Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Proteins and Enzymes
Uploaded by
Aww AddCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Proteins and Enzymes
Uploaded by
Aww AddCopyright:
Available Formats
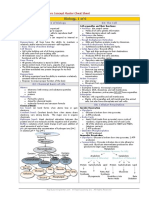
PROTEINS AND ENZYMES Important Proteins in the Body
Proteins
1. Structural Proteins
The most abundant organic compound in living The most abundant class of proteins in
organisms. nature which are fibrous and stringy
Is responsible for the 15% body dry weight. and because of this formation.
These are polymers made up of a chain of the Its main function is to provide
basic building blocks called amino acids. mechanical support. On a larger scale,
Any class of nitrogenous organic compounds they also allow the body to move.
that consist of large molecules composed of Keratin: hair, quills, feathers, horns,
one or more long chains of amino acids. beaks.
Collagen is the most abundant
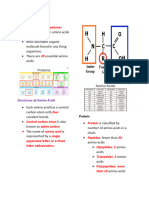
Amino Acids
mammalian protein and the main
These are composed of carbon, hydrogen, component of connective tissues.
oxygen, nitrogen, and sometimes sulfur. Elastin: Arteries, Lungs, Bladder, Skin,
Organisms use 20 essential amino acids for the Elastic Ligaments Cartilage
formation of different proteins.
It is made up of an amino group (-NH2), a 2. Enzymatic Proteins
carboxyl group (-COOH), and a hydrocarbon the All chemical processes in the body need
R group (side chain). a large amount of energy (needs several
Different amino acids differ only on their side hundred degree centigrade).
chain. Human body temperature is 37°C and
any slight increase in temperature can
be fatal.
Special types of proteins called enzymes
catalyze or speed up chemical reactions
at low temperatures.
All enzymatic proteins are Globular
Proteins with a specific Tertiary Shape.
Active Site: The part of the Enzyme that
Amino acids are linked by peptide bonds,
acts a Catalyst. The rest of the Enzyme
formed between the amino group of one amino
is much larger and is involved
acid and the carboxyl group of the next.
in maintaining the specific shape of the
A peptide or polypeptide is a chain of amino enzyme.
acids linked by peptide bonds.
Different combination of 20 amino acids are How do enzymes work?
responsible for the variety of proteins in living
The Activation Energy of a reaction is
organisms.
lowered by putting stress on
A human body is capable of producing about 12 the bonds within a molecule, or
amino acids to form proteins. by holding molecules close together.
This increases the likelihood of a
Essential Amino Acids reaction, and
These are amino acids that cannot synthesize. so lowers the energy required to begin
Either directly or indirectly obtained from other it.
animal and plant sources. Food digestion involves different
Food sources rich in proteins: meat, fish, beans, enzymes, like amylase for starch,
nuts, milk products, flour, and certain protease for protein, and lipase for
vegetables. lipid.
Observing balanced diet is important to provide the Characteristics of Enzymatic Proteins
body with adequate 20 essential amino acids for the a. Enzymes are highly specific. An enzyme can
growth and maintenance of the body’s activities. catalyze only a specific chemical reaction. The
Typical mammalian cell may contain 10,000 enzyme maltase specifically catalyzes the
different kinds of protein working on diverse array of breakdown of maltose into simple sugars.
functions.
b. Enzymes are required in minute amounts. One type of white blood cells called B
molecule of catalase can breakdown of five lymphocytes in response to an antigen.
million molecules of hydrogen peroxide in one Antigen: foreign substance in the body
second. A particular antibody can only recognize
a specific antigen.
c. Enzyme reactions are affected by temperature.
Antibody destroys disease-causing cells
Most enzymes are active only at body
via cell lysis or by aggregating the cells
temperature (37°C), but become inactive at
via agglutination.
very low temperature. Different enzymes hare
Antibody can also detoxify foreign
optimum working temperatures.
substances that may cause damage or
d. Enzyme reactions are affected by pH. Amylase death to affected cells.
works best at pH 7 and becomes denatured or Immunoglobulin: found in blood and
destroyed, at highly acidic or basic conditions. fluids, controls infections of body
tissues, IgG is most abundant.
e. Enzymes are affected by substrate
concentration. Increasing Substrate
5. Regulatory/Signal Proteins
Concentration increases the rate of reaction.
