Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tudy Buddy: Ias 8 Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and Errors
Uploaded by
Abdullah Al Amin MubinOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tudy Buddy: Ias 8 Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and Errors
Uploaded by
Abdullah Al Amin MubinCopyright:
Available Formats
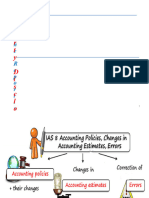
IAS 8 ACCOUNTING POLICIES,
CHANGES IN ACCOUNTING ESTIMATES AND ERRORS
DEFINITION
The objective of this Standard is to prescribe the criteria for selecting and changing accounting policies, the accounting treatment
and disclosure of changes in accounting policies, accounting estimates and corrections of errors.
ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Accounting Policies are the specific principles, bases, conventions, rules and practices applied by an entity in preparing and
presenting financial statements.
dy
• Examples of accounting policies:
• Alternative presentation of government grant (IAS 20)
• FIFO or Weighted average method of inventory valuation (IAS 2)
ud
• Fair value model of cost model for investment properties (IAS 40)
Changes in accounting policy will be very rare and should be made only if
B
COMPULSORY CHANGE (The change is required by an
IFRS), or
u dy VOLUNTARY CHANGE (The change will result in a more
appropriate presentation of events or transactions in the
financial statements of the entity, providing more reliable
St
and relevant information.
N.B. Revaluation of non-current assets should not be treated as changes in accounting policy
(I.e. no retrospective effect for revaluation)
FR
ACCOUNTING TREATMENT FOR CHANGES IN ACCOUNTING POLICIES
&
• A change in accounting policy must be applied retrospectively
• Retrospective application means that the new accounting policy is applied to transactions and events as if it had always been
FA
in use. In other words, at the earliest date such transactions or events occurred, the policy is applied from that date.
• This involves restating opening balances of current year and comparative previous year
A
C
C
A
P-6 Find us at Facebook - ACCA FA & FR Study Buddy
ACCOUNTING ESTIMATES
Estimates involve judgments based on the latest available, reliable information and are applied in determining the useful lives of
property, plant and equipment, provisions, fair values of financial assets and liabilities and actuarial assumptions relating to
defined benefit pension schemes.
Management applies judgement based on information available at the time
Examples of accounting estimates:
• Useful life or residual value of a non-current asset (IAS 16)
• Provision made for future loss or expenses (IAS 37)
A change in accounting estimate must be applied prospectively
dy
ud
ACCOUNTING POLICIES VS ACCOUNTING ESTIMATES
B
ACCOUNTING POLICIES ACCOUNTING ESTIMATES
1. It is principles/Measurement basis.
2. Retrospective adjustments
3. FIFO or Weighted average method of inventory valuation
dy
Amounts/Patterns
Prospective adjustments
u
Estimating the recoverability of receivables at the year end, i.e. bad
debts, Useful Life of Non-Current assets
St
ERRORS:
FR
Errors discovered during a current period which relate to a prior period may arise through:
• Mathematical mistakes
• Mistakes in the application of accounting policies
&
• Misinterpretation of facts
• Omissions
• Fraud
FA
• Prior period errors correct retrospectively.
IS THE PRIOR PERIOD IS MATERIAL?
