Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Quiz-Hematologic System
Uploaded by
Bi B BelleOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing Quiz-Hematologic System
Uploaded by
Bi B BelleCopyright:
Available Formats
NURSING QUIZ
A REVIEW OF HEMATOLOGIC SYSTEM
(30 points)
Specific Instructions:
1. In one to two paragraphs, explain the relevance of Hematologic System to Respiratory
System and Cardiovascular System, in the process of OXYGENATION (10 points)
Here, the cardiovascular system consists of the heart and the arteries and veins that convey
blood throughout the body. It carries oxygen from the air we breathe to cells throughout the
body. The pumping of the heart drives this blood flow through the arteries, capillaries, and
veins. One set of blood vessels circulates blood through the lungs for gas exchange. The other
vessels fuel the rest of the body. Again, the heart pumps oxygenated blood out of the left
ventricle and into the aorta to begin systemic circulation. After the blood has supplied cells
throughout the body with oxygen and nutrients, it returns deoxygenated blood to the right
atrium of the heart. The deoxygenated blood shoots down from the right atrium to the right
ventricle. The heart then pumps it out of the right ventricle and into the pulmonary arteries
to begin pulmonary circulation. The blood moves to the lungs, exchanges carbon dioxide for
oxygen, and returns to the left atrium. The oxygenated blood shoots from the left atrium to
the left ventricle below, to begin systemic circulation again.
More so, the cardiovascular and respiratory systems work together to sustain the body with
oxygen and to remove carbon dioxide. Pulmonary circulation facilitates the process of
external respiration; deoxygenated blood flows into the lungs. It absorbs oxygen from tiny air
sacs (the alveoli) and releases carbon dioxide to be exhaled. Systemic circulation facilitates
internal respiration; oxygenated blood flows into capillaries through the rest of the body. The
blood diffuses oxygen into cells and absorbs carbon dioxide.
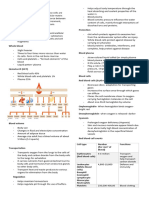
2. Describe and identify the functions of each blood component (5 points each):
Blood Component Description Functions
PLASMA - Plasma is the - The main job of
liquid component the plasma is to
of blood and it is a transport blood
mixture of water, cells throughout
sugar, fat, protein, your body along
and salts. with nutrients,
waste products,
antibodies, clotting
proteins, chemical
messengers such
as hormones, and
proteins that help
maintain the
body's fluid
balance.
FORMED ELEMENTS:
1. RED BLOOD CELLS - Red cells contain a
Hemoglobin - The red blood cells special protein
(also called called hemoglobin,
erythrocytes or which helps carry
RBC’s) are known oxygen from the
for their bright red lungs to the rest of
colour, red cells the body and then
returns carbon
are the most dioxide from the
abundant cell in body to the lungs
the blood, so it can be
accounting for exhaled. Blood
about 40 to 45% of appears red
its volume. The because of the
shape of a red large number of
blood cell is a red blood cells,
biconcave disk which get their
with a flattened colour from the
center, in other hemoglobin. The
words, both faces percentage of
of the disc have whole blood
shallow bowl-like volume that is
indentations (a red made up of red
blood cell looks blood cells is called
like a donut) the hematocrit
and is a common
measure of red
blood cell levels.
2. WHITE BLOOD CELLS
- White blood cells
- White Blood Cells
protect the body
(also called
from infection
leukocytes or
(that is they serve
WBC) are part of
as a defense
the body’s
against all
immune system
pathogens in
and the WBC in
human body).
the cells comprises
recognizable
granule-like
structures. Types
of white blood
cells are
granulocytes
(neutrophils,
eosinophils, and
basophils),
monocytes, and
lymphocytes (T
cells and B cells).
They are much
fewer in number
than red blood
cells, accounting
for about 1% of
the blood and they
3. PLATELETS
are colourless,
since these lack
haemoglobin. - Platelets help the
blood clotting
process (or
- Platelets (also coagulation) by
called gathering at the
thrombocytes) are site of an injury,
irregular, disc- sticking to the
lining of the
shaped element in injured blood
the blood that vessel, and
assists in blood forming a platform
clotting. on which blood
coagulation can
occur.
