Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Muscles Involved in Swallowing: Function
Uploaded by
Ericka LingaroOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Muscles Involved in Swallowing: Function
Uploaded by
Ericka LingaroCopyright:
Available Formats
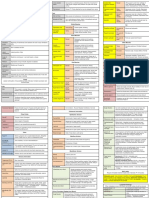
Muscles Involved in Swallowing
Innervated by Muscle Function
Obicularis oris * Seal lips/mouth Part of musculature
V ‘sling’ to create
Trigeminal (S)
Facial
Tense
cheek
to
maintain
food
btwn
molars
tone
necessary
for
VII
Buccinator
*
Help
close
mouth
positive
pressure
Facial
(M)
Active
during
sucking
buildup
during
bolus
propulsion
Temporalis
Retract
mandible
Raise
mandible
to
Masseter
CLOSE
jaw
Masticatory
V
Medial
pterygoid
Brace
mandible
Trigeminal
Lower
mandible
to
OPEN
jaw
Lateral
pterygoid
Protrude
mandible
Rotary
motion
of
jaw
Superior
Curl
tongue
tip/sides
longitudinal
up
Intrinsic
Tongue
Shorten
tongue
Inferior
Curl
tongue
tip/sides
XII
longitudinal
down
Hypoglossal
Narrow
&
Lengthen
Transversus
(Occupy
same
tongue
space
in
tongue;
Bolus
prep,
Widen
&
Flatten
Verticalis
fibers
interlace)
formation,
tongue
positioning,
Hyoglossus
Pull
tongue
back
transport
toward
hyoid
bone
XII
Genioglossus
Protrude
tongue
Extrinsic
Lower
tongue
Hypoglossal
Styloglossus
Raise
&
Retract
tongue
IX
Raise
floor
of
tongue
to
approx
tongue
to
Glossopharyng
Palatoglossus
*
palatoglossal
arch
to
close
off
oropharynx
XII
Hypoglossal
Geniohyoid
Protract
hyoid
Lower
mandible
Raise
&
Stabilize
Mylohyoid
Raise
&
Stabilize
Suprahyoid
V tongue, mouth floor
hyoid
Trigeminal Anterior belly
of digastric Lower mandible to OPEN jaw WHILE hyoid Depress mandible
Posterior belly is held in place to OPEN jaw
VII of digastric
Facial Retract hyoid
Stylohyoid
Lengthen mouth floor
Omohyoid
Infrahyoid
XII Pull mandible
Thyrohyoid Raise thyroid cartilage/larynx to hyoid
Hypoglossal inferiorly to
Sternohyoid Lower thyroid cartilage OPEN jaw
Lower hyoid
Sternothyroid
SpeechRamblings.weebly.com
Muscles Involved in Swallowing
V
Trigeminal
Tensor veli palatini Tense soft palate
X
Levator
veli
palatini
*
Raise
&
Retract
soft
palate
Elevate
&
Retract
palate
to
assist
w/VP
closure
and
seal
back
oral
Vagus
Palatal
cavity
Palatoglossus
*
Raise
posterior
tongue
XII
Lower
and
pull
forward
soft
palate
to
contact
back
of
tongue
Hypoglossal
Seal
back
oral
cavity
from
oropharynx
via
VP
closure
Uvular
Raise
uvula
Brace
soft
palate
Thyroarytenoid
Regulate
tension
of
VF
Transverse
arytenoid
Oblique
Adduct
VF
Adduct
false
folds
X
arytenoid
Laryngeal
Recurrent
Lateral
laryngeal
cricoarytenoid
branch
of
Posterior
Vagus
ABduct
VF
(at
end
of
swallow)
cricoarytenoid
Interarytenoid
Approximate
arytenoids
to
epiglottis
Aryepiglottic
Lower
epiglottis
Thyroepiglottic
V
Cricopharyngeus
Relax
UES
to
allow
passage
of
bolus
(Vagus)
IX
Stylopharyngeus
Glossopharyng
Raise
&
Shorten
Palatopharyngeus
*
Lower
palate
pharynx
Raise
&
Retract
palate
to
assist
w/VP
closure
and
seal
oral
cavity
Raise
larynx
Pharyngeal
Salpingopharyngeus
XI
(Accessory)
Raises
soft
palate
to
seal
nasopharynx
Superior
pharyngeal
Part
of
musculature
‘sling’
to
create
tone
constrictor
*
necessary
for
positive
pressure
buildup
Narrow
pharyngeal
during
bolus
propulsion
lumen
X
Middle
pharyngeal
Vagus
constrictor
Bolus
transport
XI
Inferior
pharyngeal
(Distalmost
component
of
PES)
(Accessory)
constrictor
- Muscles involved in creating pressure for bolus propulsion are indicated with *
- All of the floor of the mouth muscles (geniohyoid, mylohyoid, anterior belly of digastric) attach to
