Professional Documents
Culture Documents
02 - Hydrocarbon - 25-04-2021 - Paper
Uploaded by
ArchanaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
02 - Hydrocarbon - 25-04-2021 - Paper
Uploaded by
ArchanaCopyright:
Available Formats
The Leader In Chemistry .....
NEET-2021-22 [XIIth Batch]
Test-02 Hydrocarbon
RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * *
Target Marks : 180 Date : 25/04/2021
Time : 50 min Sub. : Chemistry
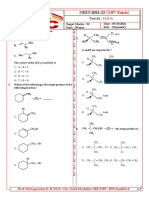
1. Find out (B) in the following reaction. AlCl
8. CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – CH3 Δ3 CH3 CH CH3
|
CH3 CH3
|
CH3– C CH2 – Cl Na
ether
A is Above reaction is an example of :
| 1) isomerization 2) polymerization
CH3
3) cracking 4) de-hydrogenation
9. What is the major product of the reaction?
1) 2)
hv
+ Br2 ?
Br
3) 4) Br
1) 2)
2. Symmetrical alkanes are prepared by :
1) Wurtz reaction 2) Frankland reaction
3) Kolbe’s reaction 4) All 3) Br 4)
Br
3. Which of the following alkane will be formed in high
yield by Wurtz reaction? 10. The order of reactivity of halogens in aliphatic
substitution reactions is
1) 2) 1) Br2 > Cl2 > F2 2) Cl2 > Br2 > F2
3) F2 > Cl2 > Br2 4) F2 > Br2 > Cl2
3) 4) 11. Halogenation of alkanes is an example of
1) Electrophilic substitution
4. The compounds formed at anode in the electrolysis 2) Nucleophilic substitution
of an aqueous solution of CH3COOK are:
3) Free radical substitution
1) C2H6 and CO2 2) C2H4 and CO2
4) Oxidation
3) CH4 and H2 4) CH4 and CO2
CH3
|
H SO 4
12. CH3CH2 C CH CH3 2
P
heat (Major)
5. I. II. III. | |
CH3 OH
Which of the following orders in correct for the ease What is the major product P in the above reaction ?
of decarboxylation of these acids? CH3
1) I > II > III 2) III > II > I |
1) CH3CH2 CH CH CH2
3) II > I > III 4) II > III > I
6. The treatment of CH3MgX with CH3 CH3
CH3C C – H produces | |
2) CH3 CH CH CH CH2
1) CH4 2) CH3 – CH = CH2
H H CH 3
| | |
3) CH3C C – CH3 4) CH3– C = C –CH3 3) CH CH C CH CH
3 2 2
|
7. In alkanes, the bond angle is CH 3
1) 109.50 2) 109 0
3) 120 0 4) 180 0 CH3 CH3
| |
4) CH3CH2 C C CH3
Prof. Motegaonkar S. R. M.Sc. Che. Gold Medalist, SET/NET--JRF Qualified 1
H
19. Observe the following reactions and predict the
2
13. The reaction, RC CR Lindlar's
catalyst gives the main
nature of A and B.
product as
RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * *
HBr
1) cis-Alkene 2) trans-Alkene B
H 2O 2
3) Alkane 4) None of these
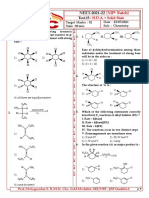
14. In the reaction,
HBr Alc.KOH n
B C Re
A
d
Propane.
Ni / 473 573K 1) A and B both are
What is 'A' ?
