Professional Documents
Culture Documents
(BSN2-2) CMCA Lec - Lesson No.4
Uploaded by
Abish Julienne Pecundo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views5 pagesThis document outlines the key concepts around sexuality and sexual identity. It discusses:
1. Normal sexuality involves feelings of desire without guilt or anxiety between consenting partners.
2. Sexuality is influenced by developmental, cultural, religious, ethical, lifestyle, health, and medication factors.
3. Gender identity and role develop through childhood based on biological sex, social and cultural norms. Sexual identity involves an inner sense of being male or female which may differ from biological gender.
Original Description:
Original Title
[BSN2-2] CMCA Lec - Lesson No.4
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document outlines the key concepts around sexuality and sexual identity. It discusses:
1. Normal sexuality involves feelings of desire without guilt or anxiety between consenting partners.
2. Sexuality is influenced by developmental, cultural, religious, ethical, lifestyle, health, and medication factors.
3. Gender identity and role develop through childhood based on biological sex, social and cultural norms. Sexual identity involves an inner sense of being male or female which may differ from biological gender.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views5 pages(BSN2-2) CMCA Lec - Lesson No.4
Uploaded by
Abish Julienne PecundoThis document outlines the key concepts around sexuality and sexual identity. It discusses:
1. Normal sexuality involves feelings of desire without guilt or anxiety between consenting partners.
2. Sexuality is influenced by developmental, cultural, religious, ethical, lifestyle, health, and medication factors.
3. Gender identity and role develop through childhood based on biological sex, social and cultural norms. Sexual identity involves an inner sense of being male or female which may differ from biological gender.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
LECTURE\POWERPOINT
[TRANS] LESSON 4: SEXUALITY & SEXUAL IDENTITY
OUTLINE • How appealing parents or other adult role models portray
I Normal Sexuality their gender roles may also influence how a child envisions
II Sexuality himself or herself
A Biologic Gender o Gender role is also culturally influenced
B Gender Identity ▪ Filipino cultural influence
C Gender Role
i Development of Gender Identity
D Factors Affecting Sexuality FACTORS AFFECTING SEXUALITY
III Stages of Sexuality 1. Developmental Considerations
A Infancy o Sexuality is the only distinguishing trait present at
B Preschool Period conception
C School-age Child o Gender, or sex, influences behavior throughout life
D Adolescent
E Young Adult
2. Culture
F Middle-age Adult
G Older Adult o Every culture has its own norms dictating duration of
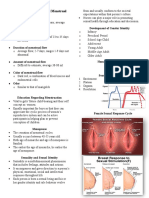
IV Human Sexual Response Cycle sexual intercourse, methods of sexual stimulation
A Phases of the Sexual Response Cycle and sexual positions
i Normal Sexual Behavior o Some cultures promote childhood sexual play,
B Physiologic Changes Associated with the Sexual Response polygamy/monogamy, and puberty rites including
Cycle male circumcision
i Phase 1: Excitement
o Religious beliefs promote beliefs on
ii Phase 2: Plateau
iii Phase 3: Orgasmic premarital/extramarital coitus, homosexuality, and
iv Phase 4: Resolution decisions on circumcision (male and female)
C Controversies about Female Orgasm
D Influence of the Menstrual Cycle on Sexual Response 3. Religion
E Influence of Pregnancy on Sexual Response o Some view organized religion as having a generally
V Types of Sexual Orientation negative effect on expression of sexuality
VI Types of Sexual Expression
o Sexual expression other than male-female coitus
VII Disorders of Sexual Functioning
are considered unnatural by some
o Concept of virginity came to be synonymous with
