Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Advanced-Chem Q1 LP7
Uploaded by
Francesca BuenoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Advanced-Chem Q1 LP7
Uploaded by
Francesca BuenoCopyright:
Available Formats
SMILE
(SIMPLIFIED MODULE INTENDED FOR LEARNING ENCOUNTERS)
Learner’s Packet
Name:
Section: Date:
ADVANCED CHEMISTRY
(Q1_LP7)
BACKGROUND INFORMATION FOR LEARNERS:
Chemical formulas are symbolic representations of substances. These chemical
symbols express the elements present and the ratios in which the atoms are combined. They
are also used as basis in classifying substances. Written on the balloons are examples of
chemical formulas.
This learning packet is concerned of writing the chemical formulas of ionic compounds
and molecular compounds.
LEARNING COMPETENCY WITH CODE:
LC: Write the chemical formula of inorganic compounds.
Specific Objectives:
1. Distinguish between inorganic ionic compounds and inorganic molecular compounds
2. Write the chemical formulas of inorganic ionic compounds and inorganic molecular
compounds.
ACTIVITIES/ EXERCISES:
ACTIVITY 1: ORGANIC AND INORGANIC COMPOUNDS
In general, what element differentiates an organic compound from inorganic
compound? Organic compounds are carbon-containing compounds like, methane (CH 4)
butane (C4H10) and ethanol (CH3CH2OH). Inorganic compounds are compounds that contain
elements other than carbon, such as, sodium chloride (NaCl), ferrous sulfate (FeSO 4) and
nitric acid (HNO3). Therefore, it is the presence of the element carbon that differentiates
organic from inorganic compound. However, there are carbon-containing compounds which
are considered inorganic such as, carbon dioxide (CO 2), carbon monoxide (CO) and the
polyatomic ions, cyanide (CN-1), bicarbonate (HCO3-1) and carbonates (CO3-2).
Classify each of the following compounds as organic or inorganic compound. Write OC
if the compound is organic and IC if it is inorganic.
1. magnesium bromide (MgBr2) 4. potassium hydroxide (KOH)
2. Sulphur dioxide (SO2) 5. Ethylene (C2H4)
3. Propane (C3H8) 6. Lithium chloride (LiCl)
ACTIVITY 2: IONIC COMPOUNDS
Inorganic compounds can be classified into ionic compounds and molecular
compounds. Ionic compound is composed of cation (+ charged ion) and anion (- charged ion).
Generally, it is composed of metal and non-metal.
metal nonmetal
lithium bromide Li+1 Br-1 LiBr
cation anion
Here are some other examples of ionic compound. Please take note how the chemical
formulas are written; potassium bromide (KBr), zinc chloride (ZnCl2) and aluminum oxide
(Al2O3). Conventionally, the cation is written first followed by the anion. Below is the list of
common cations and anions in which you need to be familiar of in writing chemical formulas.
