Professional Documents
Culture Documents
For Improving and Protecting Plant Health: Nitrogen Iodine
Uploaded by
Pao Becerra EOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
For Improving and Protecting Plant Health: Nitrogen Iodine
Uploaded by
Pao Becerra ECopyright:
Available Formats
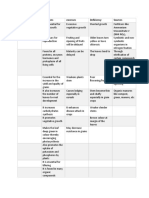
19 PLANT NUTRIENTS
FOR IMPROVING AND PROTECTING PLANT HEALTH
Plants use minerals present in the soil and water in order to grow and flourish. Just like with humans, if they don’t get enough of these nutrients it can seriously affect their health.
Ensuring proper plant nutrition by using fertilizers (organic and mineral) to supplement the nutrients already available in the soil is essential for plant health.
Here’s a look at 19 nutrients than can benefit plant health (in addition to improving yields):
NITROGEN
Nitrogen is an essential component of
IODINE
Iodine has been found to be associated
amino acids for building proteins, nucleic with enzymes in plants. Research suggests
acids and chlorophyll which converts the that it is important for biological processes
sun’s energy into sugars. It is vital for such as photosynthesis, energy metabolism
plant metabolism, growth and health. and calcium-signaling. Iodine deficiency
delays flowering and disrupts root,
leaf and fruit development as well
PHOSPHORUS
as plants’ environmental and climatic
stress defenses.
Phosphorus is vital for energy storage
and transfer and membrane integrity
in plants. Particularly important in early
growth stages, it promotes tillering,
root development, early flowering
SODIUM
Sodium is essential in transporting
and ripening. CO2 during photosynthesis for
a limited number of plants.
For other plant species,
COBALT
because it is chemically and
structurally very similar to
potassium, it can also fulfill
Cobalt is an essential component of some many of the roles played by
enzymes and co-enzymes that can affect potassium, including metabolic ones.
the growth and metabolism of plants. It
is also necessary for nitrogen (N) fixation
COPPER
which occurs within the nodules of legumes.
Cobalt can increase seeds’ drought
tolerance and reduce plant stress.
Copper plays a key role in nitrogen and
hormone metabolism and is needed for
many enzyme activities in plants, as well
POTASSIUM
as for chlorophyll and seed production.
Deficiencies can lead to crop failure
and increased susceptibility to diseases
Potassium has major functions in
such as ergot.
enzyme activation, transpiration and
the transport of assimilates (the
IRON
products of photosynthesis). It
helps plants to retain water during
droughts, provides strength to plant
cell walls and decreases susceptibility Iron is another essential component for
to diseases and insects. creating chlorophyll and also serves
SULPHUR
as a catalyst for cell division which is
central to plant growth. Many plants
also use iron for their enzyme functions.
CALCIUM
Sulphur is integral to all living plant A lack of iron results in yellowing leaves
cells and helps to produce amino acids and poor fruit quality and quantity.
involved in chlorophyll production,
Calcium is needed for biomembrane proteins and vitamins. It contributes
maintenance. It helps in cell wall
MANGANESE
to plant growth and seed formation,
stabilization as an enzyme activator, in improves winter hardiness and helps
osmoregulation and in the cation-anion plants resist diseases.
balance and thus also plays important Manganese plays a key role in a variety
roles in resistance to diseases and of plant functions including photosynthesis,
abiotic stresses such as drought, enzyme activation, respiration and
heat and cold. nitrogen assimilation. Deficiencies can
cause weaker structural resistance against
pathogens and less tolerance to drought
and heat stress.
MAGNESIUM
SILICON
Magnesium is central to the production
of chlorophyll which is needed for
photosynthesis and healthy green leaf
tissue. It reduces crop stress caused Silicon increases plant vigor and
by exposure to the sun and high improves tolerance to abiotic stresses
temperatures, while a deficit can often such as drought, salinity or heavy metals.
cause stunted growth. It enhances plant cell walls’ strength and
structure, increasing resistance to plant
diseases and insect pests. Good silicon
nutrition stimulates photosynthesis and
BORON
improves grain production.
Boron is required for cell wall synthesis
MOLYBDENUM
and cell expansion. Boron deficiency
disrupts reproductive growth, shoot
SELENIUM
and root growth and pollen viability
and hence influences seed set and Molybdenum is used by plants to
yield. A lack of boron can result in reduce nitrates into usable forms
deformed leaves and poor quality Because selenium is chemically and for biological nitrogen fixation
of harvested product. similar to sulphur, it is taken up inside by certain species. Insufficient
plants via sulphur transporters molybdenum means some plants
inside the roots. Studies show that can’t fix nitrogen from the air to
selenium improves plant growth make proteins and can hinder
CHLORINE
Chlorine improves plant productivity,
NICKEL
Nickel is important in plant seed
ZINC
Zinc participates in chlorophyll
and increases tolerance to
biotic and abiotic stresses.
normal plant growth.
plays a role in photosynthesis and is germination, photosynthesis, enzyme formation, is needed to activate many
needed for osmosis and ionic balance. functions and nitrogen metabolism. enzymes in plants and is needed for
It can help to minimize water loss during A deficiency affects plant growth, plant immune responses. As a result,
stressful dry periods and enhance antioxidant systems and response it is important for increasing plant
disease resistance. to stress. resistance to diseases and pests.
