Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pharmaceutical Suppositories
Uploaded by
Ralph Aubrey CulhiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pharmaceutical Suppositories
Uploaded by
Ralph Aubrey CulhiCopyright:
Available Formats
SAINT MARY’S UNIVERSITY
BAYOMBONG, NUEVA VIZCAYA 3700
SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND NATURAL SCIENCES
PHARMACY DEPARTMENT
Name: Culhi, Ralph Aubrey B.
Year/Course: BSP-2
Pharmaceutics 1 (LEC)
Pharmaceutical Suppositories
Objectives
At the end of the topic, students should be able to:
1. Determine the different dosage forms which are intended for insertion to body cavities.
2. Describe the rationale for using suppository as an alternative to orally administered medicines.
3. Determine the bases used in its preparation.
4. Appreciate the advantages associated with these dosage forms.
5. Determine the appropriate storage, packaging and labeling of this dosage form.
6. Give examples of drugs formulated as suppositories or pessaries.
To accomplish the objectives of this topic, students will be asked to answer the following questions to
be submitted as attached file in the LMS
Guide questions for this topic
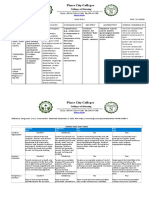
1. Differentiate rectal, vaginal, and urethral suppositories as to shape, size and use/application.
Suppositories Shape Size Application
Rectal Bullet shaped/Pencillike ½ to 1 inch Using the narrow end of the
shaped suppository it is inserted through
the rectum of the patient.
Vaginal Round oval/Egg shaped 5 mm in diameter, 50 mm Inserted through the female
about 2 inch in length genital/vagina
Urethral Slender Pencillike shape 3 to 6 mm in diameter and Inserted through the urethra of a
approximately 140 mm male/female genital with the narrow
about 5 ½ inch long end first.
2. Describe the attributes/characteristics, composition, and uses/application of intrauterine drug
delivery, vaginal insert and ring, and vaginal gel.
Characteristics Uses/Application Composition
Intrauterine A small object placed Inserted into the uterus An intrauterine device is a
Drug Delivery inside the uterus above the (womb) to prevent highly effective, small, T-
endometrium that is active pregnancy. shaped birth control
or medicated if it contains device made of flexible
a therapeutic agent This plastic and copper.
system is a drug/device
combination that slowly
releases the active
ingredient.
Vaginal Insert A flexible, latex-free To use a vaginal ring, Contains the hormones
and Ring plastic ring that's inserted you squeeze the ring and estrogen and
into the vagina. insert it into your progesterone, which are
vagina (like inserting a released over a three-
tampon). It stays in your week period.
vagina for three weeks.
You then take it out and
throw it away and wait
seven days before inserting
a new ring.
Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms, Drug Delivery Systems and Medical Devices 1
SAINT MARY’S UNIVERSITY
BAYOMBONG, NUEVA VIZCAYA 3700
SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND NATURAL SCIENCES
PHARMACY DEPARTMENT
Vaginal Gel An anti-infective used to Wash hands before and Containing metronidazole
treat bacterial vaginitis. after use. Screw the at a concentration of 7.5
applicator to the tube and mg/g (0.75%). The gel is
squeeze the tube gently to formulated at pH 4.0. The
fill the applicator. Lie on gel also contains
your back, part and bend carbomer 934P, edetate
your knees. Insert disodium, methylparaben,
the applicator tip high in propylparaben, propylene
the vagina and push the glycol, and sodium
plunger to release the gel hydroxide.
into the vagina.
3. Describe the classifications of suppository bases.
Classifications Of Suppository Description/Definition
Bases
Fatty or Oleaginous Bases Fatty bases are the most commonly used suppository bases, owing to the
fact that cocoa butter belongs to this group of substances. Many
hydrogenated fatty acids of vegetable oils, such as palm kernel oil and
cottonseed oil, are among the other fatty or oleaginous materials used in
suppository bases.
