Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Activity # 3: ISBAR: Kristian Karl B. Kiw-Is BSN Iv-A
Uploaded by
Karl KiwisOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Activity # 3: ISBAR: Kristian Karl B. Kiw-Is BSN Iv-A
Uploaded by
Karl KiwisCopyright:
Available Formats
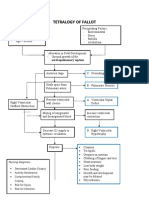
Activity # 3: ISBAR
KRISTIAN KARL B. KIW-IS
BSN IV-A
I Name: Kristian Karl B. Kiw-is
Role: Student Nurse
Ward: BGHMC Medical ward
I am calling because of the case of my patient who is suffering from TOF.
S Baby Mu, an 8 week (2month) OLD-old infant, was admitted to Pediatrics (MEdical)
Ward. Regarding the systemic inquiry of Baby Mu, there was cyanosis, Passed urine
normally, No fevers or rigors (Temperature – 37 C), Not in pain, Alert and non-lethargic,
Mild bluish discoloration of lips and tongue, SaO2 83%, Heart rate: 156 bpm RR:
48/min, anterior fontanelle normal. During the onset of Respiratory distress at birth he
was rendered resuscitation, given CPAP and PEEP to maintain oxygenation to lungs.
His breathing was monitored, routine blood exam was done including ABG. Continuous
monitoring oxygen saturation was also done.
.
He was given feeding via TPN (6ml/kg/2 hourly). Cardiac catheterization was also done
to assess for cardiac anomaly.
He was monitored for temperature elevation post-operatively – If pyrexial, he was
given vancomycin and gentamicin. Additional medications were aspirin, frusemide,
spironolactone and paracetamol PRN. His feeding was increased to 150ml/kg/day via
bottle
B Baby Mu, an 8 week (2month) OLD-old infant, was admitted to Pediatrics (MEdical)
Ward with an ongoing IVF of 0.9 NACL x KVO since birth due to severe systemic cyanosis
caused by several congenital heart problems. Soon after birth, he suffered from (z)
(A)cute (R)espiratory (D)istress, where his initial SaO2 was only about 72%. On
appearance, he was dark complexion looking and his peripheries were cold and
cyanotic. He was started on biphasic continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) via an
apnea mask and was also given positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) as additional
help. His CPAP was delivered using nasal cannula the following day after his SaO2
increased to 80% and he remained on CPAP for the first 5 days after birth, which
subsequently was weaned off. Antenatal scans found pulmonary atresia, overriding
aorta, and ventricular septal defect (VSD). Bay Mu underwent Echocardiogram and CXR
and the findings was consistent with Tetralogy of Fallot in his CXR it was found that he
has cardiomegaly.
Cardiology experts advised surgery to establish a connection between aorta and
pulmonary artery to increase pulmonary blood flow.
A shunt was inserted via median sternotomy. Echo post-op showed good flow in small
pulmonary arteries and patent central shunt.
Continue monitoring oxygen saturation – aim to keep above 75%
An ECG was performed.
A Monitor vital signs, peripheral pulses, and capillary refill by comparing measurements.
Assess and record the cardiac rate.
Observation of cyanotic attacks.
Give a knee-chest position.
Observe for signs of decreased sensory: lethargy, confusion, and disorientation.
Monitor intake and output adequately.
Provide adequate rest time.
Collaboration in the examination serial ECGs, chest radiographs, administration of anti-
dysrhythmias.
Collaboration of oxygen.
Collaboration IV fluid administration.
R Surgery for tetralogy of Fallot involves open-heart surgery to correct the defects
(intracardiac repair) or a temporary procedure that uses a shunt.
Continue monitoring oxygen saturation – aim to keep above 75%
Continue administering medical and nursing management.
Refer accordingly
Close monitoring after operation.