You might also like
- For Improving and Protecting Plant Health: Nitrogen ChlorineDocument1 pageFor Improving and Protecting Plant Health: Nitrogen ChlorineRahmat SunaryaNo ratings yet
- For Improving and Protecting Plant Health: Chlorine NitrogenDocument1 pageFor Improving and Protecting Plant Health: Chlorine Nitrogencarlos mosqueraNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGYDocument4 pagesBIOLOGYNadine PascuaNo ratings yet
- Mineral Ions For GrowthDocument1 pageMineral Ions For GrowthnaduniNo ratings yet
- Roles of The 16 Essential Nutrients inDocument4 pagesRoles of The 16 Essential Nutrients inAbas S. AcmadNo ratings yet
- Mineral Nutrition in PlantsDocument32 pagesMineral Nutrition in PlantsSourabh DhanetiaNo ratings yet
- palaniraj2011Document11 pagespalaniraj2011Duyên PhạmNo ratings yet
- Udvardi 2013 Revisao Rizobio LeguminosaDocument28 pagesUdvardi 2013 Revisao Rizobio LeguminosaAna CláudiaNo ratings yet
- Prospects For Using Phosphate-Solubilizing MicroorDocument23 pagesProspects For Using Phosphate-Solubilizing MicroorDickdick MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Lemna SP ArmDocument16 pagesLemna SP ArmHanin Jaliyy100% (1)
- Lecture Note - Basic Botany - BIO 003-1Document49 pagesLecture Note - Basic Botany - BIO 003-1Lincoln JamesNo ratings yet
- Plant Mineral Nutrition 2014 FinalpdfDocument7 pagesPlant Mineral Nutrition 2014 Finalpdfalhajifawaz77No ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Organ Systems Lesson Explains Nutrition FunctionsDocument11 pagesPlant and Animal Organ Systems Lesson Explains Nutrition FunctionsIshs GwsNo ratings yet
- Aacs v4 Id1045Document6 pagesAacs v4 Id1045gautamaakashkumar9No ratings yet
- Physiological Responses of Sesame (Sesamum Indicum L.) To Foliar Application of Boron and Zincunder Drought StressDocument9 pagesPhysiological Responses of Sesame (Sesamum Indicum L.) To Foliar Application of Boron and Zincunder Drought StressVinh Thuc LeNo ratings yet
- Plant nutrients: Functions, excesses, deficiencies, and sourcesDocument10 pagesPlant nutrients: Functions, excesses, deficiencies, and sourcesIbukun OlaitanNo ratings yet
- Hellagrolip Nitrogenous Brochure enDocument2 pagesHellagrolip Nitrogenous Brochure enBashir A. SialNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT in Earth ScienceDocument2 pagesASSIGNMENT in Earth Sciencekaye arcedeNo ratings yet
- SOIL 2A - NUTRIENT Available Form and FunctionsDocument7 pagesSOIL 2A - NUTRIENT Available Form and FunctionsMARY ANN HUBILLANo ratings yet
- Plants and Animals Nutrition General BiologyDocument11 pagesPlants and Animals Nutrition General Biologyjaira magbanuaNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Phosphate Solvent Extract and PPC on Growth and Production of Corn PlantsDocument14 pagesEffectiveness of Phosphate Solvent Extract and PPC on Growth and Production of Corn PlantsBah RoniNo ratings yet
- Zinc in Crop Production and Interaction With PhosphorusDocument8 pagesZinc in Crop Production and Interaction With PhosphorusSebastian Garcia romeroNo ratings yet
- Plant Mineral Nutrition: July 2014Document7 pagesPlant Mineral Nutrition: July 2014Abdul SalamNo ratings yet
- Role of Macro and Micronutrient in Development and Growth of PlantDocument3 pagesRole of Macro and Micronutrient in Development and Growth of PlantÁngeles AlbinoNo ratings yet
- Seaweed (Caulerpa Lentillifera) : Its Effectiveness As An Organic Fertilizer For The Foliage of An Okra PlantDocument13 pagesSeaweed (Caulerpa Lentillifera) : Its Effectiveness As An Organic Fertilizer For The Foliage of An Okra PlantAaron CalderonNo ratings yet
- Science Y8 Notes on PhotosynthesisDocument1 pageScience Y8 Notes on PhotosynthesisNoor Hidayah SambliNo ratings yet
- Anannya Banerjee (6th Sem, Presentation) .Document11 pagesAnannya Banerjee (6th Sem, Presentation) .Soham JashuNo ratings yet
