Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ICU One Pager Cystic Lung Disease
ICU One Pager Cystic Lung Disease
Uploaded by
juan ramon milanes grageraOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ICU One Pager Cystic Lung Disease
ICU One Pager Cystic Lung Disease
Uploaded by
juan ramon milanes grageraCopyright:
Available Formats
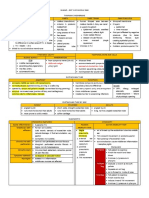
CYSTIC LUNG DISEASE by Nick Mark MD ONE onepagericu.
com Link to the
most current
@nickmmark version →
DEFINITIONS: Very Thin (<1mm) · COPD (UL) · Ritalin Lung
or no walls
EMPHYSEMA
· ɑ1AT (LL) (LL predom) Emphysema descriptors: Cyst mimics:
Are air-filled areas present within Thick walled Thin walled · Malignancy · Septic emboli · BLEBS <2 cm CYSTIC BRONCHIECTASIS –
(>4mm) CAVITY · BULLAE > 2 cm • Dilated airways (not real cysts)
the lung parenchyma? (1-4mm) · Infection · Vasculitis
· GIANT BULLAE > 30% of hemithorax
v1.0 (2020-11-15)
HONEYCOMBING –
Thin walled
(1-4mm)
CYST • ≥3 adjacent air-filled spaces
CC BY-SA 3.0
• seen with emphysema, not
with cysts
Upper Lobe predominant Diffuse Lower Lobe predominant
LANGERHANS CELL HISTIOCYTOSIS NEUROFIBROMATOSIS TYPE 1 LYMPHANGIOLYOMIOMATOSIS BIRT-HOGG-DUBE LYMPHOCYTIC INTERSITIAL
(LCH) (NF1) (LAM) (BHD) PNEUMONITIS (LIP)
· Smoking-associated inflammation · Genetic; neurofibromin (NF1) · Genetic or spontaneous, assoc. · Genetic; AD folliculin (FLCN) · Autoimmune (Sjogren’s
♂>♀ · Skin: café-au-lait spots,axillary w/ tuberous sclerosis (TSC),♀>>♂ mutation, ♀=♂ prevalence syndrome) & immunodeficiency
· Chest: UL freckling, neurofibromas, · Skin: facial angiofibromas · Kidney: chromophobe RCC (HIV) associated inflammation
predominant · Chest: UL · Kidney: Angiomyolipoma tumors · Skin: fibrofolliculomas and · Dense lymphocyte infiltrates;
‘bizarre shaped’ predominant · Chest: Uniform size angiofibromas overlap with FB
cysts & cysts, diffuse distribution · Chest: LL · Chest: LL
‘stellate shaped’ emphysema, & of cysts, Intralobular predominant Predominant cysts
centrilobular thickening, & lentiform cysts; in bronchovascular
bullae, & LL
nodules (1-5mm) fibrosis pleural effusions often presents distribution
(chylothorax) with PTX
PNEUMOCYSTIS JIROVECI PARACOCCIDIOIDOMYCOSIS LIGHT CHAIN DEPOSITION DISEASE DESQUAMATIVE INTERSTITIAL FOLLICULAR BRONCHIOLITIS
PNEUMONIA (PJP) (LCDD) PNEUMONITIS (DIP) (FB)
· Infectious; occurs in individuals · Infectious; occurs in rural workers · Lymphoproliferative disease assoc · Smoking-associated ILD often · Associated with collagen vascular
with severe immunocompromise (immunocompentent) in S. America (esp multiple myeloma) causing associated with RB-ILD; ♂>♀ disease & immunodeficiency
(HIV CD4<200, BMT, etc) ♂>♀ non-amyloid deposition of Ab;♀=♂ · Chest: LL · Chest: centrilobular
· Chest: UL · Causes diffuse LAD and can cause · Kidney: Proteinuria/nephrotic predominant and GGOs and nodules,
pneumotoceles & granulomas in many organs syndrome Subpleural/basilar sometimes with
subpleural plebs, · Chest: scattered cysts without lobar · Chest: variable predominant cysts medium to large LL
GGOs (UL if on predominance, reverse halo sign, sized cysts, of uniform small predominant cysts
PPx, LL if not; cavitations, and bronchiectasis. nodules, & LAD size with running along
peripheral associated GGOs bronchovascular
sparing GGOs) bundles
HYPERSENSITIVITY PNEUMONITIS AMYLOIDOSIS CYSTIC PULMONARY PULMONARY PAPPILLOSIS (PP) CONSTRICTIVE BRONCHIOLITIS
· Inflammation due to inhaled · Can occur with 1° or 2 ° amyloidosis METASTATIC DISEASE · Infectious; vertically transmitted · Occurs due to viral, autoimmune,
antigens, forming granulomas · Chest: diffuse peripheral thin- · Metastastic malignancy usually HPV infxn; very rare. or GVHD. Typically causes mosaic
· Usually causes GGO and mosaicism walled cysts, often also with nodules causes cavitary (thick walled) · Chest: usually endobronchial attention & bronchiectasis. Rarely
rarely may cause UL cyst formation (including endobronchial) or masses lesions. lesions, rarely diffuse pulmonary causes few small diffuse cysts
· Diffuse cysts can be seen with nodules that turn into cysts.
