Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Rey Limbago Ambag - Activity 4 - Half-Wave Rectifier
Uploaded by
Rey AmbagCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Rey Limbago Ambag - Activity 4 - Half-Wave Rectifier
Uploaded by
Rey AmbagCopyright:
Available Formats
NAME: REY LIMBAGO AMBAG DATE: 21/03/2022
SECTION: BSEE 2B SUBJECT CODE: EE 45A
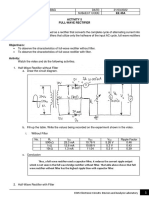
ACTIVITY 4
HALF-WAVE RECTIFIER
Introduction:
A half wave rectifier is defined as a type of rectifier that only allows one half-cycle of an AC voltage
waveform to pass, blocking the other half-cycle. Half-wave rectifiers are used to convert AC voltage to DC
voltage, and only require a single diode to construct.
Objective/s:
• To observe the characteristics of half-wave rectifier without filter.
• To observe the characteristics of half-wave rectifier with filter.
Activity:
Watch the video and do the following activities.
1. Half-Wave Rectifier without Filter
a. Draw the circuit diagram.
b. Fill-up the table. Write the values being recorded on the experiment shown in the video.
i. Without Filter
No. RL IDC VDC VAC Ripple Factor
500kΩ 14.1mA 5.38 V 6.76 V 1.194
1kΩ 6.7mA 5.46 V 6.82 V 1.164
10kΩ 0.7mA 5.49 V 6.92 V 1.153
c. Conclusion
Only the positive half-cycles pass through a half-wave rectifier, while the negative
half-cycle is blocked. A negative half-wave rectifier, on the other hand, will only allow
negative half-cycles to pass through the diode while blocking the positive half-cycle. The
orientation of the diode is the only difference between a positive and negative half wave
rectifier. The diode is now facing the opposite way. As a result, only when the AC
waveform is in its negative half cycle will the diode be forward biased. The pulsating DC
waveform we derived from the theory above is the output waveform. When a half-wave
rectifier is used without a filter, the result is as shown.
. EE45 Electronic Circuits: Devices and Analysis Laboratory 1
2. Half-Wave Rectifier with Filter
a. Draw the circuit diagram.
b. Fill-up the table. Write the values being recorded on the experiment shown in the video.
i. With Filter
No. RL IDC VDC VAC Ripple Factor
500kΩ 34.2 mA 14.11 V 1.47 V 0.41
1kΩ 18.3 mA 15.3 V 0.83 V 0.38
10kΩ 2 mA 16.7 V 0.12 V 0.36
c. Conclusion
The operation of the capacitor or the filter can be explained as follows. The
capacitor charges to the peak voltage Vm as the rectifier output voltage increases. The
rectifier output voltage tries to fall just after the positive peak. As the source voltage falls
below Vm, the capacitor will attempt to transmit current back to the diode, causing it to
be reverse biased. As a result, the diode separates/disconnects the source from the
load, and the capacitor discharges through the load until the source voltage exceeds the
capacitor voltage. The diode re-conducts, the capacitor is re-charged to the peak value
Vm, and the process is repeated.
