Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1-Shear Behaviour Slides
Uploaded by
Engr Aizaz Ahmad0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views9 pagesThis document discusses shear behavior in prestressed concrete (PSC) structures. It describes three types of cracks that can occur due to shear: flexural cracks, flexural-shear cracks, and web-shear cracks. The behavior of concrete beams in shear can be modeled using a truss analogy, where the compression struts, tension reinforcement, and shear stirrups represent the truss members. Parameters like the strut angle and reinforcement spacing influence shear resistance. Prestress increases shear strength by reducing crack angles and making stirrups more effective at crossing cracks. Recent methods for predicting shear capacity are based on simplified physical models like modified compression field theory.
Original Description:
kjk
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses shear behavior in prestressed concrete (PSC) structures. It describes three types of cracks that can occur due to shear: flexural cracks, flexural-shear cracks, and web-shear cracks. The behavior of concrete beams in shear can be modeled using a truss analogy, where the compression struts, tension reinforcement, and shear stirrups represent the truss members. Parameters like the strut angle and reinforcement spacing influence shear resistance. Prestress increases shear strength by reducing crack angles and making stirrups more effective at crossing cracks. Recent methods for predicting shear capacity are based on simplified physical models like modified compression field theory.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views9 pages1-Shear Behaviour Slides
Uploaded by
Engr Aizaz AhmadThis document discusses shear behavior in prestressed concrete (PSC) structures. It describes three types of cracks that can occur due to shear: flexural cracks, flexural-shear cracks, and web-shear cracks. The behavior of concrete beams in shear can be modeled using a truss analogy, where the compression struts, tension reinforcement, and shear stirrups represent the truss members. Parameters like the strut angle and reinforcement spacing influence shear resistance. Prestress increases shear strength by reducing crack angles and making stirrups more effective at crossing cracks. Recent methods for predicting shear capacity are based on simplified physical models like modified compression field theory.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
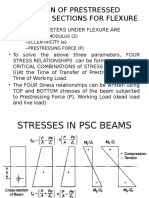
Bridge Design & Assessment
PSC ULS Design: Shear Behaviour
Dr Colin Caprani
Department of Civil Engineering
Click to edit Master subtitle style
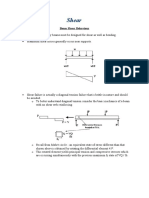
Cracking Behaviour
TYPE I: Flexural cracks; occur
in regions of high moment-to-
SFD shear ratios
TYPE II: Flexural-shear
cracks; occur in regions of
moderate moment-to-shear
ratios (MCFT)
TYPE III: Web-shear cracks;
occur in regions of high shear-
to-moment ratios (generally
near neutral axis)
BMD Dependent of section
geometry
PSC ULS Design 2
Truss Analogy
▪ A concrete beam can be thought of as resisting shear in the same way
a truss acts:
– The bottom truss chord is the tension reinforcement
– The top truss chord is the concrete in the compression zone
– The web tension chords are the shear stirrups
– The web compression chords are the concrete struts
(between cracks)
PSC ULS Design 3
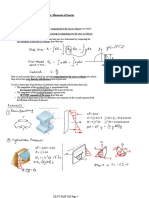
The Compression Strut
▪ Important parameters of the strut are:
– Its angle qv
– The number (spacing) of rebar across the crack
– The distance between tension and compression forces
▪ Resistance comes from:
– Web compression chord
(vertical component)
– Shear in concrete in dv
compression zone
– Stirrups qv
..and prestress!
d v cot q v V*
PSC ULS Design 4
Effect of Prestress
Prestress increases the shear strength compared to RC beams:
▪ Prestress reduces the principal tensile stress and so shear cracks occur
at flatter angles
▪ Flatter crack angles mean that reinforcing stirrups are more effective
(more can cross the crack)
▪ Inclined tendons have a vertical component opposing the applied loads,
increasing the shear strength
PSC ULS Design 5
Capacity Predictions
▪ Provisions for concrete capacity under much debate in the last 50 years
▪ Traditional methods are empirically derived
▪ Recent methods (35 years) are based simplified physical systems
PSC ULS Design 6
Accuracy of Predictions
(2004)
PSC ULS Design 7
Understanding Cracked Concrete
▪ Research at the University of Toronto have looked at the behaviour of
cracked concrete macro-, meso- and micro-scopically!
