Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 8 D A Conversion and A D Conversion
Uploaded by
Lalita Kumari0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views6 pagesThe document discusses digital-to-analog (D/A) and analog-to-digital (A/D) conversion. It explains that D/A conversion is used to translate digital data such as music or video into real-world analog signals understandable by humans. It does this using resistor networks like variable resistor dividers or binary ladders to sum weighted voltages representing each digital bit into an analog output voltage. A/D conversion is the reverse process of converting an analog voltage into a digital signal. It discusses techniques like successive approximation using comparators to iteratively approximate the analog voltage. The accuracy and resolution of both converters depends on factors like the precision of components and the number of bits in the digital signal.
Original Description:
Original Title
Unit-8-D-A-Conversion-and-A-D-Conversion
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses digital-to-analog (D/A) and analog-to-digital (A/D) conversion. It explains that D/A conversion is used to translate digital data such as music or video into real-world analog signals understandable by humans. It does this using resistor networks like variable resistor dividers or binary ladders to sum weighted voltages representing each digital bit into an analog output voltage. A/D conversion is the reverse process of converting an analog voltage into a digital signal. It discusses techniques like successive approximation using comparators to iteratively approximate the analog voltage. The accuracy and resolution of both converters depends on factors like the precision of components and the number of bits in the digital signal.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views6 pagesUnit 8 D A Conversion and A D Conversion
Uploaded by
Lalita KumariThe document discusses digital-to-analog (D/A) and analog-to-digital (A/D) conversion. It explains that D/A conversion is used to translate digital data such as music or video into real-world analog signals understandable by humans. It does this using resistor networks like variable resistor dividers or binary ladders to sum weighted voltages representing each digital bit into an analog output voltage. A/D conversion is the reverse process of converting an analog voltage into a digital signal. It discusses techniques like successive approximation using comparators to iteratively approximate the analog voltage. The accuracy and resolution of both converters depends on factors like the precision of components and the number of bits in the digital signal.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
www.bookspar.
com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
D/A Conversion and A/D Conversion
A digital-to-analog converter, or simply DAC, is a semiconductor device that
is used to convert a digital code into an analog signal. Digital-to-analog
conversion is the primary means by which digital equipment such as computer-
based systems are able to translate digital data into real-world signals that are
more understandable to or useable by humans, such as music, speech, pictures,
video, and the like. It also allows digital control of machines, equipment,
household appliances, and the like.
Variable-Resistor Network
Binary equivalent weight: The fraction of weight pushed by a binary digit
across voltage.
Variable-Resistor Network
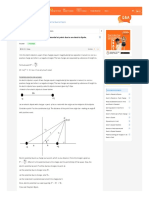
• Resistor divider
The resistor divider must do two things to change the digital input into an
equivalent analog output voltage.
1. The 20 bit must be changed to +1V, and 21 bit must be
changed to +2V, and 22 bit must be changed to +4V.
2. These three voltages representing the digital bits must be
summed together to form the analog output voltage.
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
Binary Ladders
• The binary ladder is a resistive network whose output voltage is a
properly weighted sum of the digital inputs.
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
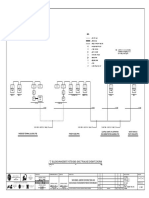
D/A Converters
• Multiple Signals Decoding a number of signals
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
Channel selection method (b) Multiplex method
• D/A Converter Testing
1. The steady-state accuracy test involves setting a known digital
number in the input register, measuring the analog output with an
accurate meter, and comparing with the theoretical value.
2. Checking for monotonicity means checking that the output voltage
increases regularly as the input digital signal increases correct
output voltage waveform for monotonicity test.
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
D/A Accuracy and Resolution
• The accuracy of the D/A converter is primarily a function of the accuracy
of the precision resistors used in the ladder and the precision of the
reference voltage supply used. Accuracy is the measure of how close the
actual output voltage is to the theoretical output voltage.
• Resolution, on the other hand, defines the smallest increment in voltage
that can be discerned. Resolution is primarily a function of the number of
bits in the digital input signal.
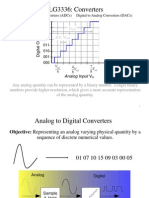
The process of converting an analog voltage into an equivalent digital signal is
known as analog-to-digital conversion
(a) Logic diagram.
(b) Comparator outputs for input voltage ranges
A/D Techniques
• Successive Approximation
– The successive –approximation method thus is the process of
approximating the analog voltage by trying 1 bit at a time
beginning with the MSB.