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- PHCP312 SyllabusDocument9 pagesPHCP312 SyllabusDanica PamintuanNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- PICU Handbook - University of Iowa Stead Family Children's HospitalDocument10 pagesPICU Handbook - University of Iowa Stead Family Children's HospitalAhmed MohammedNo ratings yet
- Examination Obstetrics Gynaecology - 3E (PDF) (UnitedVRG) PDFDocument325 pagesExamination Obstetrics Gynaecology - 3E (PDF) (UnitedVRG) PDFBernardo Fernandez SalazarNo ratings yet
- Step 2 CK PT SafetyDocument3 pagesStep 2 CK PT SafetyAhmed100% (3)
- Newborn AssessmentDocument24 pagesNewborn Assessmentvincentsharon100% (2)
- Nasal Polyps Grade IIIDocument2 pagesNasal Polyps Grade IIIRyan John Bito-onNo ratings yet
- 7-Cardiology and Respiratory MedicineDocument373 pages7-Cardiology and Respiratory Medicinethisar100% (6)
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia With Myelodysplasia RelatedDocument6 pagesAcute Myeloid Leukemia With Myelodysplasia RelatedAgus WiniNo ratings yet
- ANC and BFDocument29 pagesANC and BFRose Anne Tusi BotinNo ratings yet
- Ca 1 - Exercise - CHNDocument2 pagesCa 1 - Exercise - CHNKarl KiwisNo ratings yet
- Summary of Rle KarlDocument12 pagesSummary of Rle KarlKarl KiwisNo ratings yet
- Second Quarter Lap'S: Microsoft Powerpoint Assessment 1Document3 pagesSecond Quarter Lap'S: Microsoft Powerpoint Assessment 1Karl KiwisNo ratings yet
- Ca 1 Exercise CHN 2Document4 pagesCa 1 Exercise CHN 2Karl KiwisNo ratings yet
- TM 2022Document3 pagesTM 2022Karl KiwisNo ratings yet
- The Earth:: 1. A Prime Meridian Is A Meridian (A Line of Longitude) in A Geographical CoordinateDocument3 pagesThe Earth:: 1. A Prime Meridian Is A Meridian (A Line of Longitude) in A Geographical CoordinateKarl KiwisNo ratings yet
- Navigation CHAPTER VDocument16 pagesNavigation CHAPTER VKarl KiwisNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Procedure PresentationDocument18 pagesDiagnostic Procedure PresentationKarl KiwisNo ratings yet
- Agrarian Structures and Definitions: BY: Jhevan Aballer Helen Balisalisa Maryjoy Macabio Princess RaguindinDocument20 pagesAgrarian Structures and Definitions: BY: Jhevan Aballer Helen Balisalisa Maryjoy Macabio Princess RaguindinKarl KiwisNo ratings yet
- Registration: Comprehensive Agrarian Reform ProgramDocument15 pagesRegistration: Comprehensive Agrarian Reform ProgramKarl KiwisNo ratings yet
- PP-4. Monitoring of Fish Supply To Resorts and Setting Up of An Ecolabel CertificationDocument222 pagesPP-4. Monitoring of Fish Supply To Resorts and Setting Up of An Ecolabel CertificationKarl KiwisNo ratings yet
- Extension Education Is An Applied Behavioural Science, The Knowledge of Which Is Applied To BringDocument12 pagesExtension Education Is An Applied Behavioural Science, The Knowledge of Which Is Applied To BringKarl KiwisNo ratings yet
- The Code of Agrarian Reform (R.A. NO. 3844, AS Amended)Document28 pagesThe Code of Agrarian Reform (R.A. NO. 3844, AS Amended)Karl KiwisNo ratings yet
- Concept Map Tetralogy of FallotDocument2 pagesConcept Map Tetralogy of FallotKarl KiwisNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Agrarian Reform Program (CARP)Document20 pagesComprehensive Agrarian Reform Program (CARP)Karl KiwisNo ratings yet
- Activity 3A: Technical Study of The Business Project: Production of Gracilaria Enriched Glutinous Rice Cake/ CalamayDocument12 pagesActivity 3A: Technical Study of The Business Project: Production of Gracilaria Enriched Glutinous Rice Cake/ CalamayKarl KiwisNo ratings yet
- Large-Scale Sandfish (Holothuria Scabra) Aquaculture in Multitrophic Polyculture Ponds in Southern ChinaDocument2 pagesLarge-Scale Sandfish (Holothuria Scabra) Aquaculture in Multitrophic Polyculture Ponds in Southern ChinaKarl KiwisNo ratings yet
- Potential Nursing Diagnosis Problem Fdar / NCP: Activity # 2Document2 pagesPotential Nursing Diagnosis Problem Fdar / NCP: Activity # 2Karl KiwisNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Procedures Kristian Karl B. Kiw-Is BSN Iv-A: Diagnostic Procedure Description Purpose Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument5 pagesDiagnostic Procedures Kristian Karl B. Kiw-Is BSN Iv-A: Diagnostic Procedure Description Purpose Nursing ResponsibilitiesKarl KiwisNo ratings yet
- Asian Journal of Agriculture and Rural Development: Vlademir A. ShuckDocument15 pagesAsian Journal of Agriculture and Rural Development: Vlademir A. ShuckKarl KiwisNo ratings yet
