Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Types of Cells
Uploaded by
Paris Liang0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views1 pageTypes of Cells
Uploaded by
Paris LiangCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
TYPES OF CELLS (21/09/17)
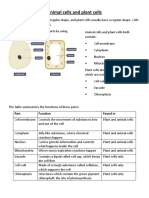
DIAGRAM 1: A PLANT CELL AS SEEN UNDER A MICROSCOPE (Kingdom: Plant)
Points to note:
1. Cell wall: made up of a material called cellulose. It
is fully permeable meaning that it allows ALL
substances to pass through.
2. Chloroplasts: this is where photosynthesis takes
place in plant cells. It contains the green pigment
chlorophyll, which is used to trap sunlight energy
for photosynthesis.
3. The vacuole is large and contains cell sap which is
a solution of water and nutrients.
4. Plant cells normally have a regular shape i.e.
rectangular or square.
DIAGRAM 2: A BACTERIUM CELL AS SEEN UNDER A MICROSCOPE (Kingdom: Monera)
1. Gelatin Capsule: protects the bacterium from
harmful chemicals.
2. Cell wall: Does not contain cellulose like
plant cell walls. Instead it is made up of
complex carbohydrates and proteins.
3. Flagellum: some bacteria has this and some
do not. It is used for movement. The cell
moves as the flagellum moves back and
forth.
4. The bacterium cell DOES NOT CONTAIN A
NUCLEUS. Instead it contains a naked strand
of DNA in the form of a chromosome.
DIAGRAM 3: AN AMOEBA AS SEEN UNDER A MICROSCOPE (Kingdom: Protoctista)
1. Pseudopods: these allow the Amoeba
to move. They are also used to
surround and take in food particles.
1. Using the diagram of the plant cell
from this hand out, and the diagram
of the animal cell from the previous
class:
a. Write down ALL the
similarities between plant
animal cells.
b. Write down ALL the differences between plant and animal cells.
2. Copy and complete the following table that compares the different types of cells.
Cell Type Prokaryote Cell wall Regular or Nucleus Flagellum Chloroplast Vacuole
or Present Irregular Present or Present or Present or Large or
Eukaryote or Absent Shape Absent Absent Absent Small
Animal
Plant
Bacterium
Amoeba
You might also like
- Learner's Book Answers: Unit 1 CellsDocument31 pagesLearner's Book Answers: Unit 1 CellsLyaz Antony91% (91)
- Collins Concise Revision Course: CSEC® Human and Social BiologyDocument32 pagesCollins Concise Revision Course: CSEC® Human and Social BiologyOsmany Madrigal100% (4)
- Gross Anatomy of Fourth VentricleDocument16 pagesGross Anatomy of Fourth VentricleRafique AhmedNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Module 2 Q1Document17 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Module 2 Q1Pril Gueta80% (10)
- Cell Bio Quiz 1Document3 pagesCell Bio Quiz 1raphaelNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Cell StructureDocument8 pagesStudent Exploration: Cell Structurelingesh tamizhanNo ratings yet
- Cytology and Chemicals of LifeDocument53 pagesCytology and Chemicals of LifeIVAN HUNCHONo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function ReviewerDocument4 pagesCell Structure and Function ReviewerLeandre Jasmine ReyesNo ratings yet
- SHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 1 Module 2 Cell Structure and Functions 1Document17 pagesSHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 1 Module 2 Cell Structure and Functions 1Dette Dominic Ballano67% (3)
- SHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 1 Module 2 - Cell Structure And-FunctionsDocument23 pagesSHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 1 Module 2 - Cell Structure And-FunctionsEmer Perez50% (2)
- Lower Secondary Science Learner 7-AnswersDocument4 pagesLower Secondary Science Learner 7-Answershiori San83% (12)
- General Biology Module 2Document11 pagesGeneral Biology Module 2Jee-Anne HerbularioNo ratings yet
- All Living Things Are Made of Cells Are The Basic Unit of in An Organism (Basic Unit of Life) Cells Come From The (Cell Division)Document10 pagesAll Living Things Are Made of Cells Are The Basic Unit of in An Organism (Basic Unit of Life) Cells Come From The (Cell Division)Christine EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Cell TypesDocument4 pagesGen Bio Cell TypesRaeson Amir ReyesNo ratings yet
- Bio Cells NotesDocument7 pagesBio Cells Notesnabita20211No ratings yet
- Q1 General Biology Rev L2Document5 pagesQ1 General Biology Rev L2Dwen Kirby VillamorNo ratings yet
- Bacteria and Archaea Are Classified As Prokaryotes ( Pro Before Karyon - Nucleus)Document2 pagesBacteria and Archaea Are Classified As Prokaryotes ( Pro Before Karyon - Nucleus)Sekar AyuNo ratings yet
