Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Johnson and Peplau Reviewer
Uploaded by
Sofia Marie Galendez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
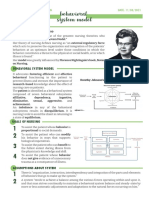
11 views3 pagesThe Behavioral Systems Model views the person as a behavioral system comprised of seven interconnected subsystems that work together to maintain homeostasis. When one subsystem is disturbed, it affects the others. The model was developed by Dorothy Johnson to foster efficient and effective behavioral functioning in patients to prevent illness. It is based on Nightingale's view that nursing helps people prevent or recover from illness. The seven subsystems are: attachment, dependency, ingestive, eliminative, sexual, aggressive, and achievement. The goal of nursing within this model is to help patients maintain stability and balance among these subsystems.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe Behavioral Systems Model views the person as a behavioral system comprised of seven interconnected subsystems that work together to maintain homeostasis. When one subsystem is disturbed, it affects the others. The model was developed by Dorothy Johnson to foster efficient and effective behavioral functioning in patients to prevent illness. It is based on Nightingale's view that nursing helps people prevent or recover from illness. The seven subsystems are: attachment, dependency, ingestive, eliminative, sexual, aggressive, and achievement. The goal of nursing within this model is to help patients maintain stability and balance among these subsystems.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views3 pagesJohnson and Peplau Reviewer
Uploaded by
Sofia Marie GalendezThe Behavioral Systems Model views the person as a behavioral system comprised of seven interconnected subsystems that work together to maintain homeostasis. When one subsystem is disturbed, it affects the others. The model was developed by Dorothy Johnson to foster efficient and effective behavioral functioning in patients to prevent illness. It is based on Nightingale's view that nursing helps people prevent or recover from illness. The seven subsystems are: attachment, dependency, ingestive, eliminative, sexual, aggressive, and achievement. The goal of nursing within this model is to help patients maintain stability and balance among these subsystems.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
THE BEHAVIORAL SYSTEM MODEL NURSING
DOROTHY E. JOHNSON Is an external force acting to preserve the organization
of the patient’s behavior by means of imposing
Background regulatory mechanisms or by providing resources while
the patient is under stress
Aug. 21, 1919 – Born in Savannah, Georgia
1942 – BSN from Vanderbilt University “A steady state is maintained through adjusting and
1948 – MSN in Public Health from Harvard adapting to internal and external forces.”
1949 – Faculty at UCLA
1977 – Retired in Florida
Johnson’s 7 Subsystems
- Johnson first proposed her model in 1968 to foster the
“efficient & effective behavioral functioning in the 1. Attachment or Affiliative Subsystem
patient to prevent illness” - Forms the basis for all social organization
- She based her model on Florence Nightingale’s belief - Promotes survival & provides a sense of
that nursing is designed to help people prevent or security
recover from illness or injury - Results in social inclusion, intimacy & the
- She borrowed ideas from systems theory to explain that formation of strong bonds
nursing is concerned with the individual as an integrated
whole 2. Dependency Subsystem
- promotes helping or nurturing behavior from
Johnson, 1990 others
The person experiencing a disease is more important - Results in approval, attention, recognition &
than the disease itself physical assistance
Behavioral Systems Model 3. Ingestive Subsystem
- Involves food intake
- The person is a behavioral system comprised of a set of - Relates to the biological need for food & the
organized, interactive, interdependent, and integrated psychological meanings & structures of social
subsystems events surrounding food consumption
- Constancy is maintained through actions & behaviors - Results in appetite satisfaction
that are regulated & controlled by biological,
psychological, and sociological factors. 4. Eliminative Subsystem
- involves behavior surrounding the excretion
Metaparadigm of waste from the body
- Includes the psychological meanings & structures
PERSON of socially acceptable behaviors for waste
- views person as having two major systems: biological elimination
and behavioral system.
