Primary English Class: Tenses Guide
Uploaded by
Evalia NuryanaPrimary English Class: Tenses Guide
Uploaded by
Evalia Nuryana1
Module of Primary English Class
Compiled by Luhung Badranuhdin
Primary Class | English Coach
Compiled by Luhung Badranuhdin
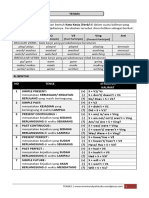
THE TENSE
1. Simple Present
Digunakan untuk menyatakan aktifitas yg dilakukan secara berulag-ulang (daily
activities)
❖ Verbal Sentence
Kalimat verbal adalah kalimat yang menggunakan kata kerja (verb). Kata
kerja (verb) yang digunakan adalah Verb-1 (s/es).
Formula:
(+) Subject + Verb-1 (-s/-es) + Object.
(-) Subject + do/does + not + Verb-1 + Object.
(?) Do/Does + Subject + Verb-1 + Object +?
(-?) Don’t/Doesn’t + Subject + Verb-1 + Object +?
Note
Auxiliary Do/Don’t Does/Doesn’t
I, You, We, She, He, It,
Subject They, Singular subject
Plural subject
Example:
Affirmative (+) Negative (-) Interrogative (?) Negative Interrogative (-?)
I walk. I don’t walk. Do I walk? Don’t I walk?
You walk. You don’t walk. Do you walk? Don’t you walk?
We walk. We don’t walk. Do we walk? Don’t we walk?
They walk. They don’t walk. Do they walk? Don’t they walk?
He walks. He doesn’t walk. Does he walk? Doesn’t he walk?
She walks. She doesn’t walk Does she walk? Doesn’t she walk?
It walks. It doesn’t walk. Does it walk? Doesn’t it walk?
Short answer
Yes answer No answer
No, I / you / we / they don’t
Yes, I / you / we / they do
2 No, he / she / it doesn’t
Yes, he / she / it does
Primary Class | English Coach
Compiled by Luhung Badranuhdin
➢ Using The Other Verbs
(Menggunakan kata kerja yg lain)
For Subject For Subject Translation
(I,You,We, They) (She, He, It, Ali, Ani) (terjemahan)
|V-1| |V (s/es) |
Borrow Borrows Meminjam
Lend Lends Meminjamkan
Buy Buys Membeli
Get Gets Mendapatkan
Give Gives Memberi
Study Studies Belajar
➢ Time Signal of Simple Present
• Seldom (jarang) • Ever (pernah)
• Always (selalu) • Never (tidak pernah)
• Usually (biasanya) • Sometimes (kadang-kadang)
• Rarely (sangat jarang) • Everytime (setiap waktu)
• Often (sering) • Every + Adverb of time
Primary Class | English Coach
Compiled by Luhung Badranuhdin
Penambahan “s/es” pada kata kerja (V)
▪ Kata kerja yang berakhiran “ss, ch, x, o, sh”
Ditambah ‘es’
V0 V(es) Translation
Guess Guesses Menebak
Watch Watches Menonton
Mix Mixes Mencampur
Go Goes Pergi
Wash Washes Mencuci
▪ Kata kerja yang berakhiran “y” yang didahului consonant.
“y” diganti ‘i’ ditambah ‘es’
V0 V(es) Translation
Fly Flies Terbang
Cry Cries Menangis
Worry Worries Khawatir
▪ Kata kerja yang berakhiran “y” yang didahului vocal.
Ditambah ‘s’
V0 V(s) Translation
Play Plays Bermain
Pay Pays Membayar
Pray Prays Berdoa
▪ Selain kata kerja yang bersyarat diatas.
