Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson 1 - Introduction To Computers, Anatomy of Computers, Input and Output Devices
Uploaded by
Kent Adrian UnatoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson 1 - Introduction To Computers, Anatomy of Computers, Input and Output Devices
Uploaded by
Kent Adrian UnatoCopyright:
Available Formats
REPUBLIC OF THE PHILIPPINES
ILOILO STATE COLLEGE OF FISHERIES
Tiwi, Barotac Nuevo, Iloilo
5007 Philippines
College of Education
Contact No.: (+63) 917-624-6100
Website: www.iscof.com.ph / Email: iscofpresident2016@gmail.com
EC 8 - Introduction to ICT Specializations II
Lesson 1: Introduction to Computers, Anatomy of Computers, Input and Output Devices
In human affairs we have reached a point where the problems that we must solve are no
longer solvable without the aid of computers. I fear not computers but the lack of them.
- ISAAC ASIMOV
Introduction to Computers
A computer can be defined as an electronic device capable of processing the data and
producing the information.
The computer system essentially comprises three important
parts.
1. Input device,
2. central processing unit (CPU) and
3. output device.
The CPU itself is made of three components namely,
1. arithmetic logic unit,
2. memory unit, and
3. control unit.
Components of a Computer System
EC 8 - Introduction to ICT Specializations II
On broad basis, a computer performs the following task:
Input: Sending the data and command to the computer is known as input.
Processing: Work done by the computer with the help of processing hardware and software to
produce results is known as processing.
Output: The result displayed by the computer is known as output.
Storage: A place to save result inside or outside the computer is known as storage.
Anatomy of Computers
The following are the parts of a desktop computer.
Power Supply
When you plug your power cable into your
computer, you are actually plugging into a socket in the
power supply unit that has been fitted inside your case.
This component is responsible for converting the 240-volt
AC mains power to low voltage DC power needed by
computer components. The power supply generates +3.3V,
+5V, +12V, -5V. These voltages must be constant, right up
to the maximum current your system will draw under load.
Monitor
Commonly known as a "screen," the monitor gives
you a visual display of what your computer is up to. Monitor
displays are divided into pixels. The higher the pixel count,
the higher the "resolution." Resolutions are measured in
Rows x Columns. Common resolution settings are 640 x
480, 800 x 600, 1024 x 768, 1280 x 1024, etc.
Mother board
The mainboard I which is sometimes called a
motherboard. This is usually the largest circuit-board in the
computer, and every other component in the computer
connects to it.
CPU
The Central Processing Unit (CPU)is usually called
either a CPU or just a Processor. The CPU is the brain of
the system. It executes all the program code from the
operating system and the applications the user runs and
processing of data. It sends CPU commands to direct the
actions of all the other components in the computer.
EC 8 - Introduction to ICT Specializations II
Main Memory or Random-Access Memory (RAM)
RAM, which stands for Random Access Memory, is the short-term memory that the compu
uses to keep track of what it's doing. If the computer loses
power, anything stored in RAM is lost.
Storage Device
Computer storage device is any type of hardware that
stores data. The most common type of storage device, which
nearly all computers have, is a hard drive.
Hard Drive
INPUT AND OUTPUT DEVICES
Input Devices
Input device is a hardware device that sends information to the
computer.
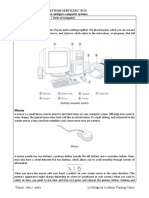
Mouse
Mouse is a pointer device. The mouse allows an
individual to control a pointer in a graphical user interface
(GUI). Utilizing a mouse, a user has the ability to perform
various functions such as opening a program or file and does
not require the user to memorize commands.
Digital camera
A type of camera that stores the pictures or video it
takes in electronic format instead of to film.
Web Cam
A camera connected to a computer that allows anyone
connected to the Internet to view still pictures or motion video
of a user.
Joystick
A computer joystick allows an individual to easily navigate
an object in a game such as navigating a plane in a flight
simulator.
Keyboard
One of the main input devices used on a computer, a
computer keyboard looks very similar to the keyboards of electric
typewriters, with some additional keys.
EC 8 - Introduction to ICT Specializations II
Microphone
Sometimes abbreviated as mic, a microphone is a
hardware peripheral that allows computer users to input audio into
their computers.
Scanner
Input device that allows a user to take an image and/or text
and convert it into a digital file, allowing the computer to read
and/or display the scanned object
Output Device
Any peripheral that receives and/or displays output from a computer. Below are some
examples of different types of output devices commonly found on a computer. Monitor
A monitor is a video display screen. Monitor is also called as Visual Display Unit (VDU) or Video
Display Terminal (VDT).
CRT (Cathode Ray Tube) Monitors are built LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) Monitors
These are very similarly to older (tube) television sets. thin and flat. They are light,
compact, take up They are heavy, bulky, take up a lot of desk very little desk space emit no
known radiation. space, and emit radiation.