- As a behavioral system with patterned, repetitive & 5. Sexual Subsystem
purposeful ways of behaving that link the person to the - involves behavior associated with procreation &
environment sexual gratification
- An individual composed of seven open & interactive - includes psychologically & socially acceptable
subsystems; a disturbance in one usually affects the behaviors such as courtship & mating results in the
others development of sex role identity & sex role behavior
- Continually strives to maintain a steady state by
adapting & adjusting to environmental forces that cause 6. Aggressive Subsystem
an imbalance; when an imbalance or health problem - involves behavior related to self- protection &
occurs, the person’s physical, social or psychological preservation of the self & society
integrity is threatened. - includes the belief that aggression is learned &
harmful & that people & property must be
HEALTH respected & protected
- A state that is affected by social, biological - includes acknowledgment of realor imaginary
psychological, and physiological factors. dangers to develop defenses to these threats
- The individual strives to maintain stability in these
factors. 7. Achievement Subsystem
- involves behavior related to manipulation of the
ENVIRONMENT environment to gain mastery & control over some
- Consists of all the factors that are not part of the aspect of oneself or environment, this control is
individual’s behavioral system, but influence the system, measured against a standard of excellence
some of which can be manipulated by the nurse to - includes intellectual, physical, creative,
achieve the health goal for the patient. mechanical & social skills
- An individual’s behavior is influenced by all the events in
the environment. It varies from culture to culture.
3 Functional Requirements of Humans
1. To be protected from noxious influences with which - A man who is an organism that lives in an unstable
the person cannot cope balance of a given system
2. To be nurtured through the input of supplies from HEALTH
the environment - A word that symbolizes movement of the personality &
3. To be stimulated to enhance growth and prevent other ongoing human processes that directs the person
stagnation towards creative and, constructive, productive &
community living
- Peplau also gave importance on the belief that for
THEORY OF INTERPERSONAL RELATIONS one’s health to be achieved & maintained, his needs
HILDEGARD PEPLAU must be met
- These needs are physiological demands and
Interpersonal Relations Model interpersonal conditions .
General Information: NURSING
- Peplau based her model on psychodynamic nursing, - Describes as a significant, therapeutic interpersonal
which she defines as using the understanding of one’s process
behavior to help others identify their difficulties - Is a human relationship between an individual who is
- In this model, the phases of nurse-patient relationship sick or has a felt need & a nurse who is educated to
reflect occurrences in personal interactions and during recognize & respond to the need for help
these phases, the nurse assumes various roles such as - Achieve its goal by promoting the patient’s
teacher, resource , counselor, leader, technical expert development of skills to deal with problems & achieve
and surrogate health; this is a mutual & collaborative process that
attempts to resolve this problem
Phase of Nurse-Patient Relationship - Views nursing process as having sequential steps that
focus on therapeutic interactions
1. Orientation Phase
- The individual has a felt need and seeks professional ENVIRONMENT
assistance - Defined as forces outside the organism & in the context
- The nurse helps the patient recognize & understand his of the socially approved way of living, from which vital
or her problem and determine his or her need for help human social processes are derived such as norms,
- Collaborative clarifying and defining of the problem. customs and beliefs
- Patient & nurse work together to understand their - However, these given conditions that lead to health
reactions to each other, mindful of potential always include the interpersonal process
influencing factors such culture, religion, personal
experiences and preconceived ideas To help clients fulfill their needs, nurses assume many
roles: NURSING ROLES
2. Identification Phase
- The patient identifies with those who can help him or 1. Role of the Stranger
her (relatedness) - The nurse must treat the patient with utmost courtesy,
- The nurse permits exploration of feelings to aid the which includes acceptance of the patient as a person &
patient in undergoing illness as an experience that due respect over his individuality
reorient feelings & strengthens positive forces in the - Coincides with identification phase
personality & provides needed satisfaction
- The patient may begin to feel a sense of belonging and 2. Role of the resource person
may gain confidence in dealing with the targeted - The nurse provides specific answers to questions which
problem include health information, advices & a simple
explanation of the healthcare team’s course of care
3. Exploitation Phase
- The patient derives the full value of the relationship as 3. Teaching Role
he moves on from a dependent role to an independent - Combination of all roles
role - Gives instructions and provides training; involves
- The nurse can project new goals to be achieved through analysis and synthesis of the learner's experience.
