Professional Documents
Culture Documents
160 ALL119K v1
Uploaded by
Yudha SetiawanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
160 ALL119K v1
Uploaded by
Yudha SetiawanCopyright:
Available Formats
VOLVO CONSTRUCTION EQUIPMENT
SERVICE BULLETIN
Language Code Group Product No. Version Date Page
GB 160 ART/ BHL/ CEX/ COA/ COS/ CWL/ EXC/ GRD/ 119 K 1 2016-10-07 1/4
PAT/ PAW/ PIP/ SSL/ WLO
Applies to models
All Articulated Haulers, All Asphalt Compactors, All Backhoe Loaders, All Compact Excavators, All Compact
Wheel Loaders, All Excavators, All Motor Graders, All Pipelayers, All Skidsteer Loaders, All Soil Compactors, All
Tracked Pavers, All Wheel Loaders, All Wheeled pavers
ONLY FOR DISTRIBUTORS / DEALERS
Biodiesel fuel for Volvo CE
NOTE!
Please pay attention to the safety instructions in the Operator's
and Service Manuals concerned.
This Service Bulletin is to be considered as technical information
only and is solely applicable for normal warranty in case of
breakdown. Proactive replacement parts are not considered to be
normal warranty.
Description
Biodiesel is a product made from renewable resources such as
vegetable oils or animal fat. Without a chemical process called
esterification, biodiesel is not suitable to use as fuel in a diesel
engine. Biodiesel that has been chemically processed into fatty
acid methyl ester (FAME) can be blended with distillate diesel fuel
and used in some diesel engines.
In Europe this FAME process biodiesel is mainly RME (Rapeseed
Methyl Ester). In USA sunflower and soy are also used as the
main base products and which can be used up to B20 (20% mix
with diesel fuel) unless a lower percentage blend is recommended
according to machine type and engine.
Unblended biodiesel is referred to as B100 because it is 100%
biodiesel.
Use of biodiesel to EN14214 standards, manufactured by the
FAME (Fatty Acid Methyl Ester) process, is now a legal
requirement in some markets. However, biodiesels manufactured
using this process are not as suitable for modern diesel engines
as conventional diesel EN590 or HVO (Hydro-treated Vegetable
Oils). HVO, which is manufactured using a different process, has
been approved for use in Volvo Construction Equipment diesel
engines of all previous and existing versions - 100% HVO, or HVO
mixed with conventional diesel in any other blends.
Volvo Construction Equipment
Feedback mail: sb@volvo.com
Language Code Group Product No. Version Date Page
GB 160 ART/ BHL/ CEX/ COA/ COS/ CWL/ EXC/ GRD/ 119 K 1 2016-10-07 2/4
PAT/ PAW/ PIP/ SSL/ WLO
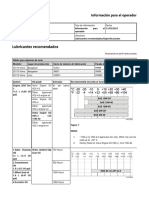
Biodiesel fuel requirements
The FAME biodiesel blends specified in the table below are
approved for use if:
• The biodiesel is pre-blended by the fuel supplier
• The biodiesel used in the blend conforms to EN14214 or ASTM
D6751
• The distillate fuel used in the blend meets fuel sulphur
requirements
• The distillate fuel used in the blend conforms to EN590 or
ASTM D975
• B1-B5 biodiesel blends conform to EN590 or ASTM D975
• B6-B7 biodiesel blends conform to EN590 or ASTM D7467
• B8-B20 biodiesel blends conform to ASTM D7467
Engine emission designation Engine size Acceptable blend Comments
EU Stage II Below D4 Up to B7
Stage IIIA / US Tier 3*
Stage IIIB / Tier 4 interim
Stage IV / Tier 4 final
EU Stage II D4 - D8 Up to B7
Stage IIIA / US Tier 3*
Stage IIIB / Tier 4 interim
Stage IV / Tier 4 final
EU Stage IV / US Tier 4 final, equipped with D4 - D8 Up to B7 Only available in less
High Sulphur Fuel Conversion Kit regulated markets
(without EATS and
EGR).