Printer
A printer is an output device responsible for
taking computer data and generating a hard copy of that
data.
Projector
It is an output device that takes images generated by a
computer or Blu-ray player and reproduce them by projection onto a
screen, wall, or another surface. In most cases, the surface projected
onto is large, flat, and lightly colored. For example, you could use a
EC 8 - Introduction to ICT Specializations II
projector to show a presentation on a large screen so that everyone in the room can see
it. Projectors can produce either still (slides) or moving images (videos). A projector is
often about the size of a toaster and weighs only a few pounds.
Speakers
A device that converts analog audio signals into the
equivalent air vibrations in order to make audible sound.
References
https://encyclopedia2.thefreedictionary.com
https://www.computerhope.com/
Kent Adrian M. Unato, LPT
Faculty
EC 8 - Introduction to ICT Specializations II
You might also like
- SERVICE TOOL CATALOG Carrier Transicold PDFDocument98 pagesSERVICE TOOL CATALOG Carrier Transicold PDFRoberto SalazarNo ratings yet
- Power Systems For AIX III - Advanced Administration and Problem DeterminationDocument946 pagesPower Systems For AIX III - Advanced Administration and Problem DeterminationgsgheneaNo ratings yet
- SLHT Grade 7 CSS Week 2Document6 pagesSLHT Grade 7 CSS Week 2princeyahweNo ratings yet
- STAHL Overhead Travelling CranesDocument44 pagesSTAHL Overhead Travelling CranesIgnacio Moratinos Castañeda100% (2)
- AIX For The System AdministratorDocument10 pagesAIX For The System AdministratorDima ShcherbakovNo ratings yet
- BCA 101 SolvedDocument15 pagesBCA 101 SolvedGhanshyam Sharma33% (3)
- Lesson 1: Understanding The Computer SystemDocument50 pagesLesson 1: Understanding The Computer SystemR-Yel Labrador BaguioNo ratings yet
- Empowerment Chapter-1Document27 pagesEmpowerment Chapter-1John Lester M. Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Basic Computer OrganizationDocument21 pagesBasic Computer OrganizationSuchit IjantakarNo ratings yet
- Diosdado P BanataoDocument4 pagesDiosdado P BanataoRolanNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Input Output Storage DevicesDocument20 pagesModule 5 Input Output Storage DevicesMohd Hafiez100% (4)
- CompTIA IT FundamentalsDocument11 pagesCompTIA IT Fundamentalsstephen efangeNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware PeripheralsDocument18 pagesComputer Hardware PeripheralsStanley Bennett100% (3)
- T L E Module 1 Grade 8Document20 pagesT L E Module 1 Grade 8Jared Floyd Lorezo100% (3)
- UGRD IT6302 Integrative Programming and Technology 1 Source Prelim Quiz 1 Prelim Quiz 2 Midterm Quiz 1 Midterm Quiz 2 Final Quiz 1 Final Quiz 2Document9 pagesUGRD IT6302 Integrative Programming and Technology 1 Source Prelim Quiz 1 Prelim Quiz 2 Midterm Quiz 1 Midterm Quiz 2 Final Quiz 1 Final Quiz 2gummy bearNo ratings yet
- Ict Hand BookDocument25 pagesIct Hand BookSamaeel UrielNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computers, Anatomy of Computers, Input and Output DevicesDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Computers, Anatomy of Computers, Input and Output DevicesAmruta SuryawanshiNo ratings yet
- TLE7 1st QuarterDocument7 pagesTLE7 1st QuarteriamzoeyreineaNo ratings yet
- On The Way To Computer and Information LiteracyDocument16 pagesOn The Way To Computer and Information LiteracyNivea Pamela Tidoy (Yhang)No ratings yet
- Tugas Kelompok Untuk BesokDocument13 pagesTugas Kelompok Untuk BesokMbh GengNo ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument65 pagesChapter Oneaddim6748No ratings yet
- Basic Computer OrganizationDocument21 pagesBasic Computer OrganizationSariska MehraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Understanding The Computer SystemDocument52 pagesLesson 1 Understanding The Computer SystemAliyah PlaceNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Teaching ICT As An Exploratory Course - OCCDocument21 pagesModule 1 - Teaching ICT As An Exploratory Course - OCCAngelica PesinoNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware Network Professional Ver.2013Document345 pagesComputer Hardware Network Professional Ver.2013Aqeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- T Is A Computer Harware Softwares Fundamentals and PartsDocument21 pagesT Is A Computer Harware Softwares Fundamentals and Partslhieeyhan77No ratings yet
