Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Computer Science - Quarter 1 - Week 1-2
Computer Science - Quarter 1 - Week 1-2
Uploaded by
Althaeya Mae GallanaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Computer Science - Quarter 1 - Week 1-2
Computer Science - Quarter 1 - Week 1-2
Uploaded by
Althaeya Mae GallanaCopyright:
Available Formats
COMPUTER SCIENCE – QUARTER 1 – WEEK 1-2
Name: Althaeya Mae Gallana
Grade & Section: Gr. 10 Einstein
TRY THIS!
1. UNIMATE
2. UNIMATION
3. ACTUATOR
4. CONTROLLER
5. SENSOR
6. MOBILE
7. STATIONARY
8. AUTONOMOUS
9. VIRTUAL
10. ROBOT
DO THIS
ACTIVITY 1: INSIDE ROBOTS
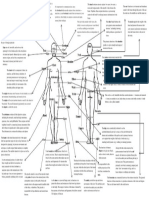
PART OS SYSTEM OF THE HUMAN BODY FUNCTION
BONES Bones come in a variety of shapes and
sizes, and they support, defend, store
calcium and fat, and produce blood cells.
HANDS In humans, bipedal locomotion frees the
hands for a predominantly manipulative
use. Fingernails protect the tips of
primates' fingers, allowing them to
ARMS manipulate objects more effectively.
In humans, bipedal locomotion frees the
hands for a primarily manipulating
purpose. Fingernails cover the tips of
FEET primates' fingers, allowing them to
manipulate objects more easily.
The feet are flexible bone, joint, muscle,
and soft tissue components that allow us
LEGS to stand upright and conduct activities
like as walking, running, and jumping.
Legs are used for standing and other sorts
of mobility, including recreational
activities like dancing, and they make up
a large part of a person's bulk. Female
legs feature greater hip anteversion and
tibiofemoral angles than male legs, but
shorter femur and tibial lengths.
SENSORY NERVOUS SYSTEM The sensory nervous system's principal
job is to send information to the brain's
central nervous system regarding external
and internal inputs. It notifies us of any
changes in the internal and external
surroundings in this way.
BRAIN The brain is a complicated organ that
regulates every action in our body,
including thought, memory, emotion,
touch, motor skills, vision, respiration,
temperature, and hunger. The central
nervous system, or CNS, is made up of
the brain and the spinal cord that extends
from it.
Guide Questions:
1. Humans and robots share a lot of characteristics. Both have arms and legs, can run, lift weights, and consume and
expend energy.
2. The sensors. The sensory organs (eyes, ears, nose, tongue, and skin) provide a lot of this information. These organs
contain specialized cells and tissues that accept raw inputs and convert them into signals that the nervous system can
understand.
CHECK YOUR UNDERSTANDING
1. Robots can do things human can’t do. And you can tell that, that thing is a robot when it can do things a person
cannot.
2. Robotics is the study of the design, building, and use of machines (robots) to do jobs that were previously
performed by humans. Robots are commonly utilized in areas such as vehicle manufacturing to perform simple
repetitive jobs, as well as in businesses where workers must work in dangerous situations.
3. Cell phone is not a robot. Giving the definition of a robot, cell phone is not a robot because robots are those that can
do anything. And is created to do better things a person can do.
APPLY THIS
Mobile and stationary robots.
Mobile robots can help by carrying those heavy part that the employees can, while stationary robot can help
assembling the parts needed to make a car.
It can help them a lot by doing the things the employees are lacking of.
They are the best choice because they can do the things the employees lacked of.
TEST YOURSELF
1. C 6. B 11. Electrical
2. C 7. D 12. Microcontrollers
3. C 8. C 13. Effectors
4. C 9. A 14. Arm
5. D 10. C 15. Remote control
PERFORMANCE TASK
Name of Robot:
Purpose:
How will it work?