EU Stage II D9 - D16 Up to B20
Stage IIIA / US Tier 3*
Stage IIIB / Tier 4 interim D11 - D16 Up to B10
Stage IV / Tier 4 final
Stage IIIB / Tier 4 interim, equipped with D11 - D16 Up to B20 Only available in less
High Sulphur Fuel Conversion Kit regulated markets
(without EATS and
EGR).
* As Tier 2 and Tier 3 emissions regulations ended in 2005 and
2010 respectively, engines produced since then typically meet
Stage ll / Stage lllA regulations, allowing their sale in less
regulated markets.
NOTE!
Failures directly caused by the use of poor quality biofuel, or any
other fuel not conforming to standards, are not factory defects and
the manufacturer’s warranty does not apply.
Language Code Group Product No. Version Date Page
GB 160 ART/ BHL/ CEX/ COA/ COS/ CWL/ EXC/ GRD/ 119 K 1 2016-10-07 3/4
PAT/ PAW/ PIP/ SSL/ WLO
Maintenance interval requirements
Additional service actions and shorter maintenance intervals are
mandatory when using biodiesel blends above B10.
Every 10 hours
- Check the engine oil and change if it rises above the maximum
fill level
- Inspect the fuel system components and replace as necessary
Half of original interval
- Change the engine oil and filter
- Replace the fuel filter(s)
Every year, regardless of operating hours
- Change the engine oil and filter
- Clean the fuel tank
Effects of biodiesel on engine oil
Using biodiesel can lead to increased oil dilution. Use engine oil
analysis tools frequently to check for fuel dilution and monitor
engine oil condition. Check the engine oil as per “Maintenance
interval requirements” and always change the engine oil if the oil
level rises above the maximum fill level.
Effects of biodiesel on fuel systems
Biodiesel dissolves and loosens some fuel system deposits.
During the initial conversion to biodiesel, loosened deposits will
travel to the fuel filters and require more frequent fuel filter
replacements.
NOTE!
Start with new fuel filters when using biodiesel for the first time.
Biodiesel is aggressive to some materials used in fuel system
components. Inspect seals, hoses, rubber and plastic
components daily. Repair or replace any components that are
damaged, softened or leaking. Clean biodiesel from painted
surfaces immediately to prevent paint damage.
Biodiesel is more sensitive to bacteria and water contamination
than distillate diesel fuel.
• Use as much fuel as possible before refilling the fuel tank in
order to prevent bacteria growth if a machine is in regular use,
e.g. use up a tank of fuel within a week regularly. In climates
where condensation is a risk, or when the machine is working
for short durations, it is recommended that fuel tank be kept
full.
• Do not use biodiesel in machines with low utilisation or
operating time.
• Do not store machines for more than 4 weeks without flushing
biodiesel out of the fuel system by operating the machine
through at least one full tank of distillate diesel fuel.
• Always follow the manufacturer’s storage recommendations
and “best-before” dates for each delivery of biodiesel.
Effects of biodiesel on exhaust after-treatment systems
Biodiesel leaves higher levels of ash in diesel particulate filters
and may require more frequent diesel particulate filter (DPF)
Language Code Group Product No. Version Date Page
GB 160 ART/ BHL/ CEX/ COA/ COS/ CWL/ EXC/ GRD/ 119 K 1 2016-10-07 4/4
PAT/ PAW/ PIP/ SSL/ WLO
regeneration and cleaning. Biodiesel can cause deviations in
temperatures and functionality of the DPF burner and may cause
fault codes or errors.
Biodiesel exhaust gas is aggressive to some materials used in
selective catalytic reduction systems (SCR) and may require
more frequent cleaning, repairing or replacing of SCR parts.
Effects of biodiesel on cold weather operation
Biodiesel has a high viscosity at temperatures below 0 ˚C (32 ˚F)
and may cause problems starting the engine. Use a fuel heater
or park machines in a heated building if possible.
Effects of biodiesel on emissions compliance
Engines are certified to comply with U.S. EPA, California and EU
emissions standards based upon
the use of test fuels with specifications established by these
regulatory agencies. Alternative fuels, including biodiesel, that
are not substantially similar to the required test fuels may
adversely affect engine emissions compliance. As a result,
Volvo does not warrant that the engine will conform to applicable
Federal or California and EU emissions limits when operated on,
or having previously being operated on, biodiesel or other
alternative fuels that are not substantially similar to specified test
fuels used for certification, nor if biodiesel / regular diesel is used
in blends that exceed the recommendations.
