Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Topic Separation Techniques Notes Part 1
Uploaded by
Jay-Ann Sampson0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views4 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views4 pagesTopic Separation Techniques Notes Part 1
Uploaded by
Jay-Ann SampsonCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Topic: Separation Techniques
Subtopic:Filtration
1)Filtration
Is a separation technique used to separate a
suspension into its components.
Filtration results in two components: a filtrate and a
residue. The filtrate is the substance that passes
through the filter paper while the residue is the
substance that remains in the filter paper.
Property that allows for the separation:
The difference in the particle size of the
components.
In a suspension, there are components of different
particle sizes. The smaller particles are able to go
through the filter paper while the larger particles
cannot go through.
Insert diagram of the Filtration apparatus
2)Crystallization:
Is a separation technique used to obtain a solid
from a solution, for example, salt from salt solution.
The solution is heated until MOST of the solvent
evaporates then allowed to cool (by removing from
the flame).
Insert diagram of the apparatus used
By evaporating much of the solvent, the resulting
solution is concentrated or saturated with the
solute. This causes the solute to fall out of solution
in the form of crystals.
To separate the crystals from the remaining
solution, the mixture can be filtered or decanted.
Property that allows separation:
Difference in boiling point/volatility of the
components
3)Evaporation to Dryness
Is used to separate a solid from a solution.
The solution is heated until ALL of the solvent
evaporates leaving the solid behind.
4)Simple Distillation
Is a separation technique used to obtain a liquid
from a solution.
Insert diagram of the apparatus
Apparatus Setup
The solution is first placed in the distillation flask. A
thermometer is inserted into the mouth of the
distillation flask by means of a stopper. The
distillation flask has a side arm that is connected to
a Liebig condenser. At the end of the condenser is
placed a receiving flask.
Carrying out the Practical Activity
1)After connecting all the apparatus together,
turn the tap on to allow a steady flow of water
to flow through the outer jacket of the
condenser.
2)Heat the solution in the distillation flask. When
the boiling point of the liquid concerned is
reached, it will vaporize, enter the condenser
where it cools and condenses to form the
liquid droplets. The droplets will be collected in the
receiving flask.
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- NIQS BESMM 4 BillDocument85 pagesNIQS BESMM 4 BillAliNo ratings yet
- Top Activist Stories - 5 - A Review of Financial Activism by Geneva PartnersDocument8 pagesTop Activist Stories - 5 - A Review of Financial Activism by Geneva PartnersBassignotNo ratings yet
- Case Study Single Sign On Solution Implementation Software Luxoft For Ping IdentityDocument5 pagesCase Study Single Sign On Solution Implementation Software Luxoft For Ping IdentityluxoftNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Retail LoansDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Retail LoansSameer ShahNo ratings yet
- ADC of PIC MicrocontrollerDocument4 pagesADC of PIC Microcontrollerkillbill100% (2)
- FE CH 5 AnswerDocument12 pagesFE CH 5 AnswerAntony ChanNo ratings yet
- Sankranthi PDFDocument39 pagesSankranthi PDFMaruthiNo ratings yet
- How To Launch Remix OS For PCDocument2 pagesHow To Launch Remix OS For PCfloapaaNo ratings yet
- Iphone and Ipad Development TU GrazDocument2 pagesIphone and Ipad Development TU GrazMartinNo ratings yet
- I I I I: Peroxid.Q!Document2 pagesI I I I: Peroxid.Q!Diego PradelNo ratings yet
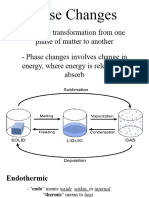
- General Chemistry 2 Q1 Lesson 5 Endothermic and Exotheric Reaction and Heating and Cooling CurveDocument19 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 Q1 Lesson 5 Endothermic and Exotheric Reaction and Heating and Cooling CurveJolo Allexice R. PinedaNo ratings yet
- Financial Management 2E: Rajiv Srivastava - Dr. Anil Misra Solutions To Numerical ProblemsDocument5 pagesFinancial Management 2E: Rajiv Srivastava - Dr. Anil Misra Solutions To Numerical ProblemsParesh ShahNo ratings yet
- Facebook: Daisy BuchananDocument5 pagesFacebook: Daisy BuchananbelenrichardiNo ratings yet
- Dakua Makadre PresentationDocument12 pagesDakua Makadre PresentationEli Briggs100% (1)
- Curriculum Guide Ay 2021-2022: Dr. Gloria Lacson Foundation Colleges, IncDocument9 pagesCurriculum Guide Ay 2021-2022: Dr. Gloria Lacson Foundation Colleges, IncJean Marie Itang GarciaNo ratings yet
- Math Review CompilationDocument9 pagesMath Review CompilationJessa Laika CastardoNo ratings yet
- EKRP311 Vc-Jun2022Document3 pagesEKRP311 Vc-Jun2022dfmosesi78No ratings yet
- Ritesh Agarwal: Presented By: Bhavik Patel (Iu1981810008) ABHISHEK SHARMA (IU1981810001) VISHAL RATHI (IU1981810064)Document19 pagesRitesh Agarwal: Presented By: Bhavik Patel (Iu1981810008) ABHISHEK SHARMA (IU1981810001) VISHAL RATHI (IU1981810064)Abhi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Project Management TY BSC ITDocument57 pagesProject Management TY BSC ITdarshan130275% (12)
- Ajmera - Treon - FF - R4 - 13-11-17 FinalDocument45 pagesAjmera - Treon - FF - R4 - 13-11-17 FinalNikita KadamNo ratings yet
- BARUDocument53 pagesBARUhueuaNo ratings yet
- Modern and Nonlinear OpticsDocument181 pagesModern and Nonlinear Opticssoma_venuNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence Techniques For Encrypt Images Based On The Chaotic System Implemented On Field-Programmable Gate ArrayDocument10 pagesArtificial Intelligence Techniques For Encrypt Images Based On The Chaotic System Implemented On Field-Programmable Gate ArrayIAES IJAINo ratings yet
- HepaDocument1 pageHepasenthilarasu5100% (1)
- 5 Minute Pediatric ConsultDocument5 pages5 Minute Pediatric Consultajescool0% (4)
- School Based INSET Interim EvaluationDocument8 pagesSchool Based INSET Interim Evaluationprinces arcangelNo ratings yet
- Final Selection Criteria Tunnel Cons TraDocument32 pagesFinal Selection Criteria Tunnel Cons TraMd Mobshshir NayeemNo ratings yet
- Upes School of Law Lac & Adr Association: PresentsDocument7 pagesUpes School of Law Lac & Adr Association: PresentsSuvedhya ReddyNo ratings yet
- BMGT 200 Assignment 2 Answer KeysDocument3 pagesBMGT 200 Assignment 2 Answer Keysharout keshishianNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Lesson 2Document31 pagesModule 1 Lesson 2Angela Rose BanastasNo ratings yet