Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gen Bio Cell Types
Uploaded by
Raeson Amir ReyesOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gen Bio Cell Types
Uploaded by
Raeson Amir ReyesCopyright:
Available Formats
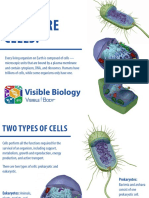
GEN BIO CELL TYPES
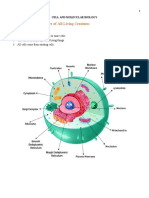
All living things are made from one or more Prokaryotic cells were here first and for
cells. A cell is the simplest unit of life and billions of years were the only form of life on
they are responsible for keeping an Earth. All prokaryotic organisms are
organism alive and functioning. unicellular.
Pro meaning “before”
Every cell is different but there are basic Karyon meaning “nucleus”
structures that are common to all cells. The single-celled organisms of the domains
Bacteria and Archaea
1) An outer boundary called the cell Eukaryotic cells appeared on earth long
membrane or plasma membrane that after prokaryotic cells but they are much
regulates the passage of materials into and more advanced. Eukaryotic organisms
out of the cell; unlike prokaryotic can be unicellular or
multicellular.
2) A gel-like substance making up cell’s Eu meaning “true”
internal environment called cytoplasm; and Karyon meaning “nucleus”
Animal cells, plant cells, fungi, and protists
3) The genetic material in the form of DNA that are eukaryotes
provides instructions to make proteins,
regulates activities, and enables cells to PROKARYOTES
reproduce.
Most ancient
Smaller in size
With simple internal structures
Enclosed by a plasma membrane encased
within a rigid cell wall.
This small size and simple structure allow these
organisms to reproduce very fast.
Plasma membrane - a semipermeable
Biologists recognize two main classifications membrane responsible for the
of cells: simple prokaryotes and the more prokaryote to allow waste products to
complex eukaryotes pass through while preventing the
diffusion of essential products to the
external environment.
Cell wall - responsible for maintaining its
shape, especially when cells are
exposed to high water influx.
Some prokaryotic cells have a capsule that Larger in size
acts as a protective layer made up of More complex structural components
polysaccharides lying outside the cell wall. All higher forms of organisms such as
fungi, plants, and protists.
Lacks a distinct nucleus but possesses an
irregular-shaped region called nucleoid Eukaryotic cells have their genetic
region. material (DNA) encased within a distinct
nucleus.
Nucleoid region- where it stores its
genetic material in the form of DNA. DNA form is linear.
Its cytoplasm is not organized into distinct These cells have many membrane-
interior compartments. bound interior compartments and their
organelles are neatly arranged.
Scattered throughout the cytoplasm are
small structures called ribosomes where The difference between the structure of
proteins are made. prokaryotes and eukaryotes is so great that
it is considered to be the most important
Some bacteria also possess a plasmid. distinction among groups of organisms.
Plasmid - an independent circular
DNA structure
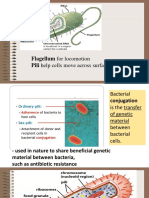
Some prokaryotes also possess
appendages like flagellum, fimbriae, and
conjugation pili.
Flagellum - a tail like appendage
which allow locomotion.
Fimbriae - an additional smaller and
bristle-like fiber that grow over the
prokaryotic cell’s surface.
o They help bacteria to attach
themselves to surfaces.
SIMILARITIES
Conjugation pili - tubular structures present
in the cell surface that function for cell-to-cell Both types of cells have cell membranes or
communication, as well as to pass DNA plasma membranes (outer covering of the
from one bacterium to the next. cell).
EUKARYOTES Both types of cells have ribosomes.
Both types of cells have DNA.
Both types of cells have a gel-like substance
making up the cell’s internal environment
known as the cytoplasm.
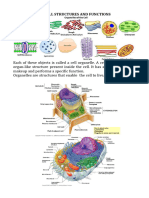
LARGE CENTRAL VACUOLE
A plant cell contains a large, singular
vacuole that is used for storage and
maintaining the shape of the cell. In
contrast, animal cells have many, smaller
vacuoles.