Water-Soluble and Water- Glycerinated gelatin and polyethylene glycols are the most common
Miscible Bases members of this group. Glycerinated gelatin suppositories are made by
dissolving granular gelatin (20%) in glycerin (70%) and then adding water
or a medication solution or suspension (10%). In the preparation of vaginal
suppositories, a glycerinated gelatin base is most commonly used, as
prolonged local action of the medicinal agent is usually desired. The
glycerinated gelatin base softens and mixes with the physiologic fluids
more slowly than cocoa butter, resulting in a slower release.
Miscellaneous Bases Lipophilic and hydrophilic suppositories are the general combinations of
miscellaneous suppositories. Lipophilic suppositories are mostly made of
fat or wax, and they melt at body temperature. Polymer or glycerin-based
hydrophilic suppositories require fluids to dissolve.
4. Give examples for each type of suppository base.
Classifications Of Suppository Examples
Bases
Fatty or Oleaginous Bases Cocoa Butter and Cottonseed Oil
Water-Soluble and Water- Glycerinated Gelatin and Polyethylene Glycols
Miscible Bases
Miscellaneous Bases Alcohols and Toluene
5. Explain the importance of suppository base in relation to drug’s bioavailability.
- Suppositories provide pharmacokinetic benefits by increasing bioavailability to
absorbable tissue, bypassing first-pass metabolism, delivering high doses of drug, and
avoiding gastric mucosa irritation. Reduced first-pass metabolism, both topical and
systemic effect, accommodates patients who have difficulty swallowing pills, and
increased drug bioavailability are the primary advantages of suppositories over other
dosage forms.
Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms, Drug Delivery Systems and Medical Devices 2
SAINT MARY’S UNIVERSITY
BAYOMBONG, NUEVA VIZCAYA 3700
SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND NATURAL SCIENCES
PHARMACY DEPARTMENT
6. What are the packaging and labeling requirements for suppositories?
- For the primary packaging of suppositories, the automated process includes five distinct
stages. The stages involved are forming, dosing, cooling, sealing, and finishing. These
stages are completed at up to 30,000 suppositories per hour in a continuous process.
Glycerin and glycerinated gelatin suppositories are packaged in tightly sealed glass
containers to prevent moisture content changes. Suppositories made with cocoa butter
are usually individually wrapped or otherwise separated in compartmented boxes to
avoid contact and adhesion. Individually wrapped light sensitive drug suppositories are
made of an opaque material, such as metallic foil. The majority of commercial
suppositories come in foil or plastic packaging. Some come in a continuous strip with
perforations that are separated by tearing. Supplied in slide boxes or plastic boxes,
suppositories are also commonly packaged.
7. What is the proper storage for suppositories?
- To avoid melting, keep the suppositories in a cool place. If the medication label
specifies, store them in the refrigerator.
8. Describe vaginal inserts and medication sticks.
- Vaginal inserts are uncoated, bullet-shaped, or ovoid tablets that are inserted into the
vagina for local effects. They're compressed and shaped to fit snugly inside the plastic
inserter devices that come with the product.
- Medication sticks are a convenient way to deliver topical medications. Medication sticks
are cylindrical in shape and weigh between 5 and 25 grams. They're usually packaged
in an applicator tube for topical application, and the applicator can be adjusted to keep
exposing new, fresh sticks from inside the tube. Sticks are commonly used for
hydration/emollient, antibacterial, sunscreen, antipruritic, and other local effects.
Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms, Drug Delivery Systems and Medical Devices 3
SAINT MARY’S UNIVERSITY
BAYOMBONG, NUEVA VIZCAYA 3700
SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND NATURAL SCIENCES
PHARMACY DEPARTMENT
Ansel’s Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms pages 364-390
Note: Use this same template for your answers to the questions.
