Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1.1.power Plant Layout
Uploaded by
BALAMBAL ROriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1.1.power Plant Layout
Uploaded by
BALAMBAL RCopyright:
Available Formats
19ME310T POWERPLANT ENGINEERING
UNIT-I THERMAL POWER PLANTS
Layout of modern coal power plant, Subsystems of thermal power plants Fuel and ash
handling, mechanical stokers, pulverisers, condensers, draught system, feed water
treatment, Heat recovery equipment - Economizers, air pre heaters and re-heaters, super
heaters and de-super heaters- Binary Cycles.
Introduction
Steam is an important medium of producing mechanical energy. Steam has the
advantage that, it can be raised from water which is available in abundance it does not react
much with the materials of the equipment of power plant and is stable at the temperature
required in the plant. Steam is used to drive steam engines, steam turbines etc. Steam power
station is most suitable where coal is available in abundance. Thermal electrical power
generation is one of the major method. Out of total power developed in India about 60% is
thermal. For a thermal power plant the range of pressure may vary from 10 kg/cm 2 to super
critical pressures and the range of temperature may be from 250°C to 650°C. The average all
India Plant load factor (P.L.F.) of thermal power plants in 1987-88 has been worked out to be
56.4% which is the highest P.L.F. recorded by thermal sector so far.
LAYOUT OF MODERN COAL POWER PLANT
A steam power plant must have following equipments :
1. A furnace to burn the fuel.
2. Steam generator or boiler containing water. Heat generated in the furnace is utilized to
convert water in steam.
3. Main power unit such as an engine or turbine to use the heat energy of steam and perform
work.
4. Piping system to convey steam and water. In addition to the above equipment the plant
requires various auxiliaries and accessories depending upon the availability of water, fuel and
the service for which the plant is intended.
Velammal Engineering College
19ME310T POWERPLANT ENGINEERING
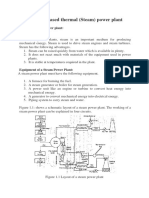
Fig.1.1 Modern thermal power plant layout
The flow sheet of a thermal power plant consists of the following four main circuits :
(i) Feed water and steam flow circuit
(ii) Coal and ash circuit
(iii) Air and gas circuit
(iv) Cooling water circuit.
A steam power plant using steam as working substance works basically on Rankine cycle.
Steam is generated in a boiler, expanded in the prime mover and condensed in the condenser
and fed into the boiler again.
The different types of systems and components used in steam power plant are as follows :
(i) High pressure boiler
(ii) Prime mover
(iii) Condensers and cooling towers
(iv) Coal handling system
Velammal Engineering College
19ME310T POWERPLANT ENGINEERING
(v) Ash and dust handling system
(vi) Draught system
(vii) Feed water purification plant
(viii) Pumping system
(ix) Air preheater, economizer, super heater, feed heaters.
Fig. 1.1 shows a schematic arrangement of equipment of a steam power station. Coal
received in coal storage yard of power station is transferred in the furnace by coal handling
unit. Heat produced due to burning of coal is utilized in converting water contained in boiler
drum into steam at suitable pressure and temperature. The steam generated is passed through
the superheater. Superheated steam then flows through the turbine. After doing work in the
turbine die pressure of steam is reduced. Steam leaving the turbine passes through the
condenser which maintain the low pressure of steam at the exhaust of turbine. Steam pressure
in the condenser depends upon flow rate and temperature of cooling water and on effectiveness
of air removal equipment. Water circulating through the condenser may be taken from the
various sources such as river, lake or sea. If sufficient quantity of water is not available the hot
water coming out of the condenser may be cooled in cooling towers and circulated again
through the condenser. Bled steam taken from the turbine at suitable extraction points is sent to
low pressure and high pressure water heaters.
Air taken from the atmosphere is first passed through the air pre-heater, where it is heated by
flue gases. The hot air then passes through the furnace. The flue gases after passing over boiler
and superheater tubes, flow through the dust collector and then through economiser, air pre-
heater and finally they are exhausted to the atmosphere through the chimney.