EE45 Electronic Circuits: Devices and Analysis Laboratory 2
You might also like
- Activity 5 - Full-Wave RectifierDocument2 pagesActivity 5 - Full-Wave RectifierRey AmbagNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 Diode As Rectifier BBN 10205 (Done)Document10 pagesLab 5 Diode As Rectifier BBN 10205 (Done)Zhamir ZhakwanNo ratings yet
- EPD Lab#9Document8 pagesEPD Lab#9Muhammad ShaheerNo ratings yet
- (ALCANTARA - BSEE-2D) Experiment 2 Final ReportDocument11 pages(ALCANTARA - BSEE-2D) Experiment 2 Final ReportLawrence Abram AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Ehsan (3050) Lab 05Document7 pagesEhsan (3050) Lab 05Antenna /// Power ElectronicsNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical EngineeringDocument5 pagesDepartment of Electrical EngineeringAntenna /// Power ElectronicsNo ratings yet
- ADE Exp 1 RA2111030010279Document13 pagesADE Exp 1 RA2111030010279HarshNo ratings yet
- The Diode in The DC and Ac CircuitDocument2 pagesThe Diode in The DC and Ac CircuitChristian EspanolNo ratings yet
- Device Exp 2 Student ManualDocument4 pagesDevice Exp 2 Student Manualgg ezNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 2Document12 pagesLab Report 2SHADOW manNo ratings yet
- EPD Lab#8Document8 pagesEPD Lab#8Muhammad ShaheerNo ratings yet
- FDC Lab ManualDocument25 pagesFDC Lab ManualtovilasNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 Single Phase Diode RectifiersDocument14 pagesLab 1 Single Phase Diode RectifiersM Hassan BashirNo ratings yet
- Group 6 Rectifiers and Filters EXP 4 - ECE005 ME51S1Document9 pagesGroup 6 Rectifiers and Filters EXP 4 - ECE005 ME51S1Jose Enrique Gonzaga100% (1)
- Full Wave Bridge ASSIGNMENTDocument2 pagesFull Wave Bridge ASSIGNMENTVesagan MessiNo ratings yet
- EL - 124 Electronic Devices & Circuits: Experiment # 06Document10 pagesEL - 124 Electronic Devices & Circuits: Experiment # 06Jawwad IqbalNo ratings yet
- Half Wave Rectifier Physics Project PDF VinilDocument12 pagesHalf Wave Rectifier Physics Project PDF Vinilteamboys536No ratings yet
- Ex.2 - Ecad 1Document6 pagesEx.2 - Ecad 1Saturn MoonNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Report: Submitted by Group Members Submitted To Date of Submission Grade/ PointsDocument23 pagesBasic Electronics Report: Submitted by Group Members Submitted To Date of Submission Grade/ PointsMahnam Nasir Nasir NaeemNo ratings yet
- KEE 4823 Power Electronic: Ac To DC Rectifier 17 APRIL 2019Document10 pagesKEE 4823 Power Electronic: Ac To DC Rectifier 17 APRIL 2019Zamil AzhariNo ratings yet
- Analog Circuits and Simulation LabDocument77 pagesAnalog Circuits and Simulation LableevasusanNo ratings yet
- Oraye - ELX20 - Lab 4 Halfwave Rectifier PDFDocument8 pagesOraye - ELX20 - Lab 4 Halfwave Rectifier PDFXheluj Sheluj ZhelujNo ratings yet
- Experiment - 4 Half Wave Rectifier Pre - Lab QuestionsDocument8 pagesExperiment - 4 Half Wave Rectifier Pre - Lab Questionsgautam KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Design and Study Full-Wave and Bridge Rectifier andDocument27 pagesDesign and Study Full-Wave and Bridge Rectifier andTayyeba100% (1)
- Dav Cps Mandi: Physics Project ReportDocument17 pagesDav Cps Mandi: Physics Project Reportparasthakur.2007xNo ratings yet
