1 SBlock Advan6264893396548698825Document4 pagesDPP1 SBlock Advan6264893396548698825Drushya SalunkeNo ratings yet
- Latihan Chemical FormulaeDocument14 pagesLatihan Chemical FormulaenaimahNo ratings yet
- Worksheet-1 (Chemical Reaction)Document6 pagesWorksheet-1 (Chemical Reaction)Sachin Garg100% (1)
- Chemistry Chapter 1.exercise 1ADocument28 pagesChemistry Chapter 1.exercise 1AAsifNo ratings yet
- Objective: Alpha Academy ChemistryDocument1 pageObjective: Alpha Academy Chemistrymuhammad AsimNo ratings yet
- Answer Two Questions From Section A, One Question From Section B, Two Questions From Section C and One Other Question. Section ADocument6 pagesAnswer Two Questions From Section A, One Question From Section B, Two Questions From Section C and One Other Question. Section AKarren MakamureNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument6 pagesChemistryAden.No ratings yet
- Chemical Formular of Compounds: Valency ElementDocument3 pagesChemical Formular of Compounds: Valency ElementNsereko AmilNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationDocument5 pagesNcert Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationJeel AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1a ChemistryDocument10 pagesExercise 1a Chemistryapi-533545229No ratings yet
- Grade 9 C7 Acids%2C Bases and Salts Worksheet.1707838055Document8 pagesGrade 9 C7 Acids%2C Bases and Salts Worksheet.1707838055Jeet shah OpNo ratings yet
- Eje Islamic f4 22 Chem 1-1Document7 pagesEje Islamic f4 22 Chem 1-1Nassrah JumaNo ratings yet
- Selina Concise Chemistry Class 9 ICSE Solutions For Chapter 1 - Language of ChemistryDocument24 pagesSelina Concise Chemistry Class 9 ICSE Solutions For Chapter 1 - Language of ChemistryfelixNo ratings yet
- Nota Kolaborasi 24Document11 pagesNota Kolaborasi 24adibdanishmirza2008No ratings yet
- 10th Chapter 3 DPPs - Metals and Non-MetalsDocument12 pages10th Chapter 3 DPPs - Metals and Non-MetalsYash KapoorNo ratings yet
- Answers of Exercise 1 (A)Document6 pagesAnswers of Exercise 1 (A)Lisa SinhaNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument6 pagesCHEMISTRYSuvadip SanyalNo ratings yet
- Module A Chemistry: Contents: (A) Common Mistakes (B) Commands Task Answering Effectively (C) Sample QuestionsDocument13 pagesModule A Chemistry: Contents: (A) Common Mistakes (B) Commands Task Answering Effectively (C) Sample QuestionsJOANNA MAGDALIN A/P JOSEPH MoeNo ratings yet
- Class X Chap 1 2016Document2 pagesClass X Chap 1 2016Kanishk AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Slot 1: Common Formula of Ions in SPM Chemistry SyllabusDocument14 pagesSlot 1: Common Formula of Ions in SPM Chemistry SyllabusThanabalan MunuswamyNo ratings yet
- 2019 49 56 Past PaperDocument10 pages2019 49 56 Past PapersikandarhammadhashmiNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Chemistry QuestionerDocument23 pagesClass 10 Chemistry QuestionerAnand HiremathNo ratings yet
- P.E.S. Pu CollegeDocument6 pagesP.E.S. Pu CollegeSamrudh BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Florence Public School Chemistry Important Questions 2018-19Document5 pagesFlorence Public School Chemistry Important Questions 2018-19Shashank K BNo ratings yet
- ICSE Selina Solution For Class 9 Chemistry Chapter 1Document19 pagesICSE Selina Solution For Class 9 Chemistry Chapter 1ABHISHEK THAKURNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Exam QuestionsDocument32 pagesChemistry Exam QuestionsLombeNo ratings yet
- Language of Chemistry'Document13 pagesLanguage of Chemistry'sanat kr pratiharNo ratings yet
- C10 Chem Holiday AssignmentDocument4 pagesC10 Chem Holiday AssignmentRaj DulariNo ratings yet
- Practise Questions For Prelims Section A Set1Document6 pagesPractise Questions For Prelims Section A Set1Dony GregorNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument7 pagesChemical Reactions and Equationstritium325No ratings yet