1) ethene 2) propene
3) ethane 4) propane 2) A and B both are
15. HBr reacts with CH2 = CH – OCH3 under anhydrous
conditions at room temperature to give
1) CH3CHO and CH3Br 3) A is & B is
2) BrCH2CHO and CH3OH
3) BrCH2 – CH2 – OCH3
4) H3C – CHBr – OCH3 4) A is & B is
ROOR
[X] [Y] ; [X]
16. CH3CH2 – CH = CH2 + HBr
Major Minor
20. H3C CH CH CH2 HBr A ; A (predominantly) is
& [Y] respectively are |
CH3
1) BrCH2CH2CH = CH2 & C2H5 – CHBr – CH3
2) C2H5–CH2CH2–Br & Br–CH2CH2–CH=CH2 1) CH3 CH CH CH3
3) C2H5 – CH2 – CH2Br & C2H5–CHBr – CH3 | |
Br CH3
4) C2H5CHBr – CH3 & C2H5 – CH2 – CH2 Br
2) CH3 CH CH CH3
17. The reaction of CH3CH = CH OH with | |
CH3 Br
HBr gives
3) CH3 CH CH2 CH2 Br
|
1) CH3CHBrCH2 OH CH3
Br
2) CH3CH2CHBr OH |
4) CH3 C CH2 CH3
|
CH3
3) CH3CHBrCH2 Br
21. Which products are formed during the addition of
Br2 on ethylene in presence of aqueous NaCl solution
4) CH3CH2CHBr Br 1) CH 2Br CH2Br 2) CH2Br CH2Cl
3) CH2Cl CH2Cl 4) Both (1) and (2)
22. Ethylene reacts with sulphur monochloride to give
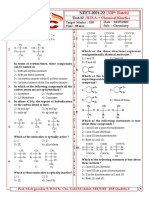
18.
1) Phosgene 2) Mustard gas
3) Ethylene chloride 4) None of these
23. dil.
H2SO4
1) 2) OH
1) OH 2)
HO
3) OH 4)
3) 4)
Prof. Motegaonkar S. R. M.Sc. Che. Gold Medalist, SET/NET--JRF Qualified 2
28. The general formula of alkynes is
24. dil. H2SO4
1) CnH2n+2 2) CnH2n
CH = CH – CH3 3) CnH2n–2 4) CnH2n–4
RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * *
29. A compound on heating with silver powder gives the
1) first member in the alkyne series. That compound
CH2 – CH – CH3 is
1) Ethyl halide
OH
2) Ethylene halide
3) Acetylene tetrahalide
2) 4) Haloform
CH – CH2 – CH3 30. The garlic smell of Acetylene is due to the presence
of
OH
1) H 2 S 2) SO 2
3) (1) and (2) 3) PH3 4) Both H2S & PH3
4) OH
CH2 – CH2 – CH3
31. CC–C C Li
/ NH
3( l)
Product :
25. CH2 on ozonolysis gives 1)
O 2)
1) + HCHO
CHO
2)
3) Both (1) and (2)
COCH3
3) 4)
4) None of these
CH3
CH2Br
32. H3C–C Product
26. N.B.S.
(A)
1) an optically active compound
2) an optically inactive compound
CH3
CH3 3) a racemic mixture
CH3 C H 4) a distereomeric mixture
CH3 C Br
33. Which of the following reacts with ammonical
N.B.S.
cuprous chloride ?
1) CH4 2) C2H2
(B)
3) C2H6 4) C6H6
Which has faster rater 34. In the reaction
1) A 2) B HgSO
CH3 – CH2C CH 4 X, the compouond X is
H SO 2 4
3) both have equal rate4) none
27. In the reaction, O
Alkaline
||
CH3 – CH = CH2 X; 'X' is 1) CH3–CH2– C – CH3
KMnO 4
2) CH3–CH2–CH2–CHO
1) propylene glycol 2) ethylene glycol
3) CH3–CH2–CH2–COOH
3) propyl alcohol 4) both 1 and 2
4) None of these
Prof. Motegaonkar S. R. M.Sc. Che. Gold Medalist, SET/NET--JRF Qualified 3
35. The acidic nature of hydrogens in acetylene can be 41. The major products (P, Q) in the given reaction
explained by the reaction with are:
1) Sodium metal
RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * *
2) Ammonical cuprous chloride solution
3) Ammonical silver nitrate solution
4) All the above
36. The colour of the precipitate formed when acetylene
1)
is passed through ammonical cuprous chloride
solution is
1) White 2) Red
3) Blue 4) Green
2)
37. In the halogenation of aromatic nucleus, the halogen
carrier, used to generate the species is :
1) Cl 2) Cl+
3) Cl– 4) Cl2– 3)
38. The attacking species in aromatic sulphonation is:
1) SO 3 2) H3SO4+
3) HSO4– 4) SO 2+
39. Xylene on oxidation with acidic KMnO4 gives: 4)
1) phthalic acid 2) isophthalic acid
3) terephthalic acid 4) all of these 42. The major product U in the following reactions is:
40. What product are formed when the following
compound is treated with Br2 in the presence of
FeBr3?
