Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ammonium Bifluoride: Product Safety Summary
Uploaded by
daniel abiaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ammonium Bifluoride: Product Safety Summary
Uploaded by
daniel abiaCopyright:
Available Formats
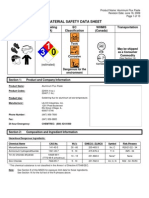
Product Safety Summary
Ammonium Bifluoride
CAS No. 1341-49-7
This Product Safety Summary is intended to provide a general overview of the chemical substance.
The information on the summary is basic information and is not intended to provide emergency
response information, medical information or treatment information. The summary should not be
used to provide in-depth safety and health information. In-depth safety and health information can
be found in the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for the chemical substance.
Names
• Ammonium bifluoride (ABF)
• Ammonium difluoride
• Ammonium acid fluoride
• Ammonium hydrogen difluoride
• Ammonium fluoride compound with hydrogen fluoride (1:1)
Product Overview
Solvay Fluorides, LLC does not sell ammonium bifluoride directly to consumers. Ammonium
bifluoride is used in industrial applications and in other processes where workplace exposures can
occur.
Ammonium bifluoride (ABF) is used for cleaning and etching of metals before they are further
processed. It is used as an oil well acidifier and in the etching of glass or cleaning of brick and
ceramics. It may also be used for pH adjustment in industrial textile processing or laundries. ABF
is available as a solid or liquid solution (in water).
Ammonium bifluoride is a corrosive chemical and contact can severely irritate and burn the skin and
eyes causing possible permanent eye damage. Breathing ammonium bifluoride can severely irritate
and burn the nose, throat, and lungs, causing nosebleeds, cough, wheezing and shortness of
breath. On contact with water or moist skin, ABF can release hydrofluoric acid, a very dangerous
acid.
Inhalation or ingestion of large amounts of ammonium bifluoride can cause nausea, vomiting and
loss of appetite. Very high or long term exposures can cause fluoride poisoning with stomach pain,
weakness, convulsions and death. Long term or repeated exposures can cause deposits of
fluorides in bones and teeth, a condition called fluorosis. This may cause pain, disability and
discoloration of teeth.
Page 1 of 6
Copyright 2009-2013, Solvay America, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Manufacture of Product
Solvay Fluorides, LLC’s affiliate in Mexico is the only North American producer of solid ABF. Solvay
Fluorides, LLC makes an ammonium bifluoride solution for sale.
Solvay manufactures solid ammonium bifluoride by mixing ammonia and anhydrous hydrogen
fluoride (liquid) together and then drying to form flakes.
2HF + NH3 NH4 HF2
Ammonium bifluoride solution is made by dissolving solid ammonium bifluoride in water.
Product Description
Ammonium bifluoride (NH4•HF2) is manufactured and sold in solid form or in aqueous solutions.
The solid is a white crystal. The solutions are clear, colorless liquids that have a slightly sharp,
pungent odor. Common industrial solution strength concentrations are between 28 and 30%.
Typical physical properties for ammonium bifluoride are provided in Table 1.
Table 1: Typical physical properties ammonium bifluoride
Solid ABF 29% ABF
Melting Point 256°F (125.6ºC) N/A
Relative Density 1.5 1.08
pH 2 (5.7 g /l) <1
Flash Point Non- flammable
Decomposition Temperature 446ºF (230ºC)
Product Uses
Ammonium bifluoride is used for cleaning and etching of metals before the metal is further
processed. It is used as an oil well acidifier and in the etching of glass or cleaning of brick and
ceramics. It may also be used for pH adjustment in industrial textile processing or laundry
applications.
Consumer products containing ammonium bifluoride are primarily products for the etching of glass
(hobby) or for ceramic and brick cleaners.
