Professional Documents
Culture Documents
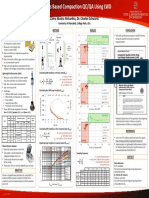
Modulus Based Compaction QC/QA Using LWD: University of Maryland, College Park
Uploaded by
RogelioBecerraFuentesOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Modulus Based Compaction QC/QA Using LWD: University of Maryland, College Park
Uploaded by
RogelioBecerraFuentesCopyright:
Available Formats
See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.
net/publication/332522846
Modulus Based Compaction QC/QA Using LWD
Poster · July 2018
DOI: 10.13140/RG.2.2.36477.20962
CITATIONS READS
0 1,262
1 author:
Zahra Afsharikia
University of Maryland, College Park
8 PUBLICATIONS 116 CITATIONS
SEE PROFILE
Some of the authors of this publication are also working on these related projects:
Transportation Pooled Fund Study TPF-5(285) View project
All content following this page was uploaded by Zahra Afsharikia on 19 April 2019.
The user has requested enhancement of the downloaded file.
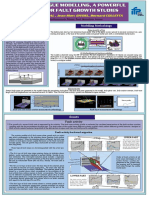
Modulus Based Compaction QC/QA Using LWD
Zahra Niosha Afsharikia, Dr. Charles Schwartz
University of Maryland, College Park, USA
INTRODUCTION METHOD RESULTS CONCLUSION
Nuclear Density Gauge (NDG) Elab at Etarget vs Measure:
1.1
Pass-Pass
ü Two draft specifications prepared in AASHTO format
during the pooled fund study for potential
• Traditional density-based methods multiple compaction q Efield
1.0 implementation:
of compaction quality control MCs in lab curve q MC
ü Measures in-situ density and 0.9
MD5 SG
moisture content (MC)
PC
MD337 GAB
Ø Does not reflect true engineering properties Efield
0.8 NY SG L1
of geomaterial NY SG L2
Etarget 0.7
Ø Does not monitor stiffness gain over time for stabilized MD404 Base
FL Base
or unconventional material Fail-Fail
0.6
Ø High costs and regulations associated with the 0.0 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0
radiation safe storage, transportation, and operation Efield/Etarget, Zorn LWD
Lightweight Deflectometer (LWD) Calculating LWD modulus on Proctor mold (Elab)
1.1
ü Measures surface deflection under applied v = Poisson’s ratio Pass-Pass
load, then calculates soil surface modulus ⎛ 2υ ⎞ 4H
2
H = height of the mold 1.0
Elab = ⎜ 1− ⎟ k D = mold diameter
⎝ 1− υ ⎠ π D
2
ü Safe, fast, and accurate measurements K = soil stiffness =F/δ
0.9
• Does not measure MC
PC
• Challenges: Calculating the LWD target modulus (Etarget) MD5 SG
0.8
1. Different LWD brands’ configurations MD337 GAB
2600 Dry Density 0.73 0.89 1.06 1.23 1.45 200
2. Effect of MC at compaction vs. testing time NY SG L1
0.7
Dry Density [kg/m3]
3. Stress effects NY SG L2
2560
E lab [Mpa]
150 Fail-Fail MD404 Base
4. Layered system effect 0.6
5. Practicality in the field and lab 2520
0.0 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0
100
• Three LWD brands employed in this study: 2480
Efield/Etarget, Olson LWD
Zorn ZFG3000, Dynatest 3031, and Olson LWD-1 1.1
9.4. Avoid placing the hands below the elevated drop weight. 50
2440 Pass-Pass
Falling Max Load Deformation sensor Plate Type of 10.
2400
APPENDIX
0 1.0 ü Maryland Department of Transportation State Highway
weight height cell buffer
LWD
type range type 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Administration funded a follow up study for
[kg] [cm] [-] [-] [mm] [-] [-] MC [%] 0.9 implementation of LWDs and replacing NDGs.