Images:
RECTAL SUPPOSITORY
Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms, Drug Delivery Systems and Medical Devices 4
SAINT MARY’S UNIVERSITY
BAYOMBONG, NUEVA VIZCAYA 3700
SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND NATURAL SCIENCES
PHARMACY DEPARTMENT
VAGINAL PESSARY/OVULE
URETHRAL SUPPOSITORY
Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms, Drug Delivery Systems and Medical Devices 5
You might also like
- Essential Drug Data for Rational Therapy in Veterinary PracticeFrom EverandEssential Drug Data for Rational Therapy in Veterinary PracticeNo ratings yet
- IPPP-II (Supp)Document85 pagesIPPP-II (Supp)Tinsaye HayileNo ratings yet
- Foreskin Renewal: The Complete Guide To All Natural Foreskin Restoration.From EverandForeskin Renewal: The Complete Guide To All Natural Foreskin Restoration.No ratings yet
- Screenshot 2024-03-22 at 09.26.47Document7 pagesScreenshot 2024-03-22 at 09.26.47tuayuNo ratings yet
- Suppositories Vaginal Suppositories: Dosage FormsDocument5 pagesSuppositories Vaginal Suppositories: Dosage FormsRye M. BirungNo ratings yet
- Know Your Medicine UPH654: Nur Sabiha MD HussinDocument176 pagesKnow Your Medicine UPH654: Nur Sabiha MD HussinSyafiyatulMunawarahNo ratings yet
- Contraceptive Choices at A Glance Chart Sexwise FpaDocument1 pageContraceptive Choices at A Glance Chart Sexwise FpaMai SomaaNo ratings yet
- Your Contraceptive Choices ChartDocument1 pageYour Contraceptive Choices ChartM Cecilia DFNo ratings yet
- Suppositories As A Dosage FormDocument11 pagesSuppositories As A Dosage FormMirumbi Kefa MomanyiNo ratings yet
- Clinical Practice Midwifery Family Planning Services: Oleh: Nur AssyahDocument10 pagesClinical Practice Midwifery Family Planning Services: Oleh: Nur AssyahWULAN SUCI WARDANINo ratings yet
- Secundum Artem: Send This Completed Form in For CE Credit Today!Document6 pagesSecundum Artem: Send This Completed Form in For CE Credit Today!randatagNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical PowdersDocument12 pagesPharmaceutical PowdersThomas Niccolo Filamor ReyesNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument125 pagesIlovepdf MergedinnyNo ratings yet
- (LR) Prep-6 Post-Lab AssignmentDocument2 pages(LR) Prep-6 Post-Lab AssignmentPompeyo Barroga Jr.No ratings yet
- C-12 Suppositories and InsertsDocument80 pagesC-12 Suppositories and InsertsYsai TomasNo ratings yet
- MEDICATION ADMINISTRATION Reviewer AbreganaMarnitoDocument7 pagesMEDICATION ADMINISTRATION Reviewer AbreganaMarnitoBlaise Anne InocNo ratings yet
- Practice School Report On Indusrial TrainingDocument25 pagesPractice School Report On Indusrial Trainingabhishek .darshaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - SuppositoriesDocument5 pagesChapter 12 - SuppositoriesAli Uy100% (1)
- The Progesterone Supplementation HandbookDocument15 pagesThe Progesterone Supplementation HandbookTsvetomiraNo ratings yet
- Transdermal Drug Delivery SystemsDocument7 pagesTransdermal Drug Delivery SystemsMARIE ERICKA ARONANo ratings yet
- Capsules and It's Technology: An Overview: ArticleDocument8 pagesCapsules and It's Technology: An Overview: ArticleR TicoaluNo ratings yet
- Paper Anticonceptivos Ingles ExponerDocument18 pagesPaper Anticonceptivos Ingles ExponermariaNo ratings yet
- Parenteral Suspension: An Overview: International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical ResearchDocument10 pagesParenteral Suspension: An Overview: International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical ResearchAnonymous 7r2h3YViNo ratings yet
- SUPPOSITORIADocument41 pagesSUPPOSITORIAZulfa SalsabellaNo ratings yet
- Instructions For Use: Step 1: Step 4Document11 pagesInstructions For Use: Step 1: Step 4Anesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Metodos AnticonceptivosDocument3 pagesMetodos Anticonceptivoshhhhhhh yhyyyyy tttttNo ratings yet