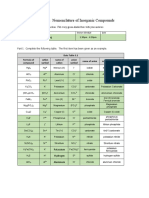
MONOATOMIC CATIONS MONOATOMIC MONOATOMIC
hydrogen H+1 CATIONS CATIONS
Lithium Li+1 WITH TWO CHARGES WITH TWO CHARGES
Sodium Na+1 copper (I) Cu+1 tin(II) Sn+2
potassium K+1 copper(II) Cu+2 tin(IV) Sn+4
Silver Ag+1 mercury(I) Hg+1 lead(II) Pb+2
magnesium Mg+2 mercury(II) Hg+2 lead(IV) Pb+4
Calcium Ca+2 gold(I) Au+1 arsenic(III) As+3
Strontium Na+2 gold(III) Au+3 arsenic(V) As+5
Barium Ba+2 iron(II) Fe+2 antimony(III) Sb+3
Zn+2 iron(III) Fe+3 antimony(V) Sb+5
Zinc
Al+3 cobalt(II) Co+2
aluminum
cobalt(III) Co+3
nickel(II) Ni+2
POLYATOMIC CATION
nickel(III) Ni+3
ammonium NH4+1
MONOATOMIC POLYATOMIC ANIONS POLYATOMIC ANIONS
-1
ANIONS bromite BrO2 hydroxide OH-1
-1 -
fluoride F-1 bicarbonate HCO3 permanganate MnO4
chloride Cl-1 cyanate CNO-1 1
-1
bromide Br--1 cyanide CN-1 nitrate NO3
-2 -1
iodide I-1 sulphate SO4 nitrite NO2
-2 -1
oxide O-2 sulphite SO3 perchlorate ClO4
-2 -1
sulphide S-2 carbonate CO3 chlorate ClO3
-2 -1
nitride N-3 oxalate C2O4 chlorite ClO2
-2
phosphide P-3 dichromate Cr2O7 hypochlorite ClO-1
-2 -1
carbide C+2 chromate CrO4 iodate IO3
-3 -1
phosphate PO4 iodite IO2
How do you think chemical formulas of ionic compounds are written? Here are the rules on
writing them;
1. Write the symbol of cation followed by the anion of a compound. Then simply criss-cross the
charges and make them as their subscripts.
ex. aluminum oxide Al+3 O-2 Al2O3
3. A subscript of one should no longer be indicated.
ex. sodium chloride Na+1 Cl-1 NaCl
calcium fluoride Ca+2 F-1 CaF2
4. If the subscripts are both divisible by a number, divided them by their greatest common factor.
ex. barium oxide Ba+2 O-2 BaO
tin(IV) oxide Sn+4 O-2 SnO2
5. If a subscript of polyatomic ion is greater than 1, enclose the polyatomic ion in parentheses.
ex. magnesium phosphate Mg+2 PO4-3 Mg3(PO 4) 2
ammonium sulfite NH4+1 SO3-2 (NH4) 2SO3
A. Now, let us have an activity to see if you have learned something in how to write chemical
formulas of ionic compounds.
Complete the table by writing the chemical formulas of the ionic compounds from the given ions.
ANION -3
Br-1 O-2 OH-1 PO4
CATION
Na+1
Ca+2
Sn+4
+1
NH4
B. Write the chemical formulas of the following ionic compounds on the space provided.
1. potassium chloride 6. lithium carbide
2. barium oxide 7. lead (IV) carbonate
3. calcium fluoride 8. ammonium chloride
4. ferric oxide 9. sodium iodide
5. aluminum hydroxide 10. mercury (II) oxide
ACTIVITY 3: MOLECULAR COMPOUNDS
MOLECULAR COMPOUNDS:
Unlike ionic compound, molecular compounds are composed non-metals. They have discrete
molecular units indicated by Greek prefixes. For example, carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide
(CO2) and diiodine pentoxide (I2O5). Greek prefixes on its name denote the number of atoms present
in the compound. Look at the figure below and study how the chemical formulas for molecular
compounds are written.
carbon monoxide carbon dioxide diiodine pentoxide
CO CO2 I2O5
1 carbon atom 1 carbon atom 2 iodine atoms
1 oxygen atom 2 oxygen atoms 5 oxygen atoms
As shown in the figure above, writing chemical formula for molecular compound is usually
straightforward. You just need to write the symbol of elements in the same order as that in its name
and translate the Greek prefixes into number by writing it as its subscript. Consider the following
examples;
GREEK PREFIXES Write the chemical formula of the following molecular compounds.
Mono 1
Di 2 1. dinitrogen monoxide
Tri 3
tetra 4 2. sulphur dioxide
penta 5
hexa 6 3. dinitrogen pentoxide
hepta 7
4. chlorine triflouride
octa 8
nona 9
5. dichlorine monoxide
deca 10
Answers: 1. N2O 2. SO2 3. N2O5 4. CF3 5. Cl2O
Write the chemical formula of the following molecular compounds.
.