Environmental advantages of FAME versus diesel fuel are:
– Renewable fuel (reduction of CO2)
– Lower particulate emissions (PM)
– Lower emissions of sulfur (SO2)
– Lower emissions of hydrocarbons (HC)
You might also like
- MGB Original Parts Catalogue PDFDocument446 pagesMGB Original Parts Catalogue PDFYarg Nitram100% (1)
- Volvo Oil Training Program - Module 7Document10 pagesVolvo Oil Training Program - Module 7Mohamed Ahmed HassaninNo ratings yet
- Nissan Almera n15 Series Service ManualDocument1,712 pagesNissan Almera n15 Series Service ManualFieru CorsuNo ratings yet
- Deutz Allis Engine Service ManualDocument7 pagesDeutz Allis Engine Service ManualLucas Valente0% (1)
- 1975 Mustang IIDocument94 pages1975 Mustang IIEDISON RAFAEL ZUMARRAGA ASPIAZUNo ratings yet
- Alternative Fuels L120G VolvoDocument3 pagesAlternative Fuels L120G Volvokianoush Volvo construction equipmentNo ratings yet
- Perkins Bio DieselDocument3 pagesPerkins Bio Dieselgagah anteroNo ratings yet
- BIODIESEL - BD20 in Industrial Apllications 200705Document28 pagesBIODIESEL - BD20 in Industrial Apllications 200705sengottaiyanNo ratings yet
- Biodiesel B20 Approval Information: Edward Lyford-Pike Michael O'DonnellDocument29 pagesBiodiesel B20 Approval Information: Edward Lyford-Pike Michael O'DonnelltstkupdhNo ratings yet
- Biodiesel B20 - Cummins InformationDocument29 pagesBiodiesel B20 - Cummins InformationIng. Jon MorenoNo ratings yet
- Mercedes Benz Biodiesel - Rev5Document11 pagesMercedes Benz Biodiesel - Rev5wurtukukNo ratings yet
- Bifuel ArticleDocument10 pagesBifuel ArticleAsmaNo ratings yet
- 420 F 10009Document3 pages420 F 10009Adriano MariniNo ratings yet
- Biodiesel Information For Mercedes-Benz Vehicles 2014 EditionDocument19 pagesBiodiesel Information For Mercedes-Benz Vehicles 2014 EditionSumathi SrinivasNo ratings yet
- Biodiesel Material CompatibilityDocument5 pagesBiodiesel Material CompatibilityKarthik MandyaNo ratings yet
- Biodiesel Fuel For Cummins EnginesDocument2 pagesBiodiesel Fuel For Cummins Enginesvictor villaseñor garciaNo ratings yet
- 2017 Dec CASE Biodiesel Guildline PDFDocument18 pages2017 Dec CASE Biodiesel Guildline PDFJUNA RUSANDI S100% (1)
- 2017 Dec CASE Biodiesel Guildline PDFDocument18 pages2017 Dec CASE Biodiesel Guildline PDFJUNA RUSANDI SNo ratings yet
- Baldwin Fuel Filters Comp Bio-Diesel Blend Eng BLLTNDocument1 pageBaldwin Fuel Filters Comp Bio-Diesel Blend Eng BLLTNSMcNo ratings yet
- PB Full Synthetic 0w 40 High Performance Engine Oil 20210209Document1 pagePB Full Synthetic 0w 40 High Performance Engine Oil 20210209jaice.colsonNo ratings yet
- Mercedes Benz Biodiesel Brochure PDFDocument18 pagesMercedes Benz Biodiesel Brochure PDFkshepard_182786911No ratings yet
- Sales Engineering Information: 4.04. Fuel Specification For DAF Diesel EnginesDocument6 pagesSales Engineering Information: 4.04. Fuel Specification For DAF Diesel EnginesBartek GrzybowskiNo ratings yet
- BRADOL Brochure ENGLISHDocument12 pagesBRADOL Brochure ENGLISHАлександр АлексеевичNo ratings yet
- Seat Alhambra 2005 Owners Manual (en) картаDocument3 pagesSeat Alhambra 2005 Owners Manual (en) картаСергій БоженкоNo ratings yet