Most adult plant cells have one large
vacuole that takes up more than 30% of the
cell's volume. At certain times and
conditions, the vacuole takes up as much as
80% of the cell’s volume!
CHLOROPLAST
Unlike animal cells, plant cells can harness
the energy of the Sun, store it in the
chemical bonds of sugar and later use this
energy. The organelle which is responsible
for this is the chloroplast. Chloroplasts
PLANT CELLS contain chlorophyll; the green pigment that
Plant cell, the basic unit of all plants. Plant gives leaves their color and absorbs light
cells, like animal cells, are eukaryotic, meaning energy.
they have a membrane-bound nucleus and
organelles. Plant cells have a distinct set of PLASMODESMATA
features and characteristics. They are different
These pores or channels are found between
to the cells of organisms from other kingdoms of
plant cell walls and allow molecules and
life.
communication signals to pass between
The cells of plants are eukaryotic. A eukaryotic individual plant cells.
cell is any cell with a ‘true’ nucleus and
organelles. This immediately separates plant SIZE & SHAPE
cells from the cells of bacteria and archaea.
Plant cells similar in shape with most cells
Plant cells are similar to animal cells in that they being rectangular or cube-shaped.
are both eukaryotic cells and have similar
organelles. However, there are a number of ANIMAL CELLS
differences between plant and animal cells.
All animal cells are multicellular. They are
eukaryotic cells. Animal cells are surrounded by
CELL WALL a plasma membrane and it contains the nucleus
and organelles that are membrane-bound.
Unlike animal cells, plant cells have a cell Unlike the eukaryotic cells of plants and fungi,
wall surrounding the cell membrane. The animal cells do not have a cell wall. This feature
cell wall provides strength and support to was lost in the distant past by the single-celled
the plant. organisms that gave rise to the kingdom
Animalia.
Animal cells are of various sizes and have
irregular shapes. Most of the cells size range
between 1 and 100 micrometers and are visible
only with the microscope. Trillions of cells are
found in the human body. There are many
different types of cells, approximately 210
distinct cell types in the adult human body.
CENTRIOLES
Animal cells have centrioles.
This is distinctly found in the animal cell,
which has the ability to replicate or make
copies by itself. It is made up of 9
microtubule bundles and their primary
function is to assist in organizing the cell
division process.
LYSOSOMES
Lysosomes are round-shaped, membrane-
bound structures containing chemicals that can
break down materials in the cell.
CILIA OR FLAGELLA
These are locomotive projections found on
the surface of the cell. They allow the cell to
move like an oar or a whip.
Cilia look like little hairs with much shorter
length.
Flagella, on the other hand, look like a whip
or tail.
SIZE & SHAPE
Animal cells shape and sizes vary greatly
from irregular shapes to round shapes
Plant and animal cells are both eukaryotic cells,
so they have several features in common, such
as the presence of a cell membrane,
cytoplasm, DNA and cell organelles, like the
nucleus, mitochondria, ribosomes, Golgi
apparatus, and endoplasmic reticulum.