NORMAL SEXUALITY purity, and sex became synonymous with sin
• Perception of being male or female and all those thoughts, o Double standards and rigid regulations exist in many
feelings, behaviors, connected with sexual gratification and religions
reproduction, including the attraction of one person to
another 4. Ethics
o Involves feelings of desire, behavior that brings o Health sexuality depends on freedom from guilt and
pleasure to oneself and one’s partner anxiety
▪ Devoid of guilt or anxiety and not compulsive o What one views bizarre, perverted or wrong may be
natural and right to another
SEXUALITY o If sexual expression is performed by consenting
• A multidimensional phenomenon that includes feelings, adults, is not harmful to them and is practiced in
attitudes, and actions privacy, it is not considered a deviant behavior
• Has both biologic and cultural components o Many accept sexual expression of various forms
• Encompasses and gives direction to a person’s physical
emotional, social and intellectual responses throughout life 5. Lifestyle
o Many are under considerable strain to perform and
BIOLOGIC GENDER function in workplace as well as at home
• Term used to denote a person’s chromosomal sex ▪ Stressors may be external (job, financial
o Male (XY) demands) or internal (competitive)
o Female (XX) o Although some couples view sexual activity as a
release from stressors of everyday life, most place
GENDER IDENTITY sex far from the top of the list of things to do
• Aka Sexual Identity is the inner sense a person has being male
or female, which may be the same as or different from 6. Health State
biologic gender o Chronic Pain
o Diabetes
GENDER ROLE o Cardiovascular diseases
• The male or female behavior a person exhibits, which, again, o Diseases of Joint and Mobility
may or may not be the same as biologic gender or gender o Surgery and Body Image
identity o Spinal Cord Injuries
o Mental Illness
DEVELOPMENT OF GENDER IDENTITY o Sexually Transmitted Disease
• Several theories exist regarding whether gender identity
7. Medications
arises from primarily a biologic or a psychosocial focus
o Some meds have side effects that affect sexual
o The amount of testosterone secreted in utero (a
functioning
process termed sex typing) may affect how gender
o Some people use illegal drugs because of their
develops)
reputed ability to heighten sexual experience, but
can have serious and even deadly side effects
IBARRA. MARIANO. ONG. PECUNDO. PERALTA. RICO. 1
[TRANS] LESSON 4: SEXUAL & SEXUAL IDENTITY
STAGES OF SEXUALITY OLDER ADULT
• Both male and female older adults continue to enjoy active
INFANCY sexual relationships
• From the day of birth, female and male babies are treated • Some men experience less erectile firmness or ejaculatory
differently by their parents force than when they were younger, but others discover that
• People generally bring girls dainty rattles and dresses with they are able to maintain an erection longer
ruffles • Older women may have less vaginal secretions because they
o They are treated more gently by parents and held have less estrogen after menopause
and rocked more than male babies
• Admonitions given babies can be different HUMAN SEXUAL RESPONSE CYCLE
o Girl – “Don’t cry, you don’t look pretty when you cry”
o Boy – “You’ve got to learn to be tougher than that if PHASES OF THE SEXUAL RESPONSE CYCLE
you’re going to make it in this world” 1. Phase 1: Excitement
2. Phase 2: Plateau
PRESCHOOL PERIOD 3. Phase 3: Orgasmic
• Children can distinguish bet. males and females as early as 2 4. Phase 4: Resolution
years of age
• By age 3 or 4 years, they can say what sex they are, and they
have absorbed cultural expectations of that sex role
o Boys – play rough-and-tumble games with other
boys
o Girls – play more quietly, although the two
frequently mix at this age
• Sex role modeling is reinforced
• They start insisting on what they want, like: what to wear,
color of their room, etc.