You might also like
- circulatory systemDocument11 pagescirculatory systemyoudhffgNo ratings yet
- 1 Anatomy and Physiology of The Circulation of The BloodDocument10 pages1 Anatomy and Physiology of The Circulation of The BloodVladislav KotovNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to the Blood Cells, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Blood Cells, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisNo ratings yet
- Cirulatory SystemDocument13 pagesCirulatory SystemmuhammadNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Blood Autosaved Compress1Document11 pagesCardiovascular Blood Autosaved Compress1KIMBERLY TAC-ALNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology - Dengue FeverDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - Dengue Feverhael yam62% (13)
- Components of BloodDocument5 pagesComponents of BloodJAYDEN JANSZNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System I: Circulation & Blood ComponentsDocument8 pagesCirculatory System I: Circulation & Blood ComponentsLeslie CuevasNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument16 pagesBloodMohsin Bhat100% (1)
- Human Anatomy and Physiology - BloodDocument16 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology - BloodAndreaNo ratings yet
- 13 - BloodDocument9 pages13 - BloodJan Leanne OrbigosoNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesFunctions of The Circulatory SystemMaria Charma AnlapNo ratings yet
- Blood Composition BreakdownDocument5 pagesBlood Composition BreakdownNatasha JeanNo ratings yet
- HSSRPTR - 07-Body Fluids and CirculationDocument15 pagesHSSRPTR - 07-Body Fluids and CirculationUnniNo ratings yet
- The Blood Clotting MechanismDocument20 pagesThe Blood Clotting Mechanismzynab123No ratings yet
- Blood Clotting Mechanism ExplainedDocument20 pagesBlood Clotting Mechanism Explainedzynab123No ratings yet
- 05 - SPSF3 05 B3 PDFDocument26 pages05 - SPSF3 05 B3 PDFCikgu Roshaila100% (1)
- Transes Anaphy BloodDocument5 pagesTranses Anaphy BloodPia LouiseNo ratings yet
- Blood (Notes)Document12 pagesBlood (Notes)Angel Rose BrillanteNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: Big PictureDocument4 pagesCirculatory System: Big PictureMaría José Castellanos GutiérrezNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology For HELLP SyndromeDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology For HELLP SyndromeRosemarie Carpio100% (1)
- Function, Physical and Chemical Properties of BloodDocument8 pagesFunction, Physical and Chemical Properties of Blooddeput_rprNo ratings yet
- Resource+Notes+on+BloodDocument4 pagesResource+Notes+on+Blood:DNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Histology of BloodDocument4 pagesLecture 7 Histology of BloodRazmine RicardoNo ratings yet
- Blood Functions and CompositionDocument11 pagesBlood Functions and Compositionchristian anchetaNo ratings yet
- Quiz Bank - Capoten (Mar-22)Document4 pagesQuiz Bank - Capoten (Mar-22)saad awanNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument6 pagesBloodAlther LorenNo ratings yet
- The Transport System in HumansDocument8 pagesThe Transport System in HumansazuraNo ratings yet
- CIRCULATORY SYSTEMDocument6 pagesCIRCULATORY SYSTEMJanelleNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument2 pagesBloodAmal BazinaNo ratings yet
- Blood and Hemopoiesis: Color Textbook of Histology, 3rd EdDocument7 pagesBlood and Hemopoiesis: Color Textbook of Histology, 3rd EdAnthony Klein Núñez AlarcónNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 11 ANAPHY TransesDocument5 pagesCHAPTER 11 ANAPHY TransesHoly HaeinNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument9 pagesBloodSheena PasionNo ratings yet