personal effort & power shifts from the nurse to the - The nurse gives much importance for self-care & in
patient delays gratification to achieve newly formed helping him understand the therapeutic plan
goals
3. Leadership Role
4. Resolution Phase - The nurse as a leader must act in behalf of the patient’s
- After the patient’s needs have been met, the best interest & at the same time enable him to make
therapeutic relations ends decisions over his care.
- The patient earns independence over his care as he - This is achieved through cooperation and active
gradually puts aside old goals & formulates new goals participation
- This is a process in which the patient free himself or
herself from identification with the nurse
Metaparadigm 5. Surrogate Role
- The patient’s dependency for his care gives the nurse a
PERSON surrogate role
- This creates an atmosphere wherein feelings previously
felt such as feelings towards her mother;
some other relationships are reactivated & nurtured
- The nurse then helps the patient & see the differences
between the nurse’s role & that of the recalled person
6. Counseling Role
- The role that has the greatest importance & emphasis in
nursing
- This role strengthens the nurse-patient relationship as
the nurse becomes a listening friend, an understanding
family member & someone who gives sound and
emphatic advises.
- Helps client understand and integrate the meaning of
current life circumstances; provides guidance and
encouragement to make changes.
You might also like
- Psychiatry NotesDocument135 pagesPsychiatry Notesmerin sunilNo ratings yet
- Berklee Intro Music Therapy PDFDocument17 pagesBerklee Intro Music Therapy PDFTheodore VaillantNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Care Pocket Guide For Hospital Physicians PDFDocument319 pagesNeonatal Care Pocket Guide For Hospital Physicians PDFelmaadawy2002100% (7)
- AOTA Statement On Role of OT in NICUDocument9 pagesAOTA Statement On Role of OT in NICUMapi RuizNo ratings yet
- Mind Magic: Building a Foundation for Emotional Well-BeingFrom EverandMind Magic: Building a Foundation for Emotional Well-BeingNo ratings yet
- 3 MDRRMC SampleDocument57 pages3 MDRRMC SampleMakoy Salonga100% (2)
- Theories of Development: Early Childhood)Document3 pagesTheories of Development: Early Childhood)Sofia Marie GalendezNo ratings yet
- Theories of Development: Early Childhood)Document3 pagesTheories of Development: Early Childhood)Sofia Marie GalendezNo ratings yet
- Theories of Development: Early Childhood)Document3 pagesTheories of Development: Early Childhood)Sofia Marie GalendezNo ratings yet
- Nola J. PenderDocument5 pagesNola J. PenderSofia Marie GalendezNo ratings yet
- Systems TheoriesDocument35 pagesSystems TheoriesJames Kurt CruzatNo ratings yet
- Roy's Adaptation ModelDocument8 pagesRoy's Adaptation Modelhanna castueraNo ratings yet
- Errata 1Document9 pagesErrata 1Doc AhsanNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment PDFDocument87 pagesWater Treatment PDFJubin KumarNo ratings yet
- Sister Callista Roy 2Document4 pagesSister Callista Roy 2Axle Kyle CorderoNo ratings yet