You might also like
- Three Main Components of a Cell: Plasma Membrane, Cytoplasm, and NucleusDocument2 pagesThree Main Components of a Cell: Plasma Membrane, Cytoplasm, and NucleusIrvin Jacob AquinoNo ratings yet
- General Biology: System Consists of TheDocument3 pagesGeneral Biology: System Consists of ThePhilipp MendozaNo ratings yet
- Premidterms NotesDocument4 pagesPremidterms NotesRenee Andrei Concepcion MozarNo ratings yet
- Mind MapDocument1 pageMind MapPramod Jaiswal81% (21)
- Revision-Map Chapter 5Document1 pageRevision-Map Chapter 5shinyy566No ratings yet
- BIOL107 - Different Cell TypesDocument4 pagesBIOL107 - Different Cell TypesJahsuah OrillanedaNo ratings yet
- Classification and evolution of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cellsDocument7 pagesClassification and evolution of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cellsjodeoiraluis josonNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology TermsDocument3 pagesCell Biology TermsHelen VicenteNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure: Abejay, Vanessa D. Balsomo, Princess Bangalan, JhayDocument64 pagesCell Structure: Abejay, Vanessa D. Balsomo, Princess Bangalan, JhayVanessaDulayAbejayNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and OrganizationDocument14 pagesCell Structure and Organizationwafa eliasNo ratings yet
- Acp1 ActDocument6 pagesAcp1 ActAldrin VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- VisibleBody Cell ComparisonDocument10 pagesVisibleBody Cell ComparisonAnjarika TripathyNo ratings yet
- Cell and Cell OrganellesDocument53 pagesCell and Cell OrganellesShiffa SaheedNo ratings yet
- DR. WZCA SEC 1 SCIENCE Revision Notes For Chapter 6Document14 pagesDR. WZCA SEC 1 SCIENCE Revision Notes For Chapter 6Cole- Min Khant KyawNo ratings yet
- Bio Cells ReviewerDocument4 pagesBio Cells ReviewerKimberly LuistroNo ratings yet
- Basic Cell Types, Cell Structure and Function,& Cell ModificationsDocument28 pagesBasic Cell Types, Cell Structure and Function,& Cell ModificationsMary Ann Gonzales Abeñon100% (1)
- Prokaryotes: "Good or True Nuclei."Document3 pagesProkaryotes: "Good or True Nuclei."Anime KpopNo ratings yet
- Biology 2Document3 pagesBiology 2Karriel AguilarNo ratings yet
- Scope of MicrobiologyDocument4 pagesScope of MicrobiologyFvckin NonsenseNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and TransportDocument4 pagesCell Structure and TransportAena Valerie CaalimNo ratings yet
- What Is A Cell - Learn Science at ScitableDocument5 pagesWhat Is A Cell - Learn Science at ScitableChristopher BrownNo ratings yet
- Cell and Molecular BiologyDocument18 pagesCell and Molecular BiologyHizzei Caballero100% (1)
- Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells: Distinguishing Their FeaturesDocument14 pagesProkaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells: Distinguishing Their FeaturesDaniella Pasilbas SabacNo ratings yet
- The Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument10 pagesThe Cell Structure and TaxonomyKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- Comparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument6 pagesComparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsRishabh JainNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio (Definitions) - Cell StructureDocument3 pagesGen Bio (Definitions) - Cell StructureMary Vhenn SamonteNo ratings yet
- Biology 1: Cell Theory Cell Structure and FunctionsDocument4 pagesBiology 1: Cell Theory Cell Structure and FunctionsEmilio Villafria IVNo ratings yet
- Cell (Biology) - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument6 pagesCell (Biology) - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediaapi-3714451100% (2)
- General Biology ReviewerDocument4 pagesGeneral Biology ReviewerJes NapiñasNo ratings yet