Sketch:
You might also like
- R-30iB Linetracking Operator Manual (B-83474EN 01)Document152 pagesR-30iB Linetracking Operator Manual (B-83474EN 01)luca secciNo ratings yet
- EDD X Bobobox CompressedDocument27 pagesEDD X Bobobox CompressedSpk ForteNo ratings yet
- Brain Structure & FunctionDocument24 pagesBrain Structure & Functionvineetya100% (4)
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science VI-Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science VI-Nervous SystemTrishia Mandapat75% (4)
- Copia de 13.12Document9 pagesCopia de 13.12INÉS TORIBIO ARGÜELLESNo ratings yet
- Parts of Brain & Their FunctionsDocument1 pageParts of Brain & Their FunctionsmmdadnanNo ratings yet
- BrainDocument3 pagesBrainWidiya BudiNo ratings yet
- Hand Anatomy: SynonymsDocument11 pagesHand Anatomy: SynonymsDharmendra BurraNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Science Chapter 2.4 & 2.5 Muscle, Tendon, Ligament and BrainDocument32 pagesForm 4 Science Chapter 2.4 & 2.5 Muscle, Tendon, Ligament and BraincmeeflyNo ratings yet
- The Development On A New Biomechatronic Prosthetic Hand Based On Under-Actuated MechanismDocument6 pagesThe Development On A New Biomechatronic Prosthetic Hand Based On Under-Actuated MechanismPravin PatoleNo ratings yet
- DLP SCIENCE 6 Q2 WK 1 Day 2Document9 pagesDLP SCIENCE 6 Q2 WK 1 Day 2Roselle Joy EgeraNo ratings yet
- Tugas B Ing WidyaDocument14 pagesTugas B Ing WidyaWidya PutriNo ratings yet
- The Sense Organs The Sense Organs The Skeletal and Muscular Systems The Respiratory System The Nervous SystemDocument34 pagesThe Sense Organs The Sense Organs The Skeletal and Muscular Systems The Respiratory System The Nervous SystemDivina Gracia Barrion CuyaNo ratings yet
- Cs6008-Human Computer Interaction Two Marks Question With Answers Unit - IDocument10 pagesCs6008-Human Computer Interaction Two Marks Question With Answers Unit - IDr.P.L. Rajarajeswari CSE departmentNo ratings yet
- Body Parts and FunctionDocument1 pageBody Parts and FunctionJean Rema GonjoranNo ratings yet
- TP24 - Human Body SIGMOD Part 2Document14 pagesTP24 - Human Body SIGMOD Part 2Bethany CookNo ratings yet
- Design Method For An Anthropomorphic Hand Able To Gesture and GraspDocument8 pagesDesign Method For An Anthropomorphic Hand Able To Gesture and Graspsaqlain saqiNo ratings yet
- JECS FR YTadesse 271574.94Document12 pagesJECS FR YTadesse 271574.94dudde niranjanNo ratings yet
- Written Report (Group6)Document4 pagesWritten Report (Group6)Joshua ValentinoNo ratings yet
- Science Unit 1Document9 pagesScience Unit 1RohanNo ratings yet
- SLM QUARTER 2 Module 2 WEEK 1Document23 pagesSLM QUARTER 2 Module 2 WEEK 1Racel AbulaNo ratings yet
- Jbhi 2017 2766249Document11 pagesJbhi 2017 2766249吳余山No ratings yet
- Chapter-1Document27 pagesChapter-1NidhiKachhawaNo ratings yet
- Emotion in TechnologyDocument1 pageEmotion in TechnologyValentina DicksonNo ratings yet
- Functions: A. The Neuron 1.cellbody: Transmit A Neurotransmitter From One Neuron To AnotherDocument4 pagesFunctions: A. The Neuron 1.cellbody: Transmit A Neurotransmitter From One Neuron To AnotherKurt Lubim Alaiza-Anggoto Meltrelez-LibertadNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument39 pagesNervous Systemespinajeff07No ratings yet
- Blue BrainDocument45 pagesBlue Brainnittala pasyanthiNo ratings yet
- Cse Final Year Hci QbankDocument53 pagesCse Final Year Hci QbankCSE DEPARTMENT REGULATION 2017No ratings yet
- Skeleton SystemDocument14 pagesSkeleton SystemDiscord YtNo ratings yet
- PIIS1364661321000565Document13 pagesPIIS1364661321000565Christo ChristoffNo ratings yet