Bentz & Collins (2006)
PSC ULS Design 8
Modified Compression Field Theory
▪ MCFT was developed mainly by
Collins & Vecchio in University
of Toronto.
▪ The main paper is from 1986.
▪ Based on average strains and
stresses over a cracked section.
▪ Equilibrium, kinematics, and
constitutive relations all used.
▪ Full MCFT requires iteration of
15 equations (Response2000)
Bentz et al (2006)
▪ Hence, in 2006 a Simplified MCFT was introduced
– This is the basis for codes in US, Canada, and now Australia
PSC ULS Design 9
You might also like
- Reinforced and Prestressed Concrete 3rd-Edition PDFDocument524 pagesReinforced and Prestressed Concrete 3rd-Edition PDFfrog1589% (9)
- CHAPTER 5 The Load Path and Load Distribution in BridgeDocument18 pagesCHAPTER 5 The Load Path and Load Distribution in BridgeLittleRed92% (12)
- Theory of Structures Assignment FinalDocument21 pagesTheory of Structures Assignment FinalManasAroraNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Prestressed-Concrete (Notes)Document17 pagesBasic Principles of Prestressed-Concrete (Notes)sharifah atiqahNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignFrom EverandReinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Lincoln 180HD Users PDFDocument96 pagesLincoln 180HD Users PDFratpacNo ratings yet
- Prestressed Concrete Lecture 1Document33 pagesPrestressed Concrete Lecture 1Talha SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Shear Strength Prediction For Reinforced Concrete Beams Without StirrupsDocument8 pagesShear Strength Prediction For Reinforced Concrete Beams Without Stirrupsjuan carlos molano toroNo ratings yet
- Development of Is:456 Shear Design Provisions-Ii: Members With Shear ReinforcementDocument10 pagesDevelopment of Is:456 Shear Design Provisions-Ii: Members With Shear ReinforcementRabin DhakalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 (Material and Basic Prestressing)Document22 pagesLecture 2 (Material and Basic Prestressing)Adam SalimiNo ratings yet
- 04 CENG8422 Shear FailureDocument33 pages04 CENG8422 Shear FailureHENOKNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Limit State Design For Flexure: Reinforced Concrete Structures I (Ceng-3111)Document50 pagesChapter 2 Limit State Design For Flexure: Reinforced Concrete Structures I (Ceng-3111)Muaz HararNo ratings yet
- CH 3iiiDocument14 pagesCH 3iiigelfeto gebreNo ratings yet
- Punching Shear Strength of Reinforced Concrete Slabs Without Transverse Reinforcement by Aurelio Muttoni PDFDocument16 pagesPunching Shear Strength of Reinforced Concrete Slabs Without Transverse Reinforcement by Aurelio Muttoni PDFNuttawuit BigGyNo ratings yet
- CE 1354 Design of RC ElementsDocument32 pagesCE 1354 Design of RC ElementsSyed Yousuf AhmedNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 1.3: Response of Civil Engineering ProjectDocument43 pagesTOPIC 1.3: Response of Civil Engineering ProjectSue IlaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document59 pagesUnit 3P S HARSHITA100% (1)
- CCL PT Slabs Brochure Eng PDFDocument15 pagesCCL PT Slabs Brochure Eng PDFSharad BornarkarNo ratings yet
- Transom Analysis ComparisonDocument38 pagesTransom Analysis ComparisonRifky NetriadyNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Ch2Document37 pagesReinforced Concrete Ch2Gaurav naddaNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Cement Concrete - Prof AquibDocument124 pagesReinforced Cement Concrete - Prof AquibarokiaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - FractureDocument145 pagesLesson 1 - FractureMMillsNo ratings yet
- Critique of Critical Shear Crack Theory For Fib Model Code Articles On Shear Strength and Size Effect of Reinforced Concrete BeamsDocument13 pagesCritique of Critical Shear Crack Theory For Fib Model Code Articles On Shear Strength and Size Effect of Reinforced Concrete Beamskrishnarao krishnarao329No ratings yet
- SAB4323 OCW Topic 1Document50 pagesSAB4323 OCW Topic 1Jang Kyoung-WonNo ratings yet