Hormones are signal proteins that
This is because more substrate molecules will
regulate body functions.
be colliding with enzyme molecules, so more
Growth factors are proteins that
product will be formed.
influence the growth and development
3. Transport Proteins of an organism.
Within cell membrane and forms a Insulin: hormone that regulates the
channel in order to move substances glucose concentration in the blood.
into and out of the cell. Usually in the form of troponin and
Selective about transporting substances tropomyosin.
Ions (sodium and potassium), sugars
6. Contractile Proteins
(glucose), proteins, messenger
molecules, etc. These proteins are found in cells to
allow movement and cause muscle
Hemoglobin in red blood cells for
contraction.
oxygen transport are examples.
They also help regulate body
Assist in either facilitated diffusion or
temperature.
active transport
Contractile proteins are in the form of
Channel Protein: opens holes in the
actin and myosin.
membrane, only one specific substance
can pass through, used in passive Animals are capable of locomotory
transport, either open or gated, it is movement and substance movement
always open-others are gated and must inside the body due to the action of
be opened for passage (in some tissues). contractile proteins.
Carrier proteins: only open at one side
7. Storage Proteins
at once, use energy to change shape,
used in active transport, open at one These proteins serve as reserves of
side because they transport substances amino acids and metal ions for future
against their concentration gradient, use.
substance might flow back out instead They are important in the growth,
of flowing in (if open at both sides), development, and maintenance of
binds the substance and moves it to the organisms.
other side. These proteins are found in egg whites
(albumin), plant seeds, and milk.
4. Defense Proteins
Plays an important role in the body’s
defense system against antibody.
Antibody: disease-causing foreign
organisms and particles like bacteria
and virus. It is produced by a specific
You might also like
- AP Biology Cheat Sheet PDFDocument7 pagesAP Biology Cheat Sheet PDFJ15No ratings yet
- Chem Brain Map PDFDocument51 pagesChem Brain Map PDFDilfon100% (4)
- Bio ReviewerDocument10 pagesBio ReviewerPau VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Proteins: Amino Acids Amino Acids Are Linked Together by Condensation To Form PolypeptidesDocument5 pages2.4 Proteins: Amino Acids Amino Acids Are Linked Together by Condensation To Form PolypeptideslhabNo ratings yet
- Acetyl Coenzyme A (Or Acetyl-Coa)Document18 pagesAcetyl Coenzyme A (Or Acetyl-Coa)micahNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument4 pagesBiomoleculesiyahh5.comNo ratings yet
- Title Layout: SubtitleDocument40 pagesTitle Layout: SubtitleDawlat SalamaNo ratings yet
- ProteinsDocument5 pagesProteinsJobelle MalihanNo ratings yet
- MetabolismDocument3 pagesMetabolismFans TimeNo ratings yet
- PhmarmacogDocument8 pagesPhmarmacogMichelle CasilangNo ratings yet
- CHONDocument4 pagesCHON2083385No ratings yet
- 2 EnzymesDocument36 pages2 EnzymesShumaim NaqviNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Metabolism and EnzymesDocument8 pagesChapter 5 Metabolism and Enzymes绿谷出久No ratings yet
- 3.07: Proteins - Types and Functions of ProteinsDocument2 pages3.07: Proteins - Types and Functions of Proteinsdeepanshujadon28No ratings yet
- Chap 1 Intro To PhysiologyDocument9 pagesChap 1 Intro To PhysiologymichelleNo ratings yet
- $RZ2YE8ODocument2 pages$RZ2YE8OCrow LordNo ratings yet
- Bio 2Document6 pagesBio 2Jaylene Kaye CabarrubiasNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids, Peptides & ProteinsDocument53 pagesAmino Acids, Peptides & ProteinsDanica RevillaNo ratings yet
- Chapter5 Bio f5Document8 pagesChapter5 Bio f5JiayingNo ratings yet
- Cchem Lec Trans 1 1Document6 pagesCchem Lec Trans 1 1MJ ArboledaNo ratings yet
- Pre-Lab 3: 1. What Is A Catalyst and A Catalysis Reaction?Document3 pagesPre-Lab 3: 1. What Is A Catalyst and A Catalysis Reaction?Trần NguyênNo ratings yet