CH3
CH3 1) 2)
CH3 CH3
Br
and
1) CH3 CH3
Br 3) 4)
CH3 CH3 43. Which of the following ions is produced when we
Br Br prepare nitrating mixture by mixing together
2) concentrated HNO3 and concentrated H2SO4?
and
CH3 CH3 1) NO 2 2) NO 2
CH3 CH3 3) NO 3 4) SO 3 H
Br
44. Aromatic compounds undergo most easily.
and
3) 1) nucleophilic substitution
CH3 CH3
2) electrophilic substitution
Br 3) nucleophilic addition
4) electrophilic addition
CH3 CH3 45. Benzene reacts with n-propyl chloride in the
presence of anhydrous AlCl3 to give predominantly:
and 1) isopropyl benzene
4)
CH3 Br CH3 2) no reaction
Br 3) n-propylbenzene
4) 3-propyl-1-chlorobenzene
Prof. Motegaonkar S. R. M.Sc. Che. Gold Medalist, SET/NET--JRF Qualified 4
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- K-Flex ST Class 0 CatalogueDocument6 pagesK-Flex ST Class 0 CatalogueBac VuNo ratings yet
- AutoPLANT EquipmentDocument2 pagesAutoPLANT EquipmentGPNo ratings yet
- Supafirefly 1Document8 pagesSupafirefly 1api-356919224No ratings yet
- CeramicDocument13 pagesCeramicJerica Lacostales LeosalaNo ratings yet
- 2023-1509 TopSolid'Design TutorialDocument53 pages2023-1509 TopSolid'Design TutorialMáy TiệnNo ratings yet
- ITP For Storage TankDocument6 pagesITP For Storage Tankittiphon3194% (17)
- Buku Tahun 5Document234 pagesBuku Tahun 5Hazyzyizuan Bin Abu HassaNo ratings yet
- Toledo Glass Pavilion AnalysisDocument4 pagesToledo Glass Pavilion Analysisbryanpansing67% (3)
- GradDocument74 pagesGradMoHamedNo ratings yet
- Anantadrishti Physics Classes: Sheet-2 Cbse and Isc Target-25 MinuteDocument2 pagesAnantadrishti Physics Classes: Sheet-2 Cbse and Isc Target-25 MinuteArchanaNo ratings yet
- 05 Solution 16-05-2021Document4 pages05 Solution 16-05-2021ArchanaNo ratings yet
- Sex Determination Class 12Document2 pagesSex Determination Class 12ArchanaNo ratings yet
- Violation of Privacy in Computers and It'S Prevention: by I ArchanaDocument7 pagesViolation of Privacy in Computers and It'S Prevention: by I ArchanaArchanaNo ratings yet
- Inheritance: 441 Linkage Exception To Independent Assortment)Document3 pagesInheritance: 441 Linkage Exception To Independent Assortment)ArchanaNo ratings yet
- 26 H.D.A. 07-10-2021 PaperDocument4 pages26 H.D.A. 07-10-2021 PaperArchanaNo ratings yet
- 15 H.D.A. Solid State 25-07-2021Document3 pages15 H.D.A. Solid State 25-07-2021ArchanaNo ratings yet
- 13 H.D.A. Solid State 11-07-2021 PaperDocument4 pages13 H.D.A. Solid State 11-07-2021 PaperArchanaNo ratings yet
- 30 Solution 23-10-2021 PaperDocument2 pages30 Solution 23-10-2021 PaperArchanaNo ratings yet
- 14 H.D.A. Solid State 18-07-2021 PaperDocument5 pages14 H.D.A. Solid State 18-07-2021 PaperArchanaNo ratings yet
- 19 H.D.A. 15-08-2021 PaperDocument3 pages19 H.D.A. 15-08-2021 PaperArchanaNo ratings yet