- GRADE IX - CHEMISTRY UT 2 - Displacement, Double DisplacementDocument2 pagesGRADE IX - CHEMISTRY UT 2 - Displacement, Double DisplacementthanunovaisnoNo ratings yet
- CHEM ASM FOR L-3 and L-4 (X)Document8 pagesCHEM ASM FOR L-3 and L-4 (X)Arsh KhanNo ratings yet
- Chem Assign 3 01 11 23Document4 pagesChem Assign 3 01 11 23Varenayam editzNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Revision Worksheet CH1Document16 pagesChemistry Revision Worksheet CH1gcubeyyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Acids Bases and Salts Important QuestionsDocument9 pagesChapter 2 Acids Bases and Salts Important QuestionsMX GamingNo ratings yet
- 07 Acids Bases and SaltsDocument7 pages07 Acids Bases and Saltsrudi_zNo ratings yet
- Bahawalpur Board: Grade 10 Chemistry 2016 GROUP 1Document11 pagesBahawalpur Board: Grade 10 Chemistry 2016 GROUP 1Arbab MazharNo ratings yet
- Half and Ionic Equations (GCSE)Document31 pagesHalf and Ionic Equations (GCSE)william.ongeri.tutoringNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School Newtown SESSION: 2021-22 Final Term Examination Class: Ix Total Marks: 80 Subject: Chemistry Time: 2 HoursDocument7 pagesDelhi Public School Newtown SESSION: 2021-22 Final Term Examination Class: Ix Total Marks: 80 Subject: Chemistry Time: 2 HoursSAMPURNA GHOSHNo ratings yet
- G10 Sem 1 Chem QP 24 08Document8 pagesG10 Sem 1 Chem QP 24 08iamperoplayer19No ratings yet
- Standard Grade Revision: Units 8 and 9Document10 pagesStandard Grade Revision: Units 8 and 9Mirtunjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Que Paper Preboard Class 10 2024Document5 pagesQue Paper Preboard Class 10 2024aswath.hemanthaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER - 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument13 pagesCHAPTER - 1 Chemical Reactions and Equationsvijusutar31No ratings yet
- Printout 67Document3 pagesPrintout 67dianajose1No ratings yet
- Chemistry NotesDocument3 pagesChemistry Notesdianajose1No ratings yet
- Subject - Chemistry Class - X: Guess PaperDocument4 pagesSubject - Chemistry Class - X: Guess Paperpromit guhaNo ratings yet
- Full Chemistry Board Exam Pattern TestDocument8 pagesFull Chemistry Board Exam Pattern TestRanjanNo ratings yet
- Questions and Answers For NCERT Book XDocument9 pagesQuestions and Answers For NCERT Book XPrabhuPalanichamyNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument6 pagesChemistrySRIJANo ratings yet
- Test Paper - Chapter - 1 (S - X)Document2 pagesTest Paper - Chapter - 1 (S - X)Víshál RánáNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and Equations NotesDocument13 pagesChemical Reactions and Equations NotesJayanthiNo ratings yet
- Getmyunin: Ncert Solution For Class 10 Science Chemical Reactions and Equations Exercise - 1Document10 pagesGetmyunin: Ncert Solution For Class 10 Science Chemical Reactions and Equations Exercise - 1Nadim BashirNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Class X CH 1 22-23Document3 pagesWorksheet Class X CH 1 22-23auselesspersonNo ratings yet
- Language of Chemistry' PDFDocument13 pagesLanguage of Chemistry' PDFsanat kr pratiharNo ratings yet
- Assignment of S BLKDocument6 pagesAssignment of S BLKShoto TodorokiNo ratings yet
- Atomic STR and Periodic Table MCQsDocument6 pagesAtomic STR and Periodic Table MCQsVaishnavi RajgopalNo ratings yet
- Refraction NumDocument1 pageRefraction NumVaishnavi RajgopalNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen TestDocument2 pagesHydrogen TestVaishnavi RajgopalNo ratings yet
- Chem RXN and EqnDocument5 pagesChem RXN and EqnVaishnavi RajgopalNo ratings yet
- Gas Law TestDocument3 pagesGas Law TestVaishnavi RajgopalNo ratings yet
- Ammonia TestDocument3 pagesAmmonia TestVaishnavi RajgopalNo ratings yet