- I. Objectives: Implementation of Policies, Guidelines, and ProceduresDocument18 pagesI. Objectives: Implementation of Policies, Guidelines, and ProceduresRose Aileen EndigadoNo ratings yet
- Brain 21370Document2 pagesBrain 21370daniel balteanNo ratings yet
- Cs6008-Human Computer Interaction Two Marks Question With Answers Unit - IDocument10 pagesCs6008-Human Computer Interaction Two Marks Question With Answers Unit - IAnirban Datta Roy.No ratings yet
- Brain Mechanism of Movements: Chapter 7: MovementDocument9 pagesBrain Mechanism of Movements: Chapter 7: MovementBOMETIVO, MA. LARA JANE G.No ratings yet
- Biological Basis of Human BehaviorDocument27 pagesBiological Basis of Human BehaviorAnanta ChaliseNo ratings yet
- Skinput TechnologyDocument22 pagesSkinput Technologyprashanth100% (1)
- Introducing: Small ScriptDocument19 pagesIntroducing: Small ScriptThiara Mutiara PasandeNo ratings yet
- Worksheet-5 Musculoskeletal-System Group3 BFFDocument79 pagesWorksheet-5 Musculoskeletal-System Group3 BFFAldrin LimcuandoNo ratings yet
- Define Human MovementDocument1 pageDefine Human MovementSheila LoverioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - The Brain and BehaviorDocument40 pagesChapter 2 - The Brain and BehaviorKaiNo ratings yet
- Soal Review UTBK Bahasa InggrisDocument2 pagesSoal Review UTBK Bahasa Inggrisulfi RosyidahNo ratings yet
- DLL - MathDocument5 pagesDLL - MathElma LacambraNo ratings yet
- Skill Enrichment Capacity Monkey Homo SapiensDocument3 pagesSkill Enrichment Capacity Monkey Homo SapiensFritzey FayeNo ratings yet
- Blue BrainDocument27 pagesBlue BrainRaghu NixelNo ratings yet
- Z Neurology-Respiracion DiafragmaDocument61 pagesZ Neurology-Respiracion Diafragmaelmer1612No ratings yet
- Seminar Report, 2011: Blue BrainDocument13 pagesSeminar Report, 2011: Blue BrainJENSONKDNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Reaction PaperDocument3 pagesNervous System Reaction PaperJohn Ruel Sanchez IINo ratings yet
- Salsabila Human BodyDocument17 pagesSalsabila Human BodySalsabilaNo ratings yet
- 2.3.1 Nervous SystemDocument60 pages2.3.1 Nervous SystemAyush BhandariNo ratings yet
- Brain Machine InterDocument8 pagesBrain Machine InterAnusha JavvajiNo ratings yet
- OBJECTIVES: at The End of The Lesson, The Pupils Are Expected ToDocument5 pagesOBJECTIVES: at The End of The Lesson, The Pupils Are Expected ToLara Patricia MarananNo ratings yet
- ACT Mechanism ToMDocument12 pagesACT Mechanism ToMMuhammad Zain NawwarNo ratings yet
- Ijirt159791 PaperDocument4 pagesIjirt159791 PaperMadhura Hande -DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- ACustomizable Wearable Robust 3 DPrinted Bionic Arm Muscle ControlledDocument6 pagesACustomizable Wearable Robust 3 DPrinted Bionic Arm Muscle ControlledLakshmi PriyaNo ratings yet
- Super Brain: Strategies to Upgrade Your Brain, Unlock Your Potential, Perform at Your Peak, and Achieve AnythingFrom EverandSuper Brain: Strategies to Upgrade Your Brain, Unlock Your Potential, Perform at Your Peak, and Achieve AnythingNo ratings yet
- Bones Worksheet2Document3 pagesBones Worksheet2Cindy Darmawan EffendyNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument28 pagesSeminar ReportlaxmikantchhipaNo ratings yet
- Thumbs UpDocument2 pagesThumbs UpAndrew JonesNo ratings yet
- Bluebrain Jyotirmoy Dash (09E01D2504) M.Tech (Software Engneering) Under The Guidance OFDocument13 pagesBluebrain Jyotirmoy Dash (09E01D2504) M.Tech (Software Engneering) Under The Guidance OFbrijeshairforceNo ratings yet
- Characterization and Evaluation of A Cable-Actuated Flexible Hand ExoskeletonDocument6 pagesCharacterization and Evaluation of A Cable-Actuated Flexible Hand ExoskeletonEbenezer MarteyNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Reaction PaperDocument3 pagesNervous System Reaction PaperJohn Ruel Sanchez IINo ratings yet