- 04 Some Basic Concept of Chemistry 09-05-2021 PaperDocument3 pages04 Some Basic Concept of Chemistry 09-05-2021 PaperArchanaNo ratings yet
- 12 H.D.A. Chemical Kinetics 04-07-2021 PaperDocument5 pages12 H.D.A. Chemical Kinetics 04-07-2021 PaperArchanaNo ratings yet
- 3511815545AFMC MBBS Information Brrochure 2018Document25 pages3511815545AFMC MBBS Information Brrochure 2018ArchanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Life Section 2-1 The Nature of MatterDocument3 pagesChapter 2 The Chemistry of Life Section 2-1 The Nature of MatterAmy GibbonsNo ratings yet
- ClearCase Basics - CompleteDocument58 pagesClearCase Basics - Completesxsund6No ratings yet
- AbusDocument27 pagesAbusMargelatu AndreyNo ratings yet
- Unit-III-SQL RDBMS: A Lalitha Associate Professor Avinash Degree CollegeDocument32 pagesUnit-III-SQL RDBMS: A Lalitha Associate Professor Avinash Degree CollegelalithaNo ratings yet
- IPM45 ClarkeDocument8 pagesIPM45 ClarkedevendratandleNo ratings yet
- Datasheet PDFDocument9 pagesDatasheet PDFValentina LópezNo ratings yet
- Theory Costant Head MethodDocument4 pagesTheory Costant Head MethodsyathirohNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Report SeminarDocument27 pagesBlockchain Report SeminarArsalan MakkiNo ratings yet
- QUIZDocument6 pagesQUIZQuerubee Donato DiolulaNo ratings yet
- Selenium Interview Questions and Answers - Click4Interviews PDFDocument3 pagesSelenium Interview Questions and Answers - Click4Interviews PDFAbhilash KvNo ratings yet
- CONICS PAST YEARS QUESTIONS Mid Semester PDFDocument5 pagesCONICS PAST YEARS QUESTIONS Mid Semester PDFYuyeen FarhanahNo ratings yet
- Electronegativity ScalesDocument8 pagesElectronegativity ScalesrashidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Walls and Buried Structures: WSDOT Bridge Design Manual M 23-50.20 Page 8-I September 2020Document56 pagesChapter 8 Walls and Buried Structures: WSDOT Bridge Design Manual M 23-50.20 Page 8-I September 2020Vietanh PhungNo ratings yet
- Gandhi GlobalDocument30 pagesGandhi Globalmayank sharmaNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Lab 1Document4 pagesEnzyme Lab 1PrincessTNo ratings yet
- Package Information: 9° (All Sides)Document5 pagesPackage Information: 9° (All Sides)MUSIC ELECNo ratings yet
- Artificial Neural Network and Its ApplicationsDocument21 pagesArtificial Neural Network and Its ApplicationsHImanshu DabralNo ratings yet
- Service ManualDocument144 pagesService ManualMariusBelecciuNo ratings yet
- Akkaya Katalog EN 2019Document66 pagesAkkaya Katalog EN 2019Juan MendozaNo ratings yet
- Log ChromiumDocument1 pageLog ChromiumA.B STUDIOSNo ratings yet
- Studio One 5 - Release NotesDocument20 pagesStudio One 5 - Release NotesFredrick Yosafat SinlaeloeNo ratings yet