- Hybrid 0W-8: Fuel Economy Gasoline Engine Lubricant 100% SyntheticDocument2 pagesHybrid 0W-8: Fuel Economy Gasoline Engine Lubricant 100% SyntheticManishRajSinghNo ratings yet
- BiodieselDocument2 pagesBiodieseligorsilva13123No ratings yet
- FUSO Engine Oil 15W-40 API CI-4: Customer AdvantageDocument2 pagesFUSO Engine Oil 15W-40 API CI-4: Customer AdvantageNelson PanchoNo ratings yet
- 8100 X-Cess 5W-40: Gasoline and Diesel Engine Oil 100% SyntheticDocument2 pages8100 X-Cess 5W-40: Gasoline and Diesel Engine Oil 100% Synthetica33313681No ratings yet
- Rowe 5w40Document2 pagesRowe 5w40ivan.breNo ratings yet
- Service Bulletin: Engine OilDocument16 pagesService Bulletin: Engine OilDan LiamNo ratings yet
- ATP-Oil A4 Brochure Proof 4aDocument33 pagesATP-Oil A4 Brochure Proof 4aDavid PomaNo ratings yet
- 6100 SYN-NERGY 5W-40 en FR Motul 15910 20220504Document4 pages6100 SYN-NERGY 5W-40 en FR Motul 15910 20220504Manuel HelmfeltNo ratings yet
- FUELDocument23 pagesFUELAgus WibowoNo ratings yet
- 8100 X-Cess 5W-40: Gasoline & Diesel Engine Oil 100% SyntheticDocument2 pages8100 X-Cess 5W-40: Gasoline & Diesel Engine Oil 100% SyntheticRadu George MotocNo ratings yet
- PSI 2016 - 08 Biofuel HVODocument2 pagesPSI 2016 - 08 Biofuel HVOCatalin UrsuNo ratings yet
- Aceites para Sd110Document2 pagesAceites para Sd110Omar MorenoNo ratings yet
- Bapco Lubricants Product BrochureDocument2 pagesBapco Lubricants Product BrochureIrfan SaeedNo ratings yet
- Recommends Oil L120G VolvoDocument3 pagesRecommends Oil L120G Volvokianoush Volvo construction equipmentNo ratings yet
- 6100 Synergie+ 10W-40: Gasoline and Diesel Engine Oil TechnosyntheseDocument2 pages6100 Synergie+ 10W-40: Gasoline and Diesel Engine Oil TechnosyntheseDan AlecsandruNo ratings yet
- Biodiesel - FaqDocument3 pagesBiodiesel - FaqsengottaiyanNo ratings yet
- Biodiesel Vehicle CompatabilityDocument8 pagesBiodiesel Vehicle CompatabilitySonthi MooljindaNo ratings yet
- Oil Approval List 2023 MC-10209265-0001Document32 pagesOil Approval List 2023 MC-10209265-0001Lemont 3vNo ratings yet
- Automotive Lubricants Product LineDocument22 pagesAutomotive Lubricants Product LineShawonMunirNo ratings yet
- 8100 X-Cess 5W-40: Gasoline and Diesel Engine Oil 100% SyntheticDocument2 pages8100 X-Cess 5W-40: Gasoline and Diesel Engine Oil 100% Synthetichoussem houssemNo ratings yet
- Synthetic Engine Oil Technology: WWW - Wst-Germany - deDocument12 pagesSynthetic Engine Oil Technology: WWW - Wst-Germany - deTudor RatiuNo ratings yet
- Frequently Asked Questions On Hvo FuelDocument3 pagesFrequently Asked Questions On Hvo FuelSidney SantosNo ratings yet
- Total LubricantsDocument3 pagesTotal LubricantsE Rudy SaputroNo ratings yet
- 8100 X-Cess 5W-40: Gasoline and Diesel Engine Oil 100% SyntheticDocument2 pages8100 X-Cess 5W-40: Gasoline and Diesel Engine Oil 100% SyntheticJmi JobsNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Intervals: Operation and Maintenance Manual ExcerptDocument65 pagesMaintenance Intervals: Operation and Maintenance Manual ExcerptmedescalanteNo ratings yet