• Social contacts bet. the child and significant adults
contribute to sexual identification NORMAL SEXUAL BEHAVIOR
• A positive self-concept grows from parental love, effective • Sexual response is a true psychophysiological experience
relationships with other, success in play activities, and gaining • There is:
skills and self control o Arousal
o Experience
SCHOOL-AGE CHILD o Orgasm
• Early school-age children typically spend play time imitating
adult roles as a way of learning gender roles PHYSIOLOGIC CHANGES ASSOCIATED WITH THE SEXUAL
• They form strong impressions of what a female or male should
RESPONSE CYCLE
be
• Grade schools have become more attuned to unisex
activities PHASE 1: EXCITEMENT
• The excitement phase (aka arousal phase / initial excitement
ADOLESCENT phase) is the first stage of the human sexual response cycle
• At puberty, as the adolescent begins the process of • Occurs as the result of any erotic physical or mental
establishing a sense of identity, the problem of final gender stimulation, such as kissing, petting, or viewing erotic images,
role identification surfaces again that lead to sexual arousal
• Problem of final gender role identification surfaces again • During the excitement stage, the body prepares for coitus, or
• Most early adolescents maintain strong ties to their gender sexual intercourse
group Table No.1 Excitement Phase
o Boys with boys SIGNS PRESENT IN SIGNS PRESENTS IN SIGNS PRESENT IN
o Girls with girls BOTH SEXES MALES ONLY FEMALES ONLY
• The advent of menstruation may provide a common bond • Increased • Penile erection • Enlargement of
for girls at this stage muscle tension • Tensing, the clitoral
• Moderate thickening, and glands
YOUNG ADULT increase in elevation of the • Vaginal
• When young adults move away from home to attend college heart rate, scrotum lubrication
or establish their own home, the change in their eating respiration, and • Partial elevation • Widening and
patterns can increase or decrease their weight that lead to blood pressure and increase in lengthening of
changes in their body image • Sex flush (less size of testicles the vaginal
prevalent in barrel
MIDDLE-AGE ADULT men than in • Separation and
• For many women and men in midlife, sexuality has achieved women; flattening of the
a degree of stability present in 75% labia majora
• A sense of masculinity of femininity and comfortable patterns of women) • Reddening of
of behavior have been established • Nipple erection the labia
• During midlife, men may begin to experience changes in (60% of men minora and
sperm production erectile power, achievement of orgasm, and most of vaginal wall
and sex drive, although these changes usually do not women) • Breast
significantly alter reproductive or sexual functioning enlargement
• Although menopause alters reproductive functioning, it does and enlarge
not physically inhibit sexual functioning areolae
IBARRA. MARIANO. ONG. PECUNDO. PERALTA. RICO. 2
[TRANS] LESSON 4: SEXUAL & SEXUAL IDENTITY
Table No.3 Orgasmic Phase
SIGNS PRESENT IN SIGNS PRESENTS IN SIGNS PRESENT IN
BOTH SEXES MALES ONLY FEMALES ONLY
• Involuntary • Rhythmic, • Approx. 5-12
spasms of expulsive contractions in
muscle groups contractions of the orgasmic
throughout the the penis at 0.8 platform at 0.8
body seconds interval seconds
• Diminished • Emission of interval
sensory seminal fluid into • Contractions of
awareness the prostatic the muscle of
• Involuntary urethra the pelvic floor
contraction of • Closing of the and uterine
PHASE 2: PLATEAU the anal internal bladder muscles
• The period during which sexual tension increases to levels sphincter sphincter • Varies pattern