Page 2 of 6
Copyright 2009-2013, Solvay America, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Exposure Potential
Workplace Exposure - Exposure can occur at either an ammonium bifluoride manufacturing
facility, a manufacturing or packaging facility that stores, packages or uses ammonium
bifluoride, or during transport. The system Solvay uses to manufacture ammonium bifluoride is a
“closed” system with very little potential for exposure to ammonium bifluoride. Other
manufacturing processes or systems in which it is used may be open or closed depending on
the equipment or application. Persons involved in maintenance, sampling and testing activities,
or in the loading and unloading of ammonium bifluoride packages are at greater risk of
exposure. Following good industrial hygiene practices will minimize the likelihood of exposure;
however, persons involved in higher risk activities should always wear proper personal
protective equipment such as rubber gloves and boots, an acid or slicker suit, acid gas
respirator, goggles and hard hat. In instances where the potential for splashes is high, a face
shield should also be worn.
Exposure limits for ammonium bifluoride (per OSHA, ACGIH, and other agencies) are listed as
the “fluoride” content rather than as ABF specifically. Please consult the Safety Data Sheet for
information concerning exposure limits.
Consumer Exposure to Products Containing Ammonium Bifluoride - Although Solvay
Fluorides, LLC does not sell ammonium bifluoride directly to consumers, it is used in some
consumer cleaning products. The user should use these products in strict adherence with the
manufacturer’s use and/or label instructions.
Environmental Releases - Spills of ammonium bifluoride should be contained and isolated
from waterways and sewers or drains. Small spills of solid ammonium bifluoride should be
swept or shoveled up and placed in suitable containers for disposal. The contaminated area
should be washed down with plenty of water. Spills of liquid ammonium bifluoride should be
diluted with large amounts of water. Lime or calcium hydroxide may be used to neutralize
contaminated water and immobilize the fluoride ions as calcium fluoride. Disposal should be in
accordance with applicable local, state or federal regulations. Persons attempting to clean up
ammonium bifluoride spills should wear proper personal protective equipment (see guidelines in
Workplace Exposure section of this document or Safety Data Sheet). If required, report spills to
the appropriate state or federal authorities.
Fires - Fires involving ammonium bifluoride should be extinguished using measures appropriate
to the circumstances and surrounding environment. Hazardous decomposition products such as
hydrogen fluoride vapor can be generated if ABF is involved in a fire. Fire fighters should wear
self-contained breathing apparatus and protective suits.
For additional information concerning ammonium bifluoride emergency response procedures,
please consult the Safety Data Sheet.
Page 3 of 6
Copyright 2009-2013, Solvay America, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Health Information
The concentrations of ammonium bifluoride typically found in consumer products may pose risk of
symptoms due to skin, ingestion or inhalation exposure. Persons suffering from eye or ingestion
exposure to consumer strength ammonium bifluoride products may experience symptoms similar to
persons exposed to industrial strength ammonium bifluoride (see below).
Exposures to industrial strength ammonium bifluoride can produce the following adverse health
affects:
Contact - Skin exposures can cause symptoms ranging from minor skin irritation to painful
redness and swelling. Severe burns can occur if treatment is delayed after exposure to
ammonium bifluoride. Eye exposure to ammonium bifluoride may result in severe eye irritation,
burns or even blindness.
Inhalation - The inhalation of ammonium bifluoride can cause symptoms ranging from nose and
throat irritation to coughing and difficulty breathing. Aspiration may cause pulmonary edema and
pneumonitis (fluid on the lungs and inflammation of the lungs). Repeated or prolonged
exposures may cause sore throat, nosebleeds and chronic bronchitis. Prolonged exposure may
cause hypocalcemia with nervous problems (tetany) and cardiac arrhythmia (reduced calcium
levels, spasms and irregular heart beat).
Ingestion - The ingestion of ammonium bifluoride may cause burns of the mouth and throat and
perforation of the esophagus and stomach. Nausea, bloody vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea,
difficulty breathing, swelling of the throat, loss of consciousness, coma and heart failure can
also occur. The ingestion of ammonium bifluoride may be fatal.
Other Effects - The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) has not determined
ammonium bifluoride to be carcinogenic (cancer causing).
