Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A Performance Based Approach To Fire and Gas Detector Mapping and Why It Matters
A Performance Based Approach To Fire and Gas Detector Mapping and Why It Matters
Uploaded by
Mashur Al JunaibiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A Performance Based Approach To Fire and Gas Detector Mapping and Why It Matters
A Performance Based Approach To Fire and Gas Detector Mapping and Why It Matters
Uploaded by
Mashur Al JunaibiCopyright:
Available Formats
A Performance Based Approach to Fire and Gas Detector Mapping and Why it Matters
Presenter: Murtaza Gandhi
Manages Fire and Gas Systems (FGS) mapping & Hazardous Area Classification (HAC) services at BakerRisk.
15+ years of experience in the process industry with 10+ years in the field of fire and gas detectors.
Extensive experience with various phases of the ISA84/IEC61511 functional safety life cycle.
A continuous member and leader of ISA at the student, local, and international level since 2001.
www.BakerRisk.com Copyright BakerRisk. All rights reserved. 1
A Performance Based Approach to Fire and Gas Detector
Mapping and Why it Matters
Presenter: Murtaza I. Gandhi, P.E. MGandhi@BakerRisk.com
Principal Engineer, BakerRisk 281-822-3100
Copyright BakerRisk. All rights reserved. July 16, 2020
Key Takeaways
1 Scenario Coverage 2 Risk Based Prioritization
Approach of Detectors
Consequence-Based Fire and Gas
Detector Mapping
3 Importance of 4 Gas Detector Mapping
Validating Models with for a Toxic Shelter
Testing
BakerRisk Webinar Series, F&G Detector Mapping 4
Outline
1. Why F&G detection studies?
i. And a brief background on mapping
2. Methodology: Consequence and Risk-Based Approach
3. Research on Scenario Coverage
o What’s happening in the industry?
o BakerRisk work process for F&G mapping
o Demo test (including NFPA)
4. Gas Detection in Toxic Shelters
BakerRisk Webinar Series, F&G Detector Mapping 5
Why F&G detection studies?
And a brief background on mapping.
Why F&G Detection Studies?
F&G Detection System facilitates a prompt mitigation response as process units become less populated
BakerRisk Webinar Series, F&G Detector Mapping 7
Why F&G Detection Studies?
How many?
Gas Where to
locate?
Other Detectors Fire
BakerRisk
F&G Studies End
F>ool©
User
Risk Consequence
Calculations Models
Acoustic
BakerRisk Webinar Series, F&G Detector Mapping 8
What’s Happening in the Industry?
• What makes F&G Studies difficult?
o HSE 8 years of offshore data – 60% of known releases were detected
o Current technical industry standards
• API Pub 2031 (1991)
• IEC 60079
• ISA TR84.00.07
• Most clients have internal standards
• Best industry practice
o Traditional studies
• Experience based
• CFD modeling involves high cost to place very few detectors
BakerRisk Webinar Series, F&G Detector Mapping 9
Definitions (ISA TR84.00.07)
• Geographic Coverage : The fraction of the geometric
area or volume of a defined monitored process area
that, if a hazard were to occur in a given geographic
location, would be detected considering the defined
voting arrangement
o In other words: % of area covered
• Scenario Coverage : The fraction of the hazard
scenarios from process equipment within a defined
and monitored process area that can be detected
considering the frequency and magnitude of the
hazard scenarios and the defined voting arrangement
o In other words : % of scenarios detected
BakerRisk’s F&G Studies and F>ool©
• BakerRisk’s F&G studies assist our clients in the placement and optimization
of fire and gas detectors.
• We use F>ool©, a proprietary software developed by BakerRisk.
o Allows detector placement and coverage to be evaluated and viewed in a 3D environment.
o Allows consequence and risk results to be imported and used to place and optimize detectors.