- Don Mariano Marcos Memorial State University South La Union Campus College of Fisheries Sto. Tomas, La UnionDocument3 pagesDon Mariano Marcos Memorial State University South La Union Campus College of Fisheries Sto. Tomas, La UnionKarl KiwisNo ratings yet
- Review of Sandfish Breeding and Rearing Methods: Rayner PittDocument8 pagesReview of Sandfish Breeding and Rearing Methods: Rayner PittKarl KiwisNo ratings yet
- Weight Gain Initial 1st 2nd 3rd 4thDocument2 pagesWeight Gain Initial 1st 2nd 3rd 4thKarl KiwisNo ratings yet
- Products From: SeaweedsDocument10 pagesProducts From: SeaweedsKarl KiwisNo ratings yet
- SEAFDEC/AQD Institutional Repository (SAIR) : This Document Is Downloaded At: 2013-07-02 07:11:51 CSTDocument53 pagesSEAFDEC/AQD Institutional Repository (SAIR) : This Document Is Downloaded At: 2013-07-02 07:11:51 CSTKarl KiwisNo ratings yet
- Holothuria Spinifera: Growth of The Hatchery-Produced Juveniles of Commercial Sea Cucumber (Theelothuria) TheelDocument6 pagesHolothuria Spinifera: Growth of The Hatchery-Produced Juveniles of Commercial Sea Cucumber (Theelothuria) TheelKarl KiwisNo ratings yet
- Specific Growth Rate Initial 1St Sampling 2Nd Sampling 3Rd Sampling 4Rth Sampling T1 T2 T3Document4 pagesSpecific Growth Rate Initial 1St Sampling 2Nd Sampling 3Rd Sampling 4Rth Sampling T1 T2 T3Karl KiwisNo ratings yet
- # of Individuals Alive T1 T2 T3Document3 pages# of Individuals Alive T1 T2 T3Karl KiwisNo ratings yet
- Artificial Reefs AND Seafarming Technologies: CmfriDocument13 pagesArtificial Reefs AND Seafarming Technologies: CmfriKarl KiwisNo ratings yet
- Tumours of Nasopharynx DhingraDocument8 pagesTumours of Nasopharynx DhingraIkmal ShahromNo ratings yet
- 1st PNSP Teaching Course FlyerDocument2 pages1st PNSP Teaching Course FlyerVmc PediaNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Clostridioides (Clostridium) Difficile Infection in Adults in 2020Document2 pagesDiagnosis and Treatment of Clostridioides (Clostridium) Difficile Infection in Adults in 2020Alem OrihuelaNo ratings yet
- Examination of A Male For Determination of PotencyDocument4 pagesExamination of A Male For Determination of PotencyHarish AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Tool Box Talk - Working in Hot WeatherDocument1 pageTool Box Talk - Working in Hot WeatherMobashir MahmoodNo ratings yet
- 23 Cervix Uteri Fact Sheet PDFDocument2 pages23 Cervix Uteri Fact Sheet PDFIrina DeaconescuNo ratings yet
- SAJD Vol 7 No 4 November 2014Document41 pagesSAJD Vol 7 No 4 November 2014Anupam BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Prostate 4.2.0.0.rel CapcpDocument26 pagesProstate 4.2.0.0.rel CapcpkarimahihdaNo ratings yet
- Log Book: Medical Surgical Nursing DepartmentDocument17 pagesLog Book: Medical Surgical Nursing DepartmentMajied MohamedNo ratings yet
- Wilderness First Aid Reference Cards: Pulse/Pressure PointsDocument7 pagesWilderness First Aid Reference Cards: Pulse/Pressure PointsTài NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of HypercalcemiaDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Hypercalcemiacarla jane bernalesNo ratings yet
- Adjuvant Icotinib Versus Observation in Patients WDocument11 pagesAdjuvant Icotinib Versus Observation in Patients WVanilson BorgesNo ratings yet
- 404 Veterinary Referral Hospital - BrochureDocument11 pages404 Veterinary Referral Hospital - BrochureJoanne FagnouNo ratings yet
- Essay - Child DevelopmentDocument2 pagesEssay - Child DevelopmentTina AroraNo ratings yet
- CHF Literature ReviewDocument5 pagesCHF Literature Reviewapi-509632460No ratings yet
- Microbes of Reproductive SystemDocument215 pagesMicrobes of Reproductive Systemkano kareNo ratings yet
- AtelectasisDocument43 pagesAtelectasismulan557100% (1)
- Absent End-Diastolic Velocity in The Umbilical Artery and Its Clinical SignificanceDocument12 pagesAbsent End-Diastolic Velocity in The Umbilical Artery and Its Clinical Significancejakob_saleanNo ratings yet
- Sheehan Syndrome Lancet Eponym 2003Document3 pagesSheehan Syndrome Lancet Eponym 2003Alejandro GuillenNo ratings yet
- Use E-MANIC' For Secondary Mania Workup: Dowden Health MediaDocument2 pagesUse E-MANIC' For Secondary Mania Workup: Dowden Health MediaJagdishVankarNo ratings yet
- Dehydration: Paul R. EarlDocument31 pagesDehydration: Paul R. EarlJaya Prabha100% (1)