- $RLW3VJ1Document3 pages$RLW3VJ1Crow LordNo ratings yet
- Sources: Dra. Santos Lecture LEA THERESE R. PACIS' TransDocument18 pagesSources: Dra. Santos Lecture LEA THERESE R. PACIS' TransJimcris Posadas HermosadoNo ratings yet
- Webcontent 146 513 1 Biomolecules 20190926165314Document2 pagesWebcontent 146 513 1 Biomolecules 20190926165314Abhishek Kumar VermaNo ratings yet
- Enzymes NotesDocument117 pagesEnzymes NotesRichel Ameryl DasocNo ratings yet
- Review Protein Dan EnzimDocument36 pagesReview Protein Dan EnzimRahma230595No ratings yet
- Biology Notes CHPTR 5Document4 pagesBiology Notes CHPTR 5Wan HasliraNo ratings yet
- Advance Biology: Quarter 3: Cell MetabolismDocument4 pagesAdvance Biology: Quarter 3: Cell MetabolismEmmanuel AzoresNo ratings yet
- Isolation of Bean Proteins: ProteinDocument14 pagesIsolation of Bean Proteins: ProteinElizabeth TanguilanNo ratings yet
- This Week's Lecture Topics: - Cell Chemistry and BioenergeticsDocument27 pagesThis Week's Lecture Topics: - Cell Chemistry and BioenergeticsHirad SalehnezhadNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: Learning ObjectivesDocument19 pagesEnzymes: Learning ObjectivesIyappan SubramaniNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids, Proteins, and EnzymesDocument62 pagesAmino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymesendale gebregzabherNo ratings yet
- ZOO 103 Lecture 09 19 ProteinsDocument12 pagesZOO 103 Lecture 09 19 ProteinsKaelyn MontefalconNo ratings yet
- Immunoglobulins: Immunoglobulins or Antibodies Are Defence Proteins Present in The Blood ToDocument10 pagesImmunoglobulins: Immunoglobulins or Antibodies Are Defence Proteins Present in The Blood ToAbhishek ThakralNo ratings yet
- Local Media5209454088282345Document19 pagesLocal Media5209454088282345Michaela Lyn Parilla MianaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6.3. EnzymesDocument13 pagesLesson 6.3. EnzymesCreeper RulezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 12 Protein MetabolismDocument7 pagesLesson 12 Protein Metabolismsaculala0291pamNo ratings yet
- Biology: 066b4349/Mar-2018-Biology-Notes PDFDocument9 pagesBiology: 066b4349/Mar-2018-Biology-Notes PDFOshein MontimorNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Brochure Gen Chem PTDocument2 pagesEnzyme Brochure Gen Chem PTAdrielNo ratings yet
- MacromoleculeDocument25 pagesMacromoleculeMuhammad AjmalNo ratings yet
- Catabolism Involves The Breaking Down of Molecules To Release Energy. ExamplesDocument4 pagesCatabolism Involves The Breaking Down of Molecules To Release Energy. ExamplesKathleen RamiloNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Nature of Enzymes: UNIT-3 3. Enzymes 1. Catalytic PropertyDocument5 pages3.1 Nature of Enzymes: UNIT-3 3. Enzymes 1. Catalytic PropertyGashaw Fikir AdugnaNo ratings yet
- Biology: Final Term: Proteins Based On Complexity/compositionDocument5 pagesBiology: Final Term: Proteins Based On Complexity/compositionRuel DagohoyNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 EnzymeDocument73 pagesUnit 2 EnzymeamrhkmhNo ratings yet
- ProteinsDocument56 pagesProteinsambotNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Summary NotesDocument12 pagesCell Biology Summary NotesQuesyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Metabolism and EnzymesDocument24 pagesChapter 5 - Metabolism and EnzymesbubabozN aOIDHao8nxNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Are Proteins A Definitive Guide of 4000+ Words (Updated)Document15 pagesEnzymes Are Proteins A Definitive Guide of 4000+ Words (Updated)mammmmNo ratings yet
- Enzymes and Proteins NotesDocument6 pagesEnzymes and Proteins NotesSarah MudaliarNo ratings yet
- RadiobiologyDocument11 pagesRadiobiologyefrenNo ratings yet
- EnzymsDocument1 pageEnzymsmilinlord443No ratings yet
- What Is Enzyme?Document7 pagesWhat Is Enzyme?rentachin18No ratings yet
- Classification of ProteinsDocument27 pagesClassification of ProteinsAlexia Mary Solei BacolodNo ratings yet
