Professional Documents
Culture Documents
14 H.D.A. Solid State 18-07-2021 Paper
Uploaded by
ArchanaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
14 H.D.A. Solid State 18-07-2021 Paper
Uploaded by
ArchanaCopyright:
Available Formats
The Leader In Chemistry .....
NEET-2021-22 [XIIth Batch]
Test-14 : H.D.A. + Solid State
RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * *
Target Marks : 180 Date : 18/07/2021
Time : 50 min Sub. : Chemistry
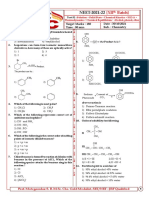
4. The product of the following SN2 reaction is
CH 3
CH 3CH 2ONa
|
1. B CH3CH 2OH
CH3– C Br A
(major)
(Major) CH3CH 2OH
|
CH 3
A and B respectively are
CH 3
|
1) CH3– C OCH 2CH 3 in both case
| 1) 2)
CH 3
CH 3
|
2) CH3– C CH 2 in both case
3) 4)
CH 3 CH3
|
3) CH3– C OCH 2CH 3 and C=CH2
| CH3 5. Which of the following alkyl bromide will give
CH 3 rearrange product under SN1 reaction?
CH 3 1)
CH3 |
4) C=CH2 and CH3– C OCH 2CH 3
CH3 |
CH 3
2)
2. Which is least reactive towards nucleophilic
substitution (SN2)?
1) CH2=CH–CH2Cl 2) (CH3)3C–Cl 3)
Cl
3) 4) CH3–CH(Cl)CH3 4)
3. In a SN2 substitution reaction of the type 6. Which of the following most reactive in SN2
reaction?
DMF
R–Br + Cl– R–Cl + Br–
1) CH3Br + OH–
CH3OH + Br–
which one of the following has the highest
relative rate? 2) CH3– CH –CH3 + OH–CH3– CH CH3 Br
| |
Br OH
CH 3
|
1) CH3– CH CH 2 Br 2) CH3– C CH 2 Br H 2O
3) CH3CH2OH CH2=CH2
| |
CH 3 CH 3
4) (CH3)3C–Br + OH–
(CH3)3COH + Br–
3) CH3CH2Br 4) CH3CH2CH2Br
Prof. Motegaonkar S. R. M.Sc. Che. Gold Medalist, SET/NET--JRF Qualified 1
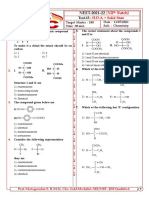
7. The structure of the major product formed in 9. The major product formed in the reaction,
the following reaction is
RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * *
is
1)
1) 2)
2)
3) 4)
3)
4)
10. , Major product (A) is :
8. The major of the following reaction is
1) 2)
1) 2)
3) 4)
3) 4)
Prof. Motegaonkar S. R. M.Sc. Che. Gold Medalist, SET/NET--JRF Qualified 2
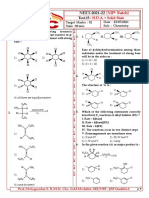
15. ?
11. Product.
RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * *
Major product of the reaction is :
Product of the reaction is
I. II.
1) 2)
III. IV.
3) 4)
V.
12. Given the major product of the following
reaction. 1) I 2) II
3) III 4) IV
16. In the given reaction :
1) 2) [X], X is
3) 4) 1) 2)
13. The reaction described as :
3) 4)
1) SE2 2) SE1 17. Compare rate of reaction with Ag NO3 or rate
3) SN2 4) SN1 of SN1 reaction :
14. Assuming no other changes, what is the effect
of doubling only the concentration of the
nucleophile in the following reaction?
(CH3)3CBr + I
(CH3)3CI + Br
1) No change 1) i > ii > iii
2) Double the rate 2) ii > iii > i
3) Triple the rate 3) iii > i > ii
4) Quadruples the rate 4) ii > i > iii
Prof. Motegaonkar S. R. M.Sc. Che. Gold Medalist, SET/NET--JRF Qualified 3
18. Among the bromides I-III given below, the 23. Which of the following S N2 reaction is the
order of reactivity SN1 reaction is : fastest?