During most exposures, ammonium bifluoride will dissociate to release hydrofluoric acid. First aid
techniques for treatment to hydrofluoric acid exposures are unique. They require a rapid response
and the use of calcium (most commonly calcium gluconate solutions or gels) to scavenge and
neutralize the fluoride ion. Please consult the Safety Data Sheet for additional information.
For more information on health effects and routes of exposure, or for information concerning proper
first aid measures, please consult the Safety Data Sheet.
Environmental Information
Ammonium bifluoride is not known to bioaccumulate or persist in the environment more than a few
days. However, it will decompose in moist environments liberating hydrofluoric acid and ammonia.
For more ecological and environmental information concerning this product, please consult the
Safety Data Sheet.
Page 4 of 6
Copyright 2009-2013, Solvay America, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Physical Hazard Information
Ammonium bifluoride is corrosive and can corrode most metals. It is not flammable or explosive.
Ammonium bifluoride will react with water (including perspiration) to form hydrofluoric acid.
Exposure of ammonium bifluoride to strong acids, strong bases, water or high temperatures can
cause decomposition. Decomposition of ammonium bifluoride will result in the liberation of
hydrogen fluoride, ammonia and nitrogen oxide gases.
For more information concerning the physical hazards of this product, please consult the Safety
Data Sheet.
Regulatory Information
Regulations may exist that govern the manufacture, sale, export, import, storage, transportation,
use and/or disposal of this chemical. These regulations can vary by city, state, country or
geographic region. Information may be found by consulting the relevant Safety Data Sheet specific
to your country or region.
Additional Information
Solvay America, Inc. www.solvaynorthamerica.com
Solvay Fluorides, LLC www.solvaychemicals.us
Solvay Fluorides, LLC Safety Data Sheets
www.solvaychemicals.us/EN/Literature/LiteratureDocuments.aspx
Contact Solvay Fluorides, LLC solvaychemicals.us@solvay.com
NJ Department of Health & Senior Services Hazardous Substance Fact Sheets
http://web.doh.state.nj.us/rtkhsfs/factsheets.aspx
This summary was prepared in October, 2009
This summary was revised September, 2013
NOTICE
To our actual knowledge, the information contained herein is accurate as of the date of this
document. However, neither Solvay America, Inc. nor any of its affiliates makes any warranty,
express or implied, or accepts any liability in connection with this information or its use. This
information is for use by persons at their own discretion and risk and does not relate to use of this
product in combination with any other substance or any other process. This is not a license under
any patent or other proprietary right. The user alone must finally determine suitability of any
Page 5 of 6
Copyright 2009-2013, Solvay America, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
information or material for any contemplated use in compliance with applicable law, the manner of
use and whether any patents are infringed. This information gives typical properties only and is not
to be used for specification purposes. Solvay America, Inc. reserves the right to make additions,
deletions or modifications to the information at any time without prior notification. Trademarks
and/or other products of the company referenced herein are either trademarks or registered
trademarks of the company mentioned or its affiliates, unless otherwise indicated.