- Is 1343-Prestress-Flexure and ShearDocument134 pagesIs 1343-Prestress-Flexure and Sheargrkvani10100% (1)
- PT Design and Const by Hemant Gor 461Document42 pagesPT Design and Const by Hemant Gor 461Toang SomsakNo ratings yet
- Intro-Rcd NotesDocument6 pagesIntro-Rcd NotesRam CaniculaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1687404814000996 Main PDFDocument16 pages1 s2.0 S1687404814000996 Main PDFgeorgeispasoiuNo ratings yet
- Design of RCC Post-Tensioned Flat SlabsDocument6 pagesDesign of RCC Post-Tensioned Flat SlabsjayadushNo ratings yet
- Design of Reinforced Concrete Structures: 11M1WCE113Document9 pagesDesign of Reinforced Concrete Structures: 11M1WCE113Saurav KumarNo ratings yet
- CIV211 - Module1Document49 pagesCIV211 - Module1Dayalan JayarajNo ratings yet
- Bond and Development Length - ACI 318-19Document67 pagesBond and Development Length - ACI 318-19ahsansaddique100% (2)
- Ruiz - Mutonni - 2009Document11 pagesRuiz - Mutonni - 2009Jackeline SantosNo ratings yet
- Pile Cap DesignDocument12 pagesPile Cap DesignBhaskar Jyoti Das100% (2)
- Prestress Presentation SAB4323 OCW Topic 1Document50 pagesPrestress Presentation SAB4323 OCW Topic 1dasdhjhkjNo ratings yet
- ALL ConcreteDocument261 pagesALL ConcreteSaman AdelNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 1Document19 pagesLecture - 1Chala Giduma WakjiraNo ratings yet
- Subject: Structural Design III Introduction of Subject: Examination SchemeDocument63 pagesSubject: Structural Design III Introduction of Subject: Examination SchemeKiran BandeNo ratings yet
- Torsion Aci DesignDocument8 pagesTorsion Aci Designabbasshaikh21682No ratings yet
- Introduction To Seismic Analysis of Irregular BridgesDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Seismic Analysis of Irregular BridgeslawanNo ratings yet
- SDIII LectureDocument210 pagesSDIII LectureKiran BandeNo ratings yet
- CE 015 03 Design For Shear and TorsionDocument40 pagesCE 015 03 Design For Shear and TorsionDARIUS DAVE CRUZNo ratings yet
- RC Beam Torsion Design To PCA Comment PDFDocument8 pagesRC Beam Torsion Design To PCA Comment PDFEngChuan LimNo ratings yet
- PDH Torsion Concrete Design PDFDocument8 pagesPDH Torsion Concrete Design PDFTaanzNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Background: Dr. C. CapraniDocument27 pages1.1 Background: Dr. C. CapraniAnamta ZehraNo ratings yet
- Anchoring in Cracked ConcreteDocument11 pagesAnchoring in Cracked Concretekjpatel2No ratings yet
- Beam Shear BehaviourDocument10 pagesBeam Shear BehaviourEr Saurabh ShahNo ratings yet
- Precast ConnectionDocument108 pagesPrecast ConnectionFreddie Koo100% (2)
- Basic Prestressed Concrete Design: Sergio F. Breña University of Massachusetts AmherstDocument62 pagesBasic Prestressed Concrete Design: Sergio F. Breña University of Massachusetts AmherstAnees RehamnNo ratings yet
- Definition of PrestressDocument26 pagesDefinition of Prestressasaad mahmood mezbanNo ratings yet
- Strasky 2004 CBCDocument17 pagesStrasky 2004 CBCMangesh kevadkarNo ratings yet
- Performance of Steel Structures During The 1994 Northridge EarthquakeDocument23 pagesPerformance of Steel Structures During The 1994 Northridge Earthquakeamare21No ratings yet
- Prepared By: 1 - Mohammad Ismail 2 - Moutasem Muhaisen Submitted To: Professor Samih QaqishDocument44 pagesPrepared By: 1 - Mohammad Ismail 2 - Moutasem Muhaisen Submitted To: Professor Samih Qaqishanon_30048258No ratings yet
- Bridges & StructuresDocument29 pagesBridges & Structuresjhoward2012npNo ratings yet
- Prestressed Concrete Design Lecture NotesDocument52 pagesPrestressed Concrete Design Lecture NotesChristopher John Natividad100% (1)
- Basic Theory of Structures: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionFrom EverandBasic Theory of Structures: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Structural Concrete: The Commonwealth and International Library: Structures and Solid Body Mechanics DivisionFrom EverandStructural Concrete: The Commonwealth and International Library: Structures and Solid Body Mechanics DivisionNo ratings yet