1. sulfur trioxide 6. Selenium dioxide
2. xenon diflouride 7. iodine trichloride
3. phosphorus tribromide 8. xenon tetraflouride
4. iodine pentaflouride 9. diodine heptoxide
5. bromine monoflouride 10. dinitrogen trioxide
ACTIVITY 4: WHERE DO I BELONG?
Let us sum up what you have learned. Let us see if you can now distinguish ionic
compounds from molecular compound and can write the correct chemical formulas. Answer
the activities that follows.
From the symbols written on the balloons below, fill in the table by grouping the
chemical formulas into ionic compounds and molecular compounds.
IONIC COMPOUNDS MOLECULAR
COMPOUNDS
ACTIVITY 5: WRITING CHEMICAL FORMULA
Write the chemical formulas of the following inorganic compounds on the space
provided after its chemical name.
potassium sulfide calcium chloride
silver nitrate tin(IV) sulfate
barium hydroxide selenium dioxide
diphosphorus ammonium
pentachloride phosphate
aluminium sulfide zinc hydroxide
tetraphosphorus bromine
decoxide monoflouride
calcium chlorate cobalt(II) nitrate
ferric oxide silver iodide
REFLECTION:
Congratulations! You have done a great job in finishing this learning packet. This time, share your
insights and questions by completing the prompts below.
Things I have learned today:
I wish to ask about
REFERENCES FOR LEARNERS:
Textbooks:
Villamar, Rufino Jr. A. Chemistry, Latest Edition. Quezon City, Metro Manila.
St Bernadette Publishing House, 2012.
Chang, Raymund. General Chemistry: The Essential Concepts, 5th
Edition. New York USA, McGraw Hill Companies Inc., 2008.
You might also like
- Writing and Naming Chemical FormulasDocument3 pagesWriting and Naming Chemical FormulasCarlo Joseph Moskito100% (1)
- Common Polyatomic Ions and Chemical CompoundsDocument4 pagesCommon Polyatomic Ions and Chemical CompoundsBhel San Pedro MarzanNo ratings yet
- Naming CompoundsDocument2 pagesNaming CompoundsTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Why Bond Anyway?Document45 pagesChemical Bonding: Why Bond Anyway?PutRi Charolin GintingNo ratings yet
- Complete NomenclatureDocument10 pagesComplete NomenclaturezainalexanderaliNo ratings yet
- CHM361-CHAPTER 5 Coordination Compound PDFDocument59 pagesCHM361-CHAPTER 5 Coordination Compound PDFEhaz100% (1)
- Chemical NomenclatureDocument7 pagesChemical NomenclatureKeith Lavin100% (1)
- General Chemistry 1 Learning CompetenciesDocument1 pageGeneral Chemistry 1 Learning CompetenciesMon ColinaNo ratings yet
- Common Ions and Their Charges: From The Table: Ions To Memorize Cations Name Cations NameDocument2 pagesCommon Ions and Their Charges: From The Table: Ions To Memorize Cations Name Cations NameChantelle W. SHUMNo ratings yet
- Naming and Formula WritingDocument15 pagesNaming and Formula WritingMeggy CaparasNo ratings yet
- Common IonsDocument3 pagesCommon IonsabdallaaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 Module 3Document6 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 Module 3Jason Vinluan CarinanNo ratings yet
- Write The Formulas For The Following Ionic Compounds:: Bonding and Naming WS 4Document2 pagesWrite The Formulas For The Following Ionic Compounds:: Bonding and Naming WS 4Bea Lha Zandra BesingaNo ratings yet
- Ion Memorization ListDocument2 pagesIon Memorization Listdchao94No ratings yet