- Developmental Humanoids: Humanoids That Develop Skills AutomaticallyDocument17 pagesDevelopmental Humanoids: Humanoids That Develop Skills AutomaticallyTanzin ThakurNo ratings yet
- 08 Handout 1Document7 pages08 Handout 1Cecille Marasigan AnzuresNo ratings yet
- Slow Cooker Manual Russel HobbsDocument16 pagesSlow Cooker Manual Russel HobbsRadu PopaNo ratings yet
- ZA20J Manuales de Operacion y SeguridadDocument104 pagesZA20J Manuales de Operacion y SeguridadNadia kristel Ayala escobarNo ratings yet
- Npi Format For Rle 1Document9 pagesNpi Format For Rle 1Patricia VasquezNo ratings yet
- Ini Bery 1Document7 pagesIni Bery 1viayNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument9 pagesIntroductionDianne Laurice Magnaye RodisNo ratings yet
- Dragon #92 - Ecology of The EttinDocument3 pagesDragon #92 - Ecology of The EttinGeorge KrashosNo ratings yet
- Pump Suction Pipe Design ConsiderationsDocument7 pagesPump Suction Pipe Design ConsiderationsAbdulrahman Al HuribyNo ratings yet
- 10 Contoh Teks Short 'Story Telling' Pendek Bahasa Inggris Unik Dan MenarikDocument13 pages10 Contoh Teks Short 'Story Telling' Pendek Bahasa Inggris Unik Dan MenarikDard TongNo ratings yet
- Project Execution Plan (GT GTD Oil Flushing)Document77 pagesProject Execution Plan (GT GTD Oil Flushing)Tao QuNo ratings yet
- Absenteeism of Employees ObjectivesDocument5 pagesAbsenteeism of Employees ObjectivesJayaprabhu PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Environmental AuditingDocument27 pagesEnvironmental Auditinghamza.bouhaouchineNo ratings yet
- The Spice House Beverage MenuDocument7 pagesThe Spice House Beverage MenuTan MaiNo ratings yet
- FPC Formation Funding, Projects & MoreDocument3 pagesFPC Formation Funding, Projects & MoreSarth FoundationNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing Chapter 5Document2 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Chapter 5Audrie Allyson GabalesNo ratings yet
- By Kareen Mezerhane Manar Naboulsi Alexander Blitch J.P KamarDocument8 pagesBy Kareen Mezerhane Manar Naboulsi Alexander Blitch J.P Kamarkam993No ratings yet
- Terrell Dickerson Permanent SurrenderDocument6 pagesTerrell Dickerson Permanent SurrenderreagandrNo ratings yet
- FH Series: 60 HZ 60 HZ 60 HZ 60 HZ 60 HZDocument132 pagesFH Series: 60 HZ 60 HZ 60 HZ 60 HZ 60 HZWilly RiosNo ratings yet
- Muscle - Re EducationDocument20 pagesMuscle - Re EducationRam RamNo ratings yet
- Basic Defrost Controller Installation Guide: Basic Controller For Refrigerated Cabinets, With Energy-Saving StrategiesDocument2 pagesBasic Defrost Controller Installation Guide: Basic Controller For Refrigerated Cabinets, With Energy-Saving StrategiesNelson DiazNo ratings yet
- Types of Heart DiseasesDocument4 pagesTypes of Heart DiseaseslalalallaNo ratings yet
- Parachute Hair Oil & The Champi by Ajita PalDocument7 pagesParachute Hair Oil & The Champi by Ajita PalXjcjdixckNo ratings yet
- CHN P1 ExamDocument23 pagesCHN P1 ExamNicholeGarcesCisnerosNo ratings yet
- Lecture 03 - Physical Applications of First - Order Differential EquationDocument2 pagesLecture 03 - Physical Applications of First - Order Differential EquationMary Joyce RoxasNo ratings yet
- Maximum Marks: 100Document35 pagesMaximum Marks: 100Yu HoyanNo ratings yet
- About Nestle ProjectDocument50 pagesAbout Nestle ProjectVartika Nagar100% (1)
- Mcafee CasbDocument119 pagesMcafee CasbTarun ChakrabartyNo ratings yet
- Gepsych: Gepsych Productive Work OutputDocument1 pageGepsych: Gepsych Productive Work OutputCarlos ReyesNo ratings yet