- Tall Buildings: The Proceedings of a Symposium on Tall Buildings with Particular Reference to Shear Wall Structures, Held in the Department of Civil Engineering, University of Southampton, April 1966From EverandTall Buildings: The Proceedings of a Symposium on Tall Buildings with Particular Reference to Shear Wall Structures, Held in the Department of Civil Engineering, University of Southampton, April 1966A. CoullRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Some Mooted Questions in Reinforced Concrete Design American Society of Civil Engineers, Transactions, Paper No. 1169, Volume LXX, Dec. 1910From EverandSome Mooted Questions in Reinforced Concrete Design American Society of Civil Engineers, Transactions, Paper No. 1169, Volume LXX, Dec. 1910No ratings yet
- Introduction to Design of Building StructuresFrom EverandIntroduction to Design of Building StructuresRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (22)
- Bridge Design & Assessment: PSC SLS Design: Deflection ExampleDocument16 pagesBridge Design & Assessment: PSC SLS Design: Deflection ExampleEngr Aizaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- 3-Shear Provisions SlidesDocument15 pages3-Shear Provisions SlidesEngr Aizaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- s11803 006 0602 5Document8 pagess11803 006 0602 5Engr Aizaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Bridge Design Project: A/Prof. Colin Caprani (CL) DR Kong Sih Ying (MA) Semester 1, 2022Document13 pagesBridge Design Project: A/Prof. Colin Caprani (CL) DR Kong Sih Ying (MA) Semester 1, 2022Engr Aizaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- A New Method For Modelling Cohesive Cracks Using Nite ElementsDocument16 pagesA New Method For Modelling Cohesive Cracks Using Nite ElementsEngr Aizaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- 4-Shear Example SlidesDocument14 pages4-Shear Example SlidesEngr Aizaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- 2-Shear Design SlidesDocument9 pages2-Shear Design SlidesEngr Aizaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Solids and Structures: A. Edalat Behbahani, J.A.O. Barros, A. Ventura-GouveiaDocument21 pagesInternational Journal of Solids and Structures: A. Edalat Behbahani, J.A.O. Barros, A. Ventura-GouveiaEngr Aizaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- University of Engineering and Technology, Peshawar Directorate of Postgraduate Studies Master Degree Program Course Registration FormDocument2 pagesUniversity of Engineering and Technology, Peshawar Directorate of Postgraduate Studies Master Degree Program Course Registration FormEngr Aizaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Table: 10.1 Education IndicatorsDocument17 pagesTable: 10.1 Education IndicatorsEngr Aizaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Torsion of Non Circular BarsDocument19 pagesModule 5 Torsion of Non Circular BarsEngr Aizaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Wisdot Bridge Manual: Chapter 8 - HydraulicsDocument58 pagesWisdot Bridge Manual: Chapter 8 - HydraulicsEngr Aizaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: Distributed Forces: Moments of Inertia: Da y R A y A P FDocument5 pagesChapter 9: Distributed Forces: Moments of Inertia: Da y R A y A P FEngr Aizaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Topics To Be Discussed: Quadrilateral ElementsDocument24 pagesTopics To Be Discussed: Quadrilateral ElementsEngr Aizaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Assignment No.3, Mechanics of Solids-II (CE-228) 4th Semester Spring 2021, Department of Civil Engineering, UET PeshawarDocument1 pageAssignment No.3, Mechanics of Solids-II (CE-228) 4th Semester Spring 2021, Department of Civil Engineering, UET PeshawarEngr Aizaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Reprinted With Permission: General Organization of A Literature Review Paper by Professor Lynne BondDocument1 pageReprinted With Permission: General Organization of A Literature Review Paper by Professor Lynne BondEngr Aizaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Principal Stresses Acting On Materials In2Dand3DDocument22 pagesPrincipal Stresses Acting On Materials In2Dand3DEngr Aizaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet Parts of A FlowerDocument3 pagesActivity Sheet Parts of A Flowersample onlyNo ratings yet