• The ADC0804
– The ADC0804 is an 8-bit CMOS microprocessor-compatible
successive –approximation A/D converter that is supplied in 20-pin
DIP. It is capable of digitizing an analog input voltage within the
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
range 0 to +5 Vdc. The digital output are both TTL- and CMOS-
compatible.
A/D Accuracy and Resolution
• Since the A/D converter is a closed-loop system involving both analog
and digital systems, the overall accuracy must include errors from both
the analog and digital positions. In determining the overall accuracy it is
easiest to separate the two sources of error.
• Quantization error
– The error inherited in any digital system due to the size of the LSB.
• Differential linearity
– It is the measure of the variation in voltage-step size that causes the
converter to change from one state to the next.
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
You might also like
- Study of Various ADCs and Compare Their Performance and ParametersDocument12 pagesStudy of Various ADCs and Compare Their Performance and ParametersijaertNo ratings yet
- Cisco System Managing de Supply ChainDocument7 pagesCisco System Managing de Supply ChainNorberto VarasNo ratings yet
- DAC and ADC Guide to Digital-Analog and Analog-Digital ConversionDocument6 pagesDAC and ADC Guide to Digital-Analog and Analog-Digital Conversionvishwanath cNo ratings yet
- Communications Lab. Experiment 6: Adc / DacDocument2 pagesCommunications Lab. Experiment 6: Adc / DacSenthil KumarNo ratings yet
- Adc and Dac by MMDocument31 pagesAdc and Dac by MMnatnael demissieNo ratings yet
- Adc DacDocument12 pagesAdc DacSonu SauravNo ratings yet
- ADC and DACDocument16 pagesADC and DACThota Indra MohanNo ratings yet
- Data Conversion Circuits ExplainedDocument11 pagesData Conversion Circuits ExplainedVarsha SenthilNo ratings yet
- Analog To Digital & Digital To Analog ConvertersDocument66 pagesAnalog To Digital & Digital To Analog ConvertersSai Krishna Kodali100% (1)
- Bel - 16 - ADC and DACDocument26 pagesBel - 16 - ADC and DACBharavi K SNo ratings yet
- Ece3430 Lecture 18Document24 pagesEce3430 Lecture 18kuser5506No ratings yet
- Mechatronics - 302050: Lecture Notes / PPT Unit IiiDocument29 pagesMechatronics - 302050: Lecture Notes / PPT Unit IiiRajesh GangwarNo ratings yet
- DAC&ADC (EngineeringDuniya - Com)Document24 pagesDAC&ADC (EngineeringDuniya - Com)ramanaidu10% (1)
- Mbed Course Notes - Analog Input and OutputDocument24 pagesMbed Course Notes - Analog Input and OutputBelkhiri MohammedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document23 pagesChapter 4Tejan Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Convert or SDocument10 pagesConvert or SDan AdrianNo ratings yet
- Adc 26.12.22Document38 pagesAdc 26.12.22Mrs.S.Divya BMENo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Lecture 41Document25 pagesUnit 6 Lecture 41Shaik Abdul SalamNo ratings yet
- Analog-To-Digital Conversion Btech IIIDocument50 pagesAnalog-To-Digital Conversion Btech IIILisa BhagatNo ratings yet
- Interfacing To The Analog WorldDocument47 pagesInterfacing To The Analog WorldRM ZhaloNo ratings yet
- Digital-to-Analog Analog-to-Digital: Interface Part IV MicroprocessorDocument30 pagesDigital-to-Analog Analog-to-Digital: Interface Part IV MicroprocessorVineeth KumarNo ratings yet
- Real Time System-2Document160 pagesReal Time System-2hanyalsalmy567No ratings yet
- A Continuously Varying Physical Quantity by A Sequence of Discrete Numerical ValuesDocument24 pagesA Continuously Varying Physical Quantity by A Sequence of Discrete Numerical ValuesnunuNo ratings yet
- Jadavpur University PPT on ADC: Workings & ApplicationsDocument35 pagesJadavpur University PPT on ADC: Workings & ApplicationsAmit BarNo ratings yet
- ADC Basics & TypesDocument77 pagesADC Basics & TypesDarshan ValaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document135 pagesChapter 1Murali ShettyNo ratings yet