the body of the mandible anteriorly and the body of the hyoid posteriorly
- Intrinsic muscles are within the tongue only. Extrinsic muscles attach to part of the skeleton
SpeechRamblings.weebly.com
You might also like
- Anatomy of Tongue and Its Applied Aspects: Presented By: Niti SarawgiDocument77 pagesAnatomy of Tongue and Its Applied Aspects: Presented By: Niti SarawgideepNo ratings yet
- Micro To MACRO Mathematical Modelling in Soil Mechanics (Trends in Mathematics)Document407 pagesMicro To MACRO Mathematical Modelling in Soil Mechanics (Trends in Mathematics)Renova HnNo ratings yet
- Stuart Jay Raj - Thai Consonant Map Full 2.2 PDFDocument2 pagesStuart Jay Raj - Thai Consonant Map Full 2.2 PDFJorge Guerrero100% (1)
- Yanson V Svistun S A Practical Guide For Learners of English PDFDocument365 pagesYanson V Svistun S A Practical Guide For Learners of English PDFЮлия Шершак100% (1)
- The Oral CavityDocument55 pagesThe Oral CavityMeren NagaNo ratings yet
- Digestion and Absorption: A Breakdown of the Digestive System and ProcessDocument2 pagesDigestion and Absorption: A Breakdown of the Digestive System and ProcessRiya BhardwajNo ratings yet
- 2.visual ArtsDocument78 pages2.visual ArtsNelson VergaraNo ratings yet
- MHC-GPX33 55 77 88Document1 pageMHC-GPX33 55 77 88Juliana Ribeiro100% (6)
- Language Learning Enhanced by Music and SongDocument7 pagesLanguage Learning Enhanced by Music and SongNina Hudson100% (2)
- Myofunctional Orthodontic Evaluation FormDocument1 pageMyofunctional Orthodontic Evaluation FormSurya DinataNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Business ManagementDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Business ManagementZintle Mini0% (1)
- Identify The Boundaries of The Infratemporal FossaDocument7 pagesIdentify The Boundaries of The Infratemporal FossaHARSHDESAI56929640No ratings yet
- B&A Performance AnalysisDocument16 pagesB&A Performance AnalysisNathalia Caroline100% (1)
- Icon-Architects Executive Profile - For HealthcareDocument14 pagesIcon-Architects Executive Profile - For HealthcareMuhammad Noshad RizviNo ratings yet
- SWOT ANALYSIS - Docx Sime DarbyDocument9 pagesSWOT ANALYSIS - Docx Sime Darbynur azfarinie ruzliNo ratings yet
- Canine Radiographs by Louisa White: Click Skeleton To EnterDocument455 pagesCanine Radiographs by Louisa White: Click Skeleton To EnteranacampsNo ratings yet
- Neuro AssessmentDocument3 pagesNeuro AssessmentTori RolandNo ratings yet
- Musculos ParaproteticosDocument63 pagesMusculos Paraproteticosestefania100% (2)
- 1562229628974192Document33 pages1562229628974192Phuong NgocNo ratings yet
- Miñano - (OS 204) PN 5 - Oral Cavity and PalateDocument2 pagesMiñano - (OS 204) PN 5 - Oral Cavity and PalateMarion Rodelle MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Murphy Manuver SLIDEDocument14 pagesMurphy Manuver SLIDEAmini GalilaNo ratings yet
- Oral Cavity (Mouth Cavity) : Dr. Aymen Ahmed Warille DR Moahip MohamedDocument57 pagesOral Cavity (Mouth Cavity) : Dr. Aymen Ahmed Warille DR Moahip MohamedNada MohammedNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of FeedingDocument17 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of FeedingConsueloNo ratings yet
- DraftDocument4 pagesDraftroyal renjunNo ratings yet
- Infra Temporal FossaDocument7 pagesInfra Temporal FossaНемосјановић ЋудмилаNo ratings yet
- Infratemporalfossa PpsDocument7 pagesInfratemporalfossa PpsНемосјановић ЋудмилаNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 VocabularyDocument9 pagesUnit 1 VocabularyAlex PinelNo ratings yet