72.4 MD5 SG
PC
Zorn 3000 10
(fix)
No Accelerometer 0.2–30 (±0.02) Solid Spring Calculating LWD modulus on the compacted layer (Efield) MD337 GAB
0.8 REFERENCES
( )
Geophone Annulus
2.5, 5, 83.8 Flat Rubber NY SG L1
Dynatest 3031
10, 15 (adj)
Yes 0–2.2 (±0.002) w/ Plug
(adj) 2ks 1− υ A = stress distribution factor
2
+2 external option E field = r0 = LWD plate radius 0.7 NY SG L2
Olson 01
10 61
Yes
Geophone
0.1–2 (±0.02) Solid Spring
Arof0the two-layer systemkof =subgrade
Figure 1—Schematic
s soil stiffness =F/δ
with modulus in the
E2 overlain field
by base MD404 • Link to the TPF-5(285) pooled fund study final report:
(adj) (adj) + external with modulus E1 Fail-Fail FL Base https://www.pooledfund.org/Details/Study/527
Adjusting target modulus for layered system (Esurface) 0.6
0.0 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 • Implementation of Lightweight Deflectometers (LWDs)
Ohaus Moisture Analyzer Efield/Etarget, Dynatest LWD for Modulus Based Compaction Quality Assurance of
ü Quick MC measurement in the field h = base Layer Thickness
10 Unbound Materials (SHA/UM/4-51)
• Soil sample is quickly heated by an d = field LWD Plate Radius
/ Esubgrade
Sampling frequency
integrated halogen dryer unit s = sample standard deviation CONTACT
2
• Continuously measures the weight ⎛ t.s ⎞ t= value from t-table for each confidence
/ E2
n=⎜ ⎟
(surface)
of the sample level and degree of freedom
⎝ e⎠ Zahra Afsharikia
EtargetEsurface
e= acceptable error
• Takes about 10 to 15 minutes depending on soil type 1
h/d=0.5 Ph.D. Candidate
h/d=1 80% 90% 95% Civil and Environmental Engineering Department
OBJECTIVE h/d=1.5 Parameter Min. Max. Avg. Min. Max. Avg. Min. Max. Avg.
nafshari@umd.edu
h/d=2 5.52 12.51 9.52 5.52 12.51 9.52 5.52 12.51 9.52
Zorn s [MPa]
Provide a straightforward procedure for using LWDs for h/d=2.5
h/d=3
LWD
n 3 13 8 7 30 18 11 50 31 Dr. Charles W. Schwartz
modulus/stiffness-based compaction QC/QA that is h/d=3.5 Dynatest
LWD
s [MPa] 9.73 37.08 23.37 9.73 37.08 23.37 9.73 37.08 23.37 Professor and Chair
9 110 45 19 - 104 30 - -
suitable for practical implementation by field inspection 0.1
0.1 1 10 100 Olson
n
s [MPa] 5.23 16.29 10.76 5.23 16.29 10.76 5.23 16.29 10.76
Civil and Environmental Engineering Department
personnel.
E1 / E2
Etarget (for base) / Esubgrade LWD
n 3 22 10 6 50 23 10 85 40 schwartz@umd.edu
Figure 2—Surface Modulus Correction for Testing on Compacted Base Layer of Finite
Thickness (h = base layer thickness, d = LWD plate radius used during field testing)
RESEARCH POSTER PRESENTATION DESIGN © 2015
www.PosterPresentations.com
View publication stats
You might also like
- ITTO Matrix 6thed MatrixDocument13 pagesITTO Matrix 6thed MatrixGillianiNo ratings yet
- Omcentrifmicroii 3Document100 pagesOmcentrifmicroii 3Emerson PenaforteNo ratings yet
- Safety Integrity Level (SIL)Document1 pageSafety Integrity Level (SIL)UKNo ratings yet
- Design of Slender Tall Buildings For Wind and EarthquakeDocument110 pagesDesign of Slender Tall Buildings For Wind and EarthquakemayasNo ratings yet
- Quester SeriesDocument244 pagesQuester Seriesiskandar rahmanNo ratings yet
- TXDOT Traffic Signal Pole FoundationDocument1 pageTXDOT Traffic Signal Pole FoundationfiercecatNo ratings yet
- Pressure Relief Systems 2014 Rev A PDFDocument118 pagesPressure Relief Systems 2014 Rev A PDFgad480100% (1)
- Epc Epcm ChartDocument1 pageEpc Epcm ChartjcerignaleNo ratings yet
- Concrete Paving Airfield PosterDocument1 pageConcrete Paving Airfield PosterdavidhmoloneyNo ratings yet