- 2 - Computer SystemDocument62 pages2 - Computer Systemdagne tomoshkeNo ratings yet
- Computer AwernesDocument145 pagesComputer AwernessekharNo ratings yet
- Broken Equipment:Do Not Try To Repair Equipment Yourself. If YouDocument14 pagesBroken Equipment:Do Not Try To Repair Equipment Yourself. If YoudARk_gEMukNo ratings yet
- Gee3 Week 2Document21 pagesGee3 Week 2angelicaelagunoyNo ratings yet
- Topic 1: Anatomy of ComputerDocument7 pagesTopic 1: Anatomy of ComputerharoonNo ratings yet
- Speaker MD - Shafiuzzaman FarukiDocument85 pagesSpeaker MD - Shafiuzzaman FarukiRaju AhammadNo ratings yet
- Learning Module CHS 7Document19 pagesLearning Module CHS 7Nelson PiconesNo ratings yet
- Grade 7Document15 pagesGrade 7Hannah EstacioNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer Hardware PeripheralsDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Computer Hardware PeripheralsedrisNo ratings yet
- Connect PeripheralsDocument13 pagesConnect Peripheralstsegadese4No ratings yet
- Resource 20230220140657 Grade 11 Computer HandoutsDocument257 pagesResource 20230220140657 Grade 11 Computer HandoutsSasidaran SasiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document50 pagesLesson 3Andre Deyniel CabreraNo ratings yet
- Tle Module 1 Grade 8Document10 pagesTle Module 1 Grade 8vhernabeth reylaNo ratings yet
- Administare-Netwrok-and-Hardware Peripheral-DevicesDocument38 pagesAdministare-Netwrok-and-Hardware Peripheral-DevicesedrisNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document36 pagesModule 1Ankit ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- M1 Yash AllabadiDocument6 pagesM1 Yash Allabadidegijon661No ratings yet
- CSS G11 Module 2Document5 pagesCSS G11 Module 2Shendelzare Silkwood Quinto AronNo ratings yet
- Week 1 CSS NC2 DocsDocument19 pagesWeek 1 CSS NC2 DocsJoshua DaaNo ratings yet
- Connect HardwareDocument23 pagesConnect HardwareYoni ManNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 Introduction To Computer Organization: Department of Computer EngineeringDocument47 pagesChapter - 1 Introduction To Computer Organization: Department of Computer EngineeringMeet GamerNo ratings yet
- Generation of ComputerDocument16 pagesGeneration of ComputerRohit UpparattiNo ratings yet
- PST - Unit 1Document16 pagesPST - Unit 1cs235114414No ratings yet
- University of Gujrat Department of Political Sciences: Assignment No.1Document9 pagesUniversity of Gujrat Department of Political Sciences: Assignment No.1Ahmad BajwaNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware Servicing: TLE 10 Simulation Module / Dry - RunDocument30 pagesComputer Hardware Servicing: TLE 10 Simulation Module / Dry - RunAngelyn LingatongNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Input Output Storage DevicesDocument18 pagesModule 5 Input Output Storage Devicesterabytes95No ratings yet
- Output Devices of Computer: Definition & ExamplesDocument22 pagesOutput Devices of Computer: Definition & Exampleshamidmasood07No ratings yet
- Introduction To ComputersDocument12 pagesIntroduction To ComputersAishah JeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Understanding The Computer SystemDocument50 pagesLesson 1: Understanding The Computer SystemR-Yel Labrador BaguioNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware Servicing IiDocument16 pagesComputer Hardware Servicing IiFacun BalagtasNo ratings yet
- Information Sheet 2Document12 pagesInformation Sheet 2Geejan Galaroza PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- Fakeye O. O. (2018) Practical Manual For Basic Computer AppDocument21 pagesFakeye O. O. (2018) Practical Manual For Basic Computer AppokunademoyinoluwaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document19 pagesLesson 1Paul MachariaNo ratings yet
- Input Output-Keyboard and MonitorDocument17 pagesInput Output-Keyboard and MonitorFredrick MugoNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware SoftwareDocument41 pagesComputer Hardware SoftwareKatheryn Rose QuilapioNo ratings yet
- ICT NOTES 2022 DiplomaDocument51 pagesICT NOTES 2022 DiplomaelishabagalwNo ratings yet
- CSC 111 Practical Lab ManualDocument49 pagesCSC 111 Practical Lab ManualLawal100% (1)
- Input and Output DevicesDocument12 pagesInput and Output Devicesaroojmalaika20No ratings yet
- HRM 412 Week 1 Lecture NoteDocument9 pagesHRM 412 Week 1 Lecture Noteebraheem636No ratings yet