Page 6 of 6
Copyright 2009-2013, Solvay America, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
You might also like
- Oleum: Product Safety SummaryDocument6 pagesOleum: Product Safety SummaryMasood KblNo ratings yet
- Aluminium Sulfat MsdsDocument8 pagesAluminium Sulfat MsdsFadel IzzaNo ratings yet
- Inbound 818143939324636145Document9 pagesInbound 818143939324636145ejinmirijin27No ratings yet
- Ammonium HeptamolybdatDocument6 pagesAmmonium HeptamolybdatRega Wahyu AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- MSDS DapDocument7 pagesMSDS DapAnonymous lVbhvJfNo ratings yet
- Ammonium Bisulfite Solution MSDSDocument5 pagesAmmonium Bisulfite Solution MSDSscribdonetwothreeNo ratings yet
- Ammonium Bifluoride: Fluorine)Document6 pagesAmmonium Bifluoride: Fluorine)Joanah Paula SanielNo ratings yet
- Voranol: Polyols For Adhesives, Coatings, Elastomers and SealantsDocument2 pagesVoranol: Polyols For Adhesives, Coatings, Elastomers and SealantsA MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Sodium Sulfite: Product Safety SummaryDocument5 pagesSodium Sulfite: Product Safety SummaryMannar1No ratings yet
- Product Safety Summary Sheet: Ammonium HydroxideDocument3 pagesProduct Safety Summary Sheet: Ammonium HydroxideusamaNo ratings yet
- Safe Handling of Hydrogen Fluoride and Hydrofluoric AcidDocument6 pagesSafe Handling of Hydrogen Fluoride and Hydrofluoric AcidMd. Maksudur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Sulfuric Acid Material Safety Data Sheet: Section 1. Product and Company IdentificationDocument5 pagesSulfuric Acid Material Safety Data Sheet: Section 1. Product and Company IdentificationDipen DoshiNo ratings yet
- Abf Msds AnfaDocument7 pagesAbf Msds AnfaalkanfilesalesNo ratings yet
- Product Safety Summary: Sodium Bisulfite SolutionDocument5 pagesProduct Safety Summary: Sodium Bisulfite SolutioncastasoftNo ratings yet
- Ortho-Phenylphenol and Sodium Ortho-Phenylphenate: Product Safety AssessmentDocument7 pagesOrtho-Phenylphenol and Sodium Ortho-Phenylphenate: Product Safety AssessmentFaldy FariskiNo ratings yet
- Photo Processing HazardsDocument10 pagesPhoto Processing HazardsErick JordanNo ratings yet
- Sulfuric Acid Material Safety Data Sheet: Section 1. Product and Company IdentificationDocument5 pagesSulfuric Acid Material Safety Data Sheet: Section 1. Product and Company IdentificationDipen DoshiNo ratings yet
- Harikaran - 2021216026Document13 pagesHarikaran - 2021216026Alagappan SPNo ratings yet
- Bleach and Incompatible FactSheet LSP 20 116Document4 pagesBleach and Incompatible FactSheet LSP 20 116Training & Recruitment GSINo ratings yet
- Group3 ElementsDocument7 pagesGroup3 ElementsPeter JimenezNo ratings yet
- 1201 Alodine, AKA DX 503Document7 pages1201 Alodine, AKA DX 503Mark Evan SalutinNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet: Section 1 - Chemical Product and Company IdentificationDocument8 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: Section 1 - Chemical Product and Company Identificationsuraj rawatNo ratings yet
- Vcas SDSDocument4 pagesVcas SDSSeoudi AbdelhafidNo ratings yet
- Aluminum Flux PasteDocument10 pagesAluminum Flux PasteMark Evan SalutinNo ratings yet
- Ammonium SulphateDocument10 pagesAmmonium SulphateMOHANAPRIYA PNo ratings yet
- MSDS Tawas PrillDocument5 pagesMSDS Tawas PrillAreIf Cron BmxStreetNo ratings yet
- Aromatic 100 Product Safety SummaryDocument3 pagesAromatic 100 Product Safety Summarygtorre77No ratings yet