A
YES MATERIAL NOT MATERIAL
C
Adjust retrospectively Not Mandatory to adjust retrospectively
C
A
P-7 Find us at Facebook - ACCA FA & FR Study Buddy
You might also like
- Access To Finance For Women Entrepreneurs in South Africa (November 2006)Document98 pagesAccess To Finance For Women Entrepreneurs in South Africa (November 2006)IFC SustainabilityNo ratings yet
- Manpower, Consultant and HR Companies of UAEDocument5 pagesManpower, Consultant and HR Companies of UAENaeem Uddin95% (20)
- Wordly Wise 7 Lesson 1Document1 pageWordly Wise 7 Lesson 1imsungbaek100% (1)
- Accounting Policies and ErrorsDocument32 pagesAccounting Policies and ErrorsTia Li100% (1)
- Consultancy Paper FinalDocument20 pagesConsultancy Paper FinalRosemarie McGuireNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 11 - Changes in Accounting Policy, Prior Period ErrorsDocument24 pagesCHAPTER 11 - Changes in Accounting Policy, Prior Period ErrorsChristian GatchalianNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Strategic Planning Matrix (QSPM) For AirasiaDocument4 pagesQuantitative Strategic Planning Matrix (QSPM) For AirasiamaliklduNo ratings yet
- PAS8 Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and ErrorsDocument8 pagesPAS8 Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and ErrorsFaith BautistaNo ratings yet
- Chapters 11 - Accounting Policies, Estimate and ErrorsDocument23 pagesChapters 11 - Accounting Policies, Estimate and ErrorsMarriel Fate CullanoNo ratings yet
- NABARD Automated Milk Collection Project PDFDocument13 pagesNABARD Automated Milk Collection Project PDFGrowel Agrovet Private Limited.100% (2)
- Chapter 7 - Gripping IFRS ICAP 2008 (Solution of Graded Questions)Document49 pagesChapter 7 - Gripping IFRS ICAP 2008 (Solution of Graded Questions)Falah Ud Din Sheryar100% (2)
- Ias 8 PDFDocument21 pagesIas 8 PDFJoedy Mae MangampoNo ratings yet
- Changing For The Better?: Accounting ChangesDocument8 pagesChanging For The Better?: Accounting ChangesJewel TomolinNo ratings yet
- Other Standards: 1 IAS 8 Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates & ErrorsDocument7 pagesOther Standards: 1 IAS 8 Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates & Errorshafeez azizNo ratings yet
- ACC2001 Lecture 5Document50 pagesACC2001 Lecture 5michael krueseiNo ratings yet
- Module 6Document12 pagesModule 6Cha Eun WooNo ratings yet
- PAS 8 - Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and ErrorsDocument37 pagesPAS 8 - Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and ErrorsPeralta Renn JethroNo ratings yet
- Cfas - Pas 8Document3 pagesCfas - Pas 8Patawaran, Janelle S.No ratings yet
- PolicyDocument52 pagesPolicyHagere EthiopiaNo ratings yet
- Module 6Document12 pagesModule 6Jomar Ramos QuinosNo ratings yet
- Pas 8 SuperfinalDocument16 pagesPas 8 SuperfinalmattNo ratings yet
- CFAS FinalsDocument3 pagesCFAS FinalsShana VillamorNo ratings yet
- Accounting Policies, Estimate and ErrorsDocument17 pagesAccounting Policies, Estimate and ErrorsMarklein DumangengNo ratings yet
- CH 12 - Accounting Policies, Estimates and ErrorsDocument3 pagesCH 12 - Accounting Policies, Estimates and ErrorsMarrian Kaye Cerbas PioratoNo ratings yet
- PAS 8 - Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and ErrorsDocument11 pagesPAS 8 - Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and ErrorsKrizzia DizonNo ratings yet
- Pas 8 Chapter 11Document2 pagesPas 8 Chapter 11Minie KimNo ratings yet
- Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and ErrorsDocument36 pagesAccounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and ErrorsHanh CaoNo ratings yet
- 03 Reporting Financial PerformanceDocument96 pages03 Reporting Financial PerformanceHimaddry SanyalNo ratings yet
- E-Portfolio: PAS 8 - Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and ErrorsDocument2 pagesE-Portfolio: PAS 8 - Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and ErrorsKaye NaranjoNo ratings yet
- University of Perpetual Help System Dalta: Calamba Campus, Brgy. Paciano RizalDocument3 pagesUniversity of Perpetual Help System Dalta: Calamba Campus, Brgy. Paciano RizalJeanette LampitocNo ratings yet