- Analog To DigitalDocument46 pagesAnalog To DigitalSaleem HaddadNo ratings yet
- Analog To Digital ConvertersDocument11 pagesAnalog To Digital Convertersمحمد ماجدNo ratings yet
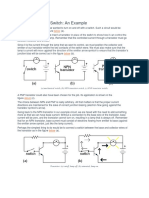
- Using A BJT As A Switch: An Example: BelowDocument10 pagesUsing A BJT As A Switch: An Example: BelowPrakhar BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- EEN11, Finals CombinedDocument105 pagesEEN11, Finals CombinedlavadiajhonNo ratings yet
- Een 11 Finals Lec1Document46 pagesEen 11 Finals Lec1lavadiajhonNo ratings yet
- Adc ConversionDocument20 pagesAdc Conversionhemantec100% (1)
- Jadavpur University: PptonDocument39 pagesJadavpur University: PptonAmit BarNo ratings yet
- Adc Dac Converter NewDocument50 pagesAdc Dac Converter NewJaya PaulNo ratings yet
- Adc DacDocument59 pagesAdc Dacamallia nadhiaratnaNo ratings yet
- DAQDocument34 pagesDAQKhairul FahzanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Adc Dac Ee 64Document28 pagesChapter 7 Adc Dac Ee 64Manish KumarNo ratings yet
- ADC DAC Guide: Analog Digital Conversion FundamentalsDocument41 pagesADC DAC Guide: Analog Digital Conversion Fundamentalskhushbubansal100% (1)
- Analog-To-Digital Converter (ADC), Digital-To-Analog Converter (DAC)Document28 pagesAnalog-To-Digital Converter (ADC), Digital-To-Analog Converter (DAC)Nishant KumarNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual DAC-SignedDocument10 pagesLab Manual DAC-Signedabidrk_21789100% (2)
- (Model No:VBMB - 002) : 8-Bit Digital To Analog Converter Interface BoardDocument56 pages(Model No:VBMB - 002) : 8-Bit Digital To Analog Converter Interface BoardSanthanu Surendran100% (1)
- Interfacing With The Analog WorldDocument20 pagesInterfacing With The Analog WorldSarah Joy ManimtimNo ratings yet
- Digital To Analog and Analog To Digital Conversion: D/A or DAC and A/D or AdcDocument50 pagesDigital To Analog and Analog To Digital Conversion: D/A or DAC and A/D or AdcsomosreeNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan Ke 13 Akusisi DataDocument117 pagesPertemuan Ke 13 Akusisi DataKautsar KuzaNo ratings yet
- Analog-To Digital Conversion (ADC or A/D) : 8 BitsDocument35 pagesAnalog-To Digital Conversion (ADC or A/D) : 8 BitsMANOJ MNo ratings yet
- Digital Measurement of Electrical QuantitiesDocument8 pagesDigital Measurement of Electrical QuantitiesMs. Bhavini KumawatNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document80 pagesLecture 5Nour Ziad Ibrahim AlkurdiNo ratings yet
- Analog DigitalDocument78 pagesAnalog DigitalAnindya BiswasNo ratings yet
- Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) and Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC)Document23 pagesAnalog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) and Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC)Preethi GopalanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Data Acquisition and Feedback Control SystemsDocument64 pagesChapter 8 Data Acquisition and Feedback Control Systemsامجد الغالبيNo ratings yet
- Adc DacDocument22 pagesAdc DacPrasad ChikkamNo ratings yet
- 8 A-D ConverterDocument30 pages8 A-D Converterneoloader145No ratings yet
- ADC Conversion GuideDocument81 pagesADC Conversion GuideUmang PatelNo ratings yet
- Teknik Konversi Data (Data Conversion) : Pendidikan Vokasional Mekatronika FT UnmDocument40 pagesTeknik Konversi Data (Data Conversion) : Pendidikan Vokasional Mekatronika FT UnmYuli Adhaning TyasNo ratings yet
- Adc 23.12.22Document83 pagesAdc 23.12.22Mrs.S.Divya BMENo ratings yet