BakerRisk Webinar Series, F&G Detector Mapping 11
Methodology:
Consequence- and Risk- Based Approach
Typical F&G Studies Workflow
Existing
Consequence/
Risk Models
Import
Define Consequence
Performance and Risk 3D Model Generate
Criteria Results Development Report
Model Prep Site Visit Detector
for Site Visit Layout
(CAD Generation,
Drawings, Optimization,
P&ID review, and
Iterative Prioritization
etc.)
Process (if needed)
BakerRisk Webinar Series, F&G Detector Mapping 13
Fire and Gas Detection
• Fire and gas detectors are located based on consequence and risk contours,
client guidelines, and industry standards.
• Gas detectors
o Point gas detectors are given coordinates and a height to show a physical location in 3D
o Line detectors are given coordinates and a height to allow them to interact with the 3D model
o Acoustic detectors are given coordinates and a height to allow them to interact with 3D model
• Fire Detectors
o Conical flame detectors , heat detectors and fusible plugs
BakerRisk Webinar Series, F&G Detector Mapping 14
F&G Model
Flammable, toxic, and fire Detector locations are
3D model is built with plot scenarios are imported from optimized and coverage
plan and site visit data Consequence Models calculated per risk calcs
BakerRisk Webinar Series, F&G Detector Mapping 15
Completed Model – 3D View
BakerRisk Webinar Series, F&G Detector Mapping 16
Model Development
Plot plan of Develop 3D
the unit model
Physical Completed
survey model
BakerRisk Webinar Series, F&G Detector Mapping 19
Plot Plan
Process Facility
Residential Campsite
BakerRisk Webinar Series, F&G Detector Mapping 20
Complete Model – 2D
BakerRisk Webinar Series, F&G Detector Mapping 21
Complete Model – 3D
BakerRisk Webinar Series, F&G Detector Mapping 22
Flammable Contours
BakerRisk Webinar Series, F&G Detector Mapping 24
Thermal Contours
BakerRisk Webinar Series, F&G Detector Mapping 25
Example Flammable Gas Detection
BakerRisk Webinar Series, F&G Detector Mapping 26
Example Fire Detection
BakerRisk Webinar Series, F&G Detector Mapping 27
Completed Model – 2D
BakerRisk Webinar Series, F&G Detector Mapping 28
Completed Model – 3D
BakerRisk Webinar Series, F&G Detector Mapping 29
Risk Based Approach
• ISA TR84.00.07
Three main components:
1. Detection Coverage
2. FG system availability
3. Mitigation Effectiveness
BakerRisk Webinar Series, F&G Detector Mapping 30
Risk Based Approach
• Quantitative Risk Analysis (QRA)
o Use QRA Societal or Individual Risk Results to calculate the detector priority
o Helps prioritizing the implementation of detectors in a phased approach
o Beneficial in performing cost benefit analysis of adding detection
Classification Societal Risk Threshold
(fatalities/year)
High >1E-4
Significant >1E-5
Suggested <1E-5
BakerRisk Webinar Series, F&G Detector Mapping 31
BakerRisk Research on Scenario Coverage
BakerRisk Test Case Study
•74 tests
Setup •Test duration between 1 and 1.5 minutes
Release •Saturated propane
•1/2″, 3/4″ , 1″ releases
Orientations •5 Directions
•Horizontal, West, East, Up, Down
•14 detectors
Detectors •Located 60 to 200 feet from release point
•3 different manufacturers
BakerRisk Webinar Series, F&G Detector Mapping 33
BakerRisk Test Case Study (cont.)
Calibration of the Calibration of Conducted randomly
difference in detector response to determine the
response with and from different response for various
without weather manufacturer release sizes,
Test 11 – 74
baffles detectors orientation and
Test 6 – 10
3 detectors were weather conditions.
Test 1 - 5
placed very close to
each other in the Tests were performed
direction of the in late morning and
release afternoon, night, and
early morning to
capture different
wind conditions
BakerRisk Webinar Series, F&G Detector Mapping 34
BakerRisk Test Case Study (cont.)