- Hazard Alert: Hydrofluoric (HF) Acid in Commercial Cleaners For VehiclesDocument2 pagesHazard Alert: Hydrofluoric (HF) Acid in Commercial Cleaners For VehiclesAaquil RaziNo ratings yet
- AluminumDocument6 pagesAluminumdavidperdanaNo ratings yet
- Medical Management Guidelines For Ammonia (NH) : General InformationDocument13 pagesMedical Management Guidelines For Ammonia (NH) : General InformationNader SmadiNo ratings yet
- Ficha Técnica - Isobutanol SigmaDocument6 pagesFicha Técnica - Isobutanol SigmaKrystle McdowellNo ratings yet
- Alumina HydratesDocument7 pagesAlumina HydratesMrutunjay Patra0% (1)
- Gps Summary ChlorineDocument5 pagesGps Summary ChlorinehamidNo ratings yet
- Bic 11117101 1 26Document19 pagesBic 11117101 1 262311271290004No ratings yet
- Bisulphite 25 LTR Liquid 38-40%Document2 pagesBisulphite 25 LTR Liquid 38-40%Eliete ArrudaNo ratings yet
- Ammonia-Code of Safety PDFDocument24 pagesAmmonia-Code of Safety PDFRajaiah JagariNo ratings yet
- PSS Allyl Chloride EpichlorohydrinDocument6 pagesPSS Allyl Chloride EpichlorohydrinOmar QasimNo ratings yet
- Aluminium Sulfat 0068Document6 pagesAluminium Sulfat 0068Fadel IzzaNo ratings yet
- Ammonium Bicarbonate Tds 2Document1 pageAmmonium Bicarbonate Tds 2thang13No ratings yet
- Water Treatment Plant Chemical Safety Presentation Complete Final 1Document21 pagesWater Treatment Plant Chemical Safety Presentation Complete Final 1api-339319779100% (1)
- Formic Acid - Chemicals ProductDocument1 pageFormic Acid - Chemicals ProductTrue StoryNo ratings yet
- SsaDocument9 pagesSsaPutri Fatmawati LubisNo ratings yet
- Save ItDocument21 pagesSave ItMer -MeNo ratings yet
- Hazardous Substance Fact Sheet: Right To KnowDocument6 pagesHazardous Substance Fact Sheet: Right To KnowmariamtkNo ratings yet
- Trimethyl Borate: Product Safety AssessmentDocument5 pagesTrimethyl Borate: Product Safety AssessmentBobyEsterandoNo ratings yet
- Ammonia Properties and HandlingDocument25 pagesAmmonia Properties and HandlingJohn Harken100% (2)
- Safety Data Sheet: Bromotrifluoromethane (Halon 1301, R13B1)Document5 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Bromotrifluoromethane (Halon 1301, R13B1)Rinny RojasNo ratings yet
- Johnsondiversey Acifoam: Acidic Foam Cleaner-DescalerDocument2 pagesJohnsondiversey Acifoam: Acidic Foam Cleaner-DescalerHamzeh AbdelhadiNo ratings yet
- 28-11-2022 - 10-18 - Wandira Danil Ramadhan - 1307622025Document9 pages28-11-2022 - 10-18 - Wandira Danil Ramadhan - 130762202513Wandira Danil RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Ammonium BicarbonateDocument6 pagesAmmonium BicarbonateRia PravitaNo ratings yet
- Safety Issue and Enviromental EffectDocument4 pagesSafety Issue and Enviromental EffectHaziq AzliNo ratings yet
- Afff May08 PDFDocument26 pagesAfff May08 PDFKeivaan BiramNo ratings yet
- Fixer G328Document8 pagesFixer G328ariNo ratings yet
- Calcium Peroxide: Product Safety SummaryDocument5 pagesCalcium Peroxide: Product Safety SummaryNasir JufriNo ratings yet
- Ammonium Sulphate ModifiedDocument13 pagesAmmonium Sulphate ModifiedAkuwh SyaSyaNo ratings yet
- AosDocument20 pagesAosHari Om Kumar VNo ratings yet
- Amorolfine ClorhidratoDocument17 pagesAmorolfine ClorhidratocarbouNo ratings yet
- Isopropyl AlcoholDocument5 pagesIsopropyl AlcoholwenigmaNo ratings yet
- Fluoridation ReviewDocument5 pagesFluoridation ReviewLESLI RODRIGUEZ BENDEZUNo ratings yet
- Industrial Surfactants: An Industrial GuideFrom EverandIndustrial Surfactants: An Industrial GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- P & P Ex 4Document24 pagesP & P Ex 4daniel abiaNo ratings yet
- StimOil MB - 3Document2 pagesStimOil MB - 3daniel abiaNo ratings yet