- Overview Of: BloodDocument4 pagesOverview Of: BloodIberisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Transport in ManDocument3 pagesChapter 7 Transport in ManSheik Mohammud Muzzammil NabybaccusNo ratings yet
- Human Body System InfographicDocument12 pagesHuman Body System InfographicDiana VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Biol 2301 - Unit 8 - Circulation StudentDocument82 pagesBiol 2301 - Unit 8 - Circulation Studentapi-664744800No ratings yet
- Learn About the Circulatory SystemDocument33 pagesLearn About the Circulatory SystemAshly EspinaNo ratings yet
- ABT Cardivascual PPDocument44 pagesABT Cardivascual PPABT SchoolNo ratings yet
- Sworts Immunilogy Cells-Of-The-Immune-SystemDocument23 pagesSworts Immunilogy Cells-Of-The-Immune-SystemꕶᗋᏦᎥꕗNo ratings yet
- The BloodDocument1 pageThe Bloodapi-363936996No ratings yet
- Blood Components, Structure, Function and OriginDocument2 pagesBlood Components, Structure, Function and OriginHyacinth CorralesNo ratings yet
- The Blood Module PDFDocument7 pagesThe Blood Module PDFCarlo MakilingNo ratings yet
- Blood Components and FunctionsDocument8 pagesBlood Components and FunctionsHaya Abdulla Rashed Al nuaimiNo ratings yet
- Pengangkutan: TransportationDocument22 pagesPengangkutan: TransportationsuhanaNo ratings yet
- Sistem Sirkulasi: Sebuah FlipbookDocument33 pagesSistem Sirkulasi: Sebuah FlipbookRatih SwandewiNo ratings yet
- Blood: A Vital Transport SystemDocument33 pagesBlood: A Vital Transport SystemCORONEL, SOPHIANo ratings yet
- Blood (Anaphy)Document8 pagesBlood (Anaphy)CORONEL, SOPHIANo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document1 pageChapter 12Nona PeriarceNo ratings yet
- The Fascinating Functions of BloodDocument7 pagesThe Fascinating Functions of BloodjustRizzeNo ratings yet
- Ch14 AA (1) .EditedDocument21 pagesCh14 AA (1) .EditedSammy DeeNo ratings yet
- Notes - BloodDocument7 pagesNotes - BloodHeri SetiadiNo ratings yet
- Answer: (1) ErythrocytesDocument8 pagesAnswer: (1) Erythrocytesnainygoyal123No ratings yet
- Forensic analysis of blood as dynamic crime scene evidenceDocument5 pagesForensic analysis of blood as dynamic crime scene evidenceiqrarNo ratings yet
- Physical Characteristics and VolumeDocument10 pagesPhysical Characteristics and Volumedeepika kushwahNo ratings yet
- Materi Cardiovascular and Circulatory SystemDocument56 pagesMateri Cardiovascular and Circulatory SystemZULFIKAR GHOZI MALIKUL AKBAR -No ratings yet
- Module 12 The Composition and Function of BloodDocument11 pagesModule 12 The Composition and Function of BloodMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- SPSF3 05 B3Document22 pagesSPSF3 05 B3Sin Ling WongNo ratings yet
- Sts - When Technology and Humanity CrossDocument18 pagesSts - When Technology and Humanity CrossBi B BelleNo ratings yet
- Project Written By:: I. Dona Imelda, Quezon City"Document8 pagesProject Written By:: I. Dona Imelda, Quezon City"Bi B BelleNo ratings yet
- NCM 105 MINERALS LECDocument8 pagesNCM 105 MINERALS LECBi B BelleNo ratings yet
- Features and functions of TCP/IP protocolDocument12 pagesFeatures and functions of TCP/IP protocolBi B BelleNo ratings yet
- Family Nursing Care Plan Chapter VIDocument3 pagesFamily Nursing Care Plan Chapter VIBi B BelleNo ratings yet
- Bioethics Is A Branch of EthicsDocument4 pagesBioethics Is A Branch of EthicsBi B BelleNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing-Family Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesCommunity Health Nursing-Family Nursing Care PlanBi B BelleNo ratings yet
- GCAS 13 - Are You an AchieverDocument1 pageGCAS 13 - Are You an AchieverBi B BelleNo ratings yet
- Catch Up Exam Prelim (Major Exam) 1Document5 pagesCatch Up Exam Prelim (Major Exam) 1Bi B BelleNo ratings yet
- Activity 6 RIZALDocument3 pagesActivity 6 RIZALBi B BelleNo ratings yet