Ditambah ‘s’
V0 V(s) Translation
Love Loves Mencintai
Rent Rents Menyewa
Like Likes Menyukai
1. Menanyakan posisi Subject
Q. W + Verb (s/es) + O?
2. Menanyakan selain posisi Subject
4
Q. W + does/do+ Subject + Verb-1?
Primary Class | English Coach
Compiled by Luhung Badranuhdin
(kata tanya)
Question Word Translation Function
Who Siapa Menanyakan subject person
Whom Siapa Menanyakan object person
What Apa Menanyakan subject/object non
person/verb
When Kapan Menanyakan waktu
Where Dimana Menanyakan tempat
Why Mengapa Menanyakan alasan
Whose Milik siapa Menanyakan kepemilikan
Which Yang mana Menanyakan pilihan
How Bagaimana Menanyakan cara/sifat
How many/much Berapa banyak Menanyakan jumlah
How long Berapa jauh/lama Menanyakan durasi/jarak
How often Seberapa sering Menanyakan kegiatan yang
berulang
How far Seberapa jauh Menanyakan jarak
E.g :
A student always goes to school by bike every morning.
1. The question by answer A student (Subject)
Who always goes to school by bike every morning?
2. The question by the answer goes (Verb)
What does a student do?
3. The question by the answer by bike (adv of manner/cara)
How does a student always go to school every morning?
4. The question by the answer school (adv of place/tempat)
Where does a student always go by bike?
5. The question by the answer every morning (time/waktu)
5 When does a student go to school by bike?
Or
How often does a student go to school by bike?
Primary Class | English Coach
Compiled by Luhung Badranuhdin
❖ Nominal Sentence
Kalimat nominal adalah kalimat yang tidak menggunakan kata kerja, melainkan
berpredikat kata sifat (adjective), kata benda (Noun), atau kata keterangan (adverb).
Formula:
(+) Subject + is/am/are + ANA.
(-) Subject + is/am/are + not + ANA.
(?) Is/Am/Are + Subject + ANA +?
(-?) Isn’t/Aren’t + Subject + ANA +?
Note
To be Am Are/Aren’t Is/Isn’t
Subject
I You, We, They, She, He, It,
Plural subject Singular subject
Example:
Affirmative (+) Negative (-) Introgative (?) Negative Interrogative (-?)
I am smart. I am not stupid. Am I smart? Aren’t I smart?
You are smart. You aren’t stupid. Are you smart? Aren’t you smart?
We are smart. We aren’t stupid. Are we smart? Aren’t we smart?
They are smart. They aren’t stupid. Are they smart? Aren’t they smart?
He is smart. He isn’t stupid. Is he smart? Isn’t he smart?
She is smart. She isn’t stupid. Is she smart? Isn’t she smart?
It is smart. It isn’t stupid. Is it smart? Isn’t it smart?
Short answer
Yes answer No answer
No, I am not
Yes, I am
No, you / we / they are not/aren’t
Yes, you / we / they are
No, he / she / it is not/isn’t
Yes, he / she / it is
➢ The other examples of ANA (Adjective/Noun/Adverb)
Adjective Noun Adverb of place
6 Beautiful Cantik Employee Karyawan At hospital Dirumah sakit
Amazing Luar biasa Teacher Guru In class dikelas
Hungry Lapar Doctor Dokter On field dilapangan
Primary Class | English Coach
Compiled by Luhung Badranuhdin
2. Present Continuous
Digunakan untuk menyatakan aktifitas yg sedang berlangsung pada saat
berlangsungnya pembicaraan.
❖ Verbal Sentence
Kata kerja (verb) yang digunakan adalah to be + V-ing.
Formula:
(+) Subject + is/am/are + V-ing + Object.
(-) Subject + is/am/are + not + V-ing + Object.
(?) Is/Am/Are + Subject + V-ing + Object +?
(-?) Isn’t/Aren’t + Subject + V-ing + Object +?
Note
To be Am Are/Aren’t Is/Isn’t
You, We,
Subject
I They,
She, He, It,
Singular subject
Plural subject
Example:
Affirmative (+) Negative (-) Interrogative (?) Negative Interrogative (-?)
I am walking. I am not walking. Am I walking? Aren’t I walking?
You are walking. You aren’t walking. Are you walking? Aren’t you walking?
We are walking. We aren’t walking. Are we walking? Aren’t we walking?
They are walking. They aren’t walking. Are they walking? Aren’t they walking?
He is walking. He isn’t walking. Is he walking? Isn’t he walking?