- Pre Course Hydro ExDocument4 pagesPre Course Hydro Exdaniel abiaNo ratings yet
- WIPC API Formula SheetDocument2 pagesWIPC API Formula Sheetdaniel abiaNo ratings yet
- Coiled Tubing Ex 2Document20 pagesCoiled Tubing Ex 2daniel abiaNo ratings yet
- Modellingbreaktimeatdiffrent ArpnDocument9 pagesModellingbreaktimeatdiffrent Arpndaniel abiaNo ratings yet
- Barrier Theory Rev ExDocument5 pagesBarrier Theory Rev Exdaniel abiaNo ratings yet
- Drilling Fluids Catalog PDFDocument47 pagesDrilling Fluids Catalog PDFNoor HadiNo ratings yet
- 44-81 - Ammonium BifluorideDocument11 pages44-81 - Ammonium Bifluoridedaniel abiaNo ratings yet
- 44-261 Ammonium ChlorideDocument31 pages44-261 Ammonium Chloridedaniel abiaNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: 1. Identification of The Substance/Preparation and of The Company/UndertakingDocument9 pagesSafety Data Sheet: 1. Identification of The Substance/Preparation and of The Company/Undertakingdaniel abiaNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet Hydrochloric Acid 25%: Revision Date: 07/04/2020 Version Number: 3.005 Supersedes Date: 22/11/2018Document29 pagesSafety Data Sheet Hydrochloric Acid 25%: Revision Date: 07/04/2020 Version Number: 3.005 Supersedes Date: 22/11/2018daniel abiaNo ratings yet
- 44-20376 - MSDS Item 1101610 - Citric AcidDocument65 pages44-20376 - MSDS Item 1101610 - Citric Aciddaniel abiaNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: According To Regulation (EC) No. 2015/830Document9 pagesSafety Data Sheet: According To Regulation (EC) No. 2015/830daniel abiaNo ratings yet
- Csm-50 Clay Control: 30years of InnovationDocument1 pageCsm-50 Clay Control: 30years of Innovationdaniel abiaNo ratings yet
- Ika-40 MSDSDocument9 pagesIka-40 MSDSdaniel abiaNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet Hydrochloric Acid 25%: Revision Date: 07/04/2020 Version Number: 3.005 Supersedes Date: 22/11/2018Document29 pagesSafety Data Sheet Hydrochloric Acid 25%: Revision Date: 07/04/2020 Version Number: 3.005 Supersedes Date: 22/11/2018daniel abiaNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: 1. Identification of The Substance/Preparation and of The Company/UndertakingDocument10 pagesSafety Data Sheet: 1. Identification of The Substance/Preparation and of The Company/Undertakingdaniel abiaNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: 1. Identification of The Substance/Preparation and of The Company/UndertakingDocument9 pagesSafety Data Sheet: 1. Identification of The Substance/Preparation and of The Company/Undertakingdaniel abiaNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet: 1. Identification of The Substance/Preparation and of The Company/UndertakingDocument7 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: 1. Identification of The Substance/Preparation and of The Company/Undertakingdaniel abiaNo ratings yet
- Clearpac: Polymer-Free Viscoelastic Surfactant Gravel-Pack FluidsDocument1 pageClearpac: Polymer-Free Viscoelastic Surfactant Gravel-Pack Fluidsdaniel abiaNo ratings yet
- Ltrahib: U Additive, The Primary Shale Inhibitor in The U System, Is A Liquid PolyamineDocument2 pagesLtrahib: U Additive, The Primary Shale Inhibitor in The U System, Is A Liquid Polyaminedaniel abiaNo ratings yet
- 316L Stainless Steel Chemical Compatibility Chart From ISM - 316l-Stainless-Steel-Chemical-Compatibility-From-IsmDocument1 page316L Stainless Steel Chemical Compatibility Chart From ISM - 316l-Stainless-Steel-Chemical-Compatibility-From-IsmchenNo ratings yet