EHLERS-DANLOS SYNDROME PROTEUS SYNDROME epitheliod metastasis, & rarely with FIRE-EATERS LUNG HYPER-IGE SYNDROME
adenocarcinomas/sarcomas as · Aspiration of flammable petroleum · Immunodeficiency/STAT3 mutation
· Genetic connective tissue disease, · Rare Genetic syndrome (AKT1) that
reported here compounds causes inflammation; causing sinopulmonary infections, &
rarely may develop diffuse cysts may present with diffuse cysts
leading to cavitary or cystic disease rarely pneumatoceles & cysts.
You might also like
- Lung - PathologyDocument34 pagesLung - Pathologyjmosser100% (3)
- Reversible and Irreversible Cell InjuryDocument55 pagesReversible and Irreversible Cell Injurygabb bbNo ratings yet
- BIND ScoreDocument2 pagesBIND Scoremahi_elsemary701175% (4)
- SWOT Analysis For The MENA RegionDocument1 pageSWOT Analysis For The MENA RegionZekriNo ratings yet
- Derm Exam Chart 1Document3 pagesDerm Exam Chart 1emilyjvaldez99No ratings yet
- Radio Lec 02 IMAGING OF COMMON INFECTIOUS DISEASEDocument4 pagesRadio Lec 02 IMAGING OF COMMON INFECTIOUS DISEASEapi-3704562No ratings yet
- Lung Patterns Made Easy (Proceedings) - DVM 360Document3 pagesLung Patterns Made Easy (Proceedings) - DVM 360dmantsioNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Tract: Mashuri, DR.,SP - Rad.,M.KesDocument102 pagesRespiratory Tract: Mashuri, DR.,SP - Rad.,M.KesMirza SullivanNo ratings yet
- GIT Causes-Alcohol LevelDocument8 pagesGIT Causes-Alcohol LevelPuteri Atiqah SyaqilaNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document55 pagesPresentation 1shiviraghuNo ratings yet
- Cystic HygromaDocument13 pagesCystic HygromaafrisiammyNo ratings yet
- Pulm TBDocument3 pagesPulm TBRinghalsNo ratings yet
- Surgical Pathology - Major and Minor Salivary GlandsDocument2 pagesSurgical Pathology - Major and Minor Salivary GlandsIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Varicose - VeinsDocument40 pagesVaricose - VeinsBibi MariamNo ratings yet
- 7 Embolism, Infarction & ShockDocument57 pages7 Embolism, Infarction & Shockجهاد مالك حاتم حسينNo ratings yet
- PracticalDocument89 pagesPracticalAthEer AhmadNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Module - PVDDocument2 pagesCardiac Module - PVDMarie MNNo ratings yet
- Group11lymphoedema and Lymphoma-1Document64 pagesGroup11lymphoedema and Lymphoma-1Basit AliNo ratings yet
- AutopsyDocument29 pagesAutopsyAkshita Amit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Blue Purple Vascular LesionsDocument5 pagesBlue Purple Vascular Lesionsnatasha_yazidNo ratings yet
- MICRO Classification of LeprosyDocument1 pageMICRO Classification of LeprosyherrerachaimNo ratings yet
- 07 Cavitary & Cystic LesionsDocument110 pages07 Cavitary & Cystic Lesionsapi-25944730100% (4)
- Neck Anatomy: Lymph NodesDocument5 pagesNeck Anatomy: Lymph NodesKiara GovenderNo ratings yet
- 1 NCM112 Sexually Transmitted Diseases de VeyraDocument9 pages1 NCM112 Sexually Transmitted Diseases de VeyraGrace OrdameNo ratings yet
- Patho RevDocument21 pagesPatho RevJo CastilloNo ratings yet
- Chest Radiology For DummiesDocument6 pagesChest Radiology For DummiesTom MallinsonNo ratings yet
- 1.pathology-Practical - Disease Affecting Uper Respiratory TractDocument34 pages1.pathology-Practical - Disease Affecting Uper Respiratory TractSounds of MindNo ratings yet
- Template (Mukmin)Document15 pagesTemplate (Mukmin)Amirul MukminNo ratings yet
- Bacterial and Parasitic Cns InfxnsDocument35 pagesBacterial and Parasitic Cns InfxnsLajja Parikh PatelNo ratings yet