• For this presentation, ½″ and ¾″
releases are considered ORIENTATION OF ½″ , ¾″ TESTS
• A total of 58 tests were conducted for
½″ and ¾″ releases
• Detectors were not moved throughout
these tests to ensure proper
comparison
• All detectors were located at 1.5ft
DOWNWIND VERTICAL (UP) CROSSWIND CROSSWIND VERTICAL
(WEST) (EAST) (DOWN)
BakerRisk Webinar Series, F&G Detector Mapping 35
BakerRisk Test Case Study Results
• Horizontal release downwind
BakerRisk Webinar Series, F&G Detector Mapping 36
BakerRisk Test Video: 0.5-inch Horizontal Case
BakerRisk Webinar Series, F&G Detector Mapping 37
Case Study – Scenario Coverage
• Considerations in the calculations
o Initiating event frequency of the release occurring is 1
o Probability of wind in the direction of release is considered 1 (winds were steady
from south-southwest, predominant wind direction)
• Based on the above considerations, scenario coverage was calculated for
each of the 5 release directions and then for the overall scenario of a
release occurring in any of the 5 directions under different wind conditions
BakerRisk Webinar Series, F&G Detector Mapping 38
Case Study - Results
Total
Total Scenario Scenario Coverage
Direction
Direction
Tests
Scenario Coverage 1oo1 Scenario Coverage 2oo2
Tests Coverage 1oo14 2oo14
Horizontal – downwind
Horizontal – downwind 14
14 100%
100% 100%
100%
Vertical – Up
Vertical – Up 10
10 0%
0% 0%
0%
West – crosswind
West – crosswind 11
11 18%
18% 18%
18%
East – crosswind
East – crosswind 11
11 82%
82% 73%
73%
Vertical - Down
Vertical - Down 12
12 100%
100% 92%
92%
All directions
All directions 58
58 62%
62% 59%
59%
The scenario coverage for release in predominant wind direction is
100% while for multiple release directions drops to 60% overall
BakerRisk Webinar Series, F&G Detector Mapping 39
NFPA Test Results –
Saturated Propane 0.3 kg/s (Medium Velocity Nozzle)
BakerRisk Webinar Series, F&G Detector Mapping 40
Toxic Gas Detection in a Shelter
Toxic Shelter
BakerRisk Webinar Series, F&G Detector Mapping 42
Toxic Gas Detection
BakerRisk Webinar Series, F&G Detector Mapping 43
F&G as a Service
Fire & Gas Detection and Fire Protection
BakerRisk Webinar Series, F&G Detector Mapping 45
References
• ISA-TR84.00.07-2018 – Guidance on the evaluation of fire, combustible gas and toxic gas
effectiveness
• “Approaches to calculate scenario coverage”, ISA PCS 2015, Gandhi et al
• “Build on your facility siting and QRA Investment: Designing an effective detection and
mitigation system”, AIChe GCPS 2019, Gandhi et al
• “Toxic gas detection in ammonia plants for Shelter-In-Place”, 61st Ammonia Conference,
Sarrack et al
• “Quantitative evaluation of fire detection coverage and mitigation effectiveness”, ISA PCS
2018, Black et al
• “Vapor mitigation testing using fixed water spray system”, FPRF, Gandhi et al
(https://www.nfpa.org/News-and-Research/Data-research-and-tools/Hazardous-
Materials/Vapor-mitigation-testing-using-fixed-water-spray-system)
• “Shelter-in-Place, reducing risk from toxic impacts”, Sarrack et al
(https://www.bakerrisk.com/news/launch-of-best-practice-guidance-series-by-bakerrisk/)
BakerRisk Webinar Series, F&G Detector Mapping 46
A Performance Based Approach to Fire and Gas Detector Mapping and Why it Matters
Murtaza Gandhi
MGandhi@BakerRisk.com
281-822-3100