- Chemical Formula Writing Worksheet PDFDocument4 pagesChemical Formula Writing Worksheet PDFkezia0% (1)
- Valency and Formulae-HandoutDocument3 pagesValency and Formulae-HandoutABHAVYA RAJNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument9 pagesCHEMISTRYXyiee ViorNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Review On Chemical Formulas With AnswersDocument4 pagesChemistry - Review On Chemical Formulas With AnswersAbdullah HassanNo ratings yet
- Common Ions and Their FormulasDocument2 pagesCommon Ions and Their FormulasReiNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry Summer Assignment 2017Document44 pagesAP Chemistry Summer Assignment 2017John SmithNo ratings yet
- List of Common Cations Name Symbol ChargeDocument4 pagesList of Common Cations Name Symbol ChargernlpzcyNo ratings yet
- Common Ions ListDocument2 pagesCommon Ions Listms.makaylacelineNo ratings yet
- Summer Assignment For AP Chemistry Class 2020-2021Document5 pagesSummer Assignment For AP Chemistry Class 2020-2021shelly zhangNo ratings yet
- ApsummerDocument5 pagesApsummerLayleeNo ratings yet
- Table For Urry Q3Document1 pageTable For Urry Q3andyNo ratings yet
- Polyatomic Ions List: Honors ChemistryDocument2 pagesPolyatomic Ions List: Honors ChemistrymandaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Coordination CompoundDocument36 pagesChapter 5 Coordination Compoundammar zakariaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Nomenclature and Formulas GuideDocument2 pagesGeneral Chemistry Nomenclature and Formulas GuideCamille AquinoNo ratings yet
- 5.9 Polyatomic CompoundsDocument3 pages5.9 Polyatomic Compoundsmichael.delaney8541No ratings yet
- 17 Polyatomic Ions S PDFDocument7 pages17 Polyatomic Ions S PDFGideon CavidaNo ratings yet
- Common Ions and Their ChargesDocument1 pageCommon Ions and Their ChargesNonbinaryBroadwayNo ratings yet
- Cations and AnionsDocument2 pagesCations and AnionsG2 Atacador, Channa Keavy B.No ratings yet
- Symbols and Names For Common Polyatomic IonsDocument1 pageSymbols and Names For Common Polyatomic IonsElixirNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature of Inorganic Compounds: Report SheetDocument3 pagesNomenclature of Inorganic Compounds: Report SheetAEsmilingNo ratings yet
- Elements (Anions) Symbol Oxidation NO. Elements (Anions) Symbol Oxidation NODocument5 pagesElements (Anions) Symbol Oxidation NO. Elements (Anions) Symbol Oxidation NOJims Cudinyerah100% (1)
- Chemical Formulas-General ChemistryDocument19 pagesChemical Formulas-General Chemistry7assan1300No ratings yet
- Element Group Cation Element Group AnionsDocument3 pagesElement Group Cation Element Group AnionsCharlotte TanNo ratings yet
- Inorganic ListDocument7 pagesInorganic ListWeronika OstrowskaNo ratings yet
- Combining capacity, oxidation number and naming of compoundsDocument9 pagesCombining capacity, oxidation number and naming of compoundsZynx DixonNo ratings yet
- CHEM& 161 - Tran - Winter 2021 Elements and Ions: What Does This Tell Us? An Element On This List Exists As ADocument2 pagesCHEM& 161 - Tran - Winter 2021 Elements and Ions: What Does This Tell Us? An Element On This List Exists As AНиколай ЛиксуновNo ratings yet