1) CH3CH2CH2CH2Br + OH–
RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * *
CH3CH2CH2CH2OH + Br–
2) CH3CH2CHBrCH3 + OH–
CH3CH2CH2CH2OH + HBr
1) III > I > II 2) III > II > I 3) CH3CH2CHBrCH3 + OH–
3) II > III > I 4) II > I > III CH3CH2CHOHCH3 + Br–
19. Which of the following compounds will be 4) CH3CH2CHBrCH3 + H2O
most reactive for SN1 reactions? CH3CH2CHOHCH3 + HBr
24. Graphite is an example of
1) 2) 1) Ionic solid 2) Covalent solid
3) Metallic crystal 4) None of these
25. In a Hexagonal crystal :
1) = = 90o; a = b = c
3) 4)
2) = = = 90o; a = b c
3) = = = 90o; a b c
4) = = 90o, = 120o; a = b c
20. Compare rate of reaction with Ag NO 3
or rate 26. The most unsymmetrical and symmetrical
of SN1 reaction systems are, respectively :
CH2–Br
1) Tetragonal, Cubic 2) Triclinic, Cubic
Br Br
3) Rhombohedral, Hexagonal
i. ii. iii. 4) Orthorhombic, Cubic
27. What are the number of atoms per unit cell
1) i > ii > iii 2) ii > iii > i and the number of nearest neighbours in a
3) iii > ii > i 4) iii > i > ii simple cubic structure ?
21. Assuming no other changes, what is the effect 1) 1, 6 2) 4, 12
of doubling both the concentration of the alkyl 3) 2, 8 4) 2, 6
halide and the nuclephile in the following 28. What are the number of atoms per unit cell
reaction? and the number of nearest neighbours in a
(CH3)3CBr + I
(CH3)3CI + Br
body centered cubic structure ?
1) 4, 12 2) 1, 6
1) No change
3) 2, 8 4) 2, 5
2) Double the rate
29. The body centered cubic cell of chromium has
3) Triples the rate a edge length of 0.288 nm. Calculate the density
4) Quadruples the rate of chromium (g/cm3) :
22. Without exception, S N2 reaction at chiral (Atomic weight = Cr = 52.0)
carbon gives : 1) 6.80 2) 7.60
1) enantiomer of substrate 3) 6.60 4) 7.23
2) product of opposite polarity 30. Molybdenum (At. wt. = 96 g mol–1) crystallizes
3) diastereomeric mixture as bcc crystal. If density of crystal is 10.3 g/cm3,
4) only one stereoisomer then radius of Mo atom is (use NA = 6 × 1023)
1) 111 pm 2) 314 pm
3) 135.96 pm 4) None of these
Prof. Motegaonkar S. R. M.Sc. Che. Gold Medalist, SET/NET--JRF Qualified 4
31. Cu, Ag, Au have close-packing of the type : 39. How much part of any corner constituent
1) Hexagonal close-packing particle actually belongs to a particular unit
cell ?
2) Cubic close-packing
RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * * RCC * *
3) Body-centred cubic packing 1 1
1) th 2) th
4) Malleability is not related to type of packing 4 6
32. The atomic radius of strontium (Sr) is 215 pm 1 1
and it crystallizes with a cubic closest packing. 3) th 4) th
8 10
Edge length of the cube is :
40. In a face centred cubic lattice, atom A occupies
1) 430 pm 2) 608.2 pm the corner positions and atom B occupies the
3) 496.53 pm 4) None of these face centre positions. If one atom of B is
33. Which one of the following is a good conductor missing from one of the face centred points,
of electricity ? the formula of the compound is
1) Diamond 2) Graphite 1) A2B 2) AB2
3) Silicon 4) Amorphous carbon 3) A2B2 4) A2B5
34. Which of the following is true for diamond ? 41. Which of the following is true about the value
of refractive index of quartz glass ?
