Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acknowledgement: Mohammed For Her Invaluable Support, Encouragement, Supervision and Useful
Uploaded by
SHAIK AHMED JAWADOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Acknowledgement: Mohammed For Her Invaluable Support, Encouragement, Supervision and Useful
Uploaded by
SHAIK AHMED JAWADCopyright:
Available Formats
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
I am grateful for the cooperation and constant encouragement from my honourable Head
of Department Dr. Syed Abu Sayeed Mohammed. His regular suggestion made my
work easy and proficient.
It is my privilege and pleasure to express our profound sense of respect, gratitude and
indebtedness to Dr. Muzammil Ahamed , Principal of HKBK college of Engineering,
to provide all the required resources for the successful completion of my seminar.
I would like to express profound gratitude to my guide Dr. Syed Abu Sayeed
Mohammed for her invaluable support, encouragement, supervision and useful
suggestions throughout this seminar work. Her moral support and guidance enabled me
to complete my work successfully.
I would also like to express my thanks to all staff members and friends for all the help
and co-ordination extended in bringing out this seminar successfully on time.
I will be failing in duty if I do not acknowledge with grateful thanks to the authors of the
references and other literatures referred to in this seminar.
Dept of Civil Engineering | H.K.B.K CE, 2017-18
INDEX
CHAPTER TITLE PAGE
NO NO
1 1.1 INTRODUCTION 01
1.2 DEFINITION? 01
1.3 WHAT IS SOIL LIQUEACTION WHY DOES IT
02-03
OCCUR?
2 LITERATURE REVIEW 04-06
2.1 EFFECTS OF FINE CONTENT 04
2.2 EFFECTS OF NON PLASTIC FINE CONTENT 04
2.3 EFFECTS OF PLASTIC FINE CONTENT 05
2.4 PLASTICITY BASED LIQUEFACTION
05
CRITERIA
2.5 EFFECTS ON PORE PRESSURE
06
GENERATION
2.6 RATE AND MAGNITUDE OF PORE
06
PRESSURE GENERATION
3 3.1 SOIL PROPERTIES DURING LIQUEFACTION 07-08
3.2 PORE WATER PRESSURE DURING
08
LIQUEFACTION
3.3 OCCURRENCE OF SOIL LIQUEFACTION 09
3.4 EARTHQUAKE LIQUEFACTION 09-10
3.5 TYPES OF FAILURE 10
3.6 FACTORS AFFCETING SOIL LIQUEFACTION 11
3.7 CONSEQUENCES OF LIQUEFACTION 11
4 SAND PHENOMENONS 12-14
4.1 QUICK SAND PHENOMENON 12-13
4.2 QUICK CLAY PHENOMENON 14
5 5.1 SOIL LIQUEFACTION TRAGEDIES 15-17
5.2 EFFECTS 18-19
5.3 MITIGATION METHODS 20-22
6 ANALYSIS OF LIQUEFACTION PRONE AREAS 23-24
7 7.1 SUMMARY 25
7.2 CONCLUSION 25
8 REFERENCES 26
Dept of Civil Engineering | H.K.B.K CE, 2017-18
ABSTRACT
“Liquefaction” A major cause of structural damage during earthquake. As one the most
hazardous event is discussed, certain analysis for soil are to be performed to understand
the behaviour of soil and its stability towards such actions on different sites and
determining the liquefaction susceptibility. On the basis of different parameters and
liquefaction susceptibility on which soil strength is considered certain Ground
Improvement Techniques (GIT) are used for Chandigarh, Kolkata, Orissa, Lucknow,
Gandhinagar, Vijaywada, Delhi, Vishakhapatnam, Pushkar, Bhuj and Kutch
accordingly. In this paper the designing of counter measures for remediation of
liquefaction with precautionary measures is being done. The objective is to take one of
the Ground Improvement Techniques accordingly to overcome the chances of
liquefaction for the each particular type of soil.
The important constraints that are to be self-addressed is Economical, sustainable and
to be socially acceptable.
Keywords—Liquefaction, Susceptibility, Ground Improvement Technique,
Remediation.