nearing orgasm, may last from 30 seconds to 30 minutes • Peak heart rate • Orgasm may of orgasm
(110-180 bpm), occur w/o including minor
Table No.2 Plateau Phase respiratory rate ejaculation surges and
SIGNS PRESENT IN SIGNS PRESENTS IN SIGNS PRESENT IN (40/min or • Ejaculation of contractions,
BOTH SEXES MALES ONLY FEMALES ONLY greater) semen through multiple
• Increased • Increased in • Retraction of the penile orgasm, or
voluntary and penile the clitoris urethra and simple intense
involuntary circumference, under the hood expulsion from orgasms similar
myotonia at the coronal • Appearance of the urethral to that of the
• Abdominal, ridge, and the orgasmic meatus male
intercostal, deepening in platform,
anal, and facial color increased in the
muscle • 50% increase in size of the outer
contraction testicular size, 1/3 of the
• Accelerated and elevation vagina and the
heart rate and close to the labia minora
respiratory rate perineum • Slight increase
and blood • Appearance of in width and
pressure a few drops of depth of the
• Sex flush mucoid inner 2/3 of the
(appearance in secretions from vagina
some men late the • Farther
in the phase; bulbourethral reddening of
spread over the glands at tip of the labia
entire body in penis; may minora
women) contain sperm • Appearance of
few drops of
mucoid
secretion from
the Bartholin’s
gland to
lubricate the
inner labia
• Farther increase
in breast size
and areolar
enlargement
PHASE 4: RESOLUTION
• Occurs after orgasm and allows the muscle to relax, blood
pressure to drop and the body to slow down from its excited
state
Table No.4 Plateau Phase
SIGNS PRESENT IN BOTH SEXES SIGNS PRESENTS IN MALES
ONLY
• Reversal of • Refractory period during
vasocongestion in 10- which the body will not
30mins; disappearance of respond to sexual
PHASE 3: ORGASMIC all signs of myotonia w/in 5 stimulation; varies,
• This phase is the climax of the sexual response cycle. mins depending on age and
• Shortest of the phases and generally lasts only a few seconds • Genital and breast return other factors, from a few
to their pre-excitement moments to hours or days
states
IBARRA. MARIANO. ONG. PECUNDO. PERALTA. RICO. 3
[TRANS] LESSON 4: SEXUAL & SEXUAL IDENTITY
• Sex flush disappears in
reverse order of INFLUENCE OF PREGNANCY ON SEXUAL RESPONSE
appearance • Pregnancy is another time in life when there is
• Heart rate, respiratory rate, vasocongestion of the lower pelvis because of the blood
blood pressure returns to supply needed by a rapidly growing fetus
normal • This causes some women to experience a first orgasm during
• Other reactions include their first pregnancy
sleepiness, relaxation, and • Following a pregnancy, many women experience increased
emotional outbursts such sexual interest because the new growth of blood vessels
as crying or laughing during pregnancy lasts for some time and continues to
facilitate pelvic vasocongestion
TYPES OF SEXUAL ORIENTATION
1. Heterosexuality
o Heterosexual is a person who finds sexual fulfillment
with a gender member of the opposite gender
2. Homosexuality
o Homosexual is a person who finds sexual fulfillment
with a member of his or her own sex
▪ Gay – homosexual men
▪ Lesbian – homosexual women
o More recent terms:
▪ MWM – “men who have sex with men”
▪ WWW – “women who have sex with women”
3. Bisexuality
o People are said to be bisexual if they achieve
sexual satisfaction from both homosexual and
heterosexual relationships
4. Transsexuality
o Transsexual or transgender person is an individual
who, although of one biologic gender, feels as if he
or she is of the opposite gender
o Such people may have sex change operations so
that they appear cosmetically as the gender they
feel that they are
5. Pansexual