- Nutrient uptake in chrysanthemum grown on various substratesDocument4 pagesNutrient uptake in chrysanthemum grown on various substratesIzza InaniNo ratings yet
- Role of Some of Mineral Nutrients in Biological Nitrogen Fixation Bulletin of PDFDocument9 pagesRole of Some of Mineral Nutrients in Biological Nitrogen Fixation Bulletin of PDFitsasweetlife sosweetNo ratings yet
- Fertilizer Management For Greenhouse VegetablesDocument19 pagesFertilizer Management For Greenhouse VegetablesMentewab EthiopiaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 PLANT AND ANIMAL NUTRITIONDocument6 pagesLesson 3 PLANT AND ANIMAL NUTRITIONNicoleNo ratings yet
- Boron Toxicity and Deficiency in Agricultural Plants: Molecular SciencesDocument20 pagesBoron Toxicity and Deficiency in Agricultural Plants: Molecular Sciencesbaka cijuNo ratings yet
- Mineral NutritionDocument12 pagesMineral Nutritionsourabh peruriNo ratings yet
- Iron nutrition in agriculture_ From synthetic chelates to biochelatesDocument12 pagesIron nutrition in agriculture_ From synthetic chelates to biochelatesAdios ANo ratings yet
- Zinc Sur Guar 2011 ArtDocument5 pagesZinc Sur Guar 2011 ArtKevine Kenmoe MocheNo ratings yet
- Ajlia. Polyphenol Review-2010 (Final)Document23 pagesAjlia. Polyphenol Review-2010 (Final)Jelena MitrovicNo ratings yet
- Understanding Chelated FertilizersDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Chelated FertilizersIntan ClaudyaNo ratings yet
- Boron Deficiency Slows Plant GrowthDocument4 pagesBoron Deficiency Slows Plant Growthendang saptiningsihNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1687157X17300288 MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S1687157X17300288 Mainnagi jainNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Plant GrowthDocument3 pagesPhotosynthesis and Plant GrowthzaivrkNo ratings yet
- NM2Document12 pagesNM2meiNo ratings yet
- Artigo 2Document13 pagesArtigo 2UliNo ratings yet
- 140 298 1 SMDocument9 pages140 298 1 SMPro GamersNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen Foliar Feeding: Has AdvantagesDocument4 pagesNitrogen Foliar Feeding: Has Advantageszikra arahmanNo ratings yet
- Welcome To PapayaDocument8 pagesWelcome To PapayaTrivedi Mma-yurNo ratings yet
- BK 1995 0600.ch001Document6 pagesBK 1995 0600.ch001Gerson OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Biofertilizer Development: Nantakorn BoonkerdDocument7 pagesBiofertilizer Development: Nantakorn BoonkerdGuillermo Jimenez LopezNo ratings yet
- Peroxido de Hidrogeno 2016 Teoria Germinacion RolDocument16 pagesPeroxido de Hidrogeno 2016 Teoria Germinacion RolAntonia MartinezNo ratings yet
- Iron Rice NatureDocument2 pagesIron Rice NatureMarcelo SonegoNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Short QuestionsDocument12 pagesNutrition Short QuestionsGhulam Baqir MazariNo ratings yet
- Module I - Soil 2Document6 pagesModule I - Soil 2cristine abridaNo ratings yet
- ZN Solubilizing Bacteria ISOLATIONDocument12 pagesZN Solubilizing Bacteria ISOLATIONLuis SierraNo ratings yet
- Film Forming Microbial Biopolymers For Commercial Applications - Vijayendra2013Document20 pagesFilm Forming Microbial Biopolymers For Commercial Applications - Vijayendra2013Carinna Saldaña - PierardNo ratings yet
- 11.modes of Plant NutritionDocument8 pages11.modes of Plant NutritionRAVINDRA PRASADNo ratings yet
- Microorganisms 10 00980Document13 pagesMicroorganisms 10 00980Fatima zahra ALTNo ratings yet
- 12856-Article Text-45865-1-10-20190909Document12 pages12856-Article Text-45865-1-10-20190909Gutierrez DieguiittoNo ratings yet
- Antioxidants in Plants and Oleaginous SeedsDocument14 pagesAntioxidants in Plants and Oleaginous SeedspauloNo ratings yet
- Lipid Oxidation and Improving The Oxidative Stability: Fereidoon Shahidi and Ying ZhongDocument13 pagesLipid Oxidation and Improving The Oxidative Stability: Fereidoon Shahidi and Ying ZhongGabriella C VicenteNo ratings yet