- Biodiesel Fleet Myth Busting: What Is Biodiesel?Document33 pagesBiodiesel Fleet Myth Busting: What Is Biodiesel?Jennifer Ceponis DaleyNo ratings yet
- Capacidades de Recarga e RecomendaçõesDocument9 pagesCapacidades de Recarga e RecomendaçõesislanmateusfrNo ratings yet
- Condition: Technical Service BulletinDocument26 pagesCondition: Technical Service BulletinMiguel ArizaNo ratings yet
- Approved Oils, MackDocument2 pagesApproved Oils, MackFernando AguilarNo ratings yet
- Texaco Delo 400 XSP-FA 5W-30Document3 pagesTexaco Delo 400 XSP-FA 5W-30Martynas StonysNo ratings yet
- Biodiesel Fuel: ASTM Standard For Biodiesel (ASTM D6751)Document7 pagesBiodiesel Fuel: ASTM Standard For Biodiesel (ASTM D6751)Jaffarudin Janu WahyudiNo ratings yet
- Volvo Section 1 Oil and FiltersDocument8 pagesVolvo Section 1 Oil and FiltersemezibNo ratings yet
- ACEA Oil Sequences Light Duty Engines Rev1 2022Document10 pagesACEA Oil Sequences Light Duty Engines Rev1 2022AfdhalNo ratings yet
- BiodieselDocument12 pagesBiodieselAlfonso MartínezNo ratings yet
- AMSOIL European Motor - 5W40Document2 pagesAMSOIL European Motor - 5W40Rafael Canizares ChiarandiNo ratings yet
- Updated Quality of Fuel Oil: ImmediatelyDocument12 pagesUpdated Quality of Fuel Oil: ImmediatelyEvreinov D.No ratings yet
- Cat Engine Crankcase FluidsDocument8 pagesCat Engine Crankcase FluidsTiago RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Pelumas Yang DirekomendasikanDocument3 pagesPelumas Yang DirekomendasikanReza SyailendraNo ratings yet
- Biodiesel Production from Used Cooking Oil: Business Advice & Training, #4From EverandBiodiesel Production from Used Cooking Oil: Business Advice & Training, #4No ratings yet
- BMW 5 & 6 Series E12 - E24 - E28 -E34 Restoration Tips and TechniquesFrom EverandBMW 5 & 6 Series E12 - E24 - E28 -E34 Restoration Tips and TechniquesNo ratings yet
- Allison Transmission HUB 016 Splitter 2Document4 pagesAllison Transmission HUB 016 Splitter 2Yudha SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Allison Transmission HUB 020 Rear Cover 2Document4 pagesAllison Transmission HUB 020 Rear Cover 2Yudha SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Schedule Daily Inspection 2021Document46 pagesSchedule Daily Inspection 2021Yudha SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Machine Card A40g 323352Document3 pagesMachine Card A40g 323352Yudha SetiawanNo ratings yet
- User Manual For Ceiba Ii Client (V2.3) : All Rights ReservedDocument103 pagesUser Manual For Ceiba Ii Client (V2.3) : All Rights ReservedYudha SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Eng GB SP A60h Stage IV V DDocument8 pagesEng GB SP A60h Stage IV V DYudha SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Matris Report 98Document53 pagesMatris Report 98Yudha SetiawanNo ratings yet
- TM-ZT503: ModelDocument5 pagesTM-ZT503: ModelYudha SetiawanNo ratings yet
- TM-ZT505H: ModelDocument5 pagesTM-ZT505H: ModelYudha SetiawanNo ratings yet
- TM-ZT504: ModelDocument5 pagesTM-ZT504: ModelYudha SetiawanNo ratings yet