o Attracted to people of any gender identity
CONTROVERSIES ABOUT FEMALE ORGASM 6. Asexual
• Freud deducted that there were two types of female o Not sexually attracted to other people
orgasms:
o Clitoral TYPES OF SEXUAL EXPRESSION
o Vaginal
• He believed that clitoral orgasms (originating from Table No.5 Sexual Expression
masturbation or other noncoital acts) represented sexual SEXUAL DEFINITION
immaturity and that only vaginal orgasms were authentic, EXPRESSION
mature form of sexual behavior in women
Sexual • Aka celibacy, a separation from
o Accordingly, he considered women to be neurotic
Abstinence sexual activity
if they could not achieve orgasm through
• Vowed state of certain religious orders
intercourse
Masturbation • Self-stimulation for erotic pleasure; it
• Masters (1998) showed that there is no physiologic difference
can also be a mutually enjoyable
bet. an orgasm achieved through intercourse and one
activity for sexual partners
achieved by direct stimulation of the clitoris
• Offers sexual release which may be
• In recent years, a subject of controversy regarding female
interpreted by the person as overall
sexuality has arisen: the existence or not of “the G Spot”
tension or anxiety relief
o First described in 1950 by the German physician
Autoerotic • Extreme practice of causing oxygen
Grafenberg, the G Spot, has been promoted as an
Asphyxia deficiency (usually by hanging) during
area of heightened erotic sensitivity
masturbation with the goal of
producing a feeling of extreme sexual
INFLUENCE OF THE MESTRUAL CYCLE ON SEXUAL RESPONSE excitement
• During the 2nd half of the menstrual cycle – the luteal phase –
Erotic • Use of visual materials such as
there is increased fluid retention and vasocongestion in a
Stimulation magazines or photographs for sexual
woman’s lower pelvis
arousal
o Because some vasocongestion is already present
Fetishism • Sexual arousal resulting from the use of
at the beginning of the excitement stage of the
certain objects or situations
sexual response, women appear to reach the
• Leather, rubber, shoes, and feet are
plateau stage more quickly and achieve orgasm
frequently perceived to have erotic
more readily during this time
qualities
o Women also may be more interested in initiating
Transvestism • Transvestite is an individual who
sexual relations at this time
dresses in the clothes of the opposite
sex; can be heterosexual,
homosexual, or bisexual
• Many are married
IBARRA. MARIANO. ONG. PECUNDO. PERALTA. RICO. 4
[TRANS] LESSON 4: SEXUAL & SEXUAL IDENTITY
Voyeurism • Obtaining sexual arousal by looking at
another person’s body REFERENCES
• Almost all children and adolescents
pass through a stage when voyeurism Notes from the discussion by Prof. Lualhati M. Floranda, DNM, RN
is appealing; this passes w/ more
active sexual expression Manila Doctors Colleges of Nursing PowerPoint Presentation
Sadomasochism • Involves inflicting pain (sadism) or
receiving pain (masochism) to
achieve sexual satisfaction
• A practice generally considered to be
w/in the limits of normal sexual
expression as long as the pain involved
is minimal and the experience is
satisfying to both sexual partners
Table No.6 Other Sexual Expression
SEXUAL DEFINITION
EXPRESSION
Exhibitionism • Revealing one’s genitals in public
Bestiality • Sexual relations w/ animals
Pedophiles • Individuals who are interested in sexual
encounters w/ children
DISORDERS OF SEXUAL FUNCTIONING
Table No.7 Disorders of Sexual Functioning
SEXUAL DEFINITION
DISORDERS
Inhibited Sexual • Lessened interest in sexual relations is
Desire normal in some circumstances, such
as after the death of a family member,
a divorce, or a stressful job change
Failure to • Failure of a woman to achieve orgasm