- International Thermocouple Color Codes - Thermocouple and Extension Grade WiresDocument1 pageInternational Thermocouple Color Codes - Thermocouple and Extension Grade WiresDan PastorNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Softening of Clayey Soil StabilizedDocument12 pagesEvaluation of Softening of Clayey Soil StabilizedsebastianNo ratings yet
- FOSROC SPECS - HDPE - P STD + Proofex 3000VDocument15 pagesFOSROC SPECS - HDPE - P STD + Proofex 3000VAjin Sharma100% (1)
- Frexuencia MuestreoDocument12 pagesFrexuencia MuestreoNico FranckNo ratings yet
- Sika® Primer PW-F: Product Data SheetDocument3 pagesSika® Primer PW-F: Product Data SheetsawwahwahNo ratings yet
- Forgeability of Magnesium AlloysDocument5 pagesForgeability of Magnesium AlloysIon BadoiNo ratings yet
- Mangaon Tee and ReducerDocument2 pagesMangaon Tee and ReducerSoham KolteNo ratings yet
- Modern Methods of Construction - SummmaryDocument21 pagesModern Methods of Construction - Summmaryadnan53No ratings yet
- State of The Art TRC1Document193 pagesState of The Art TRC1Tina FidelisNo ratings yet
- Wps For Carbon Steel THK 7.11 GtawDocument1 pageWps For Carbon Steel THK 7.11 GtawAli MoosaviNo ratings yet
- Glass Fiber Reinforced Concrete (GFRC) - Strength and Stress Strain Behavior For Different Grades of ConcreteDocument6 pagesGlass Fiber Reinforced Concrete (GFRC) - Strength and Stress Strain Behavior For Different Grades of ConcretePiyush SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Tas Worksafe RequirementsDocument43 pagesTas Worksafe RequirementsMatthew JohnstonNo ratings yet
- PaperSulfate MKDocument9 pagesPaperSulfate MKClaudinei GenesioNo ratings yet
- PDS Sika ViscoCrete-8100 enDocument3 pagesPDS Sika ViscoCrete-8100 enimeldaturualloNo ratings yet
- Inhibitor Effects of Sodium Benzoate On Corrosion Resistance ofDocument13 pagesInhibitor Effects of Sodium Benzoate On Corrosion Resistance ofRafi AwanNo ratings yet
- Concrete Work Pour ReleaseDocument1 pageConcrete Work Pour Releaseyasir khanNo ratings yet
- BASF MasterEmaco T 1200 PG Tech DatasheetDocument5 pagesBASF MasterEmaco T 1200 PG Tech DatasheetMike KuczynskiNo ratings yet
- Unit 6D Reversible and Irreversible Changes (Short Unit) : Science Year 6Document4 pagesUnit 6D Reversible and Irreversible Changes (Short Unit) : Science Year 6carrie929ukNo ratings yet
- 10 5923 J Ajps 20160601 01Document11 pages10 5923 J Ajps 20160601 01Anonymous pyYutzGNo ratings yet
- Topaz SG Enamel: Product Characteristics Product DataDocument3 pagesTopaz SG Enamel: Product Characteristics Product DataMohammad AltabbalNo ratings yet
- Saggar Works at Caughley 2004Document24 pagesSaggar Works at Caughley 2004digitalpast100% (2)
- JRD Interiors India Private Limited: Project Code - 000/JRD/CYIENT-WARNGAL/2021-2022Document3 pagesJRD Interiors India Private Limited: Project Code - 000/JRD/CYIENT-WARNGAL/2021-2022Devendra TyagiNo ratings yet
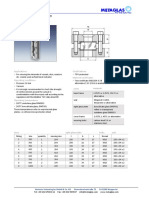
- Type LSG-P: Rectangular Sight Glass FittingsDocument1 pageType LSG-P: Rectangular Sight Glass Fittingsגרבר פליקסNo ratings yet
- Piedmont StyleDDocument1 pagePiedmont StyleDBenjamin MillerNo ratings yet
- Types of Non-Destructive Testing: Visual Inspection (VI)Document4 pagesTypes of Non-Destructive Testing: Visual Inspection (VI)masilamaniNo ratings yet
- Downloads Solimide Brochure EDocument5 pagesDownloads Solimide Brochure Es parasdNo ratings yet
- Contents - Auction - QFPIRA00IQ25 - QFPIRA00JFFI - !QFPIRA00IRN1CONCRETE DATA SHEET PDFDocument3 pagesContents - Auction - QFPIRA00IQ25 - QFPIRA00JFFI - !QFPIRA00IRN1CONCRETE DATA SHEET PDFharryNo ratings yet
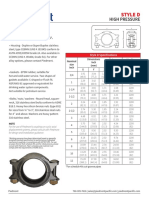
- G-CAST Catalogue (U-Drain Standard 0300-3600)Document5 pagesG-CAST Catalogue (U-Drain Standard 0300-3600)Adib KhairNo ratings yet