- Sample Project DASHBOARD REPORT - 03th October 2022 Construction WEEK No. 26Document1 pageSample Project DASHBOARD REPORT - 03th October 2022 Construction WEEK No. 26moes83No ratings yet
- A Complete Design Flow For Silicon PhotonicsDocument17 pagesA Complete Design Flow For Silicon PhotonicsnowdayNo ratings yet
- Planos 9978Document34 pagesPlanos 9978Omar50% (2)
- Hvac DBR Coca ColaDocument15 pagesHvac DBR Coca ColaPradeep Sukumaran100% (1)
- Failure Mode and Effects Analysis by BoschDocument52 pagesFailure Mode and Effects Analysis by Boschwawawa1100% (1)
- MAINTENANCE & RELIABILITY | Sealing SystemsDocument5 pagesMAINTENANCE & RELIABILITY | Sealing Systemsasimozma100% (1)
- Apd Catalog PDFDocument28 pagesApd Catalog PDFsoo RenNo ratings yet
- OSC 20-0136-067 - Instruction Manual - Ed. 1010Document216 pagesOSC 20-0136-067 - Instruction Manual - Ed. 1010Centrifugal Separator0% (1)
- Lab Analysis: 1. Downhole Fluid SamplingDocument1 pageLab Analysis: 1. Downhole Fluid SamplingSyafiq JaafarNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Operation and Maintenance of Hydropower Plants PDFDocument123 pagesGuidelines For Operation and Maintenance of Hydropower Plants PDFBishal Pokharel100% (1)
- Exfo Reference-Poster 5g-Ran v1 enDocument2 pagesExfo Reference-Poster 5g-Ran v1 enDjnsilva SilvaNo ratings yet
- Method Results Conclusion: Zahra Niosha Afsharikia, Dr. Charles SchwartzDocument1 pageMethod Results Conclusion: Zahra Niosha Afsharikia, Dr. Charles Schwartzfabian jarabaNo ratings yet
- Apex Acd Media Fill - PHXDocument23 pagesApex Acd Media Fill - PHXjaron.huNo ratings yet
- Modelling and Simulation For Warehouses and Supply Chains: Chris Staddon 24 APRIL, 2019Document11 pagesModelling and Simulation For Warehouses and Supply Chains: Chris Staddon 24 APRIL, 2019JonahNo ratings yet
- Micro Data Center Layout, Cable Management, Grounding/Bonding, Power and IDDocument2 pagesMicro Data Center Layout, Cable Management, Grounding/Bonding, Power and IDhgfdfg jhhNo ratings yet
- Data Warehouse Testing PosterDocument2 pagesData Warehouse Testing Postertedi setiadiNo ratings yet
- 2007 AAPS - Poster - High Throughput Solubility AnalysisDocument1 page2007 AAPS - Poster - High Throughput Solubility Analysismr_jpwalsh8941No ratings yet
- 9101f Form2 UlDocument10 pages9101f Form2 UlMiguel RamosNo ratings yet
- Accurate Determination of Catalyst Loading On Glassy Carbon Disk and Its Impact On Thin Film Rotating Disk Electrode For Oxygen Reduction Reaction.Document1 pageAccurate Determination of Catalyst Loading On Glassy Carbon Disk and Its Impact On Thin Film Rotating Disk Electrode For Oxygen Reduction Reaction.Muralidhar ChourashiyaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Packages Electrician Level IIDocument22 pagesAssessment Packages Electrician Level IISheela AliNo ratings yet
- Quantum Autoencoders With Enhanced Data EncodingDocument7 pagesQuantum Autoencoders With Enhanced Data EncodingfoobarukNo ratings yet
- Module 1 AssessmentDocument4 pagesModule 1 AssessmentSheela AliNo ratings yet
- DoDI 5000.02 chart email suggestionsDocument2 pagesDoDI 5000.02 chart email suggestionsjoe TNo ratings yet
- AGN 035 - Protect alternators from overloads and faultsDocument10 pagesAGN 035 - Protect alternators from overloads and faultsariwibowoNo ratings yet
- An Efficient Presentation-Architecture For Personalized ContentDocument10 pagesAn Efficient Presentation-Architecture For Personalized ContentCarsten UllrichNo ratings yet
- Ip Ccdi g5 t2 2023-24Document1 pageIp Ccdi g5 t2 2023-24api-135128257No ratings yet