- LESSON 2.3 Basic Cell TypesDocument6 pagesLESSON 2.3 Basic Cell TypessandraNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Functions PDFDocument92 pagesCell Structure and Functions PDFAishaizl100% (1)
- Biology Chapter 1 NotesDocument6 pagesBiology Chapter 1 Notesmohan.shenoy52No ratings yet
- Mrs. Anamika Sahu GulbakeDocument40 pagesMrs. Anamika Sahu GulbakeAnamika SahuNo ratings yet
- Acfrogahwtgjhymcdbhqd9juy0ihb5dgzqyobwgygm44pyrxkeh Dixuo Odyslryl Jpqgjhd4udt63zm6ot2mgudp GWKKKDFLLJD 4nxfp5i Pvcee 9pyuxltmliuwhn9qmanxfhy82jt1l4Document8 pagesAcfrogahwtgjhymcdbhqd9juy0ihb5dgzqyobwgygm44pyrxkeh Dixuo Odyslryl Jpqgjhd4udt63zm6ot2mgudp GWKKKDFLLJD 4nxfp5i Pvcee 9pyuxltmliuwhn9qmanxfhy82jt1l4s20003No ratings yet
- Unit 1 - 3Document32 pagesUnit 1 - 3Sunita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Notion 2 - Organization - of - The - OrganismDocument7 pagesNotion 2 - Organization - of - The - OrganismFadi AltananyNo ratings yet
- Act. 3 Cytology PeraltaDocument18 pagesAct. 3 Cytology PeraltaCogie PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Cell AnalogyDocument11 pagesCell AnalogyMikaella Jayne CatanaoanNo ratings yet
- Module 2 CytogeneticsDocument17 pagesModule 2 CytogeneticsFrances Riane SimoyNo ratings yet
- Spgbio NotesDocument22 pagesSpgbio NotesKaycee HeokkaidoNo ratings yet
- General BiologyDocument14 pagesGeneral BiologyMason DeidriNo ratings yet
- Biological Chemistry (Midterms)Document3 pagesBiological Chemistry (Midterms)ale.cristianNo ratings yet
- A Cell Is The Smallest Unit of A Living ThingDocument4 pagesA Cell Is The Smallest Unit of A Living ThingJONAVIE DEMALATANo ratings yet
- Group 3 Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells HandoutsDocument4 pagesGroup 3 Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells HandoutsClaire Angelie Ruaya100% (1)
- Cell Biology Assignment Gr. 3Document26 pagesCell Biology Assignment Gr. 3Lamin N CeesayNo ratings yet
- CelsszDocument6 pagesCelsszHITANSH NIJHAWANNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellDocument10 pagesChapter 2 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellKylie VillafloresNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 2Document12 pagesGen Bio 2Ma.Dulce ManalastasNo ratings yet
- Flagellum For Locomotion Pili Help Cells Move Across SurfacesDocument18 pagesFlagellum For Locomotion Pili Help Cells Move Across SurfacesEvangeline WongNo ratings yet
- CELulas 2Document21 pagesCELulas 2lizetteNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology BasicsDocument17 pagesCell Biology BasicsHizzei Caballero100% (3)
- AP Biology Unit 2 Student NotesDocument21 pagesAP Biology Unit 2 Student NotesjanaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology NotesDocument15 pagesIGCSE Biology NotesMai YoussifNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Cell Structure and Membrane Transport NotesDocument13 pagesAP Biology Cell Structure and Membrane Transport NotesJ15No ratings yet
- Prokaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsDocument5 pagesProkaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsAngelica FloraNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures and Their FunctionsDocument4 pagesCell Structures and Their FunctionsRaeson Amir ReyesNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- The Animal Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandThe Animal Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Gen BioDocument4 pagesGen BioRaeson Amir ReyesNo ratings yet
- 21st Century LiteratureDocument1 page21st Century LiteratureRaeson Amir ReyesNo ratings yet
- Research ShemsDocument4 pagesResearch ShemsRaeson Amir ReyesNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures and Their FunctionsDocument4 pagesCell Structures and Their FunctionsRaeson Amir ReyesNo ratings yet
- Auc Curriculum Overview Course Placemats - November 2023 - v3Document6 pagesAuc Curriculum Overview Course Placemats - November 2023 - v3Dora CobuzNo ratings yet