- Behavioral System ModelDocument38 pagesBehavioral System Modelmalyn1218100% (15)
- HRM Case StudyDocument21 pagesHRM Case StudyNabil Eyg Iakini100% (1)
- Dorothy E. Johnson's Behavioral System ModelDocument7 pagesDorothy E. Johnson's Behavioral System Modelms_ressyNo ratings yet
- Pothole Claim Form in PhiladelphiaDocument3 pagesPothole Claim Form in Philadelphiaphilly victorNo ratings yet
- Carmencita M. Abaquin: Prepare Me TheoryDocument3 pagesCarmencita M. Abaquin: Prepare Me TheorySofia Marie GalendezNo ratings yet
- Dorothy E. Johnson Systems TheoryDocument3 pagesDorothy E. Johnson Systems TheoryJeremy CollamarNo ratings yet
- TFN Finals First YearDocument7 pagesTFN Finals First YearavilamaaicelleNo ratings yet
- TFN Trans Part 2Document18 pagesTFN Trans Part 2ree wryNo ratings yet
- Dorothy E. JohnsonDocument1 pageDorothy E. JohnsonZaldivar PenuliarNo ratings yet
- Ob CHAPTER 20Document5 pagesOb CHAPTER 20Magandia, Janizah R.No ratings yet
- Dorothy JohnsonDocument2 pagesDorothy Johnsonyoonie catNo ratings yet
- Sister Callista RoyDocument2 pagesSister Callista RoyZaldivar PenuliarNo ratings yet
- Midterm Task 3Document6 pagesMidterm Task 3naldalovely21No ratings yet
- Dorothy Johnson TheoryDocument7 pagesDorothy Johnson Theorykamaljit kaurNo ratings yet
- Dorothy Johnson - Behavioral System ModelDocument6 pagesDorothy Johnson - Behavioral System ModelNek YasiladNo ratings yet
- Defense Mechanism (Week 11) ReviewerDocument4 pagesDefense Mechanism (Week 11) ReviewerKrisha Mabel TabijeNo ratings yet
- Dorothy JohnsonDocument8 pagesDorothy JohnsonJulie Mae LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Healt Social Well-Mental/ Emotional: Betty NeumannDocument21 pagesHealt Social Well-Mental/ Emotional: Betty NeumannTine GuibaoNo ratings yet
- TFN Roy22Document28 pagesTFN Roy22Red DinsonNo ratings yet
- Sister Callista RoyDocument12 pagesSister Callista RoyZaldivar PenuliarNo ratings yet
- Nola PenderDocument3 pagesNola PenderAlriam Twinkle MartinNo ratings yet
- TFN Midterm HandoutDocument6 pagesTFN Midterm HandoutJanelynMaeVillapazNo ratings yet
- Health and Illness: (Leavell) - The Level of Health of AnDocument2 pagesHealth and Illness: (Leavell) - The Level of Health of AnMarc Jordan EstebanNo ratings yet
- Sr. Callista Roy: Adaptation ModelDocument6 pagesSr. Callista Roy: Adaptation ModelJeremy CollamarNo ratings yet
- The Essence of Growth and MaturationDocument24 pagesThe Essence of Growth and MaturationDiana Nicole TusiapNo ratings yet
- Dorothy and RoyDocument38 pagesDorothy and RoyEMIL JNo ratings yet
- Dorothea Orem: Self-Care TheoryDocument16 pagesDorothea Orem: Self-Care TheoryHazel LezahNo ratings yet
- Dorothy Johnson's Behavioral Systems Model in NursingDocument15 pagesDorothy Johnson's Behavioral Systems Model in NursingLouis Gabriel AdayaNo ratings yet
- TFN Oral Rev ReviewerDocument6 pagesTFN Oral Rev ReviewerDela Cruz Clarizza BiancaNo ratings yet
- NCM 103 PrelimDocument6 pagesNCM 103 Prelimkwgchyrn1No ratings yet
- Funda ReviewerDocument8 pagesFunda ReviewerChamelli RobinNo ratings yet
- Dorothea Orem'sDocument4 pagesDorothea Orem'sDionne BajasNo ratings yet