- Cell Sturcture, Osmosis & Diffusion (Answer Key)Document7 pagesCell Sturcture, Osmosis & Diffusion (Answer Key)maariamshamsi2No ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 1 NotesDocument6 pagesBiology Chapter 1 Notesmohan.shenoy52No ratings yet
- General Biology Cells1Document6 pagesGeneral Biology Cells1Kristine CarvajalNo ratings yet
- Unit 1. The Organisation of Living ThingsDocument9 pagesUnit 1. The Organisation of Living ThingsEva PascualNo ratings yet
- Unit 1. The Organisation of Living ThingsDocument9 pagesUnit 1. The Organisation of Living ThingsIrenita gacha verseNo ratings yet
- 7 Science - Chapter 1-3 AnswerDocument3 pages7 Science - Chapter 1-3 Answermichael tanNo ratings yet
- A Specialized Structure Occurring in Most Cells and Separated From The Rest of The Cell by A Double Layer, The Nuclear MembraneDocument3 pagesA Specialized Structure Occurring in Most Cells and Separated From The Rest of The Cell by A Double Layer, The Nuclear MembraneGian Carlo MadriagaNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Cell StructureDocument8 pagesStudent Exploration: Cell StructureMishaNo ratings yet
- Cells NoteDocument6 pagesCells NoteYolanda JesslinaNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument5 pagesScience ReviewerLeica NicoleNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Teacher: Reda QuidetDocument25 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Teacher: Reda QuidetJuanito MerciNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure SEDocument8 pagesCell Structure SESandra FernandezNo ratings yet
- Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeDocument8 pagesCell: The Basic Unit of LifePradyun DSNo ratings yet
- Act. 3 Cytology PeraltaDocument18 pagesAct. 3 Cytology PeraltaCogie PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio DLP Activity 1 MatutinaDocument3 pagesGen Bio DLP Activity 1 MatutinaNoella Elliraine MatutinaNo ratings yet
- Neil Hubilla - Gen Bio 1 q1 Las 3Document5 pagesNeil Hubilla - Gen Bio 1 q1 Las 3Neil Jhon HubillaNo ratings yet
- Cell and Cell OrganellesDocument53 pagesCell and Cell OrganellesShiffa SaheedNo ratings yet
- CELLS 2.1: Outline: To Give A Brief Account or SummaryDocument10 pagesCELLS 2.1: Outline: To Give A Brief Account or SummaryHrithik SolaniNo ratings yet
- Sample Laboratory SheetDocument2 pagesSample Laboratory SheetMaria Karene OraaNo ratings yet
- Cell The Unit of LifeDocument7 pagesCell The Unit of Liferahilislam1144No ratings yet
- 2.2 - Cell Structure and It's FunctionsDocument4 pages2.2 - Cell Structure and It's FunctionscarlNo ratings yet
- Spgbio NotesDocument22 pagesSpgbio NotesKaycee HeokkaidoNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 1 Module 4Document13 pagesGen Bio 1 Module 4Ante,Glainry Rose Basan100% (1)
- Genbio 1Document14 pagesGenbio 1Laiza Marie LopezNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument2 pagesBiologyjsfowen18No ratings yet
- Biology Quick Notes in EnglishDocument28 pagesBiology Quick Notes in EnglishJai JaiNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Cell BiologyDocument2 pagesTopic 1 Cell BiologyEklavya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Student Handout 01 - Cell StructureDocument6 pagesStudent Handout 01 - Cell StructureJoslynn SlaytonNo ratings yet
- Rganisation of The Organism: 1 Cell Structure and OrganisationDocument26 pagesRganisation of The Organism: 1 Cell Structure and OrganisationGasterNo ratings yet
- RRL BookkeepingDocument2 pagesRRL BookkeepingNasha RelatoNo ratings yet
- Cells WebquestDocument4 pagesCells Webquestapi-347555363No ratings yet
- AY 2020 Sem 1 A104 P01 WS Team 2Document7 pagesAY 2020 Sem 1 A104 P01 WS Team 2Lim Liang XuanNo ratings yet
- Animal Cells and Plant CellsDocument4 pagesAnimal Cells and Plant CellsPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- 02 Handout 2Document13 pages02 Handout 2Janna AngelesNo ratings yet
- Cell Growth and ReproductionDocument5 pagesCell Growth and ReproductionIsrael EsmileNo ratings yet
- Week 1 cb1131 NotesDocument24 pagesWeek 1 cb1131 NotesTanisha ChowdharyNo ratings yet
- Biology CellsDocument7 pagesBiology Cellsperaltasabina70No ratings yet
- 1.2 Animal CellsDocument4 pages1.2 Animal CellsWongNo ratings yet
- CellStructureSE LandonsmithDocument5 pagesCellStructureSE LandonsmithLandon SmithNo ratings yet
- Biology Glossary TeamDocument19 pagesBiology Glossary TeamDanny MtzNo ratings yet