- Patho by DR - Elnemr (RPR)Document15 pagesPatho by DR - Elnemr (RPR)mrhazemahmed00No ratings yet
- ENT in A Nutshell 2Document28 pagesENT in A Nutshell 2Gyleen ElegioNo ratings yet
- Practical (I) Diseases of Lymph Nodes and Spleen BMS 201-FALL 2021 Prof. Iman Hewedi Iman - Hewedi@gu - Edu.egDocument38 pagesPractical (I) Diseases of Lymph Nodes and Spleen BMS 201-FALL 2021 Prof. Iman Hewedi Iman - Hewedi@gu - Edu.egRowaa SamehNo ratings yet
- Tertiary SyphilisDocument19 pagesTertiary SyphilisLakshya J BasumataryNo ratings yet
- Ulcers, Sinuses & FistulaeDocument48 pagesUlcers, Sinuses & Fistulaeawais mpNo ratings yet
- PPSLSX: Lpenipneraltnmor - TLDocument3 pagesPPSLSX: Lpenipneraltnmor - TLmarielleaudreeyNo ratings yet
- Neurosurgery Summaryupdated PDFDocument16 pagesNeurosurgery Summaryupdated PDFEl FaroukNo ratings yet
- Mesothelioma:: Benign Pleural FibromaDocument7 pagesMesothelioma:: Benign Pleural FibromaCharm MeelNo ratings yet
- Scut Report: Chest X-RayDocument1 pageScut Report: Chest X-RayJames Booth100% (4)
- ENT Deferential Diagnosis MEDADDocument22 pagesENT Deferential Diagnosis MEDADReham AshourNo ratings yet
- Lung Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 pagesLung Anatomy and PhysiologySabrinah TamayoNo ratings yet
- Acne Keloidalis Scars: Non-Frame VersionDocument48 pagesAcne Keloidalis Scars: Non-Frame Versionpinky catNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Clients With Ventilation DisordersDocument6 pagesNursing Care of Clients With Ventilation DisordersLuna MarieNo ratings yet
- Shanz - Ent 1.02 Middle EarDocument3 pagesShanz - Ent 1.02 Middle EarPetrina XuNo ratings yet
- Infectious DiseasesDocument5 pagesInfectious DiseasesAndrew BonusNo ratings yet
- All Signs in Radiology From Radiopedia: GynacDocument3 pagesAll Signs in Radiology From Radiopedia: GynacVIDYULATA NAIKNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Chest FindingsDocument5 pagesAbnormal Chest FindingsAbishek Prince100% (1)
- DPLD Shoyabbsmmu 180722070931Document128 pagesDPLD Shoyabbsmmu 180722070931nnn nnnNo ratings yet
- The Third LectureDocument14 pagesThe Third LectureMustafa AliNo ratings yet
- Chest Radiology PG 2Document109 pagesChest Radiology PG 2rumanameman107No ratings yet
- SGIAP Case Presentation LoongDocument21 pagesSGIAP Case Presentation Loongna huNo ratings yet
- Chest Radiology For Dummies PDFDocument6 pagesChest Radiology For Dummies PDF0395No ratings yet
- Quiz 1 PULMONOLOGY (Basics Table)Document2 pagesQuiz 1 PULMONOLOGY (Basics Table)Paige HardekopfNo ratings yet
- Lymphadenopathy: A. Suryaveda Aakanksha Sangwaan Aishwarya Alankar ParasharDocument21 pagesLymphadenopathy: A. Suryaveda Aakanksha Sangwaan Aishwarya Alankar ParasharfjajflkajfNo ratings yet
- Surgery Short Case - HydroceleDocument1 pageSurgery Short Case - HydroceleHeroNo ratings yet
- Thrombosis and EmbolismDocument43 pagesThrombosis and Embolismkanchana pvnNo ratings yet
- 10 Respiratory System 2Document73 pages10 Respiratory System 2Angel BumanglagNo ratings yet
- TracheaDocument2 pagesTracheaChalsey Jene LorestoNo ratings yet
- 27.neck SwellingsDocument4 pages27.neck SwellingsDurga VoraNo ratings yet
- Usmp Practica 12 Sist Resp C-Vasc Lu - Ma 21-22 May 18 Ok Ok 16may18Document200 pagesUsmp Practica 12 Sist Resp C-Vasc Lu - Ma 21-22 May 18 Ok Ok 16may18Jose SantanaNo ratings yet
- 06 1 授業前スライド 20210107用Document27 pages06 1 授業前スライド 20210107用Lan NguyenNo ratings yet
- X Ray Appearance of Chest PathologyDocument95 pagesX Ray Appearance of Chest Pathologykumarvj123No ratings yet