- TFN Callista L. RoyDocument4 pagesTFN Callista L. RoyANJELO CYRUS BIARES GARCIANo ratings yet
- 2 - Theoretical FoundationDocument5 pages2 - Theoretical FoundationLynnelljhyen MALUBAYNo ratings yet
- Nursing Theory Johnson - Behavioral System ModelDocument3 pagesNursing Theory Johnson - Behavioral System ModelANGEL BIEN LEVERIZANo ratings yet
- Calista RoyDocument21 pagesCalista Roydarlenedavid2404No ratings yet
- Group 11 BSN1 C TFN Activity 3Document11 pagesGroup 11 BSN1 C TFN Activity 3Reibenjay CamoralNo ratings yet
- Nursing Theories and Models Important Theorists: 1. Florence Nightingale-Environmental TheoryDocument8 pagesNursing Theories and Models Important Theorists: 1. Florence Nightingale-Environmental TheoryCazzel AvilesNo ratings yet
- Dorothy E. JohnsonDocument8 pagesDorothy E. JohnsonJoven JaravataNo ratings yet
- Nursing Theories SummaryDocument7 pagesNursing Theories SummaryThrecia RotaNo ratings yet
- Sr. Callista RoyDocument4 pagesSr. Callista RoyHv EstokNo ratings yet
- Nola PenderDocument9 pagesNola PenderAndrea YangNo ratings yet
- DorothyDocument2 pagesDorothyShahina ShayneNo ratings yet
- TFN MidtermDocument7 pagesTFN MidtermDimple Lexiry GloriaNo ratings yet
- Dorothy E. Johnson: Behavioral System ModelDocument15 pagesDorothy E. Johnson: Behavioral System Modelwickwax100% (1)
- TFN Chapter 11 and 12Document4 pagesTFN Chapter 11 and 12Charlette Mae Guadalupe (SHS)No ratings yet
- Ncm100 Midterm NotesDocument5 pagesNcm100 Midterm NotesJOCY MARIE C. BOLONo ratings yet
- GROUP - 4 MetaparadigmDocument5 pagesGROUP - 4 MetaparadigmRose OrtizNo ratings yet
- CU 8. Johnsons Roy NeumanDocument41 pagesCU 8. Johnsons Roy NeumanPatrick MatubayNo ratings yet
- TFN NotesDocument14 pagesTFN NotesYejiNo ratings yet
- Dorothea Orem's Self-Care Theory: Practice in 1971, Second in 1980, in 1995, and 2001Document9 pagesDorothea Orem's Self-Care Theory: Practice in 1971, Second in 1980, in 1995, and 2001Aulia Dwi RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Marife Reyes (Report)Document8 pagesMarife Reyes (Report)Francis AjeroNo ratings yet
- Additional Conceptual ModelsDocument54 pagesAdditional Conceptual Modelsgmunoz230000000945No ratings yet
- CONCEPTS OF MAN HEALTH and ILLNESDocument41 pagesCONCEPTS OF MAN HEALTH and ILLNESKiela Therese LabroNo ratings yet
- Nursing TheoristsDocument20 pagesNursing TheoristsScionNo ratings yet
- ProfessionDocument6 pagesProfessionRI NANo ratings yet
- FUNDA_LESSON1_HEALTH_AND_WELLNESSDocument5 pagesFUNDA_LESSON1_HEALTH_AND_WELLNESSAzTech 233No ratings yet
- The Balance Theory: An Approach To Organizational LeadershipFrom EverandThe Balance Theory: An Approach To Organizational LeadershipNo ratings yet
- Lab1 - Sanitation and SafetyDocument3 pagesLab1 - Sanitation and SafetySofia Marie GalendezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Family: What Is A Family?Document4 pagesLesson 1: Family: What Is A Family?Sofia Marie GalendezNo ratings yet
- Growth & DevelopmentDocument2 pagesGrowth & DevelopmentSofia Marie GalendezNo ratings yet
- Family Nursing ProcessDocument11 pagesFamily Nursing ProcessSofia Marie GalendezNo ratings yet