- Family PlanningDocument15 pagesFamily PlanningIdara AlphonsusNo ratings yet
- A Review On Effervescent TabletDocument6 pagesA Review On Effervescent TabletInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Natural Pharmaceutical Excipients, An Overview: Tasneem Ara, Amtul Barina DevaDocument7 pagesNatural Pharmaceutical Excipients, An Overview: Tasneem Ara, Amtul Barina DevaNisha SharmaNo ratings yet
- ContraceptionDocument21 pagesContraceptionSinar InarNo ratings yet
- Artificial Family PlanningDocument36 pagesArtificial Family PlanningKaye Honeylee ManibogNo ratings yet
- Soft Gel FormulationDocument12 pagesSoft Gel FormulationIndu nutraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Pharmacy: Riaz Rahman 48Document85 pagesIntroduction To Pharmacy: Riaz Rahman 48Nispap Harami RJNo ratings yet
- A Review On Chewable TabletsDocument11 pagesA Review On Chewable TabletsThuận TVNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Humans: Contraception: J. J. Marshall-Thompson Cape Biology Unit 1 20 APRIL, 2020Document26 pagesSexual Reproduction in Humans: Contraception: J. J. Marshall-Thompson Cape Biology Unit 1 20 APRIL, 2020Lavinia LaviaNo ratings yet
- Your Complete Guide To Birth Control Methods in The PhilippinesDocument8 pagesYour Complete Guide To Birth Control Methods in The PhilippinesJobert John BatallonesNo ratings yet
- Family Planning PDFDocument6 pagesFamily Planning PDFCaezzar SangcupanNo ratings yet
- Formulasi Pasta AloeveraDocument6 pagesFormulasi Pasta AloeveraFitri MaesaNo ratings yet
- SuppositoriesDocument12 pagesSuppositoriesJAKE BENZYN TENo ratings yet
- 5 Produtos Semissólidos Vaginais. Desempenho Tecnológico Considerando Parâmetros FisiológicosDocument13 pages5 Produtos Semissólidos Vaginais. Desempenho Tecnológico Considerando Parâmetros FisiológicosdeniscandeiasNo ratings yet
- Suppositories Inserts SticksDocument5 pagesSuppositories Inserts SticksDee Pañares100% (1)
- Intra Peritoneal (IP)Document21 pagesIntra Peritoneal (IP)Proud PharmacistNo ratings yet
- 4.1 - Doge and Doges FormsDocument28 pages4.1 - Doge and Doges FormsNo IdeaNo ratings yet
- Parenteral Suspension An OverviewDocument10 pagesParenteral Suspension An OverviewIrma LaumbuNo ratings yet
- Drug Study OndansetronDocument3 pagesDrug Study OndansetronDustin Jade Olli100% (2)
- Vol4 Issue3 11Document7 pagesVol4 Issue3 11ABHINABA GUPTANo ratings yet
- Formulation and Evaluation of Tooth Gel From Aloe Vera Leaves ExtractDocument6 pagesFormulation and Evaluation of Tooth Gel From Aloe Vera Leaves Extractshafira putri pertiwiNo ratings yet
- C. Explain The Principles of Drug AdministrationsDocument6 pagesC. Explain The Principles of Drug AdministrationsAubrey Nicole MacapagalNo ratings yet
- Pi Glycerine SuppositoriesDocument2 pagesPi Glycerine SuppositoriesMey KhNo ratings yet
- Tablet Hisap 5Document9 pagesTablet Hisap 5Rizka NurNo ratings yet
- Parasite Control GuideDocument16 pagesParasite Control GuideEduard MelinteNo ratings yet
- BIRTcontrol LecDocument3 pagesBIRTcontrol LecYUAN CAÑASNo ratings yet
- ContraceptionDocument21 pagesContraceptionMA. JYRELL BONITONo ratings yet
- Dosage Forms (Also Called Unit Doses) Are PharmaceuticalDocument8 pagesDosage Forms (Also Called Unit Doses) Are PharmaceuticalDeepak SinghNo ratings yet
- Making Medicines That Children Can Take - Nunn - 2003Document4 pagesMaking Medicines That Children Can Take - Nunn - 2003neutrinomuonNo ratings yet
- 834 Ijar-10870 PDFDocument6 pages834 Ijar-10870 PDFBhavin VoraNo ratings yet
- Veterinary Dosage FormsDocument22 pagesVeterinary Dosage FormsSolomonNo ratings yet
- Removing Medication From An AmpuleDocument2 pagesRemoving Medication From An AmpuleMichael Bon MargajaNo ratings yet
- Birth Control PillsDocument1 pageBirth Control PillsBryan CaesarNo ratings yet