1) Diamond is a good conductor of electricity
1) Same in all directions
2) Diamond is soft
2) Different in different directions
3) Diamond is a bad conductor of heat 3) Cannot be measured
4) Diamond is made up of C, H and O 4) Always zero
35. Sodium metal crystallizes as a body-centred 42. Edge length of unit cell of chromium metal is
cubic lattice with the cell edge 4.29 Å. What is 287 pm with bcc arrangement. The atomic radius
the radius of sodium atom ? is of the order :
1) 1.857 × 10–8 cm 2) 2.371 × 10–7 cm 1) 124.27 pm 2) 287 pm
3) 3.817 × 10–8 cm 4) 9.312 × 10–7 cm 3) 574 pm 4) 143.5 pm
36. A compound is formed by elements X and Y. 43. The sharp melting point of crystalline solids is
This crystallizes in the cubic structure when due to
atoms X are the corners of the cube and atoms 1) A regular arrangement of constituent particles
Y are at the centre of the body. The simplest observed over a short distance in the crystal
formula of the compound is : lattice
1) XY 2) XY2 2) A regular arrangement of constituent particles
observed over a long distance in the crystal
3) X2Y 4) XY4
lattice
37. Three elements A, B and C crystallize into a
3) Same arrangement of constituent particles in
cubic solid lattice. Atoms A occupy the corners,
different directions
B atoms, the cube centres and C atoms, the
4) Different arrangement of constituent particles
edge. The formula of the compound is :
in different directions
1) ABC 2) ABC2
44. In a cubic unit cell, seven of the eight corners
3) ABC3 4) ABC4 are occupied by atoms A and centres of faces
38. If a is the length of the side of a cube, the are occupied by atoms B. The general formula
distance between the body centered atom and of the compound is :
one corner atom in the cube will be : 1) A7B6 2) A7 B12
3) A7 B24 4) A24 B7
3 3
1) a 2) a 45. A metal X crystallises in a face-centered cubic
4 2
arrangement with the edge length 862 pm. What
2 4 is the shortest separation of any two nuclei of
3) a 4) a the atom ?
3 3
1) 406 pm 2) 707 pm
3) 862 pm 4) 609.6 pm
Prof. Motegaonkar S. R. M.Sc. Che. Gold Medalist, SET/NET--JRF Qualified 5
You might also like
- Organic Chemistry Help! Practice Exam Window For Xula-O1e2Document7 pagesOrganic Chemistry Help! Practice Exam Window For Xula-O1e2Kristia Stephanie BejeranoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 HydrocarbonDocument25 pagesChapter 5 Hydrocarbonmeshal retteryNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual for The Elements of Polymer Science and EngineeringFrom EverandSolution Manual for The Elements of Polymer Science and EngineeringRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Sub-Grade Water ProofingDocument16 pagesSub-Grade Water Proofingdkpandey50% (2)
- (02-12-14) AlkenesDocument4 pages(02-12-14) Alkenessasi.curieNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Max. Marks: 61 Section - I (Single Correct Choice Type)Document6 pagesChemistry Max. Marks: 61 Section - I (Single Correct Choice Type)VENKATA SRI RAM KOTIPALLI iitjkkdNo ratings yet
- Haloalkane & Haloarene - DPP 03Document4 pagesHaloalkane & Haloarene - DPP 03girirajsonghNo ratings yet
- General Organic Chemistry-02 - Solved ProblemsDocument10 pagesGeneral Organic Chemistry-02 - Solved ProblemsRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Alkenes (Fasi)Document3 pagesAlkenes (Fasi)kjjkimkmkNo ratings yet
- Selina Concise Chemistry Solutions Class 10 Chapter 12 Organic ChemistryDocument54 pagesSelina Concise Chemistry Solutions Class 10 Chapter 12 Organic ChemistryKrishnaPriyaNo ratings yet
- Wa0005Document5 pagesWa0005rishigullipalli2007No ratings yet
- Part (B) : Chemistry: Major Test - 4 (Main) Chemistry (CodeDocument12 pagesPart (B) : Chemistry: Major Test - 4 (Main) Chemistry (CodeAmit HhcbjNo ratings yet
- 26 H.D.A. 07-10-2021 PaperDocument4 pages26 H.D.A. 07-10-2021 PaperArchanaNo ratings yet