She is walking. She isn’t walking. Is she walking? Isn’t she walking?
It is walking. It isn’t walking. Is it walking? Isn’t it walking?
➢ Using The Other Verb-ing
(Menggunakan kata kerja bentuk –ing yg lain)
Translation
Verb-1 Verb-ing
(terjemahan)
Borrow Borrowing Meminjam
Lend Lending Meminjamkan
Buy Buying Membeli
7 Gets Getting Mendapatkan
Give Giving Memberi
Study Studying Belajar
Primary Class | English Coach
Compiled by Luhung Badranuhdin
2. Menanyakan posisi Subject
Q. W + is + V-ing + O?
2. Menanyakan selain posisi Subject
Q. W + is/am/are + Subject + V-ing?
E.g:
My friends are finishing the task in the class.
a. The question by the answer my friends (Subject)
Who is finishing the task in the class?
b. The question by the answer my (possessive adjective in Subject)
Whose friends are finishing the task in the class?
c. The question by the answer the task (Object benda)
What are my friends finishing in the class?
d. The question by the answer in the class (adv of place/tempat)
Where are my friends finishing the task?
➢ Time signal of Present Continuous
• Now (sekarang) • At present (sekarang/saat ini)
• Right now (sekarang juga) • At moment (sekarang/saat ini)
• Still (masih) • Tonight (malam ini)
Nominal sentence pada Present Continuous sama dangan nominal sentence pada
Simple Present
Primary Class | English Coach
Compiled by Luhung Badranuhdin
3. Present Present Perfect
Digunakan untuk menyatakan aktifitas yg telah lengkap dilakukan dimasa lampau
hasilnya masih bisa dilihat sampai sekarang (sudah).
❖ Verbal Sentence
Kata kerja (verb) yang digunakan adalah Has/Have + Verb-3.
Formula:
(+) Subject + has/have + Verb-3 + Object.
(-) Subject + has/have + not + Verb-3 + Object.
(?) Has/Have + Subject + Verb-3 + Object +?
(-?) Hasn’t/Haven’t + Subject + Verb-3 + Object +?
Note
Auxiliary Have/Haven’t Has/Hasn’t
I, You, We,
They, She, He, It,
Subject Singular subject
Plural subject
E.g:
Affirmative (+) Negative (-) Interrogative (?) Negative Interrogative (-?)
I have walked. I haven’t walked. Have I walked? Haven’t I walked?
You have walked. You haven’t walked. Have you walked? Haven’t you walked?
We have walked. We haven’t walked. Have we walked? Haven’t we walked?
They have walked. They haven’t walked. Have they walked? Haven’t they walked?
He has walked. He hasn’t walked. Has he walked? Hasn’t he walked?
She has walked. She hasn’t walked. Has she walked? Hasn’t she walked?
It has walked. It hasn’t walked. Has it walked? Hasn’t it walked?
➢ Using The Other Verb-3
(Menggunakan kata kerja bentuk –ke 3 yg lain)
Regular verb (V0 + d/ed)
Translation
Verb-1 Verb-2 Verb-3
(terjemahan)
Borrow Borrowed Borrowed Meminjam
Admire Admired Admired Mengagumi
9
Arrange Arranged Arranged Menyusun
Arrive Arrived Arrived Tiba
Avoid Avoided Avoided Menghindari
Help Helped Helped Menolong
Primary Class | English Coach
Compiled by Luhung Badranuhdin
Irregular verb (tidak beraturan)
Translation
Verb-1 Verb-2 Verb-3
(terjemahan)
Become Became Become Menjadi
Lend Lent Lent Meminjamkan
Buy Bought Bought Membeli
Get Got Got/Gotten Mendapatkan
Give Gave Given Memberi
Meet Met Met Bertemu
1. Menanyakan posisi Subject
Q. W + has + Verb-3 + O?
2. Menanyakan selain posisi Subject
Q. W + has/have + Subject + Verb-3?
E.g:
Jane has watched a movie since her mother arrived home.
a. The question by the answer Jane (Subject)
Who has watched a movie since her mother arrived home?
b. The question by the answer watched (Verb)
What has she done since her mother arrived home?
c. The question by the answer a movie (Object benda)
What has she watched since her mother arrived home?
d. The question by the answer since her mother arrived home (adv of time/waktu)
When has she watched a movie?