- ECE 51 - Lab Activity 1 PDFDocument5 pagesECE 51 - Lab Activity 1 PDFJules Nikko Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 14-1Document4 pagesExperiment No 14-1afrahakbar3No ratings yet
- Al-Balqa' Applied University: Electronics LabDocument54 pagesAl-Balqa' Applied University: Electronics Labahmad abufaresNo ratings yet
- Full Wave Rectifier Single Phase ReportDocument10 pagesFull Wave Rectifier Single Phase ReportAmer Al-khorasaniNo ratings yet
- Lab Report: Engr. Wasim Iqbal Submitted byDocument7 pagesLab Report: Engr. Wasim Iqbal Submitted byسید کاظمیNo ratings yet
- 20013122-034-EDC Lab Manual#4Document22 pages20013122-034-EDC Lab Manual#4Usama MughalNo ratings yet
- KEC151P - Lab - Experiments - UPDATED ONEDocument34 pagesKEC151P - Lab - Experiments - UPDATED ONEAkshat GuptaNo ratings yet
- 3rd Semester Lab 201Document36 pages3rd Semester Lab 201Noor HussainNo ratings yet
- Ee Lab Report 10Document6 pagesEe Lab Report 10mustafasid1912No ratings yet
- Electronics Devices Lab - Exp 2 - Mid Term - Fall 22-23 - ACSDocument19 pagesElectronics Devices Lab - Exp 2 - Mid Term - Fall 22-23 - ACSdark lionNo ratings yet
- Electronic Components Circuits: (Diode Characteristies - Rectifier - Clipper)Document14 pagesElectronic Components Circuits: (Diode Characteristies - Rectifier - Clipper)em2200139No ratings yet
- Diod RectifierDocument35 pagesDiod RectifierRizalNo ratings yet
- ElectronicsDocument72 pagesElectronicszaidlateefNo ratings yet
- Learning Objectives:: Topic 2.4.2 - RectificationDocument12 pagesLearning Objectives:: Topic 2.4.2 - RectificationgtchsekharNo ratings yet
- Plate 2Document12 pagesPlate 2James EricNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 2 ReportDocument40 pagesLaboratory 2 ReportRn NatNo ratings yet
- Full Wave Centre Tapped Rectifier: Experiment No. 5Document4 pagesFull Wave Centre Tapped Rectifier: Experiment No. 5Mohsin Iqbal Department of Electrical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- LAB 2 ReportDocument14 pagesLAB 2 ReportDelos Santos, Jayson C.No ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicsDocument8 pagesBasic Electronicsengineer.chiranjitNo ratings yet
- Electronics Lab 2019Document37 pagesElectronics Lab 2019Noor HussainNo ratings yet
- Chap-4 Diode CircuitsDocument17 pagesChap-4 Diode Circuitsvishal mishraNo ratings yet
- Sepic Converter Design and Operation: by Gregory SharpDocument21 pagesSepic Converter Design and Operation: by Gregory SharpSingam SridharNo ratings yet
- MtE-205 EPD LAB 09Document6 pagesMtE-205 EPD LAB 09Syed Suleman Ayub - Section-BNo ratings yet
- Class +2 SciDocument16 pagesClass +2 SciARYANNo ratings yet
- Eee 04Document10 pagesEee 04farah.hoque.cseNo ratings yet
- Electronics-1 Lab 3, FA20-BEE-3C-146Document9 pagesElectronics-1 Lab 3, FA20-BEE-3C-146Souban JavedNo ratings yet
- Exp 5 Diodes 05Document5 pagesExp 5 Diodes 05api-3717843No ratings yet
- (Final)Document16 pages(Final)saurabhNo ratings yet
- Black and WhiteDocument10 pagesBlack and Whiteanurag0000rawatNo ratings yet
- Electronics 1Document42 pagesElectronics 1Shanti Emmanuelle EscabarteNo ratings yet
- Half Wave Rectifier ProjectDocument8 pagesHalf Wave Rectifier Projectritesh singh55% (31)
- Untitled DocumentDocument12 pagesUntitled Documentaadietya11129No ratings yet
- Exp2Document13 pagesExp2Karim 325No ratings yet
- EE 45A Activity 3 Zener DiodeDocument2 pagesEE 45A Activity 3 Zener DiodeRey AmbagNo ratings yet