- Handout Atom, Elemen, Molokul Ion PK AktoDocument51 pagesHandout Atom, Elemen, Molokul Ion PK Aktoanna suikenuuNo ratings yet
- Monatomic and Polyatomic IonsDocument2 pagesMonatomic and Polyatomic Ionsaku 223No ratings yet
- CHEM Semis BubbaDocument5 pagesCHEM Semis BubbaNorlyn Mae MarcialNo ratings yet
- Ionic Puzzle ActivityDocument4 pagesIonic Puzzle ActivityEngr Mumtaz0% (1)
- 10 - Ionic Bonding ActivityDocument4 pages10 - Ionic Bonding Activityapi-292000448No ratings yet
- Cations and Anions in Metals and NonmetalsDocument2 pagesCations and Anions in Metals and NonmetalsPuji RetnowatiNo ratings yet
- LIST OF CATIOS AND ANIONSDocument7 pagesLIST OF CATIOS AND ANIONSrituNo ratings yet
- Katyon Ve Anyon TablosuDocument1 pageKatyon Ve Anyon TablosuhelenNo ratings yet
- Chm361 Chapter 5Document34 pagesChm361 Chapter 5syamimiafrinaNo ratings yet
- PCQA supplement: Common cations and anionsDocument4 pagesPCQA supplement: Common cations and anionsrnlpzcyNo ratings yet
- NomenclatureDocument68 pagesNomenclatureel tetraNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgAKjYyPDA8imA1n06RTHYhmcZyQfXBSGYi5Ul3iZ4tznc3KA75jGjJ5z79-K8DlCA4lS6s4YPAGa9JU3hUpukNLW3ARrct1BFVU1FITpLNKtizdLNeJ4PgnikitvzfS2ImJ2ohAnBH4JZbIDocument2 pagesACFrOgAKjYyPDA8imA1n06RTHYhmcZyQfXBSGYi5Ul3iZ4tznc3KA75jGjJ5z79-K8DlCA4lS6s4YPAGa9JU3hUpukNLW3ARrct1BFVU1FITpLNKtizdLNeJ4PgnikitvzfS2ImJ2ohAnBH4JZbIbenjamin.morenoNo ratings yet
- Fe CL Fe CL Fecl: Charge of The Ion Oxidation States of Transition MetalsDocument1 pageFe CL Fe CL Fecl: Charge of The Ion Oxidation States of Transition MetalsSuzaki KurushiNo ratings yet
- Common Ions and Their ChargesDocument2 pagesCommon Ions and Their ChargesSJ SuingNo ratings yet
- Write The Names For The Following Compounds: 1. C HDocument4 pagesWrite The Names For The Following Compounds: 1. C HOshauntae FosterNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 01 Dated 05072021Document1 pageWorksheet 01 Dated 05072021Jeny SharmaNo ratings yet
- Coordination Compounds: Structures, Nomenclature and IsomerismDocument34 pagesCoordination Compounds: Structures, Nomenclature and Isomerismatikah roshanNo ratings yet
- Ion ReferenceDocument2 pagesIon Referenceapi-254514513No ratings yet
- Task 4Document1 pageTask 4Francesca BuenoNo ratings yet
- Advancechem Q1 LP4Document7 pagesAdvancechem Q1 LP4Francesca BuenoNo ratings yet
- Copy-Of-Q2 STE Advanced ChemistryDocument58 pagesCopy-Of-Q2 STE Advanced ChemistryFrancesca BuenoNo ratings yet
- Oral Cammunication Module 1 Q1Document22 pagesOral Cammunication Module 1 Q1Joan Bolano Binondo100% (1)
- Pre Calculus ReviewerDocument4 pagesPre Calculus ReviewerFrancesca BuenoNo ratings yet
- Task 7Document1 pageTask 7Francesca BuenoNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport Mechanisms ExplainedDocument13 pagesCell Transport Mechanisms ExplainedFrancesca BuenoNo ratings yet
- Dhaka University Microbiology Syllabus 2015-2017Document33 pagesDhaka University Microbiology Syllabus 2015-2017Janus MalikNo ratings yet
- Cos1911 ZschimmerDocument1 pageCos1911 ZschimmerrezaNo ratings yet
- Module 8 RationaleDocument3 pagesModule 8 RationaleG INo ratings yet
- Technical Data Sheet: Board Type in Line With EN 622-5Document2 pagesTechnical Data Sheet: Board Type in Line With EN 622-5JulioG.CamposCadenaNo ratings yet