➢ Time Signal of Present Perfect
• Already (sudah) • Since (sejak)
• Recently (baru-baru ini) • Just (baru saja)
10 • Lately (akhir-akhir ini) • Not...yet (belum)
• Until now (sampai sekarang) • Up to now (sampai saat ini)
Primary Class | English Coach
Compiled by Luhung Badranuhdin
❖ Nominal Sentence
To be yang digunakan adalah has/have + been.
Formula:
(+) Subject + has/have + been + ANA.
(-) Subject + has/have + not + been + ANA.
(?) Has/Have + Subject + been + ANA +?
(-?) Hasn’t/Haven’t + Subject + been + ANA +?
Note
Auxiliary Have/Haven’t Has/Hasn’t
I, You, We,
They, She, He, It,
Subject Singular subject
Plural subject
Example:
Affirmative (+) Negative (-)
I have been at home. I haven’t been at home.
You have been at home. You haven’t been at home.
We have been at home. We haven’t been at home.
They have been at home. They haven’t been at home.
He has been at home. He hasn’t been at home.
She has been at home. She hasn’t been at home.
It has been at home. It hasn’t been at home.
Interrogative (?) Negative Interrogative (-?)
Haven’t I been at home? Haven’t I been at home?
Haven’t you been at home? Haven’t you been at home?
Haven’t we been at home? Haven’t we been at home?
Haven’t they been at home? Haven’t they been at home?
Hasn’t he been at home? Hasn’t he been at home?
Hasn’t she been at home Hasn’t she been at home?
11 Hasn’t it been at home? Hasn’t it been at home?
Primary Class | English Coach
Compiled by Luhung Badranuhdin
1. Menanyakan posisi Subject
Q. W + has + been + ANA?
2. Menanyakan selain posisi Subject
Q. W + has/have + Subject + been + ANA?
E.g:
They have been in London since 2015.
a. The question by the answer they (Subject)
Who has been in London since 2015?
b. The question by the answer in London (Adv of place/tempat)
Where have they been in London since 2015?
c. The question by the answer since 2015 (adv of time/waktu)
When have they been in London?
12
Primary Class | English Coach
Compiled by Luhung Badranuhdin
4. Simple Past
Digunakan untuk menyatakan aktifitas yg telah terjadi pada waktu tertentu
dimasa lampau.
❖ Verbal Sentence
Kata kerja (verb) yang digunakan adalah Verb-2.
Formula:
(+) Subject + Verb-2 + Object.
(-) Subject + did + not + Verb-1 + Object.
(?) Did + Subject + Verb-1 + Object +?
(-?) Didn’t + Subject + Verb-1 + Object +?
Note
Auxiliary Did
Subject All Subjects
Example:
Affirmative (+) Negative (-) Interrogative (?) Negative Interrogative (-?)
I walked. I didn’t walk. Did I walk? Didn’t I walk?
You walked. You didn’t walk. Did you walk? Didn’t you walk?
We walked. We didn’t walk. Did we walk? Didn’t we walk?
They walked. They didn’t walk. Did they walk? Didn’t they walk?
He walked. He didn’t walk. Did he walk? Didn’t he walk?
She walked. She didn’t walk Did she walk? Didn’t she walk?
It walked. It didn’t walk. Did it walk? Didn’t it walk?
Short answer
Yes answer No answer
Yes, I / you / we / they / she / he did No, I / you / we / they / she / he didn’t
13
Primary Class | English Coach
Compiled by Luhung Badranuhdin
1. Menanyakan posisi Subject
Q. W + Verb-2 + O?
2. Menanyakan selain posisi Subject
Q. W + did+ Subject + Verb-1?
E.g:
Merry put her books on the table yesterday.
a. The question by the answer Merry (Subject)
Who put her books on the table yesterday?
b. The question by the answer put (Verb)
What did Merry do yesterday?
c. The question by the answer her books (Object benda)
What did Merry put on the table yesterday?
d. The question by the answer on the table (adv of place/tempat)
Where did Merry put her books yesterday?
e. The question by the answer yesterday (adv of time/waktu)
When did Merry put her books on the table?