- Enzim&Protein RevDocument52 pagesEnzim&Protein Revkamilah rafaNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids and ProteinsDocument48 pagesAmino Acids and ProteinsSteph VeeNo ratings yet
- Amino AcidsDocument7 pagesAmino Acidsrida khanNo ratings yet
- c18 Enzymes Vitamins HormonesDocument3 pagesc18 Enzymes Vitamins HormonesShashank KukretiNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY NotesDocument9 pagesANATOMY Notescheven gryka uyNo ratings yet
- The Side of Chain of Glycine.: in Ala - Cys - Met - Ser - Tyr, The N - Terminal Is What?Document13 pagesThe Side of Chain of Glycine.: in Ala - Cys - Met - Ser - Tyr, The N - Terminal Is What?John Yman MaglenteNo ratings yet
- Class1, Macromolecular AnalysisDocument34 pagesClass1, Macromolecular AnalysisArup SheeNo ratings yet
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- United States: Patent OfficeDocument3 pagesUnited States: Patent OfficePappu PandeyNo ratings yet
- Rubber Bond GuideDocument187 pagesRubber Bond GuidesaleemasimstarNo ratings yet
- Are We Really Made of StarsDocument7 pagesAre We Really Made of StarsMerlita TuralbaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 Projectile MotionDocument2 pagesExperiment 3 Projectile MotionChristopherHiladoNo ratings yet
- Slide 6 Solar Ponds PlantsDocument25 pagesSlide 6 Solar Ponds PlantsPriyanshu AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Chemistry and Pharmacy: Tanya Sharma, Vinika Tyagi, Megha BansalDocument6 pagesSustainable Chemistry and Pharmacy: Tanya Sharma, Vinika Tyagi, Megha BansalLind AguilarNo ratings yet
- Earthquake EngineeringDocument16 pagesEarthquake Engineeringsamratdebbarman100% (1)
- Post Lab FC 2Document2 pagesPost Lab FC 2Adv Sandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Laws of MotionDocument57 pagesLaws of MotionakinaasirNo ratings yet
- Modern PhysicsDocument74 pagesModern PhysicsLàXsun ShrèsthàNo ratings yet
- Ngss and SBG UnitDocument1 pageNgss and SBG Unitapi-288746414No ratings yet
- Study Area: 37 Page 2 of 21Document1 pageStudy Area: 37 Page 2 of 21Hana HananeNo ratings yet
- Membrane Gas-Solvent Contactor Trials of CO2 Absorption From SyngasDocument10 pagesMembrane Gas-Solvent Contactor Trials of CO2 Absorption From SyngascurlychemNo ratings yet
- Sec 3 Chemistry Practice QuestionsDocument4 pagesSec 3 Chemistry Practice Questionschong56100% (1)
- Length ? ? ? Kilogram ? ? ? S M G/CM M KM CM KG Ms ML KG/M SDocument2 pagesLength ? ? ? Kilogram ? ? ? S M G/CM M KM CM KG Ms ML KG/M SKamrul Hasan SagarNo ratings yet
- Yadira Lopez - Cycles of Matter VocabularyDocument5 pagesYadira Lopez - Cycles of Matter Vocabularyapi-449637637No ratings yet
- Serwaypse8 Ch15probs FinalDocument48 pagesSerwaypse8 Ch15probs FinalBrian Lim50% (2)
- My L1 Antianginal DrugsDocument22 pagesMy L1 Antianginal DrugsDrGajanan VaishnavNo ratings yet
- Physical Science SHS 1.2 Stellar Evolution and The Formation of Heavier Elements PDFDocument26 pagesPhysical Science SHS 1.2 Stellar Evolution and The Formation of Heavier Elements PDFEzekiel Lapitan100% (1)
- Plastics Are A Wide Range Of: o o o o o o o o oDocument4 pagesPlastics Are A Wide Range Of: o o o o o o o o oVlad GorandaNo ratings yet
- Water Supply 1Document41 pagesWater Supply 1Emmanuel BuhwaNo ratings yet
- Management of Environmental Quality: An International JournalDocument13 pagesManagement of Environmental Quality: An International JournalJosé Antonio MaquénNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 2nd Parallel Assessment SampleDocument3 pagesGrade 11 2nd Parallel Assessment SampleElaiza Tautho100% (1)
- Introduction To System of Linear EquationDocument44 pagesIntroduction To System of Linear EquationEzekiel LapitanNo ratings yet
- 9 Enhanced Oil Recovery-1Document23 pages9 Enhanced Oil Recovery-1Muneeb AhmadNo ratings yet
- Aflas EngDocument11 pagesAflas EngVictor Flores ResendizNo ratings yet
- 2 Resume On Atomic TheoryDocument23 pages2 Resume On Atomic TheoryacepNo ratings yet
- SS 316Document3 pagesSS 316Deepak SinghNo ratings yet