- School Based Vaccination For Import To QVACDocument3 pagesSchool Based Vaccination For Import To QVACMarita SibugNo ratings yet
- Although These Creatures Look Just Like Their Lesser Kin, They Are Far More Deadly and CunningDocument1 pageAlthough These Creatures Look Just Like Their Lesser Kin, They Are Far More Deadly and CunningSennalNo ratings yet
- NeuroradiologiDocument76 pagesNeuroradiologiVanessa JuventiaNo ratings yet
- Albularyo Folk Healing: Cultural Beliefs On Healthcare Management in Partido District, Camarines Sur, PhilippinesDocument28 pagesAlbularyo Folk Healing: Cultural Beliefs On Healthcare Management in Partido District, Camarines Sur, PhilippinesANGELICA AYCARDO FLORESNo ratings yet
- Trypanosomiasis LectureDocument62 pagesTrypanosomiasis LectureHoriaNo ratings yet
- CONCEPT MAP FistulaDocument1 pageCONCEPT MAP FistulaDaryl TarucNo ratings yet
- Neuropati Perifer PDFDocument21 pagesNeuropati Perifer PDFNadya SandyaNo ratings yet
- Case Study Pulmonary TuberculosisDocument19 pagesCase Study Pulmonary TuberculosisJester GalayNo ratings yet
- Urology Written EssaysDocument12 pagesUrology Written EssaysTien Dung NguyenNo ratings yet
- Health 9 - Q2 - M5Document17 pagesHealth 9 - Q2 - M5Joy VillafloresNo ratings yet
- Acute Pancreatitis: Chris Mathew KoshyDocument100 pagesAcute Pancreatitis: Chris Mathew KoshyabelNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDocument68 pagesRheumatic Heart DiseaseFuji Khairunnisa0% (1)
- Dug Study NCPDocument4 pagesDug Study NCPYamete KudasaiNo ratings yet
- Peritoneal Dialysis - Associated Peritonitis: Suggestions For Management and Mistakes To AvoidDocument9 pagesPeritoneal Dialysis - Associated Peritonitis: Suggestions For Management and Mistakes To AvoidAbidi HichemNo ratings yet
- Cancer Case StudyDocument33 pagesCancer Case StudyBorlongan PaulineNo ratings yet
- Developmental Stages Hand OutDocument2 pagesDevelopmental Stages Hand OutMarjule DechavezNo ratings yet
- DR Anil Dissertation 2014Document144 pagesDR Anil Dissertation 2014Syed FurqanNo ratings yet
- (Lib24.vn) De-Thi-Thu-Vao-Lop-10-Mon-Tieng-Anh-Nam-Hoc-2019-2020-Thanh-Pho-Ha-NoiDocument5 pages(Lib24.vn) De-Thi-Thu-Vao-Lop-10-Mon-Tieng-Anh-Nam-Hoc-2019-2020-Thanh-Pho-Ha-NoiMin Tae HanNo ratings yet
- M1Post-Task Coursera ActivityDocument3 pagesM1Post-Task Coursera ActivityAira Estandian GutierrezNo ratings yet
- PSORIATIC ARTH Mac365Document22 pagesPSORIATIC ARTH Mac365meteabNo ratings yet
- THE BOWEL NOSODES Paterson BookDocument17 pagesTHE BOWEL NOSODES Paterson BookShasta Triri100% (1)
- Health Gain Brocher BrochureDocument2 pagesHealth Gain Brocher Brochuremksnake77No ratings yet
- 2 - Review of AyurvedaDocument65 pages2 - Review of AyurvedaVENU B ANo ratings yet
- BS 7th EB Counseling ReportsDocument3 pagesBS 7th EB Counseling ReportsAreej AkramNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument6 pagesCoronary Artery DiseaseDivya PriyaNo ratings yet
- Definitions, Pathophysiology, and Evaluation of Chronic DiarrhoeaDocument12 pagesDefinitions, Pathophysiology, and Evaluation of Chronic Diarrhoeamariana gamboa zapataNo ratings yet
- Mcqs IV Year Students SurgeryDocument38 pagesMcqs IV Year Students SurgeryAbdimajiidNo ratings yet
- (Download PDF) Introduction To Public Health Schneider Online Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument42 pages(Download PDF) Introduction To Public Health Schneider Online Ebook All Chapter PDFpeter.hamilton807100% (6)