- Term 1 - Grade 8 Science CH 7 Cell Structure and FunctionDocument3 pagesTerm 1 - Grade 8 Science CH 7 Cell Structure and Functionprakashjoshi23aprilNo ratings yet
- Las 2 (Biology)Document12 pagesLas 2 (Biology)Renz GahumNo ratings yet
- Formatif F4Document33 pagesFormatif F4Mia nina Marn najmiNo ratings yet
- 7cups Certificate#5Document1 page7cups Certificate#5Paris LiangNo ratings yet
- UntitlemdDocument6 pagesUntitlemdParis LiangNo ratings yet
- 7cups Certificate#1Document1 page7cups Certificate#1Paris LiangNo ratings yet
- Dictionary Teaching GuideDocument8 pagesDictionary Teaching GuideParis LiangNo ratings yet
- Answers Quiz Diffusion, OsmosisDocument5 pagesAnswers Quiz Diffusion, OsmosisParis LiangNo ratings yet
- PreviewDocument4 pagesPreviewParis LiangNo ratings yet
- Holistic Approach To The Eq. Probl. FINAL VERSION1Document28 pagesHolistic Approach To The Eq. Probl. FINAL VERSION1lukakrusicNo ratings yet
- Body Lesson 1Document10 pagesBody Lesson 1Vadim BulbakNo ratings yet
- Science6 ST1 Q2Document2 pagesScience6 ST1 Q2Joseph PederisoNo ratings yet
- Excretion: Unit - Human Physiology Chapter 17Document8 pagesExcretion: Unit - Human Physiology Chapter 17edeceNo ratings yet
- Blood Cell Formation (Hematopoiesis)Document44 pagesBlood Cell Formation (Hematopoiesis)Ery BureniNo ratings yet
- Dr. Witra Irfan, SP.B (K) V - DVTDocument29 pagesDr. Witra Irfan, SP.B (K) V - DVTmuhammad azharanNo ratings yet
- Endometriosis & AdenomyosisDocument41 pagesEndometriosis & AdenomyosisAzim Syahmi Abd RazakNo ratings yet
- Total Laparoscopic Hysterectomy (TLH) : Patient Information Patient InformationDocument7 pagesTotal Laparoscopic Hysterectomy (TLH) : Patient Information Patient InformationMUKUL SAXENANo ratings yet
- Recommended Books and ResourcesDocument3 pagesRecommended Books and Resourcesharmanikumar95No ratings yet
- Bloody Easy PDFDocument164 pagesBloody Easy PDFJenny JeongNo ratings yet
- The Paris System For Reporting Urinary CytologyDocument66 pagesThe Paris System For Reporting Urinary CytologyRawa MuhsinNo ratings yet
- Puzzle Human Body OrgansDocument3 pagesPuzzle Human Body OrgansMaria Zennin ReballosNo ratings yet
- Iii. Hasil Dan PembahasanDocument10 pagesIii. Hasil Dan PembahasanHarditya FirdhausNo ratings yet
- PL001-A1 Advance Steel PDFDocument1 pagePL001-A1 Advance Steel PDFpaúl quicañoNo ratings yet
- LESSON EXEMPLAR IN SCIENCE 10. Co2Document15 pagesLESSON EXEMPLAR IN SCIENCE 10. Co2Hazel HazeNo ratings yet
- A Case Study of Splenic Hemangiosarcoma in A Bitch and Its Surgical ManagementDocument3 pagesA Case Study of Splenic Hemangiosarcoma in A Bitch and Its Surgical ManagementWira KusumaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Respiratory System Feghiu I., Tacu L. Lutan VDocument55 pagesPathophysiology of Respiratory System Feghiu I., Tacu L. Lutan VLunguVictoriaNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario 3 - Musco-Skeletal SystemDocument3 pagesCase Scenario 3 - Musco-Skeletal SystemWill KnightNo ratings yet
- Govt. Girls High School Pura Heeran, SialkotDocument7 pagesGovt. Girls High School Pura Heeran, SialkotFizza cooks foodNo ratings yet
- Medical-Surgical Nursing: An Integrated Approach, 2E: Nursing Care of The Client: Integumentary SystemDocument36 pagesMedical-Surgical Nursing: An Integrated Approach, 2E: Nursing Care of The Client: Integumentary Systemtanmai nooluNo ratings yet
- Fohoway BCM-finalDocument18 pagesFohoway BCM-finalAmitabh TripathiNo ratings yet
- Haemostasis: Case StudyDocument19 pagesHaemostasis: Case StudyTusabe FredNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document29 pagesChapter 4skywalkerNo ratings yet
- ANP2001 Female Reproductive System LAB QUIZ PDFDocument5 pagesANP2001 Female Reproductive System LAB QUIZ PDFJerilee SoCute WattsNo ratings yet
- RCSD or RCCD Peripheral WITHDocument2 pagesRCSD or RCCD Peripheral WITHEmma LiamNo ratings yet
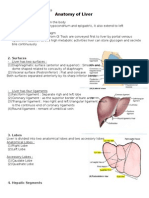
- Anatomy of LiverDocument2 pagesAnatomy of LiverelsafirdaaaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 11 Gross Morphology of The Chick Embryo Gallus Gallus PDFDocument3 pagesExercise 11 Gross Morphology of The Chick Embryo Gallus Gallus PDFMichaela FayeNo ratings yet
- Fish Physiology 1Document17 pagesFish Physiology 1Shyamol BoseNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE YR 5 (2021) HUMAN CIRCULATORY SYSTEM PART 1 - Google Forms ModulDocument6 pagesSCIENCE YR 5 (2021) HUMAN CIRCULATORY SYSTEM PART 1 - Google Forms ModulwidNo ratings yet