- DuctSox DesignManualDocument20 pagesDuctSox DesignManualPanduNo ratings yet
- Curs Ginkgo BilobaDocument7 pagesCurs Ginkgo BilobaAnamaria RizacNo ratings yet
- HSSRPTR - +1 Chemistry Focus Area NotesDocument58 pagesHSSRPTR - +1 Chemistry Focus Area NotesAbduk100% (2)
- Dual-Combustion Cycle Thermodynamics ExplainedDocument17 pagesDual-Combustion Cycle Thermodynamics ExplainedMae Anj100% (1)
- ALP Testing SOPDocument6 pagesALP Testing SOPUMMID WashimNo ratings yet
- CIR 113-123 Class Notes 2023Document98 pagesCIR 113-123 Class Notes 2023Kabelo SerageNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1Document16 pagesWorksheet 1All photos CloudNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 - Calibration of Volumetric GlasswareDocument22 pagesExperiment 2 - Calibration of Volumetric GlasswareJoemer Absalon Adorna73% (15)
- Sikagard 63n PdsDocument4 pagesSikagard 63n PdsHendro YuniantoNo ratings yet
- Iec 60216-2-2005Document19 pagesIec 60216-2-2005Laurindo SousaNo ratings yet
- Forensic Science International: Marianne Hädener, Sina Vieten, Wolfgang Weinmann, Hellmut MahlerDocument6 pagesForensic Science International: Marianne Hädener, Sina Vieten, Wolfgang Weinmann, Hellmut MahlerlunahermannNo ratings yet
- Surface Characterization of ZnO Nanorods Grown by Chemical Bath DepositionDocument6 pagesSurface Characterization of ZnO Nanorods Grown by Chemical Bath DepositionMbulanga CrispinNo ratings yet
- CL - 1000i Immunofluorescence Analyzer.Document6 pagesCL - 1000i Immunofluorescence Analyzer.bikouvoNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.1 TitrationDocument4 pagesExperiment No.1 Titrationoc dhogs TvNo ratings yet
- Tosoh Zeolite Brochure English Rev2017 3Document12 pagesTosoh Zeolite Brochure English Rev2017 3Taha ObedNo ratings yet
- Preparation and Reactions of Coordination Compounds: Oxalate ComplexesDocument11 pagesPreparation and Reactions of Coordination Compounds: Oxalate ComplexesMONROY RAMIREZ ANDRES FELIPENo ratings yet
- Waterproofing: Waterstops For Expansion and Construction JointsDocument27 pagesWaterproofing: Waterstops For Expansion and Construction JointsgarusingheNo ratings yet
- A Civil Works: Site Quality - Weekly ReportDocument4 pagesA Civil Works: Site Quality - Weekly ReportISGEC KPCL ProjectNo ratings yet
- Delayed-Action AcceleratorDocument3 pagesDelayed-Action AcceleratorMOHD FIRDAUSNo ratings yet
- Volumetric Recievers-A ReviewDocument20 pagesVolumetric Recievers-A ReviewDany ValverdeNo ratings yet
- Quarter-3-Module-3-in-Gen-Chem-2.2nd Edition 2021 - RemovedDocument16 pagesQuarter-3-Module-3-in-Gen-Chem-2.2nd Edition 2021 - RemovedEfren James ParasNo ratings yet
- CO2 Adsorption Enhanced by Nitrogen-Rich BiocharDocument8 pagesCO2 Adsorption Enhanced by Nitrogen-Rich BiocharKhaled Abou AlfaNo ratings yet
- Confirmatory Tests For Cation (Chemistry)Document9 pagesConfirmatory Tests For Cation (Chemistry)Hetav PatelNo ratings yet
- MSP 06 002 KFGTPDocument104 pagesMSP 06 002 KFGTPmohammed younesNo ratings yet
- Julie Bui - Building Dna GizmosDocument3 pagesJulie Bui - Building Dna Gizmosapi-5226505140% (2)
- Handgun-MUS601010101QUICK GUIDE A4 ING v2Document2 pagesHandgun-MUS601010101QUICK GUIDE A4 ING v2dongNo ratings yet