- Review of Literature on Burnout among Healthcare Workers during COVID-19Document6 pagesReview of Literature on Burnout among Healthcare Workers during COVID-19Bi B BelleNo ratings yet
- Prelim Major Nursing ResaerchDocument4 pagesPrelim Major Nursing ResaerchBi B BelleNo ratings yet
- Ravi KantDocument1 pageRavi KanthimeltoujoursperitusNo ratings yet
- 20 Common Defense Mechanisms for AnxietyDocument8 pages20 Common Defense Mechanisms for AnxietyAbhishek NegiNo ratings yet
- Shot List TemplateDocument2 pagesShot List Templateapi-525636391No ratings yet
- Group 1 RRLSDocument4 pagesGroup 1 RRLScyrusarckreibagoNo ratings yet
- Css Islamic History Culture1 2009Document2 pagesCss Islamic History Culture1 2009abdul basit khanNo ratings yet
- Electric BellsDocument36 pagesElectric Bellsmedassan7No ratings yet
- PSMB Certified Trainer Curriculum StructureDocument19 pagesPSMB Certified Trainer Curriculum StructureFlankerSparrowNo ratings yet
- 500 Chess Exercises Special Mate in 1 MoveDocument185 pages500 Chess Exercises Special Mate in 1 MoveRégis WarisseNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Year 11 Spring Break RevisionDocument90 pagesKami Export - Year 11 Spring Break Revisionbkhmnrq4d6No ratings yet
- Picasso's Blue Period - WikipediaDocument24 pagesPicasso's Blue Period - WikipediaDinesh RajputNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document26 pagesChapter 4Kritika JainNo ratings yet
- WK 4 Exam 2 Key ConceptsDocument24 pagesWK 4 Exam 2 Key ConceptsKrystel LahomNo ratings yet
- Billy: Bookcase SeriesDocument4 pagesBilly: Bookcase SeriesDImkaNo ratings yet
- IO Question Bank: The PromptDocument3 pagesIO Question Bank: The PromptAvijeetNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - Chapter 17 Job Order Costing Costing Chapter 17 Learning Objectives 1 DistinguishDocument25 pagesDokumen - Tips - Chapter 17 Job Order Costing Costing Chapter 17 Learning Objectives 1 DistinguishNouman SheikhNo ratings yet
- Defamation of Public Officials Under American Rule of LawDocument9 pagesDefamation of Public Officials Under American Rule of LawSugar Fructose GalactoseNo ratings yet
- Revised Revenue Code of Puerto Galera 2010Document157 pagesRevised Revenue Code of Puerto Galera 2010Jesselle MamintaNo ratings yet
- Athangudi TilesDocument84 pagesAthangudi TilesSMITH DESIGN STUDIONo ratings yet
- Four Modes of DeliveryDocument21 pagesFour Modes of DeliveryRyan AbellaNo ratings yet
- Mmk265 Marketing Research Major Project (3) 1.doc 22891Document26 pagesMmk265 Marketing Research Major Project (3) 1.doc 22891dnlkabaNo ratings yet
- Aquatic Animal Protection Act 2017 1960Document8 pagesAquatic Animal Protection Act 2017 1960Subham DahalNo ratings yet
- Tall Buildings Case Studies of John Hancock Centre and Sears TowerDocument75 pagesTall Buildings Case Studies of John Hancock Centre and Sears TowerShanikAromgottilNo ratings yet
- TQ International Course Guide - CompressedDocument40 pagesTQ International Course Guide - CompressedgermanNo ratings yet
- C01 Globalisation: The Global Village?Document21 pagesC01 Globalisation: The Global Village?Mat RoyNo ratings yet
- HTML5 Student BookDocument297 pagesHTML5 Student BookJovent FalloyNo ratings yet
- MITSUMI M49SP-2K stepping motor datasheetDocument2 pagesMITSUMI M49SP-2K stepping motor datasheetMarcos George0% (1)
- Sample Third Grade LessonsDocument10 pagesSample Third Grade Lessonsapi-214652729No ratings yet
- Recorder SongsDocument15 pagesRecorder SongsBich LeNo ratings yet
- Pike County Sheriff Forms Major Crimes Task Force For Unsolved MurdersDocument2 pagesPike County Sheriff Forms Major Crimes Task Force For Unsolved MurdersAndy Burgoon100% (1)
- Ejercicio de Writing Formal EmailsDocument4 pagesEjercicio de Writing Formal EmailsArianna ContrerasNo ratings yet