- MSC International Sustainability Management ESCP Business SchoolDocument7 pagesMSC International Sustainability Management ESCP Business SchoolbouayadNo ratings yet
- Author ACMDocument6 pagesAuthor ACMOshin LujanNo ratings yet
- Top Down Proteomics Using Online Polymer Reversed Phase (PLRP) Nanocapillary-LC Coupled Fourier Transform Mass SpectrometryDocument1 pageTop Down Proteomics Using Online Polymer Reversed Phase (PLRP) Nanocapillary-LC Coupled Fourier Transform Mass Spectrometryapi-26001949No ratings yet
- Modelling Fault Growth in Layered ModelsDocument2 pagesModelling Fault Growth in Layered ModelsRobert BlaireauNo ratings yet
- Sea Risk Basel III To Basel Iv2Document1 pageSea Risk Basel III To Basel Iv2abcNo ratings yet
- Defense Acquisition Life Cycle Compliance Baseline (Pre-Tailoring)Document2 pagesDefense Acquisition Life Cycle Compliance Baseline (Pre-Tailoring)Chit Win MaungNo ratings yet
- demo2LabDocument5 pagesdemo2LabSergio FeitozaNo ratings yet
- IIT Tirupati Masterplan Zoning RequirementsDocument2 pagesIIT Tirupati Masterplan Zoning RequirementsAr Jilfin Shelto KumarNo ratings yet
- Wayang Windu Unit-2 CDM ProgramDocument1 pageWayang Windu Unit-2 CDM ProgramRizki GeovaniNo ratings yet
- Is Valid Only With Original Photo ID: Railway Recruitment BoardDocument3 pagesIs Valid Only With Original Photo ID: Railway Recruitment Boardpankaj yadavNo ratings yet
- SWOT-Analyse ISO /TS 16949:2009Document1 pageSWOT-Analyse ISO /TS 16949:2009Nedra DebbechNo ratings yet
- NT1000 - Spindle 1Document1 pageNT1000 - Spindle 1Felipe SalesNo ratings yet
- Cloud Testing PDFDocument13 pagesCloud Testing PDFLavanyenNo ratings yet
- PCCFD PosterDocument2 pagesPCCFD PosterMahfoud AMMOURNo ratings yet
- Shutdown Matrix for Condensate Stabilizer 1Document2 pagesShutdown Matrix for Condensate Stabilizer 1Carlos Aquino HanccoNo ratings yet
- P843 GEM Poster - JK CiDocument1 pageP843 GEM Poster - JK CiTsubasa OozoraNo ratings yet
- In Edit State:save Key: 0.4mV/V 6mV/VDocument5 pagesIn Edit State:save Key: 0.4mV/V 6mV/VJulian HortaNo ratings yet
- Cost Benefit Analysis and Exploration of Cost Energy Perfo - 2016 - Procedia Com PDFDocument5 pagesCost Benefit Analysis and Exploration of Cost Energy Perfo - 2016 - Procedia Com PDFrifnaNo ratings yet
- Duct ProgressDocument24 pagesDuct Progressriki.jayaNo ratings yet
- Composite / Steel Cost Comparison: Utility: Composites Offer The FollowingDocument11 pagesComposite / Steel Cost Comparison: Utility: Composites Offer The FollowingMitu Leonard-GabrielNo ratings yet
- It Impact Zone: Technical Security: Featured Technology SolutionsDocument5 pagesIt Impact Zone: Technical Security: Featured Technology SolutionsSapaNo ratings yet
- SmallgroupresultsreportDocument1 pageSmallgroupresultsreportapi-392364749No ratings yet
- The Ambulatory Glucose Profile Opportunities For EnhancementDocument27 pagesThe Ambulatory Glucose Profile Opportunities For EnhancementyuriescaidaNo ratings yet
- Baltimore County Bicycle and Pedestrian Plan-2022 Draft Plan AppendicesDocument92 pagesBaltimore County Bicycle and Pedestrian Plan-2022 Draft Plan Appendicesapi-634035982100% (1)
- Sccurriculumresultsreport 2Document1 pageSccurriculumresultsreport 2api-392364749No ratings yet
- Technical Approach and Methodology: Dam Rehabilitation & Improvement Project (DRIP), IndiaDocument5 pagesTechnical Approach and Methodology: Dam Rehabilitation & Improvement Project (DRIP), Indiaanon_693862934No ratings yet
- SSP Poster - Final VersionDocument1 pageSSP Poster - Final Versionapi-324155293No ratings yet
- PLUMBINGDocument5 pagesPLUMBINGvillanuevarey14No ratings yet