- Teknik Akusisi Data: I Putu Elba Duta Nugraha, S.T., M.TDocument29 pagesTeknik Akusisi Data: I Putu Elba Duta Nugraha, S.T., M.TAl UlyaNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation Lecture 7 +8Document39 pagesInstrumentation Lecture 7 +8Afaaq HussainNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Practical Design of Digital Circuits: Basic Logic to MicroprocessorsFrom EverandPractical Design of Digital Circuits: Basic Logic to MicroprocessorsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- 504 Conversion Time Exceeded: PricingDocument1 page504 Conversion Time Exceeded: PricingLalita KumariNo ratings yet
- Ferro Dia para Magnetism PDFDocument11 pagesFerro Dia para Magnetism PDFShanna-Kay Wood-Davidson100% (1)
- WWW Electrical4u Com Comparison of Type I and Type II SuperconductorsDocument6 pagesWWW Electrical4u Com Comparison of Type I and Type II SuperconductorsLalita KumariNo ratings yet
- Superconductivity: 1 What Is A Type I and A Type II Superconductor?Document4 pagesSuperconductivity: 1 What Is A Type I and A Type II Superconductor?Lalita KumariNo ratings yet
- T36 CountersDocument17 pagesT36 Countersmanish 123No ratings yet
- New Photon Density Rate Equation For Fabry-Perot Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers (FP Soas)Document8 pagesNew Photon Density Rate Equation For Fabry-Perot Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers (FP Soas)Lalita KumariNo ratings yet
- A Brief About Ripple Counter With Circuit and Timing DiagramsDocument12 pagesA Brief About Ripple Counter With Circuit and Timing DiagramsLalita KumariNo ratings yet
- WWW Electrical4u Com Comparison of Type I and Type II SuperconductorsDocument6 pagesWWW Electrical4u Com Comparison of Type I and Type II SuperconductorsLalita KumariNo ratings yet
- Signal Energy and PowerDocument6 pagesSignal Energy and PowersandeepNo ratings yet
- WWW Ques10 Com P 3295 Draw Explain Block Diagram of Basic Communicatio 1Document2 pagesWWW Ques10 Com P 3295 Draw Explain Block Diagram of Basic Communicatio 1Lalita KumariNo ratings yet
- Zener diode basics for voltage regulationDocument4 pagesZener diode basics for voltage regulationLalita KumariNo ratings yet
- Elec Info 2Document19 pagesElec Info 2Nabeel MuqarrabNo ratings yet
- WWW Electrical4u Com Comparison of Type I and Type II SuperconductorsDocument8 pagesWWW Electrical4u Com Comparison of Type I and Type II SuperconductorsLalita KumariNo ratings yet
- Types of Control Systems - Linear and Non Linear Control SystemDocument8 pagesTypes of Control Systems - Linear and Non Linear Control SystemLalita KumariNo ratings yet
- Analog Communication - DSBSC ModulatorsDocument2 pagesAnalog Communication - DSBSC ModulatorsLalita Kumari100% (1)
- Laser Diode Characteristics: Share This PostDocument5 pagesLaser Diode Characteristics: Share This PostLalita KumariNo ratings yet
- BEST Question Bank - Digital ElectronicsDocument157 pagesBEST Question Bank - Digital Electronicsabhinav_pundir0% (1)
- Questions & Answers: V KQ RDocument4 pagesQuestions & Answers: V KQ RLalita KumariNo ratings yet
- XII Physics Chapter 1 Module 4 Lecture ContentDocument22 pagesXII Physics Chapter 1 Module 4 Lecture ContentLalita KumariNo ratings yet
- XII Physics Chapter 1 Module 4 Lecture ContentDocument22 pagesXII Physics Chapter 1 Module 4 Lecture ContentLalita KumariNo ratings yet
- HWK 1Document2 pagesHWK 1Lalita KumariNo ratings yet
- Abrupt PN Junctions Analytical SolutionsDocument9 pagesAbrupt PN Junctions Analytical Solutionsombraga1896No ratings yet
- Design of a rectangular microstrip patch antenna for WLAN applicationsDocument3 pagesDesign of a rectangular microstrip patch antenna for WLAN applicationsLalita KumariNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Lab ManualDocument27 pagesMicroprocessor Lab Manualibadullah mdNo ratings yet
- How Bipolar Transistors Work and the Early EffectDocument4 pagesHow Bipolar Transistors Work and the Early EffectLalita KumariNo ratings yet
- Zener diode basics for voltage regulationDocument4 pagesZener diode basics for voltage regulationLalita KumariNo ratings yet
- A. Ece-129Document6 pagesA. Ece-129ankit gangwarNo ratings yet