Dept of Civil Engineering | H.K.B.K CE, 2017-18
You might also like
- Kisssoft Tut 006 E Shaft EditorDocument11 pagesKisssoft Tut 006 E Shaft EditorBeytullah AcarNo ratings yet
- Corrossion Control of Underwater PilesDocument23 pagesCorrossion Control of Underwater Pilesvaradha s nairNo ratings yet
- FMEA - Diesel GeneratorDocument42 pagesFMEA - Diesel GeneratorAhmed67% (3)
- ING Agile TransformationDocument9 pagesING Agile TransformationJohn AraqueNo ratings yet
- GE July 1976 Foundations and Earthworks For Cylindrical Steel Storage TanksDocument113 pagesGE July 1976 Foundations and Earthworks For Cylindrical Steel Storage Tanksselvakumar100% (1)
- Prescriptive Measures For Man-Made Slopes and Retaining WallsDocument80 pagesPrescriptive Measures For Man-Made Slopes and Retaining WallsCostel Constantin MarmotaNo ratings yet
- DLL Science 6 q2 W5gtuDocument4 pagesDLL Science 6 q2 W5gtuGeoffrey Tolentino-Unida67% (6)
- Complete Final Year Project BE CIVILDocument75 pagesComplete Final Year Project BE CIVILSHAIK AHMED JAWADNo ratings yet
- GEO Publication No. 1 - 2009Document78 pagesGEO Publication No. 1 - 2009Gunnar KumarNo ratings yet
- Project Bach No 22Document55 pagesProject Bach No 22AbijithNo ratings yet
- Full ThesisDocument171 pagesFull ThesisShifat Hossain KhanNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Self Compacting ConcreteDocument89 pagesProject Report On Self Compacting ConcretePirpasha Ujede0% (1)
- Hydrological Procedure No 27 (HP 27) PDFDocument64 pagesHydrological Procedure No 27 (HP 27) PDFAgungNurFauziNo ratings yet
- A Thesis Submitted in The Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements For The Degree of Bachelor of TechnologyDocument53 pagesA Thesis Submitted in The Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements For The Degree of Bachelor of TechnologyMagesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Batch 19 FinalDocument71 pagesBatch 19 FinalCivil EngineersNo ratings yet
- FCE 411 - Geotechnical Engineering II 2019-2020-1Document58 pagesFCE 411 - Geotechnical Engineering II 2019-2020-1Dennis OG100% (1)
- Geopolymaer Concrete Project Report From Global Academy of Technology (Published On 27/05/2018) As Per The VTU GuidelinesDocument59 pagesGeopolymaer Concrete Project Report From Global Academy of Technology (Published On 27/05/2018) As Per The VTU GuidelinesVijay kumar100% (1)
- Marble Waste Bonafide - HariDocument6 pagesMarble Waste Bonafide - HariHarihara PriyadharshanNo ratings yet
- Discourse Analysis in The ESL ClassroomDocument18 pagesDiscourse Analysis in The ESL ClassroomAli Alfaridzi100% (2)
- CrystallizationDocument18 pagesCrystallizationsravankumar6686% (7)
- dpr1 PDFDocument189 pagesdpr1 PDFShashank PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Jurnal CementDocument150 pagesJurnal Cementg-46005995No ratings yet
- Specs-Div 07Document33 pagesSpecs-Div 07Osama KheadryNo ratings yet
- Relation Between Permability Settlement of SoilDocument58 pagesRelation Between Permability Settlement of SoilAshok DasariNo ratings yet
- ThesisRahmanM M20120701040Document137 pagesThesisRahmanM M20120701040Mohammed KhennoufNo ratings yet
- 1822 B.E Mech Batchno 33Document52 pages1822 B.E Mech Batchno 33Sentot SubrotoNo ratings yet
- Project Report 2Document12 pagesProject Report 2Rajnish RanjanNo ratings yet
- Durability of Concrete Monograph 03092020Document118 pagesDurability of Concrete Monograph 03092020Urvasi Vandana TalapalaNo ratings yet
- Project FinalDocument39 pagesProject FinalbctumcNo ratings yet
- Report On Wet Air OxidationDocument83 pagesReport On Wet Air OxidationAnkita RoyNo ratings yet
- Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion of Mooring Systems For Floating Offshore InstallationsDocument40 pagesMicrobiologically Influenced Corrosion of Mooring Systems For Floating Offshore InstallationsKAYODE0% (1)
- B.E Civil Batchno 16Document42 pagesB.E Civil Batchno 16SHANMUGAVEL KUMARNo ratings yet
- Final BTP Report - CE19B089Document62 pagesFinal BTP Report - CE19B089Addandi Ashrith Reddy ce21b002No ratings yet