- Haloalkenes and HaloarenesDocument38 pagesHaloalkenes and Haloarenesshashwat201008No ratings yet
- 02 H.D.A. SN1 and SN2 Reaction 10-08-2021Document2 pages02 H.D.A. SN1 and SN2 Reaction 10-08-2021tejas naigaonkarNo ratings yet
- Universiti Kuala Lumpur: Malaysian Institute of Chemical & Bioengineering TechnologyDocument4 pagesUniversiti Kuala Lumpur: Malaysian Institute of Chemical & Bioengineering TechnologyNufar MohmdNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: Daily Practice ProblemsDocument5 pagesOrganic Chemistry: Daily Practice ProblemsArihant KumarNo ratings yet
- WPT Centre Xi Iit Che Key 30-1-23Document3 pagesWPT Centre Xi Iit Che Key 30-1-23pinnaacleclasses salemNo ratings yet
- 6.DAY-8 CHE - Organic Chemistry Electron Migration Effects & Reagents - 25-05-2020 PDFDocument7 pages6.DAY-8 CHE - Organic Chemistry Electron Migration Effects & Reagents - 25-05-2020 PDFRamakrishna ReddyNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemicstryDocument5 pagesOrganic ChemicstryEve LeeNo ratings yet
- Reaction Kinetics (5) : Xuan Cheng Xiamen UniversityDocument27 pagesReaction Kinetics (5) : Xuan Cheng Xiamen Universityahmadhelmiase7621No ratings yet
- 12th NEET ANSWERS - 30 - 04 - 2023Document9 pages12th NEET ANSWERS - 30 - 04 - 2023studyloverx1234No ratings yet
- 474 - CHM 222Document68 pages474 - CHM 222Tariq AbdullahiNo ratings yet
- Locate The Longest Continuous Chain To Determine The Parent NameDocument2 pagesLocate The Longest Continuous Chain To Determine The Parent NamesyikinNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopy Nuclear Magnetic ResonanceDocument54 pagesSpectroscopy Nuclear Magnetic ResonanceDamar Nurwahyu BimaNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1 Organic Chemistry NAME: - SECTIONDocument1 pageProblem Set 1 Organic Chemistry NAME: - SECTIONDom GudezNo ratings yet
- Alkanes: 1.1 Classification of HydrocarbonDocument33 pagesAlkanes: 1.1 Classification of HydrocarbonKhizra TehreemNo ratings yet
- 11 Aldehyde Ketone and C-Acids 19-02-2022 MCQ With SolutionsDocument26 pages11 Aldehyde Ketone and C-Acids 19-02-2022 MCQ With SolutionsANIKET BATTINWARNo ratings yet
- CHM3201 Lab Report S2 2019-2020Document42 pagesCHM3201 Lab Report S2 2019-2020Halimatun MustafaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Problem SetDocument10 pagesOrganic Chemistry Problem SetBermonica Alvior SatuitoNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 4 - Cycloalkanes and StereochemDocument9 pagesProblem Set 4 - Cycloalkanes and StereochemKatrina Louise GonzalesNo ratings yet
- VPTS-3B 18-03-2021Document7 pagesVPTS-3B 18-03-2021Aayush NagpalNo ratings yet
- XI-Chemistry Chapter test-13-Hydrocarbons-SolutionsDocument3 pagesXI-Chemistry Chapter test-13-Hydrocarbons-Solutionsprateek yadavNo ratings yet
- Elimination ReactionDocument6 pagesElimination ReactionDxng 1No ratings yet
- Neet OrganicDocument3 pagesNeet Organicpinnaacleclasses salemNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument97 pagesOrganic ChemistrysairishwanthpannalaNo ratings yet
- Xicbse Che Asst 1 AnsDocument3 pagesXicbse Che Asst 1 Anstanishkakannan3253No ratings yet
- January HW Sec 6Document3 pagesJanuary HW Sec 6Freya SawNo ratings yet
- ND CPT Xi Neet Che 22-01-24Document4 pagesND CPT Xi Neet Che 22-01-24pinnaacleclasses salemNo ratings yet
- Oc PT 2 - Student Copy - (Eng)Document6 pagesOc PT 2 - Student Copy - (Eng)Ramkumar SundaramNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument9 pagesChemistryAyushmanNo ratings yet
- 02.10.22 - SR - STAR CO-SC (MODEL-A&B) - Jee - Adv - 2019 - P1 - PTA-3 - KEY & SOLDocument8 pages02.10.22 - SR - STAR CO-SC (MODEL-A&B) - Jee - Adv - 2019 - P1 - PTA-3 - KEY & SOLOrganic PrasadNo ratings yet
- MCMP 204 Exam #FinalDocument9 pagesMCMP 204 Exam #FinalChauncey NguyenNo ratings yet