- On Saturdays, Go To The Card Shop and Choose Passwordmachine. Put in The Following CodesDocument38 pagesOn Saturdays, Go To The Card Shop and Choose Passwordmachine. Put in The Following CodesYudha SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Boiler Efficiency - (10 Questions)Document3 pagesBoiler Efficiency - (10 Questions)THEOPHILUS ATO FLETCHERNo ratings yet
- En Perkins 10 50Document2 pagesEn Perkins 10 50Djamel Beddar100% (1)
- Fuse Box Diagram Volkswagen Golf IV - Bora (Mk4 1997-2004)Document14 pagesFuse Box Diagram Volkswagen Golf IV - Bora (Mk4 1997-2004)Rabia GhabagNo ratings yet
- Manual d3 Engine-30.08.08Document102 pagesManual d3 Engine-30.08.08sudhakarrajam200293% (14)
- IC2238074Document2 pagesIC2238074Fatjet MrrukuNo ratings yet
- Process Design Criteria: 3$&+$&+$&$LIME PLANTDocument19 pagesProcess Design Criteria: 3$&+$&+$&$LIME PLANTJorch GalvanNo ratings yet
- Project Proposal HHODocument30 pagesProject Proposal HHOJaishree ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Energy Transformation at The Shell Rhineland Refinery - Project REFHYNEDocument11 pagesEnergy Transformation at The Shell Rhineland Refinery - Project REFHYNEmsantosu000No ratings yet
- GEK28156c-Gas Turbine Equipment PreservationDocument12 pagesGEK28156c-Gas Turbine Equipment Preservationkarim karim100% (1)
- The 1.8 Turbo Gasoline: Drive Your IdeasDocument4 pagesThe 1.8 Turbo Gasoline: Drive Your Ideasmechatronics overviewNo ratings yet
- Reimbursement Form MPacisDocument3 pagesReimbursement Form MPacisDhexter VillaNo ratings yet
- Amm 787 1871Document6 pagesAmm 787 1871Nikhil KambleNo ratings yet
- BiofuelsDocument5 pagesBiofuelsDhruv SinghalNo ratings yet
- Engine Cranks But Not StartDocument4 pagesEngine Cranks But Not StartAntonio MejicanosNo ratings yet
- Manual Formacion D722-B, D1005-E, D1105-B y D1703-BDocument16 pagesManual Formacion D722-B, D1005-E, D1105-B y D1703-BTerah Pio100% (1)
- BB 12.h 4030.sounding TableDocument286 pagesBB 12.h 4030.sounding TableToni ToniNo ratings yet
- Hvac and Refrigiration System: Group 1Document52 pagesHvac and Refrigiration System: Group 1Jessa Mae CatabayNo ratings yet
- Incini-Cone SelectionGuide 420Document8 pagesIncini-Cone SelectionGuide 420Thaiminh Vo100% (1)
- Proposal - JU6H-UF68 - 200 HP at 1750 RPMDocument10 pagesProposal - JU6H-UF68 - 200 HP at 1750 RPMMaurilio Batista de LimaNo ratings yet
- Manual Bosch m744 Me744 EobdDocument66 pagesManual Bosch m744 Me744 EobdshayNo ratings yet
- Proposal For The Supply of Petroleum ProductsDocument2 pagesProposal For The Supply of Petroleum Productsvincent adzinyo75% (4)
- Chapt1 - Classification & ParametersDocument94 pagesChapt1 - Classification & ParameterspeterNo ratings yet
- Catalagram: A Refining Technologies PublicationDocument44 pagesCatalagram: A Refining Technologies PublicationMón Quà Vô GiáNo ratings yet
- BMEF17M001 ICE Assignment 2Document9 pagesBMEF17M001 ICE Assignment 2Muhammad Javed IqbalNo ratings yet
- InteliLite AMF25 Wiring - MCCBSCTRL ModelDocument1 pageInteliLite AMF25 Wiring - MCCBSCTRL Modelsoufienne b.yahmed0% (1)
- Weekly Lift Truck Pre-Use Check Sheet: Operator Signature: Supervisor SignatureDocument2 pagesWeekly Lift Truck Pre-Use Check Sheet: Operator Signature: Supervisor Signaturetemter gandaNo ratings yet