- Asta Analytical MethodsDocument4 pagesAsta Analytical Methodsravivarmahyd8173No ratings yet
- The Growth of Tomato Seedlings Inoculated With Co-Cultivated Piriformospora Indica and Bacillus PumilusDocument8 pagesThe Growth of Tomato Seedlings Inoculated With Co-Cultivated Piriformospora Indica and Bacillus PumilusNayo PalomequeNo ratings yet
- Old Man and The Sea - SummaryDocument3 pagesOld Man and The Sea - SummaryPearNo ratings yet
- Profil Hematologi Dan Gambaran Morfologi Darah Sapi Bali (Bos Sundaicus) Yang Dipelihara Di Tempat Pembuangan Akhir Alak Kota KupangDocument13 pagesProfil Hematologi Dan Gambaran Morfologi Darah Sapi Bali (Bos Sundaicus) Yang Dipelihara Di Tempat Pembuangan Akhir Alak Kota KupangKeju Mozarella ChizzuNo ratings yet
- 1/ Giới Thiệu: 1.1 Thuyết tiến hóaDocument36 pages1/ Giới Thiệu: 1.1 Thuyết tiến hóaNgô Thị Thắng LợiNo ratings yet
- Losing Weight With HunaDocument11 pagesLosing Weight With Hunashila353No ratings yet
- Introduction To Statistics and Its ApplicationsDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Statistics and Its ApplicationsVarshney NitinNo ratings yet
- Reading Exercises 0627Document22 pagesReading Exercises 0627lydianDNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Family Therapy History Theory and Practice 6th EditionDocument24 pagesTest Bank For Family Therapy History Theory and Practice 6th EditionKaraKentygbc100% (51)
- Fungsi Protein - Andri Josua SianiparDocument30 pagesFungsi Protein - Andri Josua SianiparAndri Josua SianiparNo ratings yet
- Seed Germination Experiment Revised Final Copy 2Document8 pagesSeed Germination Experiment Revised Final Copy 2sally ngNo ratings yet
- African History Notes BookletsDocument86 pagesAfrican History Notes BookletsJus DaisyNo ratings yet
- Tissues Practical ExamDocument95 pagesTissues Practical ExamMarch AthenaNo ratings yet
- Selina Concise Biology Solutions Class 6 Chapter 3 Cell - The Structure and FunctionsDocument10 pagesSelina Concise Biology Solutions Class 6 Chapter 3 Cell - The Structure and FunctionsFLANTAMOCKNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 Mitosis and Meiosis Pre LabDocument1 pageLab 3 Mitosis and Meiosis Pre LabS. Spencer0% (2)
- 3C Development of Organisms PDFDocument74 pages3C Development of Organisms PDFBryan YeohNo ratings yet
- 3is Q2 MODULE 2.1Document10 pages3is Q2 MODULE 2.1dfgerbrcNo ratings yet
- Total RNA Isolation and CDNA Synthesis From Bixa Orellana BarkDocument5 pagesTotal RNA Isolation and CDNA Synthesis From Bixa Orellana BarkIzzatizyanHamdanNo ratings yet
- Literature Review UalDocument7 pagesLiterature Review Ualfeiaozukg100% (1)
- Aquaculture: Mohamed M. Refaey, Dapeng Li, Xing Tian, Kommaly Onxayvieng, Rong TangDocument8 pagesAquaculture: Mohamed M. Refaey, Dapeng Li, Xing Tian, Kommaly Onxayvieng, Rong Tangbrucella06No ratings yet
- Format Kisi-Kisi Penilaian Kls IX Semester GenapDocument20 pagesFormat Kisi-Kisi Penilaian Kls IX Semester GenapJam'a AntoniusNo ratings yet
- Suggestive Questions of Icse 2023 BiologyDocument5 pagesSuggestive Questions of Icse 2023 BiologySwethanaNo ratings yet
- Biography of Dr. Salim AliDocument5 pagesBiography of Dr. Salim AliSalimNo ratings yet
- 04nov201802113802 Amanpreet Kaur 118-121Document4 pages04nov201802113802 Amanpreet Kaur 118-121Cecilla Rosa PatiamNo ratings yet
- Agricultural MicrobiologyDocument3 pagesAgricultural MicrobiologyAshu SinghNo ratings yet
- NemoDocument333 pagesNemoash krisNo ratings yet
- Ibbc Form 2Document4 pagesIbbc Form 2For StudyNo ratings yet
- Isolate Bacterial Colonies Streak Plate MethodDocument5 pagesIsolate Bacterial Colonies Streak Plate MethodBryant Ken JavierNo ratings yet
- Cellular Structure and Function: Main Idea DetailsDocument3 pagesCellular Structure and Function: Main Idea Detailsfatema buhussainNo ratings yet