- Plant Food FertilizersDocument15 pagesPlant Food FertilizersRonald Cortezano100% (1)
- Handbook of Fertilizers - Their Sources, Make-Up, Effects, and UseFrom EverandHandbook of Fertilizers - Their Sources, Make-Up, Effects, and UseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- 2019 CI Report - KEPRI - HRSG #1Document21 pages2019 CI Report - KEPRI - HRSG #1Gloria Del Carmen Muñoz RamirezNo ratings yet
- Reactor Design and Analysis (MHU)Document164 pagesReactor Design and Analysis (MHU)Chengsi WuNo ratings yet
- Common Assessment Practice #6 (389623) : Read The Following and Answer The Questions BelowDocument26 pagesCommon Assessment Practice #6 (389623) : Read The Following and Answer The Questions BelowSourFroggyNo ratings yet
- MTK - Dilute Solution and Phase RuleDocument40 pagesMTK - Dilute Solution and Phase Rulesaby.svarghese.met14No ratings yet
- Understanding Global PM2.5 Concentrations and Their Drivers in RecentDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Global PM2.5 Concentrations and Their Drivers in Recent張御霆No ratings yet
- Cement-Based SupercapacitorDocument4 pagesCement-Based Supercapacitordr.titaniumNo ratings yet
- Soil Structure and Clay MineralsDocument19 pagesSoil Structure and Clay MineralsSangam AcharyaNo ratings yet
- DRR11-L7.Hydrometeorological HazardsDocument3 pagesDRR11-L7.Hydrometeorological HazardsSigma ImposiumNo ratings yet
- Earth & Life Science-Q2-M2Document14 pagesEarth & Life Science-Q2-M2Yen SantosNo ratings yet
- Global Precipitation MeasurementDocument1 pageGlobal Precipitation MeasurementMrinal SinghNo ratings yet
- ICSE2015 Call4paper 1stDocument2 pagesICSE2015 Call4paper 1stbinhNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument15 pagesChemistry ProjectgUD bOiNo ratings yet
- Five-Day Weather ForecastDocument1 pageFive-Day Weather ForecastErica McClainNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document3 pagesAssignment 4Akarsh PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Essay 3 Draft 3 1Document7 pagesEssay 3 Draft 3 1api-609945085No ratings yet
- 2018 Index IEEE Journal of Photovoltaics Vol. 8Document54 pages2018 Index IEEE Journal of Photovoltaics Vol. 8hakimkorichiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Biochemistry LaboratoryDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Biochemistry LaboratoryKatrina DeveraNo ratings yet
- PlasticbagbannedDocument80 pagesPlasticbagbannedSunita ChayalNo ratings yet
- Tsunami WebquestDocument3 pagesTsunami Webquestapi-264090085No ratings yet
- CONVERTEAM Completes Full-Scale Testing of First HTS Coil For A Hydroelectric GeneratorDocument2 pagesCONVERTEAM Completes Full-Scale Testing of First HTS Coil For A Hydroelectric GeneratorRicky MenonNo ratings yet
- Bigodi TORDocument14 pagesBigodi TORdas_s13No ratings yet
- CNS: GEAS 2 Review Questions and SolutionsDocument5 pagesCNS: GEAS 2 Review Questions and SolutionsEdward Roy “Ying” AyingNo ratings yet
- Material Science Notes: Brief But Effective Chapter 1. INRODUCTION 1 .1 Historical PerspectiveDocument33 pagesMaterial Science Notes: Brief But Effective Chapter 1. INRODUCTION 1 .1 Historical PerspectivePrathap MulagapakaNo ratings yet
- The Thermodynamics of Refrigeration - Principles of Natural Gas Cryogenic Process PDFDocument13 pagesThe Thermodynamics of Refrigeration - Principles of Natural Gas Cryogenic Process PDFRatnin PanityingNo ratings yet
- Vertical GardensDocument20 pagesVertical GardensMarsha MianNo ratings yet
- Tpss 435: Chapter 6: Cation Exchange ReactionsDocument11 pagesTpss 435: Chapter 6: Cation Exchange ReactionsRonny NguyenNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Physics: XT Yt XYDocument5 pagesNuclear Physics: XT Yt XYJessica VarmaNo ratings yet
- Man Made DisasterDocument31 pagesMan Made Disastersam 1No ratings yet
- Rocks (Contd.) : Note 6 Class 9 Sedimentary RocksDocument3 pagesRocks (Contd.) : Note 6 Class 9 Sedimentary RockssubhaseduNo ratings yet