- Non & Pharmacologic GoutDocument1 pageNon & Pharmacologic GoutRalph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- Pharm Med 1 Lec - Assignment No. 1Document2 pagesPharm Med 1 Lec - Assignment No. 1Ralph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity 2 - Drug Information SourcesDocument2 pagesLab Activity 2 - Drug Information SourcesRalph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Adenosine Triphosphate in The MetabolicDocument1 pageThe Importance of Adenosine Triphosphate in The MetabolicRalph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 - Pharm InfoDocument2 pagesLab 1 - Pharm InfoRalph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- Lab. 1-Background of The Plant, Preparation of Crude Drug and Official SamplingDocument7 pagesLab. 1-Background of The Plant, Preparation of Crude Drug and Official SamplingRalph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- Lab. 2-Moisture and Determination (Gravimetric Method)Document5 pagesLab. 2-Moisture and Determination (Gravimetric Method)Ralph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- CULHI - 5087 - Evolution of Pharmacy EssayDocument2 pagesCULHI - 5087 - Evolution of Pharmacy EssayRalph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- Saint Mary's University: Experiment 1: Common Laboratory Apparatus / EquipmentDocument2 pagesSaint Mary's University: Experiment 1: Common Laboratory Apparatus / EquipmentRalph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- 1O Reasons Why Physical Fitness Is ImportantDocument1 page1O Reasons Why Physical Fitness Is ImportantRalph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- Culhi, R III Research PhySci2019-2020Document3 pagesCulhi, R III Research PhySci2019-2020Ralph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 (I) As in Bit TriviaDocument5 pagesLesson 2 (I) As in Bit TriviaRalph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- Related StudiesDocument1 pageRelated StudiesRalph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity 1 Common Laboratory Apparatus & GlasswaresDocument6 pagesLaboratory Activity 1 Common Laboratory Apparatus & GlasswaresRalph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- PerdevDocument1 pagePerdevRalph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts About Matter: Test BankDocument12 pagesBasic Concepts About Matter: Test BankRalph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document2 pagesChapter 2Ralph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- CFE 101 - Activity 1, 2nd TermDocument1 pageCFE 101 - Activity 1, 2nd TermRalph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- PD EssayDocument1 pagePD EssayRalph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- Class SchedDocument1 pageClass SchedRalph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- Saint Mary's University: Experiment 1: Common Laboratory Apparatus / EquipmentDocument2 pagesSaint Mary's University: Experiment 1: Common Laboratory Apparatus / EquipmentRalph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts About Matter: Test BankDocument12 pagesBasic Concepts About Matter: Test BankRalph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity 1 Common Laboratory Apparatus & GlasswaresDocument6 pagesLaboratory Activity 1 Common Laboratory Apparatus & GlasswaresRalph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- PerdevDocument1 pagePerdevRalph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- CFE 101 - Activity 1, 2nd TermDocument1 pageCFE 101 - Activity 1, 2nd TermRalph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- PD EssayDocument1 pagePD EssayRalph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document2 pagesChapter 2Ralph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- Related StudiesDocument1 pageRelated StudiesRalph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- Class SchedDocument1 pageClass SchedRalph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- List of Books PDFDocument29 pagesList of Books PDFDevansh Agarwal75% (4)