www.bakerrisk.com
www.BakerRisk.com Copyright BakerRisk. All rights reserved. 47
Upcoming BakerRisk Webinar:
API Recommended Practice 1173, Pipeline Safety Management Systems
Date: September 10, 2020
Presenter: Stephanie Salazar
www.BakerRisk.com Copyright BakerRisk. All rights reserved. 48
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5814)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- HLC-8320GPC OperatorsManual GDocument199 pagesHLC-8320GPC OperatorsManual GPrianurraufikachmadNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Wireless Multigas Detector Unit PDFDocument39 pagesWireless Multigas Detector Unit PDFIkechukwu Isaac100% (1)
- Fire Extinguishers - SOWDocument2 pagesFire Extinguishers - SOWMashur Al JunaibiNo ratings yet
- MODEL: GF0771 Description: Speaker: FeaturesDocument3 pagesMODEL: GF0771 Description: Speaker: FeaturesMashur Al JunaibiNo ratings yet
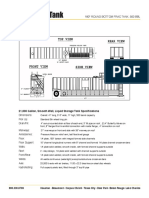
- 180° Round Bottom Frac Tank, 500 BBL: 21,000 Gallon, Smooth Wall, Liquid Storage Tank SpecificationsDocument1 page180° Round Bottom Frac Tank, 500 BBL: 21,000 Gallon, Smooth Wall, Liquid Storage Tank SpecificationsMashur Al JunaibiNo ratings yet
- Autorae Lite: Autorae Lite Automated Bump and Calibration Station For Toxirae 3Document2 pagesAutorae Lite: Autorae Lite Automated Bump and Calibration Station For Toxirae 3Mashur Al JunaibiNo ratings yet
- Product Specification Sheet: One Company - One Complete Fluid SolutionDocument2 pagesProduct Specification Sheet: One Company - One Complete Fluid SolutionMashur Al JunaibiNo ratings yet
- Technical Offer Sample 1Document4 pagesTechnical Offer Sample 1Mashur Al JunaibiNo ratings yet
- Equip Spec Sheets - FracDocument2 pagesEquip Spec Sheets - FracMashur Al JunaibiNo ratings yet
- Scott CylinderDocument5 pagesScott CylinderMashur Al Junaibi100% (1)
- Technical Offer Sample 3Document9 pagesTechnical Offer Sample 3Mashur Al JunaibiNo ratings yet
- Personal 4 Gas Monitor: Carbon Monoxide Hydrogen Sulphide Oxygen Flammable GasesDocument4 pagesPersonal 4 Gas Monitor: Carbon Monoxide Hydrogen Sulphide Oxygen Flammable GasesMashur Al JunaibiNo ratings yet
- Calibration Gas DatasheetDocument15 pagesCalibration Gas DatasheetMashur Al JunaibiNo ratings yet
- Hot Work Program: Company NameDocument12 pagesHot Work Program: Company NameMashur Al JunaibiNo ratings yet
- My Company Short Service Employee (SEE) ProgramDocument6 pagesMy Company Short Service Employee (SEE) ProgramMashur Al JunaibiNo ratings yet
- BW Clip Se: Maintenance-Free Single-Gas DetectorsDocument2 pagesBW Clip Se: Maintenance-Free Single-Gas DetectorsMashur Al JunaibiNo ratings yet
- Log of Work-Related Injuries and Illnesses: OSHA's Form 300Document3 pagesLog of Work-Related Injuries and Illnesses: OSHA's Form 300Mashur Al JunaibiNo ratings yet
- 1.10 Short Service Employee PolicyDocument7 pages1.10 Short Service Employee PolicyMashur Al JunaibiNo ratings yet
- Workplace Hazard Assessment Form: Task Hazard(s) PPE Required Notes DepartmentDocument2 pagesWorkplace Hazard Assessment Form: Task Hazard(s) PPE Required Notes DepartmentMashur Al JunaibiNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Prevention of Dropped / Unsecured Objects at HeightsDocument22 pagesGuidelines For Prevention of Dropped / Unsecured Objects at HeightsMashur Al JunaibiNo ratings yet