- Tribology and Tribochemistry of Diamond Like Carbon (DLC) CoatingsDocument34 pagesTribology and Tribochemistry of Diamond Like Carbon (DLC) Coatingssandeep1reddy-10No ratings yet
- Natural Surfactant FloodingDocument52 pagesNatural Surfactant FloodingjonahotuankemeNo ratings yet
- Surfactant Complete.............Document145 pagesSurfactant Complete.............Shalin CNo ratings yet
- 2 FULL N PDFDocument8 pages2 FULL N PDFJayaprabhu PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Starting I VIIDocument7 pagesStarting I VIIvivekNo ratings yet
- A Laboratory Study On The Stabilization of Marine Clayusing Saw Dust and LimeDocument38 pagesA Laboratory Study On The Stabilization of Marine Clayusing Saw Dust and LimeManas Ranjan DashNo ratings yet
- FYP Final Report 2018-2022 Final Document UpdatedDocument38 pagesFYP Final Report 2018-2022 Final Document UpdatedSyed Saad AhmedNo ratings yet
- Full ThesisDocument127 pagesFull ThesisMuhammad AsranNo ratings yet
- FYP B Final Report Kevin Juan 1001954608Document77 pagesFYP B Final Report Kevin Juan 1001954608kevinjuan070501No ratings yet
- AbstractDocument11 pagesAbstractYana SarahNo ratings yet
- B.E Civil Batchno 21Document54 pagesB.E Civil Batchno 21Mallesh ViruNo ratings yet
- 06 May 2017 221509117EF8XS16XAnnexure-Prefeasibilityreport PDFDocument109 pages06 May 2017 221509117EF8XS16XAnnexure-Prefeasibilityreport PDFjyothiNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Technical Innovation in Modern Engineering & Science (IJTIMES)Document13 pagesInternational Journal of Technical Innovation in Modern Engineering & Science (IJTIMES)pavan kumar tNo ratings yet
- TH3223Document83 pagesTH3223matchamilk55No ratings yet
- Training Report On Construction of Resedential BuildingDocument39 pagesTraining Report On Construction of Resedential BuildingAr G S YadavNo ratings yet
- Remote Monitoring and Intelligent Controls of Cathodc Protection System of Gas Transmissino PipelinesDocument96 pagesRemote Monitoring and Intelligent Controls of Cathodc Protection System of Gas Transmissino PipelinesToro JulioNo ratings yet
- Bonafide Certificate: Signature SignatureDocument8 pagesBonafide Certificate: Signature SignatureMOHAMED RIYAAZ N ANo ratings yet
- Concrete ProjectDocument36 pagesConcrete ProjectperadhivansachinNo ratings yet
- Optimisation Mix Design and Suppress The Alkali Silica ReactionDocument50 pagesOptimisation Mix Design and Suppress The Alkali Silica ReactionAZIRANo ratings yet
- B.E Civil Batchno 16Document46 pagesB.E Civil Batchno 16SHANMUGAVEL KUMARNo ratings yet
- Turbine Manufacturing B.H.E.L., Haridwar: Bachelor of Technology IN Mechanical EngineeringDocument41 pagesTurbine Manufacturing B.H.E.L., Haridwar: Bachelor of Technology IN Mechanical Engineeringshubham bhattNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Self Compqcting ConcreteDocument86 pagesProject Report On Self Compqcting Concreteassssad20000No ratings yet
- Table of ContentsDocument6 pagesTable of ContentsDaveRaphaelDumanatNo ratings yet
- Tile Waste - Sufia Lari - UpdatedDocument47 pagesTile Waste - Sufia Lari - UpdatedSyed BelalNo ratings yet
- OmarKalifaHammudaPSChE2019 ThesisDocument36 pagesOmarKalifaHammudaPSChE2019 ThesisMurtibaahshe HDNo ratings yet
- Training Report On Construction of Residential BuildingDocument39 pagesTraining Report On Construction of Residential BuildingRupesh MandalNo ratings yet
- Air QualityDocument67 pagesAir QualityMike MatshonaNo ratings yet
- 078 019 Pragya Chapter 6 (Final)Document118 pages078 019 Pragya Chapter 6 (Final)Pragya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Self Compacting Concret1Document50 pagesSelf Compacting Concret1Bham KumarNo ratings yet
- Effect of Bore Water On Cement-PlasterDocument68 pagesEffect of Bore Water On Cement-Plasterpune1000No ratings yet
- 1987 Michigan DNR Statement Regarding Illegality of Coal Ash Dumping in Lake MichiganDocument261 pages1987 Michigan DNR Statement Regarding Illegality of Coal Ash Dumping in Lake MichiganLakeMichiganFilesNo ratings yet
- Optimization and Analysis of Hydraulic Fracturing CBMDocument58 pagesOptimization and Analysis of Hydraulic Fracturing CBMManuel LealNo ratings yet