- Lecture 34 PDFDocument5 pagesLecture 34 PDFSonuNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Edexcel GCEDocument24 pagesChemistry: Edexcel GCEaquu174015100% (1)
- O Level Chemistry Practical Guide PDFDocument161 pagesO Level Chemistry Practical Guide PDFAlinaitwe JohnNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Analysis ManualDocument58 pagesPharmaceutical Analysis Manualsrisabarigiri net centerNo ratings yet
- Merck Price List 2019Document568 pagesMerck Price List 2019Miftah RahmanNo ratings yet
- Silver and Palladium Recycling From The Secondary ResourcesDocument5 pagesSilver and Palladium Recycling From The Secondary ResourcesAFLAC ............No ratings yet
- Buffers and The HendersonDocument49 pagesBuffers and The HendersonABDUL HANANNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Chemistry of Inorganic MedicalsDocument21 pagesPharmaceutical Chemistry of Inorganic MedicalsJuliane Caniele Indiongco0% (2)
- Solubility Rules: Name - Chem Worksheet 15-1Document1 pageSolubility Rules: Name - Chem Worksheet 15-1Mohamed El-sherbinyNo ratings yet
- Chris CodesDocument12 pagesChris CodesHasan CosalevNo ratings yet
- 7 - SALT - 07 (NH4Cl)Document2 pages7 - SALT - 07 (NH4Cl)sham24102007No ratings yet
- October 2012 Hi Tech MagazineDocument37 pagesOctober 2012 Hi Tech MagazineeiribooksNo ratings yet
- 11.practical Organic ChemistryExercise PDFDocument25 pages11.practical Organic ChemistryExercise PDFRaj PandeyNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2020: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Chemistry (4CH1) Paper 1CDocument23 pagesMark Scheme (Results) January 2020: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Chemistry (4CH1) Paper 1Cmostafa barakat85% (13)
- Solution PreparationDocument32 pagesSolution PreparationMin AungNo ratings yet
- Chemistry SummaryDocument132 pagesChemistry SummarySebuta HuzaimaNo ratings yet
- 78 128Document51 pages78 128Anonymous qKeDFDNo ratings yet
- Science Notes - Lession-2 - Acids, Bases & Salts (Chemistry)Document34 pagesScience Notes - Lession-2 - Acids, Bases & Salts (Chemistry)Himanshi guptaNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes For Class 12 CBSE Chemistry, Amines - TopperlearningDocument11 pagesRevision Notes For Class 12 CBSE Chemistry, Amines - TopperlearningRishabh BhandariNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Chemistry 0620/61Document8 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Chemistry 0620/61sovow33568No ratings yet
- AminesDocument8 pagesAminesvandv printsNo ratings yet
- KALREZ DupontDocument20 pagesKALREZ DupontNet WalkerNo ratings yet
- Advanced-Chem Q1 LP7Document6 pagesAdvanced-Chem Q1 LP7Francesca BuenoNo ratings yet
- Utilization of Water Hyacinth and Banana Wastes Compost in Reclamation of Sandy Soils For Increasing Growth, Yield of CowpeaDocument10 pagesUtilization of Water Hyacinth and Banana Wastes Compost in Reclamation of Sandy Soils For Increasing Growth, Yield of CowpeaKanhiya MahourNo ratings yet
- CrystallizationDocument279 pagesCrystallizationRajendra Shrestha100% (2)
- ART-7052 HE Technical Data Sheet: DescriptionDocument4 pagesART-7052 HE Technical Data Sheet: Descriptionfrancisca ferrerNo ratings yet
- Exam in General ChemistryDocument4 pagesExam in General ChemistryArnel Metillo0% (1)
- P-Block 15 To 16 GroupDocument38 pagesP-Block 15 To 16 GroupBharti GoelNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and Salts AKHS 2020 - Complete NotesDocument27 pagesAcids, Bases and Salts AKHS 2020 - Complete NotesKim SewoonNo ratings yet