- Change in Accounting Estimates and Accounting Policies PDFDocument8 pagesChange in Accounting Estimates and Accounting Policies PDFMika MolinaNo ratings yet
- APC 403 PFRS For SEs (Section 5)Document4 pagesAPC 403 PFRS For SEs (Section 5)AnnSareineMamadesNo ratings yet
- Pas 8 Cfas PDFDocument6 pagesPas 8 Cfas PDFAndreaaAAaa TagleNo ratings yet
- CF Module 8 - Acctg Pol. Estimate and Errors 8Document16 pagesCF Module 8 - Acctg Pol. Estimate and Errors 8Jomic QuimsonNo ratings yet
- Change in Accounting PolicyDocument5 pagesChange in Accounting PolicySandia EspejoNo ratings yet
- CFAS Millan CHAPTERS 11-13Document8 pagesCFAS Millan CHAPTERS 11-13Maria Mikaela ReyesNo ratings yet
- AS - 1 - Disclosure - of - Accounting - Policies CH-4Document7 pagesAS - 1 - Disclosure - of - Accounting - Policies CH-4lucifersdevil68No ratings yet
- IAS 8: Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and ErrorsDocument6 pagesIAS 8: Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and ErrorsmuhammadTzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11: Accounting Policies, Estimate and Errors Pas 8: The Procedure Is Not To Correct Past DepreciationDocument2 pagesChapter 11: Accounting Policies, Estimate and Errors Pas 8: The Procedure Is Not To Correct Past DepreciationJan DecemberNo ratings yet
- Topic 8 - IAS 8 (Eng) - SVDocument40 pagesTopic 8 - IAS 8 (Eng) - SVHONG NGUYEN THI KIMNo ratings yet
- Ind As On Measurement Based On Accounting PoliciesDocument38 pagesInd As On Measurement Based On Accounting Policiespulkitddude_24114888No ratings yet
- IND AS 8 Raw PDFDocument41 pagesIND AS 8 Raw PDFrajesh reddyNo ratings yet
- Workbook 6 (July 2022)Document60 pagesWorkbook 6 (July 2022)Sansaar KandhroNo ratings yet
- 11 Ias 8Document5 pages11 Ias 8Irtiza AbbasNo ratings yet
- IAS 8 - Accounting Policies Estimates and ErrorsDocument12 pagesIAS 8 - Accounting Policies Estimates and ErrorsThuỷ TiênnNo ratings yet
- Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and ErrorsDocument32 pagesAccounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and ErrorsAmrita TamangNo ratings yet
- IFA II Chap - 5 2016Document15 pagesIFA II Chap - 5 2016teddymaru7No ratings yet
- Topic 8Document10 pagesTopic 8huongkhue9aNo ratings yet
- IAS 8 - Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and ErrorsDocument8 pagesIAS 8 - Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and ErrorsGodfrey MakurumureNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 PAS 8 Notes (EDITED)Document3 pagesChapter 5 PAS 8 Notes (EDITED)Chara Joy Cortes RomagaNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Framework - PAS 8Document15 pagesConceptual Framework - PAS 8Dewdrop Mae RafananNo ratings yet
- (Self-Study) Topic 8Document10 pages(Self-Study) Topic 8voanh1346No ratings yet
- Unit 1 - IAS 8: Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and Errors Class Presentation - Daniel KamothoDocument41 pagesUnit 1 - IAS 8: Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and Errors Class Presentation - Daniel KamothoJansher Khan DawarNo ratings yet
- Cfas Lesson 5 (Activity)Document4 pagesCfas Lesson 5 (Activity)Michelle CabezoNo ratings yet
- Unit Number/ Heading Learning OutcomesDocument10 pagesUnit Number/ Heading Learning OutcomesariesNo ratings yet
- PPSAS 3 - Accounting Policies Changes in Accounting EstimatesDocument24 pagesPPSAS 3 - Accounting Policies Changes in Accounting EstimatesLeonardo Don Alis CordovaNo ratings yet
- 4 MFRS108Document34 pages4 MFRS108Dont RushNo ratings yet
- NAS 8 Accounting Policy V1Document10 pagesNAS 8 Accounting Policy V1binuNo ratings yet
- Accounting Changes and ErrorsDocument31 pagesAccounting Changes and Errorslascona.christinerheaNo ratings yet
- IAS 8zzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzDocument2 pagesIAS 8zzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzWeiling TanNo ratings yet
- AS 1 Disclosure of Accounting PoliciesDocument6 pagesAS 1 Disclosure of Accounting PoliciesAnanya SharmaNo ratings yet
- 10accounting ChangesDocument31 pages10accounting ChangesLily DaniaNo ratings yet
- D Ias 8Document21 pagesD Ias 8Daniel MNo ratings yet