Achieve can be a result of poor sexual
Orgasm technique, concentrating too hard on
achievement, or negative attitudes
toward sexual relationships
Erectile • Formerly referred to as impotence;
Dysfunction (ED) inability of a man to produce or
maintain an erection long enough for
vaginal penetration or partner
satisfaction
Premature • Ejaculation before penile-vaginal
Ejaculation contact
• Term also often used to mean
ejaculation before the sexual
partner’s satisfaction has been
achieved
Persistent Sexual • Excessive and unrelenting sexual
Arousal arousal in the absence of desire
Syndrome • May be triggered by medication or
(PSAS) psychological factors
Pain Disorders • Because the reproductive system has
a sensitive nerve supply, when pain
occurs in response to sexual activities,
it can be acute and severe and impair
a person’s ability to enjoy this segment
of their life
Vaginismus • Involuntary contraction of the muscle
at the outlet of the vagina when coitus
is attempted that prohibits penile
penetration
• May occur in women who have been
raped
Dyspareunia & • Pain during coitus
Vestibulitis • This can occur because of
endometriosis (abnormal placement
of endometrial tissue), vestibulitis
(inflammation of the vestibule),
vaginal infection, or hormonal
changes
IBARRA. MARIANO. ONG. PECUNDO. PERALTA. RICO. 5
You might also like
- A List of 2600 NSFW Sub RedditsDocument11 pagesA List of 2600 NSFW Sub RedditsDhruv Mullick0% (1)
- The Sexual SelfDocument67 pagesThe Sexual SelfJan Efraime Rian Sapla Marquez100% (2)
- G-Spots: The Clitoris, A-Spot, G-Spot and U-SpotDocument4 pagesG-Spots: The Clitoris, A-Spot, G-Spot and U-SpotraviikumarNo ratings yet
- Normal SexualityDocument27 pagesNormal SexualityschxzerrydawnNo ratings yet
- Vico, Niecolle P. BSMT 1C REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM CONCEPT MAP 2 PDFDocument2 pagesVico, Niecolle P. BSMT 1C REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM CONCEPT MAP 2 PDFNiecolle VicoNo ratings yet
- Health8 1st QTR Lessons 1 3 Human SexualityDocument58 pagesHealth8 1st QTR Lessons 1 3 Human Sexualityxie liNo ratings yet
- Lou Sullivan Diaries (1970-1980) and Theories of Sexual EmbodimentDocument252 pagesLou Sullivan Diaries (1970-1980) and Theories of Sexual EmbodimentfenixscribdNo ratings yet
- GST Session 1 Gender Awareness 101 Sex and GenderDocument30 pagesGST Session 1 Gender Awareness 101 Sex and GendernabillahNo ratings yet
- Gender and Society: Course PACK inDocument32 pagesGender and Society: Course PACK inUlieng cornNo ratings yet
- F2. The Sexual Self Part 1Document25 pagesF2. The Sexual Self Part 1JANINE ANN MAGQUILAT100% (1)
- (M4) The Sexual SelfDocument4 pages(M4) The Sexual SelfMA. LUISA ANNE SORIANONo ratings yet
- PD 100 - Second LectureDocument4 pagesPD 100 - Second LectureSVPSNo ratings yet
- Understanding The SelfDocument10 pagesUnderstanding The SelfRenz GoleNo ratings yet
- 2 NCM207-Sexuality PregnancyDocument4 pages2 NCM207-Sexuality PregnancyVhiance Czaramae LahuranNo ratings yet
- 2 NCM207-Sexuality PregnancyDocument4 pages2 NCM207-Sexuality PregnancyVhiance Czaramae LahuranNo ratings yet
- B. The Sexual SelfDocument37 pagesB. The Sexual SelfPaul Winston RegaladoNo ratings yet
- 1.18 Psychia - Human Sexuality (Dr. Obra, 2021)Document3 pages1.18 Psychia - Human Sexuality (Dr. Obra, 2021)Danila BagrovNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument4 pagesReviewerJaymax the FirstNo ratings yet
- Gender and SocietyDocument5 pagesGender and Societyjosembrimon551973No ratings yet
- Mother and Child ReviewerDocument2 pagesMother and Child ReviewerMarie anneNo ratings yet
- MAPEHDocument11 pagesMAPEHsyvansantiago05No ratings yet