Steam condensing system consists of the following:
(i) Condenser
(ii) Cooling water
(iii) Cooling tower
(iv) Hot well
(v) Condenser cooling water pump
(vi) Condensate air extraction pump
(vii) Air extraction pump
Velammal Engineering College
19ME310T POWERPLANT ENGINEERING
(viii) Boiler feed pump
(ix) Make up water pump.
A steam power plant using steam as working substance works basically on Rankine cycle.
1. Coal and ash circuit
2. Air and gas circuit
3. Feed water and steam flow circuit
4. Cooling water circuit.
1. Coal and ash circuit
In this circuit, the coal from the storage is fed to the boiler through coal handling
equipment for the generation of steam. Ash produced due to the combustion of coal is
removed to ash storage through ash-handling system.
2. Air and Gas circuit
Air is supplied to the combustion chamber of the boiler either through F.D or I.D
or by using both. The dust from the air is removed before supplying to the combustion
chamber.
The exhaust gases carrying sufficient quantity of heat and ash are passed through
the air-heater where the exhaust heat of the gases is given to the air and then it is passed
through the dust collectors where most of the dust is removed before exhausting the
gases to the atmosphere through chimney.
3. Feed water and Steam circuit
The steam generated in the boiler is fed to the steam prime mover to develop the
power. The steam coming out of prime mover is condensed in the condenser and then fed
to the boiler with the help of the pump.
The condensate is heated in the feed-heaters using the steam tapped from
different points of the turbine. The feed heaters may be of mixed type or indirect heating
type.
Some of the steam and water is lost passing through different components of the
system; therefore, feed water is supplied from external source to compensate this loss.
The feed water supplied from external sourced is passed through the purifying plant to
reduce the dissolved salts to an acceptable level. The purification is necessary to avoid
the scaling of the boiler tubes.
4. Cooling water circuit
The quantity of cooling water required to condense the steam is considerably large and it
is taken either from lake, river or sea. The cooling water is taken from the upper side of
Velammal Engineering College
19ME310T POWERPLANT ENGINEERING
the river, it is passed through the condenser and heated water is discharged to the lower
side of the river. Such system of cooling water supply is possible if adequate cooling
water is available throughout the year. This system is known as open system.
When the adequate water is not available, them the water coming out from the
condenser is cooled either in cooling pond or cooling tower. The cooling is effected by
partly evaporating the water. This evaporative loss is nearly 2 to 5% of the cooling water
circulated in the system.
To compensate the evaporative loss, the water from the river is continuously
supplied. When the cooling water coming out of the condenser is cooled again and
supplied to the condenser is cooled again and supplied to the condenser then the system
is known as closed system.
When the water coming out from the condenser is discharged to river downward
side directly, the system is known as open system. Open system is economical than
closed system provided adequate water is available throughout the year.
Working of the thermal power
Steam is generated in the boiler of thermal power plant using the heat of the fuel
burned in the combustion chamber. The steam generated is passed through steam turbine
where part of its thermal energy is converted into mechanical energy which is further used
for generating electric power.
Merits:
(i) Higher efficiency
(ii) Lower cost
(iii) Ability to burn coal especially of high ash content, and inferior coals.
(iv) Reduced environmental impact in terms of air pollution
(v) Reduced water requirement
(vi) Higher reliability and availability
Demerits:
(i) There are more chances of explosion as coal burns like a gas
(ii) Coal transportation is quite complicated.