- Introduction To Computers.Document26 pagesIntroduction To Computers.thomasNo ratings yet
- 21st Century EducationDocument5 pages21st Century EducationKent Adrian UnatoNo ratings yet
- The Impact of ICT On SocietyDocument5 pagesThe Impact of ICT On SocietyKent Adrian UnatoNo ratings yet
- Usage of ICT in Daily LifeDocument5 pagesUsage of ICT in Daily LifeKent Adrian UnatoNo ratings yet
- Evolution of ComputersDocument7 pagesEvolution of ComputersKent Adrian UnatoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ICTDocument4 pagesIntroduction To ICTKent Adrian UnatoNo ratings yet
- Project 1 - Making A Poster - RubricDocument1 pageProject 1 - Making A Poster - RubricKent Adrian UnatoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Computer Viruses, Worms and VaccineDocument4 pagesLesson 2 - Computer Viruses, Worms and VaccineKent Adrian UnatoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Family Life Cycle and StagesDocument3 pagesLesson 5 - Family Life Cycle and StagesKent Adrian UnatoNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Requirements Throughout The Lifecycle: Nutrition, The Human Life Span, or The MaximumDocument33 pagesNutritional Requirements Throughout The Lifecycle: Nutrition, The Human Life Span, or The MaximumKent Adrian UnatoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1. Definition and Importance of AgricultureDocument2 pagesLesson 1. Definition and Importance of AgricultureKent Adrian UnatoNo ratings yet
- College of Education: Major 11 Marriage and Family RelationshipsDocument4 pagesCollege of Education: Major 11 Marriage and Family RelationshipsKent Adrian UnatoNo ratings yet
- Flowtite Fittings GuideDocument24 pagesFlowtite Fittings GuideakilasrivatsavNo ratings yet
- FO SolutionDocument16 pagesFO Solutionsumit1975No ratings yet
- ETW 400 BrochureDocument4 pagesETW 400 Brochurenimaboat4589No ratings yet
- E1-42 Pin AssignmentDocument3 pagesE1-42 Pin AssignmentAhmed Jamal KhanNo ratings yet
- 1 OSI MODEL - PpsDocument24 pages1 OSI MODEL - PpsSaif ShaikhNo ratings yet
- M6 Series Diagnostic Ultrasound System Service ManualDocument266 pagesM6 Series Diagnostic Ultrasound System Service ManualBruno AraújoNo ratings yet
- Trusted Platform ModuleDocument12 pagesTrusted Platform ModuleabcNo ratings yet
- SRT 1F K-Shelf Tests ProcedureDocument116 pagesSRT 1F K-Shelf Tests ProcedureMihaelNo ratings yet
- SHS TVL Ict Animation Week 5 - Objects To Be Measured - Melita PascuaDocument5 pagesSHS TVL Ict Animation Week 5 - Objects To Be Measured - Melita PascuaBook_AinjelleNo ratings yet
- Directsoft32: Programming SoftwareDocument8 pagesDirectsoft32: Programming SoftwareSilvia Del RioNo ratings yet
- Samyung BNW 50Document2 pagesSamyung BNW 50Aldrine Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Ictp211 PrelimsDocument10 pagesIctp211 PrelimsparcongieselaNo ratings yet
- Sliding Gate Motor Installation Manual: (Sentry PCB)Document15 pagesSliding Gate Motor Installation Manual: (Sentry PCB)Francois VaaltynNo ratings yet
- Stihl FS25-4 Service ManualDocument45 pagesStihl FS25-4 Service ManualJoshua RoyNo ratings yet
- Colour TV Set: ModelsDocument19 pagesColour TV Set: ModelsLefter TironNo ratings yet
- Riserbond App GuideDocument44 pagesRiserbond App GuidefiskitNo ratings yet
- Indra: Cabinet NameDocument1 pageIndra: Cabinet NameBoualem AisNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 ICT Mid Term 2023Document4 pagesGrade 5 ICT Mid Term 2023KISAKYE ANTHONYNo ratings yet
- OracleRedefinition SPCMGMT Final ReorgDocument23 pagesOracleRedefinition SPCMGMT Final Reorgsricharitha6702No ratings yet
- Automatic Transaxle Diag Trouble CodesDocument3 pagesAutomatic Transaxle Diag Trouble CodesSteven Casey JonesNo ratings yet
- MGD2004D FL Ybs PDFDocument10 pagesMGD2004D FL Ybs PDFEverton DoradoNo ratings yet
- Model XCGSM - GSM and GPRS Cellular Modem Option Card For Data Station Plus and Modular ControllerDocument4 pagesModel XCGSM - GSM and GPRS Cellular Modem Option Card For Data Station Plus and Modular ControllerShesharam ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Numerical Computing: 2.1 NumbersDocument24 pagesNumerical Computing: 2.1 NumbersUzma AzamNo ratings yet
- RS-232 and RS-485 Serial Network Interfaces: NI FP-1000, NI FP-1001Document3 pagesRS-232 and RS-485 Serial Network Interfaces: NI FP-1000, NI FP-1001Flor Mitma AyvarNo ratings yet