- Alims - Approved Terminology - Routes and Methods of Administration - October 2014Document2 pagesAlims - Approved Terminology - Routes and Methods of Administration - October 2014Katarina R.M.No ratings yet
- Quality Agreement Guideline Final December 2009 Clean Appendix ADocument12 pagesQuality Agreement Guideline Final December 2009 Clean Appendix AflongNo ratings yet
- AsthmaDocument2 pagesAsthmaMarya Fanta C LupuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Introduction To Medical DevicesDocument7 pagesLecture 1 - Introduction To Medical DevicesApoorva GangulyNo ratings yet
- Suprefact DepotDocument42 pagesSuprefact DepotImran KhanNo ratings yet
- Management of Premature Contractions With ShatavarDocument5 pagesManagement of Premature Contractions With ShatavarSinta AgustinaNo ratings yet
- AspirinDocument5 pagesAspirinNishit Patel50% (2)
- Pharmaceutical Technology, Mar 2, Volume 36, Issue 3, Pp. 58-72Document11 pagesPharmaceutical Technology, Mar 2, Volume 36, Issue 3, Pp. 58-72rosamir8No ratings yet
- GCP Flash CardDocument3 pagesGCP Flash CardSok YeeNo ratings yet
- MerckDocument14 pagesMerckShruthi RNo ratings yet
- Swetha ResumeDocument4 pagesSwetha ResumeSushma VallamdasNo ratings yet
- CombinepdfDocument177 pagesCombinepdfPrincess RonsableNo ratings yet
- Permethrin TechnicalDocument5 pagesPermethrin TechnicalHuyen NguyenNo ratings yet
- MAPS Psychedelics and Self Discovery Autumn 2007Document32 pagesMAPS Psychedelics and Self Discovery Autumn 2007jancitojancito100% (4)
- StinaDocument5 pagesStinaKaaya GodfreyNo ratings yet
- Prescription Drug Abuse Crisis in NYS - Comprehensive ApproachDocument26 pagesPrescription Drug Abuse Crisis in NYS - Comprehensive ApproachNew York SenateNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CARDIODocument17 pagesDrug Study CARDIODiannetotz Morales100% (1)
- Patent Term Extension Strategies in The Pharmaceutical IndustryDocument14 pagesPatent Term Extension Strategies in The Pharmaceutical IndustryRushi PatelNo ratings yet
- Doses Carpenter: MamíferosDocument14 pagesDoses Carpenter: MamíferosBruna MoreiraNo ratings yet
- Clarification Billing by CGHS Empanelled Hospitals 10 Nov 22Document3 pagesClarification Billing by CGHS Empanelled Hospitals 10 Nov 22Nilesh SethNo ratings yet
- BCS WHO Classification QAS04 109rev1 Waive Invivo BioequivDocument45 pagesBCS WHO Classification QAS04 109rev1 Waive Invivo BioequivjjmuruzaNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Critical Review of ICH Q8, Q9 and Q10 From A Generic Pharmaceutical Industry View PointDocument12 pagesAnalysis and Critical Review of ICH Q8, Q9 and Q10 From A Generic Pharmaceutical Industry View PointARMANDO JOSE RIVERO LAVERDENo ratings yet
- Amoxicillin 3 X 1Document1 pageAmoxicillin 3 X 1MeilindaLaurensiaFebrihiantoNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Mechanism: MemantineDocument4 pagesName of Drug Mechanism: MemantineCarlmeister Ambray JudillaNo ratings yet
- History of Pharmaco G NosyDocument13 pagesHistory of Pharmaco G NosyYogesh BagadNo ratings yet
- Hospital Evacuation Plan ChecklistDocument5 pagesHospital Evacuation Plan ChecklistMadyo Puguh SusantoNo ratings yet
- Phytochemical Composition of Bryophyllum PinnatumDocument3 pagesPhytochemical Composition of Bryophyllum PinnatumAfaf AshariNo ratings yet
- Characterization of Adsorption Behavior by Solid Dosage Form Excipients in Formulation DevelopmentDocument8 pagesCharacterization of Adsorption Behavior by Solid Dosage Form Excipients in Formulation DevelopmentKietNo ratings yet
- 14.natural GumsDocument10 pages14.natural Gumsparuldutt1996No ratings yet