- Noc21 Ee75Document2 pagesNoc21 Ee75Lalita KumariNo ratings yet
- Pelton Turbine Operation and DesignDocument22 pagesPelton Turbine Operation and DesignManuel CaipoNo ratings yet
- Step by Step Guide: How To Update Institute'S Profile in Navttc-PmsDocument15 pagesStep by Step Guide: How To Update Institute'S Profile in Navttc-PmsMohammad AtherNo ratings yet
- 15ec743-Real Time SystemsDocument33 pages15ec743-Real Time SystemsNIRANJAN LNo ratings yet
- How To Switch From Reactive Maintenance To Preventive Maintenance - Complete Transition GuideDocument18 pagesHow To Switch From Reactive Maintenance To Preventive Maintenance - Complete Transition GuidematshonaNo ratings yet
- Building 8 CO PDFDocument5 pagesBuilding 8 CO PDFDelmar GicaNo ratings yet
- Autonomy IDOL Server Technical Brief 1204 Rev1Document6 pagesAutonomy IDOL Server Technical Brief 1204 Rev1Mark AldissNo ratings yet
- User Manual: Director's CutDocument40 pagesUser Manual: Director's CutTenNo ratings yet
- AocvDocument5 pagesAocvgowripNo ratings yet
- 8086 MicroprocessorDocument24 pages8086 Microprocessorsamrat kumar100% (1)
- Schrack Power PCB Relay RPII/2: General Purpose Relays PCB RelaysDocument2 pagesSchrack Power PCB Relay RPII/2: General Purpose Relays PCB RelaysCor GratNo ratings yet
- John Sloman EconomicsDocument4 pagesJohn Sloman Economicsdevyansh.dhall2807No ratings yet
- Pid Loop Simulator: ProcessDocument10 pagesPid Loop Simulator: ProcessBenjamin FonsecaNo ratings yet
- Building Management System (BMS) Basic Trunkline Schematic Diagram 2Document3 pagesBuilding Management System (BMS) Basic Trunkline Schematic Diagram 2Anonymous NcB95G6XwNo ratings yet
- L828/L829 Ferroresonant Constant Current RegulatorDocument1 pageL828/L829 Ferroresonant Constant Current RegulatorSantiagoNo ratings yet
- Ina 122Document14 pagesIna 122Wasang Juwi PracihnoNo ratings yet
- Purple Finder PDFDocument12 pagesPurple Finder PDFsahil jadonNo ratings yet
- SANTRO Hatchback BrochureDocument10 pagesSANTRO Hatchback Brochureronak chandranNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Civil Engineering (Engineering Method)Document11 pagesIntroduction To Civil Engineering (Engineering Method)ongica jamesNo ratings yet
- Avaya Aura Contact Center and Call Center EliteDocument8 pagesAvaya Aura Contact Center and Call Center EliteCấn Mạnh TrườngNo ratings yet
- Mini Project On Emerging Phase of Banking IndustryDocument9 pagesMini Project On Emerging Phase of Banking IndustryPrince PanwarNo ratings yet
- Multi-Stage Amplifier GainDocument28 pagesMulti-Stage Amplifier Gainhaitham78h100% (1)
- CN CS203 Lab ManualDocument36 pagesCN CS203 Lab ManualSarthak Singh ChandelNo ratings yet
- Project Manager O&G Subsea in Houston TX Resume Donald MarkeyDocument4 pagesProject Manager O&G Subsea in Houston TX Resume Donald MarkeyDonaldMarkeyNo ratings yet
- Timing Aware Dummy Metal Fill MethodologyDocument3 pagesTiming Aware Dummy Metal Fill MethodologyraveneyesdeadNo ratings yet
- Railml® 3 Simple Example Step Part 2: Interlocking Railml® 3.1 Tutorial Simple Example Step-By-Step Part 2: Interlocking StepDocument68 pagesRailml® 3 Simple Example Step Part 2: Interlocking Railml® 3.1 Tutorial Simple Example Step-By-Step Part 2: Interlocking Steptap.jackson6255No ratings yet
- Interfacing Clinical LaboratoryDocument25 pagesInterfacing Clinical Laboratorylanlinux8849No ratings yet
- 8000io CutsheetDocument2 pages8000io CutsheetPadmo PadmundonoNo ratings yet
- Computer Vision and Action Recognition A Guide For Image Processing and Computer Vision Community For Action UnderstandingDocument228 pagesComputer Vision and Action Recognition A Guide For Image Processing and Computer Vision Community For Action UnderstandingWilfredo MolinaNo ratings yet
- Symbol Explanations For Commissioning DiagramDocument8 pagesSymbol Explanations For Commissioning DiagramBrahim CherguiNo ratings yet