- Leica MP InstructionsDocument60 pagesLeica MP Instructionsamoebahydra100% (1)
- VEQU MS CV 001 MS - Geotechnical Soil Investigation - Rev.ADocument44 pagesVEQU MS CV 001 MS - Geotechnical Soil Investigation - Rev.ATranThuTrangNo ratings yet
- Effect of Consumption of The Nutrient-Dense, Freshwater Small FishDocument17 pagesEffect of Consumption of The Nutrient-Dense, Freshwater Small FishFaisalNo ratings yet
- Carboguard 891: Selection & Specification DataDocument4 pagesCarboguard 891: Selection & Specification DataPrakashNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - Syntax Tree Diagram in Japanese Tree Diagram in Japanese From Deep StructureDocument94 pagesDokumen - Tips - Syntax Tree Diagram in Japanese Tree Diagram in Japanese From Deep StructureAdisaka M HendiyantoNo ratings yet
- CAT 950 Oil SpecDocument8 pagesCAT 950 Oil SpecbarazamelNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus Instrumentation Control Lab.Document3 pagesCourse Syllabus Instrumentation Control Lab.Monique OrugaNo ratings yet
- Doubtnut Today: Ques No. Concept For Jee - Chapter Quadratic Equations 1. BasicsDocument14 pagesDoubtnut Today: Ques No. Concept For Jee - Chapter Quadratic Equations 1. BasicsrajiNo ratings yet
- ERGNOMICSOFTRACTORvol 16 No 1Document112 pagesERGNOMICSOFTRACTORvol 16 No 1Yosun KarasuNo ratings yet
- Year 4 5 6 SimilesDocument5 pagesYear 4 5 6 SimilesRachel FaizatulNo ratings yet
- Welding HandbookDocument48 pagesWelding HandbookMohan Prasad.M93% (27)
- Thermosonication and Optimization of Stingless Bee Honey ProcessingDocument15 pagesThermosonication and Optimization of Stingless Bee Honey ProcessingsyazaqilahNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Psychology G11Document4 pagesFinal Exam Psychology G11Meetali ArchitNo ratings yet
- Agilent 1290 Infinity UHPLCDocument20 pagesAgilent 1290 Infinity UHPLCSebastián LuceroNo ratings yet
- Time TableDocument1 pageTime TableAbhishek ChandraNo ratings yet
- Wind Load Provisions and Steel Specifications For RussiaDocument10 pagesWind Load Provisions and Steel Specifications For Russialazy5100% (1)
- The Merk IndexDocument182 pagesThe Merk IndexReply choice100% (1)
- Relationships Mark MansonDocument31 pagesRelationships Mark MansonBao NgocNo ratings yet
- Close-Up B1+ Workbook Unit 7 PDFDocument6 pagesClose-Up B1+ Workbook Unit 7 PDFkyriaki tsigounakiNo ratings yet
- Desoldering Tool: Designed For Lead FreeDocument2 pagesDesoldering Tool: Designed For Lead FreeMarco Antonio Ortiz RomeroNo ratings yet
- B00H83LE66 SoftArchive - Net WomenDocument102 pagesB00H83LE66 SoftArchive - Net WomensuzukishareNo ratings yet
- TPM RCMDocument15 pagesTPM RCMflih khadidjaNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular AccidentDocument29 pagesCerebrovascular AccidentMarites GalvezNo ratings yet
- Carrie Jenkins - What Love Is - and What It Could Be-Hachette (Perseus) (2017)Document185 pagesCarrie Jenkins - What Love Is - and What It Could Be-Hachette (Perseus) (2017)Angélica Pena-Martínez100% (2)
- Protected Areas in The PhilippinesDocument7 pagesProtected Areas in The PhilippinesPaula TobiasNo ratings yet
- Sensors 23 04580 With CoverDocument23 pagesSensors 23 04580 With CoverMuhammad AirlanggaNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table WorksheetDocument23 pagesPeriodic Table Worksheetlakshmi ghayathri N.M.No ratings yet