➢ Time Signal of Simple Past
• Yesterday (kemarin) • Last night (semalam/tadi malam)
• This morning (tadi pagi) • Last week (minggu lalu)
• Two days ago (dua hari lalu) • Last month (bulan lalu)
• Time + ago (.....lalu) • Last + time (......lalu)
14
Primary Class | English Coach
Compiled by Luhung Badranuhdin
❖ Nominal Sentence
❖ To be yang digunakan adalah Was/Were.
Formula:
(+) Subject + was/were + ANA.
(-) Subject + was/were + not + ANA.
(?) Was/Were + Subject + ANA +?
(-?) Was/Were + Subject + ANA +?
Note
To be Was/Wasn’t Were/Weren’t Was/Wasn’t
Subject
I You, We, They, She, He, It,
Plural subject Singular subject
Example:
❖ (+)
Affirmative Negative (-) Introgative (?) Negative Interrogative (-?)
❖ Wasn’t I at home?
I was at home. I wasn’t at home. Was I at home?
❖
You were at Weren’t you at home?
❖home. You weren’t at home. Were you at home?
❖home.
We were at We weren’t at home. Were we at home? Weren’t we at home?
They were❖at home. They weren’t at home. Were they at home? Weren’t they at home?
❖ Wasn’t he at home?
He was at home. He wasn’t at home. Was he at home?
She was at home. She wasn’t at home. Was she at home? Wasn’t she at home?
It was at home. It wasn’t at home. Was it at home? Wasn’t it at home?
Short answer
Yes answer No answer
No, I was not
Yes, I was
No, you / we / they weren’t
Yes, you / we / they were
No, he / she / it wasn’t
Yes, he / she / it was
15
Primary Class | English Coach
Compiled by Luhung Badranuhdin
2. Menanyakan posisi Subject
Q. W + was + O?
2. Menanyakan selain posisi Subject
Q. W + was/were + Subject + Verb-1?
E.g:
Henry was at the office when it was raining.
a. The question by the answer Henry (Subject)
Who was at the office when it was raining?
b. The question by the answer at the office (adv of place/tempat)
Where was Henry when it was raining?
c. The question by the answer when it was raining (adv of time/waktu)
When was Henry at the office?
16
Primary Class | English Coach
Compiled by Luhung Badranuhdin
5. Simple Future
Digunakan untuk menyatakan aktifitas yg akan dilakukan dimasa yg akan
datang.
❖ Verbal Sentence
Kata kerja (verb) yang digunakan adalah Will + Verb - 1.
Formula:
(+) Subject + will + Verb-1+ Object.
(-) Subject + will + not + Verb-1 + Object.
(?) Will + Subject + Verb-1 + Object +?
(-?) Won’t + Subject + Verb-1 + Object +?
Note
Auxiliary Will/Won’t Shall
All Subjects
I
Subject
We
Example:
Affirmative (+) Negative (-) Interrogative (?) Negative Interrogative (-?)
I will go holiday. I won’t go holiday. Will I go holiday? Won’t I walk?
You will go holiday. You won’t go holiday. Will you go holiday? Won’t you walk?
We will go holiday. We won’t go holiday. Will we go holiday? Won’t we walk?
They will go holiday. They won’t go holiday. Will they go holiday? Won’t they walk?
He will go holiday. He won’t go holiday. Will he go holiday? Won’t he walk?
She will go holiday. She won’t go holiday. Will she go holiday? Won’t she walk?
It will go holiday. It won’t go holiday. Will it go holiday? Won’t it walk?