- Herangga Bima Sadewa - (21030112120013) - Nugraheni Dwiandini - (21030112130118) - PFDDocument1 pageHerangga Bima Sadewa - (21030112120013) - Nugraheni Dwiandini - (21030112130118) - PFDHanif Nur FahriNo ratings yet
- جامعة أم القرى ماجستير العمارة المستدامةDocument21 pagesجامعة أم القرى ماجستير العمارة المستدامةat gazzazNo ratings yet
- Poster Ecoc Rimini 030921Document1 pagePoster Ecoc Rimini 030921Jaya Kumar KbNo ratings yet
- Variable Airflow Terminal UnitDocument7 pagesVariable Airflow Terminal UnitKhánh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Encapsulated Sample Rheometer (Premier ESR)Document10 pagesEncapsulated Sample Rheometer (Premier ESR)Amie SedlockNo ratings yet
- Caribbean Examinations Council: Timetable May-June 2013Document12 pagesCaribbean Examinations Council: Timetable May-June 2013Ashley Maxwell0% (1)
- Grima&Wypych-Discrete Element Simulation Validation Impact Plate Transfer StationDocument18 pagesGrima&Wypych-Discrete Element Simulation Validation Impact Plate Transfer StationJoaquín NarváezNo ratings yet
- 1959 Cessna 172 ManualDocument25 pages1959 Cessna 172 ManualRoberto Fernandez Sanzo100% (1)
- Main Equipment List ISBLDocument4 pagesMain Equipment List ISBLPaula Vargas ANo ratings yet
- Description Trade Size FOB PriceDocument9 pagesDescription Trade Size FOB PricePao JiménezNo ratings yet
- Alco Injection SystemDocument25 pagesAlco Injection SystemAniket KshirsagarNo ratings yet
- Solution To Problem 638 - Deflection of Cantilever Beams - Strength of Materials ReviewDocument4 pagesSolution To Problem 638 - Deflection of Cantilever Beams - Strength of Materials ReviewJhundel Factor PajarillagaNo ratings yet
- Series Variable Displacement Piston Pumps ...............................Document5 pagesSeries Variable Displacement Piston Pumps ...............................Daniel VuletaNo ratings yet
- Tech Spe RoboShot Spraymec 8100 VC TDSDocument18 pagesTech Spe RoboShot Spraymec 8100 VC TDScaludio martinezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11-12Document44 pagesLecture 11-12Chauhdary Fazeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Affnan's Aquaponics: Improving Siphon Design for Greater EfficiencyDocument16 pagesAffnan's Aquaponics: Improving Siphon Design for Greater EfficiencyJuan Carlos FernandezNo ratings yet
- M-VF Series: Safety Excess Flow ValveDocument5 pagesM-VF Series: Safety Excess Flow ValvebiomenggNo ratings yet
- My Final Project (ARJUN)Document86 pagesMy Final Project (ARJUN)Brijesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Mig Sonic 200 CVCC Service ManualDocument65 pagesMig Sonic 200 CVCC Service Manualbuggy bugger100% (1)
- Engine Room Watch Takeover ChecklistDocument1 pageEngine Room Watch Takeover ChecklistZipronNo ratings yet
- Tib 19 Submersible Motor Pumps Vs Lineshaft TurbinesDocument5 pagesTib 19 Submersible Motor Pumps Vs Lineshaft Turbinesmeeraksam42No ratings yet
- Rotary Shaft Seals: Common Rotary Seal ProfilesDocument2 pagesRotary Shaft Seals: Common Rotary Seal ProfilesEarl HarbertNo ratings yet
- Zenit Grey Series Submersible Pumps CatalogueDocument12 pagesZenit Grey Series Submersible Pumps CatalogueDeiv JaviNo ratings yet
- Time Dependent Analysis in SAP2000Document7 pagesTime Dependent Analysis in SAP2000Reynaldo Valdez HerreraNo ratings yet
- Product Profile: TL-Series (TLY) Servo MotorsDocument2 pagesProduct Profile: TL-Series (TLY) Servo MotorsINGENIERIA MECANICA Y DE CONTROLNo ratings yet
- Design, Codes and Guidelines: 10.1 OverviewDocument3 pagesDesign, Codes and Guidelines: 10.1 OverviewMiljan TrivicNo ratings yet