- IAS-8 Accounting Policies, Change in Accounting Estimates and Errors ObjectiveDocument6 pagesIAS-8 Accounting Policies, Change in Accounting Estimates and Errors ObjectiveAbdullah Al Amin MubinNo ratings yet
- Engagement Essentials: Preparation, Compilation, and Review of Financial StatementsFrom EverandEngagement Essentials: Preparation, Compilation, and Review of Financial StatementsNo ratings yet
- Tudy Buddy: ObjectiveDocument4 pagesTudy Buddy: ObjectiveAbdullah Al Amin MubinNo ratings yet
- Tudy Buddy: Ias 36 - Impairment of AssetsDocument2 pagesTudy Buddy: Ias 36 - Impairment of AssetsAbdullah Al Amin MubinNo ratings yet
- Tudy Buddy: Ifrs 15 - Revenue From Contracts With CustomersDocument2 pagesTudy Buddy: Ifrs 15 - Revenue From Contracts With CustomersAbdullah Al Amin MubinNo ratings yet
- Ias 36 - Impairment of Assets ObjectiveDocument9 pagesIas 36 - Impairment of Assets ObjectiveAbdullah Al Amin MubinNo ratings yet
- So Assets Should Be Shown in The SOFP As 70,000$Document3 pagesSo Assets Should Be Shown in The SOFP As 70,000$Abdullah Al Amin MubinNo ratings yet
- IAS-8 Accounting Policies, Change in Accounting Estimates and Errors ObjectiveDocument6 pagesIAS-8 Accounting Policies, Change in Accounting Estimates and Errors ObjectiveAbdullah Al Amin MubinNo ratings yet
- Ias 2Document4 pagesIas 2Abdullah Al Amin MubinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - 7Document82 pagesLecture 6 - 7Abdullah Al Amin MubinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document44 pagesLecture 8Abdullah Al Amin MubinNo ratings yet
- ACC3201Document6 pagesACC3201natlyh100% (1)
- Bs. Accountancy (Aklan State University) Bs. Accountancy (Aklan State University)Document9 pagesBs. Accountancy (Aklan State University) Bs. Accountancy (Aklan State University)JANISCHAJEAN RECTONo ratings yet
- Income and Substitution EffectsDocument1 pageIncome and Substitution EffectspenelopegerhardNo ratings yet
- Letter of Intent For Financial AssistanceDocument9 pagesLetter of Intent For Financial AssistanceecsanjuanNo ratings yet
- EU Compendium of Spatial PlanningDocument176 pagesEU Compendium of Spatial PlanningVincent NadinNo ratings yet
- E. Sharath Babu, Founder & CEO, Food King: Entrepreneurs Non-Tech EntrepreneursDocument3 pagesE. Sharath Babu, Founder & CEO, Food King: Entrepreneurs Non-Tech Entrepreneurssundar666No ratings yet
- Punjab Spatial Planning StrategyDocument12 pagesPunjab Spatial Planning Strategybaloch47No ratings yet
- Toolkit Materiality Assessment 2022 - FINALDocument36 pagesToolkit Materiality Assessment 2022 - FINALtrader123No ratings yet
- MBM 207 QB - DistanceDocument2 pagesMBM 207 QB - Distancemunish2030No ratings yet
- Hindalco Annual Report FY2007Document135 pagesHindalco Annual Report FY2007hennadNo ratings yet
- 1.pmsby - Scheme in Brief PDFDocument1 page1.pmsby - Scheme in Brief PDFRanjit RjtNo ratings yet
- LIST OF YGC and AYALA COMPANIESDocument3 pagesLIST OF YGC and AYALA COMPANIESJibber JabberNo ratings yet
- Tonota Lephaneng Ward ReportDocument11 pagesTonota Lephaneng Ward Reportmokane.mokane1No ratings yet
- Name: Grade: SubjectDocument5 pagesName: Grade: SubjectArkar.myanmar 2018100% (1)
- Criticisms of The Ifrs Conceptual FrameworkDocument9 pagesCriticisms of The Ifrs Conceptual FrameworkTHOMAS ANSAHNo ratings yet
- Lead - Talent Management & ODDocument2 pagesLead - Talent Management & ODanshatNo ratings yet
- Econ PBLDocument14 pagesEcon PBLapi-262407343No ratings yet
- Retirement QuestionDocument2 pagesRetirement QuestionshubhamsundraniNo ratings yet
- Bibliography Financial CrisisDocument41 pagesBibliography Financial CrisisaflagsonNo ratings yet
- Equinox Is A Boutique Investment Bank and ConsultingDocument1 pageEquinox Is A Boutique Investment Bank and ConsultingRoderick SumalloNo ratings yet
- POL 346 Paper - Ghana and IMFDocument19 pagesPOL 346 Paper - Ghana and IMFGian-Paolo MendozaNo ratings yet
- Operations Management Essay Operations Management EssayDocument4 pagesOperations Management Essay Operations Management EssayShirley Soriano-QuintoNo ratings yet
- Dea Aul - QuizDocument5 pagesDea Aul - QuizDea Aulia AmanahNo ratings yet
- Technological Developments of Metal Casting TechnologyDocument32 pagesTechnological Developments of Metal Casting TechnologyEr Widodo0% (1)