- Chem 2016Document4 pagesChem 2016Shubhankar ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Green Park Educational Institutions, Namakkal: Long Term - Chemistry (Worksheet)Document4 pagesGreen Park Educational Institutions, Namakkal: Long Term - Chemistry (Worksheet)Monalisa PremkumarNo ratings yet
- OCHEM Practice FinalsDocument13 pagesOCHEM Practice FinalsNoleNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and Arenes Q and AnsDocument66 pagesHaloalkanes and Arenes Q and AnsSandhya. SNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Letter 203/1/2016: General Chemistry 1BDocument22 pagesTutorial Letter 203/1/2016: General Chemistry 1BLeigh MakanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Ii (Ecf 0024) Tutorial 5: CH CHCH CHCH OHDocument3 pagesChemistry Ii (Ecf 0024) Tutorial 5: CH CHCH CHCH OHutpNo ratings yet
- Ef0c00890 Si 001Document6 pagesEf0c00890 Si 001Austin SmithNo ratings yet
- Chemistry (P-2) Question PaperDocument8 pagesChemistry (P-2) Question PaperRiya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons Work SheetDocument30 pagesHydrocarbons Work SheettarunvishalgrNo ratings yet
- Isomerism DPPDocument4 pagesIsomerism DPPRAGHUL MNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document5 pagesTutorial 1nurqistina hanani HananNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon (SCH Sir)Document5 pagesHydrocarbon (SCH Sir)ArthGadaNo ratings yet
- Alkane PDFDocument5 pagesAlkane PDFRavi Kiran KoduriNo ratings yet
- Alkane Jee-Advance Level-1Document5 pagesAlkane Jee-Advance Level-1Ravi Kiran KoduriNo ratings yet
- DPT 31 Xii Centre Rasi Che Iit 07-12-23Document4 pagesDPT 31 Xii Centre Rasi Che Iit 07-12-23Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- Feb 14 Sheet 1Document1 pageFeb 14 Sheet 1joulinajmeh334No ratings yet
- Réarrangement RadicalaireDocument5 pagesRéarrangement RadicalaireRaf Belo100% (1)
- Anantadrishti Physics Classes: Sheet-2 Cbse and Isc Target-25 MinuteDocument2 pagesAnantadrishti Physics Classes: Sheet-2 Cbse and Isc Target-25 MinuteArchanaNo ratings yet
- Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance: KnowledgeDocument2 pagesChromosomal Theory of Inheritance: KnowledgeArchanaNo ratings yet
- Inheritance: 441 Linkage Exception To Independent Assortment)Document3 pagesInheritance: 441 Linkage Exception To Independent Assortment)ArchanaNo ratings yet
- Sex Determination Class 12Document2 pagesSex Determination Class 12ArchanaNo ratings yet
- 05 Solution 16-05-2021Document4 pages05 Solution 16-05-2021ArchanaNo ratings yet
- Violation of Privacy in Computers and It'S Prevention: by I ArchanaDocument7 pagesViolation of Privacy in Computers and It'S Prevention: by I ArchanaArchanaNo ratings yet
- 30 Solution 23-10-2021 PaperDocument2 pages30 Solution 23-10-2021 PaperArchanaNo ratings yet
- 26 H.D.A. 07-10-2021 PaperDocument4 pages26 H.D.A. 07-10-2021 PaperArchanaNo ratings yet
- 32 Solution Solid State Chem Kinetics Thermo Chem Equi HDA Alc PheDocument4 pages32 Solution Solid State Chem Kinetics Thermo Chem Equi HDA Alc PheArchanaNo ratings yet
- 13 H.D.A. Solid State 11-07-2021 PaperDocument4 pages13 H.D.A. Solid State 11-07-2021 PaperArchanaNo ratings yet
- 15 H.D.A. Solid State 25-07-2021Document3 pages15 H.D.A. Solid State 25-07-2021ArchanaNo ratings yet
- 04 Some Basic Concept of Chemistry 09-05-2021 PaperDocument3 pages04 Some Basic Concept of Chemistry 09-05-2021 PaperArchanaNo ratings yet
- 19 H.D.A. 15-08-2021 PaperDocument3 pages19 H.D.A. 15-08-2021 PaperArchanaNo ratings yet
- 12 H.D.A. Chemical Kinetics 04-07-2021 PaperDocument5 pages12 H.D.A. Chemical Kinetics 04-07-2021 PaperArchanaNo ratings yet
- 02 - Hydrocarbon - 25-04-2021 - PaperDocument4 pages02 - Hydrocarbon - 25-04-2021 - PaperArchanaNo ratings yet