- GFG - Gas Detection: Standard Definitions For The IndustryDocument2 pagesGFG - Gas Detection: Standard Definitions For The Industrygplese0No ratings yet
- Domestic Hydrogen QRA ARUPDocument144 pagesDomestic Hydrogen QRA ARUPkzlpNo ratings yet
- OGPEDocument2 pagesOGPEVincent GabrielNo ratings yet
- FM Global Property Loss Prevention Data Sheets: Fire Protection For Gas Turbines and Electric GeneratorsDocument43 pagesFM Global Property Loss Prevention Data Sheets: Fire Protection For Gas Turbines and Electric GeneratorsTailieukythuat DataNo ratings yet
- Author Reply Form Reviewer 1Document1 pageAuthor Reply Form Reviewer 1Gabriel Denis DevianNo ratings yet
- Electronic Nose Current StatusDocument21 pagesElectronic Nose Current StatusokujuveNo ratings yet
- Handbook Gas Utilisation FacilitiesDocument23 pagesHandbook Gas Utilisation FacilitiesJack TouNo ratings yet
- Sensepoint XCD Ds01077 v5 0213 EmeaiDocument8 pagesSensepoint XCD Ds01077 v5 0213 Emeaijoaofelipe.msNo ratings yet
- Assignment No: 03 Applications of Chemical SensorsDocument14 pagesAssignment No: 03 Applications of Chemical SensorsJannat fatima100% (1)
- S 9.24P - PPE Category Level ChartDocument1 pageS 9.24P - PPE Category Level ChartWILLIAMNo ratings yet
- Air Quality With MQ135Document5 pagesAir Quality With MQ135praveen_kodgirwarNo ratings yet
- d778 PDFDocument147 pagesd778 PDFwilson chaconNo ratings yet
- Informatsiya Drager Polytron Ir PDFDocument4 pagesInformatsiya Drager Polytron Ir PDFSandip JoardarNo ratings yet
- Complete Gas Sensor CircuitDocument9 pagesComplete Gas Sensor Circuitsethuraghul100% (1)
- Instruction Manual: Feel The Energy. Feel The FreshnessDocument12 pagesInstruction Manual: Feel The Energy. Feel The FreshnessShivaprasad Hc PatelNo ratings yet
- H G M U VIS: Georgi Todorov Nikolov, Boyanka Marinova Nikolova, Marin Berov MarinovDocument6 pagesH G M U VIS: Georgi Todorov Nikolov, Boyanka Marinova Nikolova, Marin Berov MarinovRamaDinakaranNo ratings yet
- P5504mew SWK 10 SS V PPR 001 - ADocument14 pagesP5504mew SWK 10 SS V PPR 001 - Avignesh558855No ratings yet
- Controlador y CalibradorDocument374 pagesControlador y CalibradorIrving Pineda100% (1)
- Open Smart Technology LimitedDocument20 pagesOpen Smart Technology LimitedAliNo ratings yet
- Vinnem 2018Document10 pagesVinnem 2018priyanka barikNo ratings yet
- BRE - 212 Gas Contaminated LandDocument12 pagesBRE - 212 Gas Contaminated LandAntonino MancinelliNo ratings yet
- Manual de JL269LCDDocument4 pagesManual de JL269LCDJohannita Chavez GalanNo ratings yet
- Solarpak: Solar Charger For Rae PowerpakDocument2 pagesSolarpak: Solar Charger For Rae Powerpaknapoleon5976No ratings yet
- Coal Bed Methane Drilling For DummiesDocument45 pagesCoal Bed Methane Drilling For Dummiesalisaron100% (1)
- Hazid WorksheetDocument2 pagesHazid WorksheetHarry SiswajiNo ratings yet
- Unitor Combi MateDocument3 pagesUnitor Combi MateAnonymous 8rb48tZSNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Permit HolderDocument22 pagesAssessment of Permit HolderdhaspNo ratings yet
- GSM Based Industrial Security System: Abstract: Security and Automation Is A PrimeDocument6 pagesGSM Based Industrial Security System: Abstract: Security and Automation Is A PrimeMuhammed JaleelNo ratings yet