Velammal Engineering College
You might also like
- Boiler Operation Engineer Exam, Interview Q&A, Terminology, and Boiler OverviewFrom EverandBoiler Operation Engineer Exam, Interview Q&A, Terminology, and Boiler OverviewNo ratings yet
- Jagan Steam Power PlantDocument101 pagesJagan Steam Power PlantMahender VangalaNo ratings yet
- Construction and Working of Thermal Power PlantDocument5 pagesConstruction and Working of Thermal Power Plantdibyenindus100% (1)
- Power Plant FamiliarisationDocument110 pagesPower Plant FamiliarisationmrdipakwaghNo ratings yet
- Boiler Emergency OperationsDocument2 pagesBoiler Emergency OperationsAnudeep Chittluri67% (3)
- Thermal Power PlantDocument27 pagesThermal Power Plantvenki249100% (1)
- Thermal Power PlantsDocument24 pagesThermal Power Plantslakshmigsr6610100% (1)
- Report #1: Alternating-Current Project: Steam-Electric Power PlantDocument41 pagesReport #1: Alternating-Current Project: Steam-Electric Power PlantKian TecsonNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power Plant Project ReportDocument63 pagesThermal Power Plant Project Reportasutoshjena28171% (24)
- NTPC Training ReportDocument83 pagesNTPC Training Reportpankajpnd1100% (1)
- Code: Btpp/Turbine/007/Vacuum Raising Guidelines For Condenser Vacuum Raising PreconditionDocument5 pagesCode: Btpp/Turbine/007/Vacuum Raising Guidelines For Condenser Vacuum Raising PreconditionPrakash ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power Generation Plant or Thermal Power StationDocument157 pagesThermal Power Generation Plant or Thermal Power Stationgteklay100% (1)
- Valve Schedule PDFDocument119 pagesValve Schedule PDFAmit Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Gajendra KumarDocument23 pagesGajendra KumarGAJENDRA KUMARNo ratings yet
- Steam Drum LevelsDocument11 pagesSteam Drum LevelsAnith kumar Reddy100% (1)
- Thermal Power Plant - EeDocument20 pagesThermal Power Plant - EePrabhat Chandra100% (1)
- Steam Turbine Stop Valve TestingDocument22 pagesSteam Turbine Stop Valve TestingAbdulyunus Amir100% (3)
- 2013edusat Lecture On STEAM PLANTDocument101 pages2013edusat Lecture On STEAM PLANTKishore KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Steam PlantDocument102 pagesSteam PlantPrakhar Shukla100% (1)
- Mechanical Engineering Project - Thermal Power Plant Study - WWW - Amie.nbcafe - inDocument24 pagesMechanical Engineering Project - Thermal Power Plant Study - WWW - Amie.nbcafe - inbtdoss72100% (1)
- Mannual Thermal Engineering Lab-IIDocument75 pagesMannual Thermal Engineering Lab-IIShivansh Bajpai100% (1)
- Thermal Power PlantDocument35 pagesThermal Power PlantAngelaa DassNo ratings yet
- 01 Properties of SteamDocument35 pages01 Properties of SteamDeepanshu Sehgal100% (1)
- Thermal Power Plants (Steam Power Plants) : Instructor: Engr. Intisar Ali SajjadDocument51 pagesThermal Power Plants (Steam Power Plants) : Instructor: Engr. Intisar Ali SajjadVishal PatelNo ratings yet
- Steam Power Plant and BoilersDocument101 pagesSteam Power Plant and Boilersjamunaa83100% (1)
- Unit - 1 Coal Based Thermal Power Plants Layout of Thermal Power Plant and Its Working PrincipleDocument154 pagesUnit - 1 Coal Based Thermal Power Plants Layout of Thermal Power Plant and Its Working PrincipleMadhu Mitha100% (1)
- Header & Piping SizingDocument9 pagesHeader & Piping Sizingmedicbest0% (1)
- Thermodynamic analysis of geothermal heat pumps for civil air-conditioningFrom EverandThermodynamic analysis of geothermal heat pumps for civil air-conditioningRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Introduction To CFPPDocument34 pagesIntroduction To CFPPVenkat CherukuriNo ratings yet
- Steam Power PlantDocument7 pagesSteam Power PlantsuganyaNo ratings yet