- Rey Ambag - PE - 34 - Unit - 2 - Activity - 2022Document1 pageRey Ambag - PE - 34 - Unit - 2 - Activity - 2022Rey AmbagNo ratings yet
- Circular Cylindrical CoordinateDocument4 pagesCircular Cylindrical CoordinateRey AmbagNo ratings yet
- Bios CarloDocument5 pagesBios CarloRey AmbagNo ratings yet
- RMsE LectureDocument148 pagesRMsE Lectureuplbseles100% (10)
- R2868Document2 pagesR2868Maman SulaemanNo ratings yet
- OC - Lect - 01 Aziz AlhaidariDocument34 pagesOC - Lect - 01 Aziz Alhaidariabdulaziz saif ali mansoorNo ratings yet
- 117 4416568 Rev04 PDFDocument24 pages117 4416568 Rev04 PDFharvey89No ratings yet
- TV TOSHIBA 19a30Document11 pagesTV TOSHIBA 19a30Eibar016No ratings yet
- Earthing Training PDFDocument6 pagesEarthing Training PDFSwarup NayakNo ratings yet
- PLL Loss of Lock ChecklistDocument3 pagesPLL Loss of Lock ChecklistLeslie WrightNo ratings yet
- 20 Watt Class-A Power AmplifierDocument4 pages20 Watt Class-A Power AmplifierArmin CuturicNo ratings yet
- STK4211V: 2-Channel 70 W Min AF Power Amplifier (Split Power Supply)Document3 pagesSTK4211V: 2-Channel 70 W Min AF Power Amplifier (Split Power Supply)mundomusicalmeriaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - DC MachineDocument82 pagesChapter 4 - DC Machinepsksiva13No ratings yet
- Chave Nivel AltoDocument40 pagesChave Nivel AltoNorval SantosNo ratings yet
- Super FinishingDocument8 pagesSuper FinishingUttara GargNo ratings yet
- Toshiba 27730 - MB11 27WLT56BDocument84 pagesToshiba 27730 - MB11 27WLT56BvideosonNo ratings yet
- Automatic Night Lamp With Morning AlarmDocument3 pagesAutomatic Night Lamp With Morning AlarmJohn IsraelNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Calibration Procedure: Dps14 AdjustmentDocument31 pages1.1 Calibration Procedure: Dps14 AdjustmentAnthony GonzalesNo ratings yet
- MOS Mismatch Pelgrom1998Document4 pagesMOS Mismatch Pelgrom1998dick freebirdNo ratings yet
- SOT223Document5 pagesSOT223X'mix ĐreamerNo ratings yet
- Electrical - SymbolDocument2 pagesElectrical - Symbolpriyanshsingh97100% (1)
- Transistores Mosfet de PotenciaDocument15 pagesTransistores Mosfet de PotenciaLuis SanchezNo ratings yet
- ECT AssignmnetDocument18 pagesECT AssignmnetJayanthiKathiresanNo ratings yet
- TN1215 TN1220 Tyn612 Tyn812 Tyn1012 PDFDocument13 pagesTN1215 TN1220 Tyn612 Tyn812 Tyn1012 PDFePotyNo ratings yet
- Trask Mixer MusingsDocument15 pagesTrask Mixer MusingsFraesenfresseNo ratings yet
- LED Technology Presentation (Rev Kuwait)Document63 pagesLED Technology Presentation (Rev Kuwait)AV Shrinivas100% (3)
- Datasheet Rfid Id-20Document12 pagesDatasheet Rfid Id-20Diego GuamánNo ratings yet
- Coating WackerDocument105 pagesCoating WackerRahul YadavNo ratings yet
- Camera Link Repeaters - Splitters, Repeaters, Mux: What Is The Weightage of in GATE Exam? 9 1.22Document5 pagesCamera Link Repeaters - Splitters, Repeaters, Mux: What Is The Weightage of in GATE Exam? 9 1.22Sri ShandilyaNo ratings yet
- Datasheet k3325Document8 pagesDatasheet k3325Heriberto Flores AmpieNo ratings yet
- Inspection Data Sheet (I.D.S.) : Company Job. Country RevisionDocument2 pagesInspection Data Sheet (I.D.S.) : Company Job. Country Revisionbrome2014No ratings yet
- Lenovo D153aDocument51 pagesLenovo D153amarco100% (1)
- Band Theory in Solid StateDocument4 pagesBand Theory in Solid StatePaulami Bose100% (1)