Short answer
Yes answer No answer
Yes, I / you / we / they / she / he will No, I / you / we / they / she / he won’t
17
Primary Class | English Coach
Compiled by Luhung Badranuhdin
1. Menanyakan posisi Subject
Q. W + will + Verb-1 + O?
2. Menanyakan selain posisi Subject
Q. W + will+ Subject + Verb-1?
E.g:
The workers will go on strike next month.
a. The question by the answer The workers (Subject)
Who will go on strike next month?
b. The question by the answer go on (Verb)
What will the workers do next month?
c. The question by the answer next month (adv of time/waktu)
When will the workers go on strike?
➢ Time Signal of Simple Future
• Tomorrow (besok) • The day after tomorrow (besok lusa)
• Later (nanti) • Sometime (suatu saat nanti)
• Next week (minggu depan)
• Some days later (beberapa hari nanti)
• This weekend (akhir pekan ini)
• Next month (bulan depan)
• Soon (segera)
• Next + time (....depan)
18
Primary Class | English Coach
Compiled by Luhung Badranuhdin
❖ Nominal Sentence
❖ To be yang digunakan adalah Will + be.
Formula:
(+) Subject + will + be + ANA.
(-) Subject + will + not + be + ANA.
(?) Will + Subject + be + ANA +?
(-?) Won’t + Subject + be + ANA +?
Note
Auxiliary Will/Won’t be Shall
All Subjects
I
Subject
We
Example:
❖ (+)
Affirmative Negative (-) Introgative (?) Negative Interrogative (-?)
❖ Won’t I be there?
I will be there. I won’t be there. Will I be there?
❖
You will be there. You won’t be there. Will you be there? Won’t you be there?
❖
❖
We will be there. We won’t be there. Will we be there? Won’t we be there?
They will be ❖
there. They won’t be there. Will they be there? Won’t they be there?
❖ Won’t he be there?
He will be there. He won’t be there. Will he be there?
She will be there. She won’t be there. Will she be there? Won’t she be there?
It will be there. It won’t be there. Will it be there? Won’t it be there?
19
Primary Class | English Coach
Compiled by Luhung Badranuhdin
6. Modal Auxiliary
❖ Verbal Sentence
Kata kerja (verb) yang digunakan adalah Modal Auxiliary + Verb-1.
Formula:
(+) Subject + Modal Auxiliary + Verb-1+ Object.
(-) Subject + Modal Auxiliary + not + Verb-1 + Object.
(?) Modal Auxiliary + Subject + Verb-1 + Object +?
(-?) (Modal Auxiliary + not) + Subject + Verb-1 + Object +?
Modal Auxiliary:
Present form Past form Translation
Can Could
Dapat/bisa
Can’t Couldn’t
May Might
Mungkin/boleh
Mayn’t Mightn’t
Must Had to
Harus/wajib
Mustn’t Didn’t have to
Shall Should Shall = akan (I & We)
Shan’t Shouldn’t Should = seharusnya (all subject)
Will Would
Akan
Won’t Wouldn’t
Ought to Semestinya/ seharusnya
Seharusnya/ sebaiknya/
Had better
semestinya
20
Primary Class | English Coach
Compiled by Luhung Badranuhdin
▪ Positive Sentence
Modal
Subject Verb-1 Object
Auxiliary
I
You Can
We
They
She
He
May Speak English
It
Ali Must
Ani
▪ Negative Sentence
Modal
Subject Verb-1 Object
Auxiliary+not
I
Cannot
You
We Can’t
They
May not
She
Mayn’t
Speak English
He
It
Ali Must not
Ani Mustn’t
▪ Introgative Sentence
Modal Question
Subject Verb-1 Object
Auxiliary Mark
I
Can You
We
They
May She Speak English
He
It
Must Ali
Ani
21
Primary Class | English Coach
Compiled by Luhung Badranuhdin
▪ Negative Introgative Sentence
(Modal Question
Subject Verb-1 Object
Auxiliary+not) Mark
I
Can’t You
We
They
Mayn’t She Speak English
He
It
Mustn’t Ali
Ani
▪ Question Word Sentence (Object)
Question
Question Word Auxiliary Subject Verb-1
mark
I
Can You
We
They
May She Speak
He
It
Must Ali
Ani
Tidak boleh ada 2 atau lebih modal auxiliary dalam satu kalimat.