- Dry Cooling Systems1.2Document40 pagesDry Cooling Systems1.2paragmishra1986No ratings yet
- Power Plant EngineeringDocument74 pagesPower Plant EngineeringPranesh Ka100% (1)
- Unit - I Steam Power PlantsDocument32 pagesUnit - I Steam Power Plantsrsankarganesh MECH-HICET100% (1)
- PP 9th Meeting GENERATING STATIONS Thermal Power PlantDocument5 pagesPP 9th Meeting GENERATING STATIONS Thermal Power PlantJohn Kenneth LoricoNo ratings yet
- Thermal EngineeringDocument10 pagesThermal Engineeringlokeshdhangar842No ratings yet
- EXP-1 Steam Power PlantDocument7 pagesEXP-1 Steam Power PlantsejalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electrical Power Systems: by K.rajendraDocument101 pagesIntroduction To Electrical Power Systems: by K.rajendrak rajendraNo ratings yet
- Physics 4.Document5 pagesPhysics 4.SOLAIMANNo ratings yet
- T Project ReportDocument63 pagesT Project ReportArif AhmadNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power StationDocument6 pagesThermal Power StationAnkit RajNo ratings yet
- Steam Power PlantDocument6 pagesSteam Power PlantKarthikn AltocNo ratings yet
- Ukai Thermal Power Plant-Eman Refai Abdelkhaliq-Sec 3Document13 pagesUkai Thermal Power Plant-Eman Refai Abdelkhaliq-Sec 3eman.refai13lcsNo ratings yet
- Expt. # 03 Study of A Steam Turbine Power PlantDocument6 pagesExpt. # 03 Study of A Steam Turbine Power PlantSajeeb SarkerNo ratings yet
- Lecture No 3Document4 pagesLecture No 3Musa KhanNo ratings yet
- Exp 1Document7 pagesExp 1HR HabibNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil and Mechanical Engineering Unit III Classification of Power PlantsDocument21 pagesBasic Civil and Mechanical Engineering Unit III Classification of Power PlantsSiman NapstervkkNo ratings yet
- Hydroelectric Power Plants Convert Power PlantDocument4 pagesHydroelectric Power Plants Convert Power Plantuikeshekhar610No ratings yet
- Jaipur: Vivekananda Institute of TechnologyDocument29 pagesJaipur: Vivekananda Institute of TechnologyAashish SangwanNo ratings yet
- CoalDocument48 pagesCoallekoringoeNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power PlantDocument31 pagesThermal Power PlantfefwerewNo ratings yet
- Jaipur: Vivekananda Institute of TechnologyDocument29 pagesJaipur: Vivekananda Institute of TechnologyAnonymous ytZsBOVNo ratings yet
- Me Lab 3Document27 pagesMe Lab 3Jerome Vega AndesNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power PlantDocument29 pagesThermal Power PlantSiri VenniNo ratings yet
- Selections of Powerplants LocationDocument4 pagesSelections of Powerplants LocationMostafa GadelrabNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Engineering MTPP-1Document13 pagesPower Plant Engineering MTPP-1devendra pratapNo ratings yet
- Rohini 86450143586Document8 pagesRohini 86450143586Anksupriya BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Cycles:: Unit I Thermal Power PlantsDocument33 pagesThermodynamic Cycles:: Unit I Thermal Power PlantsbernabasNo ratings yet
- Us DixitDocument10 pagesUs Dixitmusu MukeshNo ratings yet
- Site Selection For Thermal Power PlantDocument3 pagesSite Selection For Thermal Power PlantNehaKashyapNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power Plant: Shubham Thakur 13BME8149 5MEL3 Mechanical EngineeringDocument34 pagesThermal Power Plant: Shubham Thakur 13BME8149 5MEL3 Mechanical EngineeringMos MohNo ratings yet
- + Air Fig.1. Production of Electrical Energy by Steam Power Plant Exhaust SteamDocument38 pages+ Air Fig.1. Production of Electrical Energy by Steam Power Plant Exhaust Steamsrihari_bhadabhagniNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power Plant Diagram All You Need To Know About ItDocument7 pagesThermal Power Plant Diagram All You Need To Know About Itngoc hoangNo ratings yet