- Focus: Family Health Gender and Human SexualityDocument3 pagesFocus: Family Health Gender and Human SexualityjhaysonbagaoiNo ratings yet
- Sexual DisorderDocument4 pagesSexual DisorderMary Belle OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Gas Introduction-Chapt.1Document47 pagesGas Introduction-Chapt.1Rei ChanNo ratings yet
- Sexual DisorderDocument14 pagesSexual DisorderAndalNo ratings yet
- Prelim MaternalDocument18 pagesPrelim MaternalJohn MajanNo ratings yet
- Learning Objectives: Understanding The Self Module 1 - Sexual SelfDocument11 pagesLearning Objectives: Understanding The Self Module 1 - Sexual SelfMiss MegzzNo ratings yet
- Perdev AdolescenceDocument32 pagesPerdev AdolescenceandrewNo ratings yet
- Gendso FinalsDocument5 pagesGendso FinalsJustin AprueboNo ratings yet
- DEVPSYCH 8 - Psychosocial Development in Early ChildhoodDocument3 pagesDEVPSYCH 8 - Psychosocial Development in Early ChildhoodRedgie G. GabaneNo ratings yet
- 108-Midterm TopicsDocument5 pages108-Midterm TopicsLeslie John PalaposNo ratings yet
- Gad ReviewerDocument2 pagesGad ReviewerHannah Jane ApariciNo ratings yet
- Dimension of GenderDocument11 pagesDimension of GenderJohn Lloyd PedritaNo ratings yet
- Sex Gender and SexualityDocument15 pagesSex Gender and SexualityChristine Joy DelenNo ratings yet
- DEVPSYCH 12 - Psychosocial Development in AdolescenceDocument4 pagesDEVPSYCH 12 - Psychosocial Development in AdolescenceRedgie G. GabaneNo ratings yet
- Module 12 Sexual SelfDocument25 pagesModule 12 Sexual Selfprincess marieNo ratings yet
- S5 - Social, Cultural, Belief & Sexual Value - Jan 21, 2021Document32 pagesS5 - Social, Cultural, Belief & Sexual Value - Jan 21, 2021Siti Hadijah Aspan, M.PHNo ratings yet
- Humansexuality and Sexua L Dysfu N Cti Ons: 1 7 .1 Normal SexualityDocument18 pagesHumansexuality and Sexua L Dysfu N Cti Ons: 1 7 .1 Normal Sexualitymiss betawiNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Reviewer GensocDocument8 pagesFinal Exam Reviewer GensocSean Oliver BiguerasNo ratings yet
- DevPsych ReviewerDocument17 pagesDevPsych ReviewerMaria Tena TapayanNo ratings yet
- Love, Gender, and Sexuality NotesDocument4 pagesLove, Gender, and Sexuality NotesLyra Kassandra M. BorjaNo ratings yet
- Gender Sensitivity For Young AdultsDocument23 pagesGender Sensitivity For Young AdultsJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- Gender and Human SexualityDocument25 pagesGender and Human SexualityAshlene CruzNo ratings yet
- Sexual SelfDocument25 pagesSexual SelfMJ OcañaNo ratings yet
- Belo - Ucsp Group 1Document36 pagesBelo - Ucsp Group 1Milamil OñezNo ratings yet
- Gender SocietyDocument6 pagesGender SocietyRhave AbogNo ratings yet
- UTSDocument51 pagesUTSandreesaccharineNo ratings yet
- UTS - Module 4 Sexualself StudentDocument6 pagesUTS - Module 4 Sexualself StudentkimberlyfritzzunigaNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Module 2Document4 pagesMaternal and Child Module 2AmethystNo ratings yet
- PDEVDocument7 pagesPDEVSteph CaronanNo ratings yet
- QLife NonBinaryPeopleDocument2 pagesQLife NonBinaryPeoplepmika88888888No ratings yet
- Week 2 GENSOC Lessons 1 3 1Document59 pagesWeek 2 GENSOC Lessons 1 3 1Shereen Grace GaniboNo ratings yet
- Revised Study GuideDocument6 pagesRevised Study GuideWinter BacalsoNo ratings yet
- Culture & Psychology (CHAPTERS 7-10)Document14 pagesCulture & Psychology (CHAPTERS 7-10)The UnknownNo ratings yet
- LGBTQ YouthDocument98 pagesLGBTQ YouthApril Rose Airoso - AramburoNo ratings yet
- The-Sexual-Self LectureDocument109 pagesThe-Sexual-Self LectureElaine Fiona VillafuerteNo ratings yet
- Sex and GenderDocument28 pagesSex and GenderMark Porcadilla100% (1)