22
Primary Class | English Coach
Compiled by Luhung Badranuhdin
❖ Nominal Sentence
Kata kerja (verb) yang digunakan adalah Modal Auxiliary + be + ANA.
Formula:
(+) Subject + Modal Auxiliary + be + ANA.
(-) Subject + Modal Auxiliary + not + be + ANA.
(?) Modal Auxiliary + Subject + be + ANA +?
(-?) (Modal Auxiliary + not) + Subject + be + ANA +?
▪ Positive Sentence
Modal
Subject be ANA
Auxiliary
I
You Can
We
They
She May be successful
He
It
Ali Must
Ani
▪ Negative Sentence
Modal
Subject be ANA
Auxiliary+not
I
Cannot
You
We Can’t
They
May not
She
Mayn’t
be successful
He
It
Ali Must not
Ani Mustn’t
23
Primary Class | English Coach
Compiled by Luhung Badranuhdin
▪ Introgative Sentence
Modal Question
Subject be ANA
Auxiliary Mark
I
Can You
We
They
May She be successful
He
It
Must Ali
Ani
▪ Negative Introgative Sentence
(Modal Question
Subject be ANA
Auxiliary+not) Mark
I
Can’t You
We
They
Mayn’t She be successful
He
It
Mustn’t Ali
Ani
▪ Question Word Sentence (Object)
Question
Question Word Auxiliary Subject be
mark
I
Can You
We
They
May She be
He
It
Must Ali
24 Ani
Primary Class | English Coach
Compiled by Luhung Badranuhdin
➢ More Examples:
❖
(+) She can solve the problem.
(-) He can’t visit the museum.
(?) Can you go to the shopping mall?
(+) He could ride the horse.
(-) I couldn’t attend the party.
(?) Could I use your bicycle, please?
❖
(+) We may reach Delhi on Sunday.
May (-) You mayn’t leave to Hyderabad today.
(?) May I go to beach to spend holiday?
(+) They might get a chance.
Might (+) We might have helped you.
(+) The situation might be getting worse.
❖
(+) I shall go to beach tomorrow.
Shall (-) We shan’t work six days a week.
(?) Shall I read book tomorrow?
(+) You should attend the class regularly.
Should (-) Jonny shouldn’t abide by his promise.
(?) Should people work sincerely.
❖
(+) Either Peter or I must leave now.
Must (+) You must take breakfast early in the morning.
(?) Must I take interval.
(+) She had to be generous.
Had to (-) He didn’t have to visit his friend once in a while.
(?) Did we have to help the poor?
25
Primary Class | English Coach
Compiled by Luhung Badranuhdin
7. Conditional Sentence
(Kalimat pengandaian/bersyarat)
❖ Conditional sentence type 1
Kelimat pengandaian yang menunjukkan kemungkinan terjadi dimasa depan jika
syaratnya terpenuhi (future possible).
Formula:
If Simple Present, Simple Future
Or
Simple Future if Simple Present
Example:
✓ If she comes home, I will tell her about the exam.
✓ You will pass the exam if you study hard.
✓ If I have a lot of money, I will treat you.
❖ Conditional sentence type 2
Kelimat pengandaian yang menunjukkan pengandaian yang berlawanan atau
bertentangan dengan kenyataan yang ada di masa sekarang (present unreal).
Formula:
If Simple Past, Past Future
Or
Past Future if Simple Past
The fact: Simple Present, so Simple Present
Or
Simple Present because Simple Present
Notes:
Auxiliary Were
26
Subject All Subjects
Primary Class | English Coach
Compiled by Luhung Badranuhdin
Example:
✓ If he didn’t listen to my advice, he would be confused there.
Fact: He listens to my advice so he isn’t confused there.
✓ If it were Sunday, I would invite you to go to Bali.
Fact: It isn’t Sunday so I don’t invite you to go to Bali.
✓ If she were a beautiful flower, I would be a bee.
Fact: she isn’t a beautiful flower so I’m not a bee.
Note:
1. Fakta selalu berkebalikan/berlawanan dengan Conditional sentence-
nya.