- Class 4. Steam Power PlantDocument37 pagesClass 4. Steam Power PlantsureshlalNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power PlantDocument7 pagesThermal Power PlantMamta SinghNo ratings yet
- Generation of Electric PowerDocument108 pagesGeneration of Electric Powermausam sharmaNo ratings yet
- 38 Thermal Power PlantDocument26 pages38 Thermal Power PlantSwaraj TodankarNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesFrom EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesNo ratings yet
- Lubrication System of An I.C. EngineDocument6 pagesLubrication System of An I.C. EngineBALAMBAL RNo ratings yet
- Fig.17 Steps in Coal HandlingDocument6 pagesFig.17 Steps in Coal HandlingBALAMBAL RNo ratings yet
- Theories of Combustion in SI EngineDocument4 pagesTheories of Combustion in SI EngineBALAMBAL RNo ratings yet
- Part-C (5 X 14 70 Marks)Document4 pagesPart-C (5 X 14 70 Marks)BALAMBAL RNo ratings yet
- Hoken Boiler 2015 CatalogueDocument8 pagesHoken Boiler 2015 CatalogueJose Lorenzo Toral100% (1)
- Steam Boiler Telugu NotesDocument10 pagesSteam Boiler Telugu Notesavksk22100% (6)
- Reheater 1 Upper Weld Location Sketch (Section B-B) Project: Kusile Power StationDocument14 pagesReheater 1 Upper Weld Location Sketch (Section B-B) Project: Kusile Power StationBranko FerenčakNo ratings yet
- Boiler Checklist ReportDocument4 pagesBoiler Checklist ReportgedearthanaNo ratings yet
- Hydro Test Valves S.N Valve Valve Name BMD/TMD Emd C and I OPN Remark SDocument4 pagesHydro Test Valves S.N Valve Valve Name BMD/TMD Emd C and I OPN Remark Sritesh agarwalNo ratings yet
- Types - Of.boilers Draught Thermal - PlantDocument11 pagesTypes - Of.boilers Draught Thermal - PlantPraveen PandeyNo ratings yet
- Steam EnginesDocument1 pageSteam Enginesmember1000No ratings yet
- IBR FormsDocument204 pagesIBR FormsRajivharolikarNo ratings yet
- John Thompson Boiler Development and Training CentreDocument2 pagesJohn Thompson Boiler Development and Training CentreMohit ComputerNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1-To Study Cochran and Babcock and Wilcox BoilersDocument8 pagesExperiment No. 1-To Study Cochran and Babcock and Wilcox BoilersShahedNo ratings yet
- OM Power StationsDocument95 pagesOM Power StationsAditi SinghNo ratings yet
- BoilersDocument8 pagesBoilersKarthiKeyanNo ratings yet
- Feedwater Heater - Regeneration Analysis - HandbookDocument19 pagesFeedwater Heater - Regeneration Analysis - HandbookAnonymous wIPMQ5rhNo ratings yet
- Railwaylocomotiv 36 NewyuoftDocument426 pagesRailwaylocomotiv 36 NewyuoftKrishna VamsiNo ratings yet
- BinderDocument1 pageBinderRajni GargNo ratings yet
- Original Biography of Richard TrevithickDocument3 pagesOriginal Biography of Richard TrevithickracbabyNo ratings yet
- Signal List Aux BoilerDocument1 pageSignal List Aux BoilerMd.Jahangir alamNo ratings yet
- SGT PDFDocument383 pagesSGT PDFDushyanthkumar DasariNo ratings yet
- Manajemen Resiko Kegagalan Pada Proses Start Up Boiler Dan Turbin Di Pltu Krakatau Daya Listrik Dengan Enterprise Risk ManagementDocument8 pagesManajemen Resiko Kegagalan Pada Proses Start Up Boiler Dan Turbin Di Pltu Krakatau Daya Listrik Dengan Enterprise Risk ManagementDewi Nurul AuliaNo ratings yet
- Questions and AnswersDocument22 pagesQuestions and AnswersMuhammad NasimNo ratings yet
- Lesson 05 - Main Steam CycleDocument20 pagesLesson 05 - Main Steam CycleAlvaro ObispoNo ratings yet
- Unit: Pltu Bolok Area: UNIT #1 Equipment Standard Measurement Point Unit Minggu 1 Minggu 2 Minggu 3 Minggu 4 StatusDocument18 pagesUnit: Pltu Bolok Area: UNIT #1 Equipment Standard Measurement Point Unit Minggu 1 Minggu 2 Minggu 3 Minggu 4 StatusAchmad Zaki MubarokNo ratings yet