- Background:: Nursing Process TheoryDocument5 pagesBackground:: Nursing Process TheorySofia Marie GalendezNo ratings yet
- Culture Care Diversity & Universality Theory: Madeleive LeiningerDocument4 pagesCulture Care Diversity & Universality Theory: Madeleive LeiningerSofia Marie GalendezNo ratings yet
- Growth & DevelopmentDocument2 pagesGrowth & DevelopmentSofia Marie GalendezNo ratings yet
- Title: Improvement in The Appropriate Antimicrobial Usage For Treating PediatricDocument23 pagesTitle: Improvement in The Appropriate Antimicrobial Usage For Treating PediatricSofia Marie GalendezNo ratings yet
- Growth & DevelopmentDocument2 pagesGrowth & DevelopmentSofia Marie GalendezNo ratings yet
- Midwifery LedDocument15 pagesMidwifery LedRizka Dita Hidayati100% (1)
- 270 lbs. man's 6-meal diet and workout planDocument10 pages270 lbs. man's 6-meal diet and workout planYuuki XDNo ratings yet
- Training Needs Analysis FormDocument4 pagesTraining Needs Analysis FormLizjasmine DimayaNo ratings yet
- Dr.maimoona - Gynecology-محولDocument6 pagesDr.maimoona - Gynecology-محولAbdelNasser TawfiekNo ratings yet
- 2020 Corportate Sustainability ReportDocument22 pages2020 Corportate Sustainability ReportMohamed KannouNo ratings yet
- MSDSDocument3 pagesMSDSSiti Nurjanah SeptianiNo ratings yet
- Obamacare Ushers in New Era For The Healthcare IndustryDocument20 pagesObamacare Ushers in New Era For The Healthcare Industryvedran1980No ratings yet
- 100 Item Exam On Fundamentals of Nursing - Pulse - Blood Pressure PDFDocument12 pages100 Item Exam On Fundamentals of Nursing - Pulse - Blood Pressure PDFJawad AkbarNo ratings yet
- CUI Texto Examen Multimedia Nivel 6 Curso BasicoDocument2 pagesCUI Texto Examen Multimedia Nivel 6 Curso BasicobertoniramiroNo ratings yet
- Anatomia SufletuluiDocument1 pageAnatomia SufletuluiAlexandrina DeaşNo ratings yet
- Pesticide ApplicationDocument5 pagesPesticide ApplicationPrashant GurjarNo ratings yet
- A Critical Review of The Effect of Working Conditions On Employee PerformanceDocument11 pagesA Critical Review of The Effect of Working Conditions On Employee PerformanceStephanie Bacunawa0% (1)
- PDF Biaya MaternityDocument2 pagesPDF Biaya MaternityKurnia Yuliyanti RahayuNo ratings yet
- Nurs 5019 - Soap Note 41-60 Year OldDocument7 pagesNurs 5019 - Soap Note 41-60 Year Oldapi-308904543100% (1)
- VGEC 2024_Thư mời hội nghịDocument8 pagesVGEC 2024_Thư mời hội nghịkhongquantam101010No ratings yet
- CPT 2021 guide for identifying medical proceduresDocument7 pagesCPT 2021 guide for identifying medical proceduresChester FernandezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Alpaca andDocument9 pagesIntroduction To The Alpaca andMai Chi PhạmNo ratings yet
- 2023 AHAR: PIT Estimates of Homelessness in The U.S.Document117 pages2023 AHAR: PIT Estimates of Homelessness in The U.S.Santiago Adolfo OspitalNo ratings yet
- Crimes 3 MalaysiaDocument18 pagesCrimes 3 MalaysiaismailNo ratings yet
- PIL For Sudafed DecongestantDocument2 pagesPIL For Sudafed DecongestantOdunlamiNo ratings yet
- Managing STEM AthletesDocument13 pagesManaging STEM Athletesanon_629662799No ratings yet
- Connectors 2Document14 pagesConnectors 2Irene SánchezNo ratings yet