- Temporomandibular Joint Anatomy and DisordersDocument30 pagesTemporomandibular Joint Anatomy and DisordersRonny Araya AbarcaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - English ConsonantsDocument5 pagesLecture 3 - English ConsonantsAtul JaniNo ratings yet
- Teeth Anatomy2Document33 pagesTeeth Anatomy2Omar RamadanNo ratings yet
- Mouth Tongue and Salivary GlandsDocument52 pagesMouth Tongue and Salivary GlandsIrfan FalahNo ratings yet
- A16 Digestion and Absorption Biology NotesDocument1 pageA16 Digestion and Absorption Biology Notesservoculus machatteNo ratings yet
- Miñano - (OS 204) PN 1 - Anatomy of FaceDocument2 pagesMiñano - (OS 204) PN 1 - Anatomy of FaceMarion Rodelle MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Trans Savi Oto Lec 07 Anatomy and Physiology of Oral Cavity and Pharynx 1st SemDocument16 pagesTrans Savi Oto Lec 07 Anatomy and Physiology of Oral Cavity and Pharynx 1st SemJoherNo ratings yet
- 2-Places of ArticulationDocument1 page2-Places of ArticulationEjub BašićNo ratings yet
- (PLM) Oral Cavity Salivary Glands Pharynx and EsophagusDocument9 pages(PLM) Oral Cavity Salivary Glands Pharynx and EsophagusJovilyn SilongaNo ratings yet
- Deleterious Effects of Oral Habits: A ReviewDocument4 pagesDeleterious Effects of Oral Habits: A ReviewDrshubhankar Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- New Phonetics PresentationDocument16 pagesNew Phonetics PresentationAryNo ratings yet
- Tongue AnatomyDocument3 pagesTongue Anatomykaruparthi sripravallikaNo ratings yet
- Miñano - (OS 204) PN 1 - Anatomy of FaceDocument2 pagesMiñano - (OS 204) PN 1 - Anatomy of FaceMarion Rodelle MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Introduction To Linguistics (FINAL TERM)Document7 pagesReviewer in Introduction To Linguistics (FINAL TERM)Aira MaeNo ratings yet
- Asan Tajweed BookDocument26 pagesAsan Tajweed BookIrfan KarigarNo ratings yet
- Speech Organs and Their Functions: Chapter - 5 PhoneticsDocument6 pagesSpeech Organs and Their Functions: Chapter - 5 PhoneticsDadaso KhotNo ratings yet
- EmocijeDocument2 pagesEmocijeDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- TONGUE Seminar by MeDocument84 pagesTONGUE Seminar by MeArpita SankhwarNo ratings yet
- Digestive System PearsonDocument179 pagesDigestive System PearsonJan Jesty CaiquetNo ratings yet
- Oral CavityDocument57 pagesOral CavityArif NabeelNo ratings yet
- Ortho 5Document4 pagesOrtho 5Helpers 48No ratings yet
- Concepto Castillo MoralesDocument7 pagesConcepto Castillo MoralesOdontoEspecialNo ratings yet
- 7 Neutral ZoneDocument32 pages7 Neutral Zoneفاطمة الجش.No ratings yet
- Digestive System With HighlightsDocument177 pagesDigestive System With HighlightsReinand Joseff ServanoNo ratings yet
- Digestion and AbsorptionDocument48 pagesDigestion and AbsorptionOm SambheNo ratings yet
- Mela Restania (372015002) Phonetics and PhonologyDocument17 pagesMela Restania (372015002) Phonetics and PhonologymellaNo ratings yet
- Oral CavityDocument105 pagesOral CavityAisha AbbasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To LanguageDocument137 pagesIntroduction To LanguagecobbyNo ratings yet
- HO1 Pedia Milestones GD Page 1Document2 pagesHO1 Pedia Milestones GD Page 1Cheng BautistaNo ratings yet
- IPA Chart for Spanish and PortugueseDocument1 pageIPA Chart for Spanish and PortugueseuclabruintizedNo ratings yet