2. Jika conditional sentence kalimat positive (+), maka The Fact adalah
kalimat negative (-)
❖ Conditional sentence type 3
Kelimat pengandaian yang menunjukkan pengandaian yang tidak mungkin terjadi
pada masa lalu atau berlawanan dengan kenyataan yang ada pada waktu
lampau(Penyesalan/Regret).
Formula:
If Past Perfect, Past Future Perfect
Or
Past Future Perfect if Past Perfect
The fact: Simple Past, so Simple Past
Or
Simple Past because Simple Past
27
Notes:
Auxiliary Would have (been) Had (been)
Subject All Subjects
Primary Class | English Coach
Compiled by Luhung Badranuhdin
Example:
✓ Anton wouldn’t have come to her party if she hadn’t invited him
yesterday.
Fact: Anton came to her party because she invited him yesterday.
✓ He would have got a precious prize from his father if he had got a
good value in the test.
Fact: He didn’t get a precious prize from his father because he didn’t
get a good value in the test.
✓ If Romeo had driven his car carefully, he wouldn’t have got the
accident.
Fact: Romeo didn’t drive his car carefully so he got the accident.
Note:
1. Fakta selalu berkebalikan/berlawanan dengan Conditional sentence-
nya.
2. Jika conditional sentence kalimat positive (+), maka The Fact adalah
kalimat negative (-)
28
Primary Class | English Coach
Compiled by Luhung Badranuhdin
PRONOUNS
Subject Object Possessive Possessive Reflexive
Pronouns Pronouns Adjectives Pronouns Pronouns
I Me My Mine Myself
You You Your Yours Yourself
We Us Our Ours Ourselves
They Them Their Theirs Themselves
She Her Her Hers Herself
He Him His His Himself
It It Its (not used) Itself
➢ I bring my book for me because this book is mine.
29
Primary Class | English Coach
Compiled by Luhung Badranuhdin
PREPOTITIONS
30
Primary Class | English Coach
Compiled by Luhung Badranuhdin
You might also like
- Present Continuous Tense Guide for IX ClassNo ratings yetPresent Continuous Tense Guide for IX Class5 pages
- Understanding Parts of Speech and TensesNo ratings yetUnderstanding Parts of Speech and Tenses16 pages
- Simple Present and Present Progressive TensesNo ratings yetSimple Present and Present Progressive Tenses18 pages
- Understanding ASEAN and Simple Present TenseNo ratings yetUnderstanding ASEAN and Simple Present Tense15 pages
- English Grammar Essentials for MidwiferyNo ratings yetEnglish Grammar Essentials for Midwifery29 pages
- English Tenses Explained: A Comprehensive GuideNo ratings yetEnglish Tenses Explained: A Comprehensive Guide22 pages
- Worms - Reading Comprehension For Primary/elementary Children100% (1)Worms - Reading Comprehension For Primary/elementary Children2 pages
- A Design Approach & Selected Wind-Tunnel Results at High Subsonic Speeds For Wing-Tip Mounted Winglets PDFNo ratings yetA Design Approach & Selected Wind-Tunnel Results at High Subsonic Speeds For Wing-Tip Mounted Winglets PDF33 pages
- Visual Thinking Strategies for ComprehensionNo ratings yetVisual Thinking Strategies for Comprehension10 pages
- Information Bulletin: JENPAS (UG) - 2025No ratings yetInformation Bulletin: JENPAS (UG) - 202531 pages
- Sewer Network and Pumping Station DesignNo ratings yetSewer Network and Pumping Station Design4 pages
- Mitutoyo Linear Scale DRO Systems GuideNo ratings yetMitutoyo Linear Scale DRO Systems Guide34 pages
- KAMCO Company Profile and Product OverviewNo ratings yetKAMCO Company Profile and Product Overview7 pages
- Ethioworld Trading PLC: Coal Mining Feasibility100% (6)Ethioworld Trading PLC: Coal Mining Feasibility75 pages
- 02 Handout 03 Rizal and The Theory of NationalismNo ratings yet02 Handout 03 Rizal and The Theory of Nationalism2 pages