- Rubber Nanocomposites: Preparation, Properties, and ApplicationsFrom EverandRubber Nanocomposites: Preparation, Properties, and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Wear: Materials, Mechanisms and PracticeFrom EverandWear: Materials, Mechanisms and PracticeGwidon W. StachowiakNo ratings yet
- Simple 1 UpdatedDocument43 pagesSimple 1 UpdatedSHAIK AHMED JAWADNo ratings yet
- Natraj Finalcorr Plan For BecscomDocument1 pageNatraj Finalcorr Plan For BecscomSHAIK AHMED JAWADNo ratings yet
- WonderfulDocument2 pagesWonderfulSHAIK AHMED JAWADNo ratings yet
- HKBK College of EngineeringDocument51 pagesHKBK College of EngineeringkarthikNo ratings yet
- AZHAREXCELDocument12 pagesAZHAREXCELSHAIK AHMED JAWADNo ratings yet
- Article On 8TH Sem ProjectDocument46 pagesArticle On 8TH Sem ProjectSHAIK AHMED JAWADNo ratings yet
- Project Report Physico-Chemical Analysis and GisDocument71 pagesProject Report Physico-Chemical Analysis and GisSHAIK AHMED JAWADNo ratings yet
- POSTERDocument1 pagePOSTERSHAIK AHMED JAWADNo ratings yet
- Visvesvaraya Technological UniversityDocument6 pagesVisvesvaraya Technological UniversitySHAIK AHMED JAWADNo ratings yet
- Soil Liquefaction Seminar ReportDocument25 pagesSoil Liquefaction Seminar ReportSHAIK AHMED JAWADNo ratings yet
- A Seminar On Soil Liquefaction: Slide No 1Document19 pagesA Seminar On Soil Liquefaction: Slide No 1SHAIK AHMED JAWADNo ratings yet
- Front Page 1HK14CV044Document2 pagesFront Page 1HK14CV044SHAIK AHMED JAWADNo ratings yet
- Weekly Home Learning Plan For Grade 7 CelisDocument25 pagesWeekly Home Learning Plan For Grade 7 CelisAngelNicolinE.SuymanNo ratings yet
- Periodical Test in Grade 10 EnglishDocument2 pagesPeriodical Test in Grade 10 EnglishPLT Ma Alma CorpusNo ratings yet
- Nivel IvDocument4 pagesNivel IvMaria MezaNo ratings yet
- A Basic Model of Performance: Module 5.1Document11 pagesA Basic Model of Performance: Module 5.1georgecodexNo ratings yet
- Sacred Games - Vikram ChandraDocument10 pagesSacred Games - Vikram Chandradisgusting4allNo ratings yet
- 2014 Jan P2 QPDocument32 pages2014 Jan P2 QPCassidyNo ratings yet
- Tess' Fateful LifeDocument19 pagesTess' Fateful LifeSufi Ikrima Sa'adahNo ratings yet
- Ph501 Electrodynamics Problem Set 2: Princeton UniversityDocument30 pagesPh501 Electrodynamics Problem Set 2: Princeton UniversityDavidSuarezNo ratings yet
- Permutation 1Document24 pagesPermutation 1Sophia RiveraNo ratings yet
- 2-Way Slab Design To Aci Trial Version)Document8 pages2-Way Slab Design To Aci Trial Version)Abdul KabasyNo ratings yet
- J5155124 Berne, NY Tower Geotechnical Report (Sealed) 11-6-15Document25 pagesJ5155124 Berne, NY Tower Geotechnical Report (Sealed) 11-6-15ACSOtweet100% (1)
- Chapter 12Document53 pagesChapter 12HooXinjie100% (1)
- Become A Sap PP Consultant & Job Profile: Learn More About Highly Paid Jobs in ITDocument9 pagesBecome A Sap PP Consultant & Job Profile: Learn More About Highly Paid Jobs in ITHaythem NoukazNo ratings yet
- Heritage and Postmodern TourismDocument12 pagesHeritage and Postmodern TourismTeo Thema100% (1)
- Weller CatalogDocument88 pagesWeller CatalogcammellieNo ratings yet
- Sociotechnical Systems (STS) : Organizational Development Work Design People TechnologyDocument41 pagesSociotechnical Systems (STS) : Organizational Development Work Design People TechnologyAbhimita GaineNo ratings yet
- Logical and Analytical Reasoning - WorkshopDocument75 pagesLogical and Analytical Reasoning - WorkshopPuneet MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Intellectual Property RightsDocument21 pagesIntellectual Property RightsKashif FaizNo ratings yet
- ProposalDocument2 pagesProposalAndrea AquinoNo ratings yet
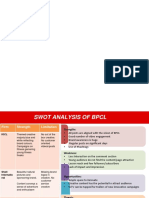
- Swot - BPCLDocument4 pagesSwot - BPCLAnkit VermaNo ratings yet
- Tourism MGT DefinitionDocument4 pagesTourism MGT DefinitionAvery Jan Magabanua SilosNo ratings yet
- Share Point Customization TricksDocument49 pagesShare Point Customization Trickssemalaiappan100% (5)
- OKRAPIDocument6 pagesOKRAPIRonan SibbalucaNo ratings yet
- Definition of TermsDocument2 pagesDefinition of TermsAbegail AbaygarNo ratings yet