- Akash Tongue FinalDocument74 pagesAkash Tongue FinalSuraj kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Taping in Pediatrics: Prior To Taping Orbicularis Oris Taping AppliedDocument2 pagesTaping in Pediatrics: Prior To Taping Orbicularis Oris Taping AppliedSatishNo ratings yet
- Explanation of PicturesDocument3 pagesExplanation of PicturesFebriani SNFLHNo ratings yet
- The Five Stages of Language Acquisition: PreproductionDocument9 pagesThe Five Stages of Language Acquisition: Preproductioneduardo menesesNo ratings yet
- Digestion and Absorption by DR Yogesh Swami Nur 1Document45 pagesDigestion and Absorption by DR Yogesh Swami Nur 1chiragm1408No ratings yet
- H, NDocument20 pagesH, NNada Atef KoraitemNo ratings yet
- Consonants Place of ArticulationDocument3 pagesConsonants Place of ArticulationPenelope Selinee LopezNo ratings yet
- Muscles of TongueDocument19 pagesMuscles of TongueShalini SinghNo ratings yet
- Alveolingual SulcusDocument8 pagesAlveolingual SulcusMrinmayee ThakurNo ratings yet
- The MouthDocument13 pagesThe MouthAjigotto ubiq.No ratings yet
- PESTLE analysis of M&S UK retail challengesDocument1 pagePESTLE analysis of M&S UK retail challengesMac Corleone0% (1)
- Name of Student: Ayush Soni Sap Id: 1000012241Document2 pagesName of Student: Ayush Soni Sap Id: 1000012241Ayush SoniNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Stabilized MaterialDocument11 pages2.3 Stabilized MaterialMamush LetaNo ratings yet
- Cyber Crime and Law ClassDocument99 pagesCyber Crime and Law ClassMohd ShifanNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Agricultural Technology Second Semester Horticulture 1 Pre-TestDocument4 pagesBachelor of Agricultural Technology Second Semester Horticulture 1 Pre-TestBaby G Aldiano Idk100% (1)
- Importance of Education: March 2015Document4 pagesImportance of Education: March 2015AswiniieNo ratings yet
- Antianginal Student222Document69 pagesAntianginal Student222MoonAIRNo ratings yet
- Covid19-Drug StudyDocument7 pagesCovid19-Drug StudynicoleNo ratings yet
- 527880193-Interchange-2-Teacher-s-Book 2-331Document1 page527880193-Interchange-2-Teacher-s-Book 2-331Luis Fabián Vera NarváezNo ratings yet
- Form of Bid SecurityDocument3 pagesForm of Bid SecurityKrishna EelaNo ratings yet
- Grade 1 Mother Tongue SyllabusDocument3 pagesGrade 1 Mother Tongue SyllabusDorz EDNo ratings yet
- AISD Fees Structure for 2023-24 Academic YearDocument2 pagesAISD Fees Structure for 2023-24 Academic YearKawsar AlamNo ratings yet
- Milking MachineDocument10 pagesMilking Machineuniversaldairy100% (2)
- Improving Oil Recovery with EOR/IOR MethodsDocument1 pageImproving Oil Recovery with EOR/IOR MethodsMuhammad Fawwad ObaidaNo ratings yet
- MalayoDocument39 pagesMalayoRoxanne Datuin UsonNo ratings yet
- BRI Divisions and Branches Level ReportDocument177 pagesBRI Divisions and Branches Level ReportCalvin Watulingas100% (1)
- Virtualization Types: OS, Hardware Emulation, and ParavirtualizationDocument7 pagesVirtualization Types: OS, Hardware Emulation, and ParavirtualizationvinoopnvNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - DynamicsDocument8 pagesChapter 2 - DynamicsTHIÊN LÊ TRẦN THUẬNNo ratings yet
- Press Release-HandoverDocument2 pagesPress Release-HandovermoblogNo ratings yet
- Speidel, M. O. (1981) - Stress Corrosion Cracking of Stainless Steels in NaCl Solutions.Document11 pagesSpeidel, M. O. (1981) - Stress Corrosion Cracking of Stainless Steels in NaCl Solutions.oozdemirNo ratings yet
- Cut Nyak Dhien: Aceh's Legendary Resistance LeaderDocument5 pagesCut Nyak Dhien: Aceh's Legendary Resistance LeaderKhoerudin KhoerudinNo ratings yet