- PD101 PrelimsDocument8 pagesPD101 PrelimsRoshanlene ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Gender Role and IdentityDocument18 pagesGender Role and IdentityDiana Rose PesimoNo ratings yet
- Sexuality and Sexual HealthDocument44 pagesSexuality and Sexual Health2023382320.jadonNo ratings yet
- Sexual Self: B E V EDocument14 pagesSexual Self: B E V EDan Jayson DingilNo ratings yet
- Distinction Sex and GenderDocument25 pagesDistinction Sex and GenderJM MillanesNo ratings yet
- GensocDocument3 pagesGensocf7pxnshq9jNo ratings yet
- Summary and Reflection IIDocument8 pagesSummary and Reflection IIJames Clarenze VarronNo ratings yet
- Understanding The SelfDocument15 pagesUnderstanding The Selfrenalyne andresNo ratings yet
- Sadomasochism Accor Sadomasochism According To Freud's Psychosexual Stages of Chosexual Stages of Development TheoryDocument10 pagesSadomasochism Accor Sadomasochism According To Freud's Psychosexual Stages of Chosexual Stages of Development TheoryDolce BbNo ratings yet
- Why Do Young People Need Comprehensive Sexuality Education?Document3 pagesWhy Do Young People Need Comprehensive Sexuality Education?ItsClarenceNo ratings yet
- Heterosexism and HomophobiaDocument6 pagesHeterosexism and HomophobiaVictorNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Gender PoliticsDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Gender PoliticsAlmiraNo ratings yet
- s11058388 - Literature ReviewDocument9 pagess11058388 - Literature ReviewAshwarya ChandNo ratings yet
- IOPC Making A Complaint Against The Police Form 2020Document7 pagesIOPC Making A Complaint Against The Police Form 2020blossomN17No ratings yet
- CasesDocument4 pagesCasesDivania GovenderNo ratings yet
- The G-Zone HandoutDocument1 pageThe G-Zone Handoutapi-646865632No ratings yet
- Fdome M3 Io Re 03Document25 pagesFdome M3 Io Re 03William Soneja CalapiniNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument2 pagesUntitled Documentapi-613937599No ratings yet
- Instructions: End Semester Examination 2021 English For Communication (HSIR 11) Time-2 HourDocument3 pagesInstructions: End Semester Examination 2021 English For Communication (HSIR 11) Time-2 Hourlilly pushparaniNo ratings yet
- Does Sex Burn Calories - Google SearchDocument1 pageDoes Sex Burn Calories - Google SearchPaul DuzNo ratings yet
- Jacqueline Foertsch - Conflict and Counterpoint in Lesbian, Gay, and Feminist Studies (2007)Document238 pagesJacqueline Foertsch - Conflict and Counterpoint in Lesbian, Gay, and Feminist Studies (2007)Ildikó HomaNo ratings yet
- Battle of The SexesDocument8 pagesBattle of The Sexesapi-623086923No ratings yet
- RESEARCH 2 LGBTQDocument6 pagesRESEARCH 2 LGBTQSo PhieNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6Document19 pagesLesson 6selma maziliNo ratings yet
- Sexual Orientation 1Document22 pagesSexual Orientation 1gmfletchNo ratings yet
- Benjamin Dent Arrest Press ReleaseDocument2 pagesBenjamin Dent Arrest Press ReleaseRyan GraffiusNo ratings yet
- Paxson Renee Research EssayDocument10 pagesPaxson Renee Research Essayapi-549210193No ratings yet
- Debate RebuttDocument3 pagesDebate RebuttDaniel Klint Richter CareNo ratings yet
- A. Laws That Led To The Implementation of Gender and Society in The College CurriculaDocument11 pagesA. Laws That Led To The Implementation of Gender and Society in The College CurriculaMaria Ana Velez CruzNo ratings yet
- Spill and Pride March Program FlowDocument1 pageSpill and Pride March Program FlowCharys KasanNo ratings yet
- Dr. Romualdo A. BernalDocument9 pagesDr. Romualdo A. BernalChristian SabaterNo ratings yet
- Gender Roles in Western and Eastern CultureDocument1 pageGender Roles in Western and Eastern CultureSulfan TabraniNo ratings yet