- WWWW WWWW Thermodynamics - 27-10-21 - PaperDocument2 pagesWWWW WWWW Thermodynamics - 27-10-21 - PaperArchanaNo ratings yet
- 3511815545AFMC MBBS Information Brrochure 2018Document25 pages3511815545AFMC MBBS Information Brrochure 2018ArchanaNo ratings yet
- Practical 03 06 J.A.N.Gimhani BST17025Document14 pagesPractical 03 06 J.A.N.Gimhani BST17025Dulanjali PereraNo ratings yet
- Surface-Mounting Rotary DIP Switch A6RSDocument4 pagesSurface-Mounting Rotary DIP Switch A6RSMuhamad PriyatnaNo ratings yet
- CLC PDFDocument10 pagesCLC PDFDEEPAK H LNo ratings yet
- Metals 10 00505Document14 pagesMetals 10 00505qwerty fkvorkcjdkNo ratings yet
- Katalog Dwi Cipta Nugraha PDF-sealsDocument6 pagesKatalog Dwi Cipta Nugraha PDF-sealsAlbertus KaryadiNo ratings yet
- Revision ChemDocument32 pagesRevision ChemNada AlbuainainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24 - Effects of Man On The EnvironmentDocument41 pagesChapter 24 - Effects of Man On The EnvironmentSashoy AustinNo ratings yet
- Cement Manufacturing: (Alan Gee-Lehigh Hanson Cement)Document20 pagesCement Manufacturing: (Alan Gee-Lehigh Hanson Cement)Mythri Metallizing Pvt Ltd ProjectsNo ratings yet
- Dictionary of Pharmacy PDFDocument71 pagesDictionary of Pharmacy PDFquynhak84No ratings yet
- Fire Classification-PrelimDocument6 pagesFire Classification-PrelimLevy DaceraNo ratings yet
- Astm A 751Document5 pagesAstm A 751Patricia MenaNo ratings yet
- Saponins: Properties, Applications and Processing: Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition February 2007Document31 pagesSaponins: Properties, Applications and Processing: Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition February 2007Việt NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Rubber, Plastics & Ceramics REvisedDocument594 pagesRubber, Plastics & Ceramics REvisedI AM NOT CHINESENo ratings yet
- Nutrição Mineral Do GergelimDocument8 pagesNutrição Mineral Do GergelimNICOLAU KLEPA DE LIMANo ratings yet
- Anexo 1. Botham, K Mayes, P. (2022) - Chapter 11 - Bioenergetics - The Role of ATP. McGraw Hill.Document9 pagesAnexo 1. Botham, K Mayes, P. (2022) - Chapter 11 - Bioenergetics - The Role of ATP. McGraw Hill.Liliana LNo ratings yet
- Final Chap 1 To 3 Rpint BrentDocument15 pagesFinal Chap 1 To 3 Rpint BrentCharles AbellanaNo ratings yet
- What Is Surface TreatmentDocument9 pagesWhat Is Surface TreatmentanitaNo ratings yet
- Research Papers On Environmental BiotechnologyDocument8 pagesResearch Papers On Environmental Biotechnologyefh4m77n100% (1)
- DGI PosterDocument1 pageDGI PostercarlosNo ratings yet
- Ahern 1977Document9 pagesAhern 1977João VazNo ratings yet
- Food Safety Is A Scientific Discipline Describing Proper HandlingDocument6 pagesFood Safety Is A Scientific Discipline Describing Proper HandlingMia ChatilaNo ratings yet
- MX Org Input List 9.3.20Document240 pagesMX Org Input List 9.3.20Efren HuertaNo ratings yet
- Dispersion of Carbon Nanotubes in Water and Non-Aqueous SolventsDocument41 pagesDispersion of Carbon Nanotubes in Water and Non-Aqueous SolventsSantiago OrtizNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: 1. Product and Company IdentificationDocument10 pagesSafety Data Sheet: 1. Product and Company IdentificationCoronavilleNo ratings yet
- Market Analysis of Saudi Arabia DetergentsDocument8 pagesMarket Analysis of Saudi Arabia Detergentsharismalak215No ratings yet
- Tab VacDocument19 pagesTab VacMiftah LuthfiNo ratings yet
- AU Instructions For Use Creatine Kinase (CK NAC)Document8 pagesAU Instructions For Use Creatine Kinase (CK NAC)Anas TjNo ratings yet
- Features and Operation of Hollow Cathode Lamps and Deuterium LampsDocument6 pagesFeatures and Operation of Hollow Cathode Lamps and Deuterium Lamps26desemberNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report 416Document18 pagesSeminar Report 416akshay kumar100% (1)